Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tachycardia Algorithm 2021
Uploaded by
Ravin DebieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tachycardia Algorithm 2021
Uploaded by
Ravin DebieCopyright:
Available Formats
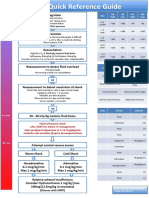
Adult tachycardia
Assess with Life threatening Synchronised DC
YES
ABCDE approach features? shock
• Give oxygen if SpO2 < 94% up to 3 attempts
1. Shock
• Obtain IV access • Sedation or anaesthesia if
• Monitor ECG, BP, SpO2, 2. Syncope conscious
record 12-lead ECG 3. Myocardial If unsuccessful:
• Identify and treat reversible causes ischaemia • Amiodarone 300 mg IV
e.g. electrolyte abnormalities, over 10–20 min
hypovolaemia causing sinus 4. Severe heart
• Repeat synchronised DC
tachycardia failure shock
UNSTABLE
STABLE
Seek expert help
NO
Is the QRS narrow (< 0.12 s)?
BROAD QRS NARROW QRS
Is QRS regular? Is QRS regular?
IRREGULAR REGULAR REGULAR IRREGULAR
Possibilities If VT (or uncertain Vagal Probable atrial
include: rhythm): manoeuvres fibrillation:
• Atrial fibrillation with • Amiodarone 300 mg IV • Control rate with
bundle branch block over 10–60 min beta-blocker
treat as for irregular If ineffective: • Consider digoxin or
narrow complex If previous certain
diagnosis of SVT with • Give Adenosine amiodarone if evidence
• Polymorphic VT bundle branch block/ (if no pre-excitation) of heart failure
(e.g. torsades de pointes) aberrant conduction: – 6 mg rapid IV bolus • Anticoagulate if
give magnesium 2 g duration > 48 h
over 10 min • Treat as for regular – If unsuccessful,
narrow complex give 12 mg
tachycardia – If unsuccessful,
give 18 mg
• Monitor ECG
continuously
If ineffective:
• Verapamil
or beta-blocker
If ineffective:
• Synchronised DC shock up to 3 attempts
• Sedation or anaesthesia if conscious
You might also like
- Pediatric Anesthesiology Review: Clinical Cases for Self-AssessmentFrom EverandPediatric Anesthesiology Review: Clinical Cases for Self-AssessmentNo ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument12 pagesTachycardiaPuskesmas Pinang JayaNo ratings yet
- Anasthetic DrugsDocument62 pagesAnasthetic DrugsMilda InayahNo ratings yet
- Symptoms Respiratory System Cardiovascular System DiagnosisDocument2 pagesSymptoms Respiratory System Cardiovascular System DiagnosisAdelina RinataNo ratings yet
- 04.06.2018 - 6 - V. Kushakovsky - Pediatric AnaesthesiaDocument46 pages04.06.2018 - 6 - V. Kushakovsky - Pediatric AnaesthesiaPhilippe KinnaerNo ratings yet
- Spinal & Epidural Anaesthesia Anatomy, Indications, Contraindications & ComplicationsDocument10 pagesSpinal & Epidural Anaesthesia Anatomy, Indications, Contraindications & ComplicationsrafiaNo ratings yet
- Spinal and Epidural Anesthesia: Anatomy, Pharmacology, TechniquesDocument101 pagesSpinal and Epidural Anesthesia: Anatomy, Pharmacology, TechniquesjedarlynNo ratings yet
- Poster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFAndy XiaoNo ratings yet
- AWARENESS UNDER ANESTHESIA: DEFINITION, TYPES, RISK FACTORS & PREVENTIONDocument27 pagesAWARENESS UNDER ANESTHESIA: DEFINITION, TYPES, RISK FACTORS & PREVENTIONagatakassaNo ratings yet
- Conscious sedation techniques and risksDocument84 pagesConscious sedation techniques and risksKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute PainDocument76 pagesManagement of Acute PainAnonymous nruHyuwtJ100% (1)
- Management of Labour Pain: Non-Pharmacological and Pharmacological MethodsDocument54 pagesManagement of Labour Pain: Non-Pharmacological and Pharmacological MethodsDr RabbiNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia Part 2Document9 pagesRegional Anesthesia Part 2Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
- Journal ClubDocument26 pagesJournal Clubysindhura23gmailcom100% (1)
- General-Anesthesia Part 2Document6 pagesGeneral-Anesthesia Part 2Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
- DIVITI Slide Prophylaxis VTE SPPD Ringkas-1Document11 pagesDIVITI Slide Prophylaxis VTE SPPD Ringkas-1Fera NurrizaNo ratings yet
- New drugs in anesthesia - Sugammadex, Cis-atracurium, Remifentanyl, PalonosetronDocument28 pagesNew drugs in anesthesia - Sugammadex, Cis-atracurium, Remifentanyl, PalonosetronSai TejeswiNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Considerations For Neuromuscular DiseaseDocument42 pagesAnesthesia Considerations For Neuromuscular Diseasesamrox54No ratings yet
