Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mental Health Status Assessment: Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology
Uploaded by
Bianx Flores DosdosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mental Health Status Assessment: Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology
Uploaded by
Bianx Flores DosdosCopyright:
Available Formats
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing
MENTAL HEALTH STATUS ASSESSMENT
Patient: Maricel A. Doquiles Student: Hasnor G. |Ditingki
8 Group: K
I. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
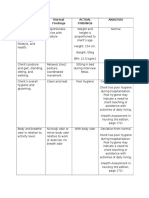
a. Appearance
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Grooming and Dress
[/ ] Well groomed Maricel is a well- groomed patient. In the manic phase, bipolar patient
[] Inappropriate use of clothing She takes a bath everyday using may wear clothes that reflect the
[] Evidence of soiled clothing Head N’ Shoulder shampoo and elevated mood: brightly colored,
[/] Use of make-up Shield soap. It’s also evident by flamboyant, attention-getting and
[] Unkempt wearing clean and brightly colored perhaps sexually suggestive. For
clothing. She wears lipstick on her woman with bipolar disorder, they
lips and put some of it on her upper may wear garnish or heavy makeup.
eyelid.
Hygiene
[ ] Any body odor No foul body odor noted in every Mostly, patients with bipolar 1
[/ ] Condition of skin, fingernails nurse- patient interaction. disorder can perform activities of
Fingernails and toenails are clean daily living such as taking a bath,
and short. going to school or even having a job
as long as compliant to medications.
Posture (note of standing)
[/] Upright Maricel stands in an upright posture. Most bipolar 1 disorder patients had
[ ] Rigid great postural sway and weaker
[] Slumped over balance.
Height* 4’8”
Weight* 48 Kg
Level of Eye Contact
[/ ] Intermittent Maricel, when she is conversing, can Eye movement analysis can be used
[ ] Occasional and fleeting maintain eye contact intermittently to discriminate patients with
[] Sustained and intense but there are episodes of sustained. depressive disorders from controls,
[ ] No eye contact The sustained eye contact is broken as well as patients with unipolar
when her name is addressed. depression.
Hair Color and Textures
[ /] Clean and healthy-looking Patient’s hair is healthy and clean Psychotic symptoms are also part of
[] Greasy with no foul odor this disorder, which can severely
[ ] Matted impact a person ability to function.
[ ] Tangled
Evidence of Scars, Tattoos, or Other Distinguishing Skin Marks
[/ ] Swelling/bruises Patient have minimal scars on upper
[ ] Birth marks and lower extremities. During
[ ] Rashes inspection, there was a round newly
healed scar approximately a half
inch at the left elbow. The patient
said it was hit on the floor.
Evaluate client’s appearance Clients can still look their age but the
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
Client appearance is just as her age grooming; mood and affect,
relative to chronological age movements and speech can be
affected.
*Indicate accurate measurements in feet.
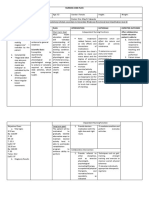
b. Motor Activity
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Tremors (trembling hands of legs) 8
[ ] continuous Drugs that treat bipolar disorder may
[ ] at specific times Patient does not manifest tremors. cause muscle stiffness cramping,
and tremors.
Tics or Other Stereotypical Movements
[ ] Facial tics Patient does not manifest facial tics,
[ ] Jerking or spastic moments jerking or spastic movements.
Mannerisms and Gestures
[/ ] Specific facial or body Patient frequently removes hair ties, Automatisms, repeated purposeless
movements during conversation next is combing her hair, then ties behaviors are often indicative of
[ ] Nail biting hair again. She does this cycle with anxiety.
[] Covering face with hands an interval of approximately every 30
[ ] Grimacing minutes
Hyperactivity
[/ ] Gets up and down out of chair Patient gets up and down out of During manic phase, patients with
[ ] Paces chair and at times goes to the bipolar disorder experience
[/ ] Unable to sit still hallway and talk to other students psychomotor agitation and seem to
and clinical instructor. She comes be in perpetual motion sitting still is
back when called by the student difficult. This continual movement
nurse assigned. She can’t remain has many ramifications: clients can
sitting for a long time. become exhausted or injure
themselves.
Restlessness or Agitation
[ ] Lots of fidgeting Patient did not demonstrate fidgeting Excessive agitation expressed in
of the hands. meaningless repetitive motion is
common, but most patients with
bipolar disorder does not manifest
these.