- General-Anesthesia Part 3Document5 pagesGeneral-Anesthesia Part 3Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
- Supraglottic Airway Devices A Review in A New Era of Airway Management 2155 6148 1000647Document9 pagesSupraglottic Airway Devices A Review in A New Era of Airway Management 2155 6148 1000647Riris SihotangNo ratings yet
- DIFFICULT AIRWAY ALGORITHM GUIDEDocument48 pagesDIFFICULT AIRWAY ALGORITHM GUIDEshikhaNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia and Sedation Outside TheatresDocument15 pagesAnaesthesia and Sedation Outside Theatresمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Pacu Tylenol PresentationDocument10 pagesPacu Tylenol PresentationStanford AnesthesiaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Anesthesia For StudentsDocument4 pagesPediatric Anesthesia For StudentsMarco TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Best Practice in ShockDocument30 pagesBest Practice in ShockFoungZanz D. LuffyzNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Tracheoesophageal Fistula RepairDocument29 pagesAnesthesia For Tracheoesophageal Fistula RepairArop AkechNo ratings yet
- Adrenaline (Anaethesia Tutorial of The Week)Document8 pagesAdrenaline (Anaethesia Tutorial of The Week)Raisa AriesthaNo ratings yet
- Regional AnesthesiaDocument54 pagesRegional AnesthesiaIdza Fariha AfriNo ratings yet
- Massive TransfusionDocument104 pagesMassive Transfusionbingkydoodle1012No ratings yet
- Controlled Hypotension: Moderator: DR V. Y. Srinivas Presenter: Dr. Ann Susan MathewDocument49 pagesControlled Hypotension: Moderator: DR V. Y. Srinivas Presenter: Dr. Ann Susan MathewAnn Susan MathewNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Anaesthesia GuideDocument1 pagePaediatric Anaesthesia GuideAndrewBeckNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthesia Made Easy 2015Document35 pagesRegional Anesthesia Made Easy 2015Jeff GulitisNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia VaporisersDocument4 pagesAnaesthesia VaporisersTAMAR HEALTHCARENo ratings yet
- Epidural AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesEpidural AnesthesiaImran MukhlessNo ratings yet
- Patient Controlled AnalgesiaDocument129 pagesPatient Controlled AnalgesiamehranerezvaniNo ratings yet
- CH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaDocument29 pagesCH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaChristian LeepoNo ratings yet
- Awareness in Anesthesia FinalisedDocument42 pagesAwareness in Anesthesia FinalisedLean CyNo ratings yet
- General Anesthetics: General Anesthesia - Characteristics Balanced AnesthesiaDocument7 pagesGeneral Anesthetics: General Anesthesia - Characteristics Balanced AnesthesiarisanataliasiburianNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid Management in Pediatrics: By: Karim Kamal, MDDocument33 pagesPerioperative Fluid Management in Pediatrics: By: Karim Kamal, MDMohammed AKNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For GeriatricDocument21 pagesAnesthesia For GeriatricintanNo ratings yet
- Monitoring PerioperatipDocument54 pagesMonitoring Perioperatipjavajavu100% (1)
- Paediatric Anaesthesia PDFDocument33 pagesPaediatric Anaesthesia PDFMarcelitaTaliaDuwiriNo ratings yet
- 029 Reddy PDFDocument59 pages029 Reddy PDFKonas Xi PalembangNo ratings yet
- Post-anesthesia hypotension and hypertension treatmentDocument4 pagesPost-anesthesia hypotension and hypertension treatmentDianne GalangNo ratings yet
- High Altitude Anaesthesia PDFDocument7 pagesHigh Altitude Anaesthesia PDFK.krishna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine, Atracurium, Cis-Atracurium, Rocuronium, VDocument1 pageComparison of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine, Atracurium, Cis-Atracurium, Rocuronium, VMarshallMcGoughNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Drug Crib Sheet-8Document1 pageAnaesthetic Drug Crib Sheet-8Tiarnán Byrne0% (2)
- Management of Post-Operative Nausea and Vomiting in Adults - The Pharmaceutical JournalDocument18 pagesManagement of Post-Operative Nausea and Vomiting in Adults - The Pharmaceutical JournalResti DwiuNo ratings yet