[ ] Clenching hands Patient did not exhibit clenching of Excessive agitation may lead the
hands. client to exhibit overt cues and also
some clients exhibit actions opposite
to what he actually feels or is
incongruent.
Aggressiveness
[ ] Overtly angry and hostile Patient did not exhibit Psychotic symptoms such as
[ ] Threatening aggressiveness and hostility. delusions and hallucinations, with
[ ] Uses sarcasm subsequent suspiciousness and
hostility may result in aggressive
behavior. It may be precipitated by
emotional triggers and can be more
aggressive and violent during acute
episodes.
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
Rigidity
[ ] Sits or stands in a rigid position Patient did not demonstrate rigidity. Dopamine function include
[ ] Arms and legs appear stiff and regulations of movements and
unyielding coordination, emotions and voluntary
decision-making ability.
Gait Patterns
[ ] Any evidence of limping Patient had a normal gait. Side effects of medications can
8
[ ] Limitation of ROM affect the musculoskeletal
[ ] Ataxia functioning of the client that can be
[ ] Shuffling exhibited by how the client moves
about.
Echopraxia (Mimicking the actions of others)
[ ] Present Patient does not mimic the actions of The frontal lobe controls the
[/ ] Absent others. organization of thought, body
movement, memories, emotions and
moral behaviour. This part of the
brain contains areas with mirror
neurons, which are never cells that
fire when we performed an action
and when we witness someone
perform the same action.
Psychomotor Retardation
[ ] Waxy flexibility Patient did not demonstrate waxy People with psychosis often have
[ ] Thinking and speech are very flexibility. Patient also does not irrational thoughts. Their speech
slow speak and think slow. maybe rapid and hard to follow and
[ ] Posture is slumped they may move from subject to
[ ] Immobile subject, losing tract of their train of
thought.
Freedom of Movement
Note any limitation in ability to move. Limitation of movement not noted. Antipsychotic medications and the
disease process itself can limit the
client’s movement.
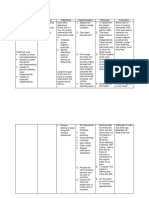
c. Speech Patterns
Quantity
[/ ] Talkative The patient is very talkative. She Patients with bipolar disorder may
[/ ] Spontaneous talks spontaneously and answers to have impaired thought process and
[ /] Expansive questions but at times exhibit flight content that is brought about by the
[ ] Paucity of ideas, loose associations and disease process.
[ ] Poverty circumstantial thinking.
Rate
[ ] Fast She speaks rapidly Patients with bipolar disorder can
[ ] Slow sometimes speak in a rapid and
[ ] Normal disorganized way.
[/ ] Pressured/Rapid
Intonation
[/ ] with appropriate emphasis Patient’s intonation is with Some patients are monotone,
[ ] monotone, without emphasis appropriate emphasis. without emphasis that can
sometimes lead into confusion for
the listener as to what the client
feels.
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
Volume (Tone)
[/ ] Loud Patient speaks in a loud voice Bipolar 1 disorder patients may
[ ] Soft speak in whispers or hushed tones
[ ] Monotone or talk loudly or yell.
[ ] Weak
[ ] Strong
Fluency and Rhythm 8
[ ] Slurred speech Patient speaks rapidly but can Bipolar 1 disorder patients may
[/ ] Clear articulate words clearly and fluently exhibit unusual speech pattern that
[ ] Hesitant which enables the listener to sometimes can be indicative of
[ /] Articulate understand what the patient say. aggression or anxiety.
[ ] Stuttering
[ ] Aphasic (describe fully)
d.General Attitude
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
General
[/ ] Cooperative (describe fully) Patient is very cooperative. When During a depressive episode patient
[ ] Uncooperative (describe fully) asked to perform self-care activities, may feel drained, in deep despair,
[/ ] Friendly/Sociable the client willingly follows (unless guilty for no reason, worthless and
[ ] Hostile (Sarcastic and irritable) she is agitated), answers questions irritable. Activities you normally
[ ] Defensive and follows simple instructions. She enjoy will hold no interest. You may
is also participative in the activities experience sudden weight loss or
conducted. gain and uncontrollable crying
spells. At your lowest moment you
may even have thoughts of suicide.
Uninterested/Apathetic* Apathy and disinterested not noted. Disruptions of the regulation of the
neurotransmitters cause the patient
to change mood, cognition and
movement suddenly.
Attentive/Interested* Patient is attentive and seems to be Bipolar disorder symptoms include
interested when we were talking. manic episodes followed by hypo
manic episodes, or extreme highs
and extreme lows and loss of
pleasure in activities.
Guarded/Suspicious* Patient did not exhibit guarding or If bipolar psychosis occurs during a
suspicious behaviour. low period or a depressive episode,
the individual may believe that
someone is trying to harm them, or
that they themselves have done
something wrong.
* Please specify assessment then explain further under justification.
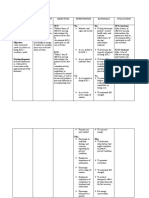
II. EMOTIONS
A. Mood
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
[ ] Depressed; despairing Patient is in euphoric state Bipolar 1 disorder requires that an
[ ] Irritable individual has at least one manic
[ ] Anxious episode. These manic episodes can
[ ] Elated cause abnormally elevated mood
[ /] Euphoric and odd behaviour that can disrupt
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
[ ] Fearful daily life. Individual with bipolar 1
[ ] Guilty often cycle between mania and
[] Labile depression, but may experience
relatively normal state in between.
b. Affect
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Congruence with Mood 8
Affect is congruent with mood. She Bipolar 1 disorder requires that an
laughs when she says/hears individual has at least one manic
something funny. episode. These manic episodes can
cause abnormally elevated mood
and odd behaviour that can disrupt
daily life. Individual with bipolar 1
often cycle between mania and
depression, but may experience
relatively normal state in between.
Consistency with Mood Patient is consistently happy and is Mood fluctuations can be evident
congruent with her facial expression according to the levels of the
neurotransmitters and their activity in
the brain.
Intensity
[ ] Flat/Blank Patient’s affect is normal. She knows While some patients are congruent,
[ ] Blunt/Constricted how to react. She laughs when she others may exhibit inappropriate
[/] Normal/Regular says/hears something funny. expression or emotions incongruent
within the context of the situation
that rages from mild to grossly
inappropriate.
Compatibility of Emotions to Certain Situations
[/ ] Appropriate Most of the time, the patient’s affect The client may exhibit inappropriate
[ ] Inappropriate is compatible to the situation, expressions of emotions or
appears sad when she talks about incongruent with situation that
her family. ranges from mild to grossly
inappropriate that depends on the
play of the neurotransmitters that
affect brain activity.
Fluctuations
[ ] Labile Patient exhibit even mood but on the Mood fluctuation depends on several
th
[/ ] Even 5 day of duty has been labile and factors including the
had shifted from normal to neurotransmitter levels, brain activity
depressed and back again. or environmental triggers.
Range
[/ ] Broad Patient exhibited broad affect with Some clients display full range of
[ ] Restricted facial expressions that match the emotional expressions that is
emotions. consistent others have restricted or
are mask-like.
Quality
[ ] Sad Most of the time, the patient is Manic behaviour: for the bipolar
[ ] Angry euthymic- is cooperative and can go subtype, people can experience
[ ] Hostile along well with the interaction but feelings of euphoria, racing
[/ ] Indifferent there are episodes of indifference thoughts, risky behaviour (sexual
[/ ] Euthymic and irritability followed by secluding financial) or sudden increase in
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
[ ] Dysphoric self in the corner then sleeping. energy or behaviour that’s out
[ ] Detached character.
[ ] Elated
[ ] Euphoric
[ ] Anxious
[ ] Animated
8
[/ ] Irritable
III. THOUGHT PROCESS
a. Form of Thought
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
[ ] Though blocking Patient manifests flight of ideas. She The individual may jump quickly
[ ] Though broadcasting tends to jump from one topic to from one topic to another (flight of
[ ] Though withdrawal another topic. The patient ability to ideas), making it hard for others to
[ ] Though insertion concentrate during a conversation. understand.
[/] Flight of ideas
[/] Associative looseness
[/] Circumstantiality
[ ] Tangentiality/Tangential thinking
[ ] Neologisms
[ ] Concrete thinking
[ ] Clang association
[ ] Word Salad
[ ] Perseveration
[ ] Echolalia
[ ] Verbigeration
[ ] Stilted language
[ ] Poverty of speech
[ ] Alogia
[ ] Latency of response
[ ] Mutism
[/] Ability to concentrate and
disturbance of attention
b. Content of Thought
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Delusions
[ ] Jealous During inclusive dates if care, the In bipolar disorder, psychosis
[ ] Control or influence patient did not experience any typically occur during a manic
[ ] Sexual delusion. episode but it can occur during a
[ ] Somatic depressive episode as well.