- Patient Monitoring1370Document53 pagesPatient Monitoring1370Ridha Surya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- DRUG THERAPY FOR HEART FAILUREDocument40 pagesDRUG THERAPY FOR HEART FAILURENiteesh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Joint Replacement Anesthesia ManagementDocument55 pagesJoint Replacement Anesthesia ManagementRaguNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Postoperative Fever BMJDocument40 pagesAssessment of Postoperative Fever BMJMario Guzmán GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- General-Anesthesia Part 1Document5 pagesGeneral-Anesthesia Part 1Dianne GalangNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Neuroradiological Procedures Premalatha SDocument48 pagesAnaesthesia For Neuroradiological Procedures Premalatha SPrema LathaNo ratings yet
- Bob Peripheral Nerve Blocks AspanDocument70 pagesBob Peripheral Nerve Blocks AspanPrunaru BogdanNo ratings yet
- Premedication: by Alif Moderator: Dr. JasmineDocument45 pagesPremedication: by Alif Moderator: Dr. JasmineAlef AminNo ratings yet
- Managing Difficult Airway in Obstetric AnesthesiaDocument3 pagesManaging Difficult Airway in Obstetric AnesthesiaRoman AureliaNo ratings yet
- Inhalational Anaesthesia Mesi IDocument84 pagesInhalational Anaesthesia Mesi IBiserat GetnetNo ratings yet
- Caudal BlockDocument6 pagesCaudal BlockAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2005 Pedi Regional - HandoutDocument44 pages2005 Pedi Regional - HandoutSandhi Prabowo100% (1)
- SFE Hyponatraemia GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSFE Hyponatraemia Guidelinessapient11No ratings yet
- Marfan'sDocument39 pagesMarfan'sRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- 0315 DVTDocument28 pages0315 DVTGavin TexeirraNo ratings yet
- 0313 Stbi PDFDocument28 pages0313 Stbi PDFadityaNo ratings yet
- Managing Pulmonary EmbolismDocument9 pagesManaging Pulmonary EmbolismBolívar IseaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageSepsis Quick Reference GuideRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- BarrettDocument10 pagesBarrettVero AguilarNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation: Management Atrial Fibrillation: ManagementDocument47 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Management Atrial Fibrillation: ManagementRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Angioedema - FinalDocument24 pagesAngioedema - FinalGavin TexeirraNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument48 pagesChest PainDoxo RubicinNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Polyendocrine SyndromesDocument12 pagesAutoimmune Polyendocrine SyndromesRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- NOAC BLEEDING MANAGEMENT Guideline v2.0 KB SMC-2Document12 pagesNOAC BLEEDING MANAGEMENT Guideline v2.0 KB SMC-2Ravin DebieNo ratings yet
- Asthma in Pregnancy NEJM 2009Document8 pagesAsthma in Pregnancy NEJM 2009Ojank16 LabalaNo ratings yet
- BarrettDocument10 pagesBarrettVero AguilarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0140673610611567 Main PDFDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S0140673610611567 Main PDFAri SamadNo ratings yet
- TIA Transient Ischemic AttackDocument28 pagesTIA Transient Ischemic AttackPritta TaradipaNo ratings yet
- EDKADocument4 pagesEDKAEllya Latifah IlyasNo ratings yet
- Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Review ArticleDocument10 pagesAneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Review ArticlekucingkucingNo ratings yet
- IJC Heart & VasculatureDocument7 pagesIJC Heart & VasculatureRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Jamainternal Rastogi 2020 Oi 200105 1608579876 4141Document9 pagesJamainternal Rastogi 2020 Oi 200105 1608579876 4141Ravin DebieNo ratings yet
- WR2 PDFDocument9 pagesWR2 PDFJoni MokodoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in The Emergency DepartmentDocument24 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Acute Gastroenteritis in The Emergency DepartmentRavin Debie100% (1)