[ ] Persecutory
[ ] Religious
[ ] Referential
[ ] Erotomanic
[ ] Nihilistic
[ ] Grandiose
[/ ] None
[ ] Suicidal Patient does not manifest The individual thinks about death a
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
[ ] Homicidal suicidal/homicidal thoughts. great deal and many contemplate or
[ ] None even attempt suicide. Depression is
highly associated with suicide.
Obsessions* Patient is not obsessed with Obsessive thinking is fairly common
anything. but rarely discussed symptom of
bipolar.
Paranoia/Suspiciousness* Patient did not
8 exhibit paranoia. Some patients have paranoid
delusions, believing that they are not
safe or that others want to hurt them.
Magical Thinking* Patient did no manifest any. Odd beliefs or magical thinking that
influences behavior and is
inconsistent with subcultural norms
can sometimes be the result of
delusions and hallucinations.
Religiosity* Patient believes in God but with no Some patients turn their faith in their
delusions. She prays when she has God into delusions for example they
problems. will believe that they are a saint or
are pregnant with the messiah.
Phobias* The patient verbalized “ginahadlok Phobias can be a minor part of some
ko ni mama nga naa dao wakwak disorders such as depression,
basta mag study ko busa mahadlok obsessive neurosis, anxiety state,
nako mugawas.” personality disorder, or
schizophrenic disorders.
Poverty of Content* Patient did not demonstrate poverty The individual says very little, or
of content. when he or she talks, there does not
seem to be much information being
conveyed.
* Please specify assessment then explain further under justification.
IV. PERCEPTUAL DISTURBANCES
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Hallucinations
[ ] Visual Patient does not manifest any of Hallucination is a false sensory
[ ] Auditory these. perception or perceptual
[ ] Gustatory experiences that do not exist in
[ ] Tactile reality. Initially, the client perceives
[ ] Olfactory hallucinations as real, but later in the
[ ] Cenesthetic illness, he may recognize them as
[ ] Kinesthetic hallucinations. Visual hallucination is
[ ] Illusions seeing images that do not exist at
[ ] Depersonalization all.
[ ] Derealization
Illusions* Patient did not manifest this. Hallucinations are distinguished from
illusions, which are misperceptions
of actual environmental stimuli.
Depersonalization* Patient did not manifest this. During episodes of psychosis,
clients are commonly disoriented to
time and place. The most extreme
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
form of disorientation is
depersonalization, in which the client
feels detached from her or his
behavior. Although he knows his
name correctly, he or she feels as if
his body belongs to someone else or
8
his spirit is detached from his body.
Derealization* Patient did not manifest this. Derealization is often see coexisting
with depersonalization.
* Please specify assessment then explain further under justification.
V. SENSORIUM AND COGNITIVE ABILITY
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Level of Alertness/Consciousness
[/ ] Clear-minded/attentive Patient is clear-minded, attentive A deeper understanding of memory
[ ] Disturbed and can focus. function and brain system has
served to refine and expand the
classification of short and long-term
memory.
Orientation
[/ ] Oriented Patient is oriented to person, place Orientation refers to the client’s
[ ] Not oriented and time. Patient is well-aware that recognition of person, place and
she is in Vicente Sotto Memorial time that is known and where she is
Medical Center- Center for and the correct day and year.
Behavioral Sciences, Cebu City.
Memory
Patient can remember the therapy The nurse directly assesses
Recent performed the day prior. memory, birth recent and remote by
asking verifiable answers.
Patient can recall who brought her to The nurse directly assesses
Remote* VSMMC – CBS. memory, birth recent and remote by
asking verifiable answers.
Patient can remember the name of The nurse directly assesses
Immediate* the student nurse. memory, birth recent and remote by
asking verifiable answers.
Patient can read, write, can count 1- Some clients have impaired
Intellectual* 100 and can memorize song lyrics cognitive functions and others do not
easily exhibit this kind of dysfunction.
Patient can remember her parents Some clients have impaired
Confabulation* and brothers. cognitive functions and others do not
exhibit this kind of dysfunction.
Intellectual
Patient knows how to speak English When assessing intellectual
and Tagalog, knows who the current functioning, the client’s level of
president is and sing her favorite formal education must be taken into
Information and vocabulary*
songs with correct lyrics. consideration. Lack of formal
education could hinder performance
in many tasks.