- Scaophoid Fractures PDFDocument6 pagesScaophoid Fractures PDFRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Aorticemergencies: Kathleen WittelsDocument12 pagesAorticemergencies: Kathleen WittelsRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Immune Related Adverse EventsDocument11 pagesImmune Related Adverse EventsRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Case Report Euglycaemic DkaDocument4 pagesCase Report Euglycaemic DkaRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Filbin 2019Document7 pagesFilbin 2019Ravin DebieNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentDocument19 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentMichael NovilloNo ratings yet
- Basic Epidemiology (E-Book)Document226 pagesBasic Epidemiology (E-Book)Ing Ching100% (12)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKenneth Narciso PerezNo ratings yet
- Genome Analysis Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)Document14 pagesGenome Analysis Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)GuruKPO93% (15)
- A Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patient Case Scenario - EditedDocument4 pagesA Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patient Case Scenario - Editedbenson gathuaNo ratings yet
- Small Incision CholecystectomyDocument8 pagesSmall Incision CholecystectomyCatalin SavinNo ratings yet
- Acute Tonsillopharyngitis: Group BDocument52 pagesAcute Tonsillopharyngitis: Group BVivekanandaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of HTNDocument57 pagesPharmacotherapy of HTNAbera JamboNo ratings yet
- Derma OSCEDocument3 pagesDerma OSCEUsama El BazNo ratings yet
- Morbidity and Mortality Review for December and JanuaryDocument68 pagesMorbidity and Mortality Review for December and Januaryndifor bonnyNo ratings yet
- ToxicologyDocument8 pagesToxicologysarguss14100% (3)
- Poultry Diseases: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment GuideDocument60 pagesPoultry Diseases: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment GuideNarayan Yadav100% (1)
- Adult Health III Final Study GuideDocument12 pagesAdult Health III Final Study GuideRyanne JNo ratings yet
- Selectividad 2014-2015 - 100 Candles PDFDocument1 pageSelectividad 2014-2015 - 100 Candles PDFEnrique FerreroNo ratings yet
- Sa Dbmas Reboc Guide 2012Document34 pagesSa Dbmas Reboc Guide 2012Tony Abott100% (1)
- Veterinary Internal Medicine Handbook for Field CasesDocument88 pagesVeterinary Internal Medicine Handbook for Field CasesShakil MahmodNo ratings yet
- Disfagia JPGN 2023Document8 pagesDisfagia JPGN 2023monicarodriguezsalas82No ratings yet
- Board Exam Review Pearls (Physician)Document6 pagesBoard Exam Review Pearls (Physician)Jo Anne100% (2)
- Bee sting linked to Henoch-Schonlein purpura case reportDocument7 pagesBee sting linked to Henoch-Schonlein purpura case reportjoshkelNo ratings yet
- Sessions 14 Nur 1491Document9 pagesSessions 14 Nur 1491BegNo ratings yet
- SCORES and CRITERIAS For Last Minute by DR RRMDocument52 pagesSCORES and CRITERIAS For Last Minute by DR RRMShweta Achuthan KuttyNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Interventions in Vascular MalformationsDocument47 pagesTherapeutic Interventions in Vascular MalformationsDr KhanNo ratings yet
- Practical Pain ManagementDocument13 pagesPractical Pain ManagementfrancistsyNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesGastric CancerMuhadis AhmadNo ratings yet
- ICD Dan Kategori Pengecualian DRAFTDocument132 pagesICD Dan Kategori Pengecualian DRAFTamita sindu kusuma100% (1)
- Manage Cellulitis at HomeDocument2 pagesManage Cellulitis at HomeAnonymous 4txA8N8etNo ratings yet
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDocument26 pagesFluid & Electrolytesanjana bhatia100% (1)
- Case Study For Pleural-EffusionDocument10 pagesCase Study For Pleural-EffusionGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Indication: Before: DuringDocument1 pageDrug Study Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Indication: Before: DuringAubrie StellarNo ratings yet
- Radiopaedia 2020 Virtual Conference June 22-25Document3 pagesRadiopaedia 2020 Virtual Conference June 22-25Prem Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Sensory DisordersDocument5 pagesSensory DisordersMartin PersianNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd 10 Isna TerbaruDocument43 pagesKode Icd 10 Isna Terbarulisna ginawatiNo ratings yet