Vocabulary* Patient knows how to speak English Client’s level of formal education
and tagalog must be taken into consideration.
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
Lack of formal education could
hinder performance in many tasks.
Can explain “if there is a will, there is Some client’s still has the ability to
a way” use abstract thinking which is to
make associations or interpretations
about a situation or comment and
8 other continually gives literal
Abstraction* translations of has evidenced
concrete thinking. Client’s level of
formal education must be taken into
consideration. Lack of formal
education could hinder performance
in this task.
* Please specify assessment then explain further under justification.
VI. IMPULSE
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Ability to Control Impulses
[ ] Aggression The patient can control her Patients with schizophrenia may
[ ] Hostility impulses, but shows suggested show dysfunctional impulsivity and
[ ] Fear provocative behavior and calms aggression. Although
[ ] Guilt down when reprimanded and when neurobiological aspects of
[ ] Affection boundaries are restated. aggression in patients with
[ ] Sexual feelings schizophrenia are still not well
understood, impulsivity, and
aggression may correlate with frontal
and temporal brain abnormalities.
VII. JUDGMENT AND INSIGHT
Assessment Justification Psychogiological Rationale
Ability to Solve Problems and When asked about her plans or how Judgment is frequently impaired in
Make Decisions* to solve problems, the client always clients with schizophrenia because
says when you pray there’s always a judgment is based on the ability to
solution. interpret the environment correctly, it
follows that the client with disordered
thought processes and
environmental misinterpretations will
have great difficulties in judging.
Knowledge About Self
[/ ] Awareness of limitations Patient is well-aware of her Increased self-knowledge and
[/ ] Awareness of consequences of limitations and consequences of awareness leads to more effective
actions actions. management of the illness.
[] Awareness of illness
Adaptive/Maladaptive Use of Coping Strategies and Ego Defense Mechanisms
Please specify here. When asked about her current Failure to acknowledge an
1. Denial condition, she does not accept that unbearable condition, failure to
she have a psychiatric problem admit reality of a situation or how
which is bipolar disorder due to her one enables the problem to
chronic depression. continue.
2.Resistance She perceives that real psychiatric Overt or covert antagonism towards
patients are those on the street remembering or processing anxiety-
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
without wearing clothes producing information.
* Please specify assessment then explain further under justification.
VIII. ATTENTION
Assessment Justification Psychobiological Rationale
Attend, Concentration, Distractibility
Patient can count 1-100 Impairment inattention is greatly
8 derived from the impairment in the
thought processing, content and
clarity of the patient. It is further
aggravated by the difficulty in
Digit Span* concentration and intellectual
functioning which precipitates into
nearly basic primitive and superficial
manner of interpretations. When
problems are let down for the client’s
analysis.
patient can spell the word “Maricel” Impairment inattention is greatly
backwards derived from the impairment in the
thought processing, content and
clarity of the patient. It is further
aggravated by the difficulty in
Spelling Backwards* concentration and intellectual
functioning which precipitates into
nearly basic primitive and superficial
manner of interpretations. When
problems are let down for the client’s
analysis.
Patient can solve basic calculations Impairment inattention is greatly
such as addition, subtraction, derived from the impairment in the
multiplication and division. thought processing, content and
clarity of the patient. It is further
aggravated by the difficulty in
Calculations* concentration and intellectual
functioning which precipitates into
nearly basic primitive and superficial
manner of interpretations. When
problems are let down for the client’s
analysis.
* Please specify assessment then explain further under justification.
Psychiatric Mental-Health Nursing | Mental Status Assessment
You might also like
- NURSINGCAREPLANDocument5 pagesNURSINGCAREPLANJulius AtencioNo ratings yet
- Body Normal Findings Actual Findings AnalysisDocument13 pagesBody Normal Findings Actual Findings AnalysisChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Part 3 Assignment - SuzukiDocument21 pagesPhysical Assessment Part 3 Assignment - SuzukiNANAMI BOLIGOR SUZUKINo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Document2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Kathleen Martinez100% (1)
- Friends or Relatives.: Week 5Document7 pagesFriends or Relatives.: Week 5Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder ReportDocument6 pagesBipolar Disorder ReportLecah DevarasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management For A Patient With Schizophrenia and Generalized AnxietyDocument23 pagesNursing Care Management For A Patient With Schizophrenia and Generalized AnxietyKimberly Ann BoricanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process For Bipolar DisorderDocument37 pagesNursing Process For Bipolar DisorderDENVER CABADINNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment 7Document5 pagesHealth Assessment 7shannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis CaseDocument29 pagesLeptospirosis CaseJp RectraNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document19 pagesCase Study 2Sumit Singh100% (1)
- Administer Medications As IndicatedDocument4 pagesAdminister Medications As IndicatedYza WagayenNo ratings yet
- Psych Vignetter VC Group 5Document20 pagesPsych Vignetter VC Group 5ErleNo ratings yet
- Somatoform, Dissociative, Anxiety, Personality DisordersDocument8 pagesSomatoform, Dissociative, Anxiety, Personality DisordersShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument10 pagesDocumentNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument21 pagesProcess RecordingROMULO NU�EZ JR.No ratings yet
- NCP For Obsessions in NCM 117 (Anxiety)Document2 pagesNCP For Obsessions in NCM 117 (Anxiety)unkown userNo ratings yet
- NCP (Psychiatric)Document6 pagesNCP (Psychiatric)Erl Joy Montaño Cañete100% (1)
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSienaNo ratings yet
- Relapse Prevention Counseling Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Sustainable Recovery: Holistic approaches to recovery and relapse preventionFrom EverandRelapse Prevention Counseling Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Sustainable Recovery: Holistic approaches to recovery and relapse preventionNo ratings yet
- DX Alcohol Withdrawal PDFDocument3 pagesDX Alcohol Withdrawal PDFSherree Hayes100% (1)
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- Henderson's 14 ComponentsDocument6 pagesHenderson's 14 ComponentsJim RashidNo ratings yet
- DELIRIUMDocument7 pagesDELIRIUMSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Assessment, DSM-IV Comparison & Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesMental Status Assessment, DSM-IV Comparison & Nursing Care PlanVinod MalepatiNo ratings yet
- Conscious Sedation: Presented byDocument101 pagesConscious Sedation: Presented byHarees Shabir100% (1)
- ASSESSMENTDocument7 pagesASSESSMENTJESSMAR GRACE PARMOSANo ratings yet
- DIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR THERAPY: Mastering DBT Skills for Emotional Resilience and Balanced Living (2024 Beginner Guide)From EverandDIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR THERAPY: Mastering DBT Skills for Emotional Resilience and Balanced Living (2024 Beginner Guide)No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument4 pagesSchizophrenia NCPDen-rashier M. Jamsuri100% (1)
- Concept of Man, Health, and IllnessDocument7 pagesConcept of Man, Health, and IllnesskathleenjanlosbanezNo ratings yet
- Self Care Deficit NCPDocument3 pagesSelf Care Deficit NCPJUSTIN ALZATENo ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument67 pagesProcess RecordingMARIAH ALEXIE GASALNo ratings yet
- 3 - Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness - Part (3) (LEC.6)Document37 pages3 - Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness - Part (3) (LEC.6)Youssif MenamNo ratings yet
- General Survey and Assessment of IntegumentaryDocument6 pagesGeneral Survey and Assessment of IntegumentaryLuzel LapuzNo ratings yet
- NCM117 NCPDocument2 pagesNCM117 NCPHANNAH MICOLE GAERLANNo ratings yet
- GUISDAN (FDAR and NCP)Document6 pagesGUISDAN (FDAR and NCP)Darcy Keith GuisdanNo ratings yet
- Care Plan On Acute Transient Psychiatric Disorder 2Document4 pagesCare Plan On Acute Transient Psychiatric Disorder 2Divya ThomasNo ratings yet
- HoplessnessDocument16 pagesHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanperezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDianne100% (2)
- Anxiety (Gangguan Kecemasan)Document9 pagesAnxiety (Gangguan Kecemasan)Eki MegaraniNo ratings yet
- Cushing'S Syndrome Female Ward Staff NAFH ProgrammeDocument23 pagesCushing'S Syndrome Female Ward Staff NAFH ProgrammeJaron JarsNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Mrs. Greene)Document9 pagesCase Study (Mrs. Greene)Trina Joy DomantayNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care Deficitnor ain b. odingNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Part 1 AssignmentDocument7 pagesPhysical Assessment Part 1 AssignmentmaryNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Using The Rancho Los Amigos Scale To Guide Treatment at Each LevelDocument28 pagesUsing The Rancho Los Amigos Scale To Guide Treatment at Each LevelMichelle GloverNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Client Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual Evaluation SDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Client Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual Evaluation SKaty PerchieNo ratings yet
- Gouty NCPDocument9 pagesGouty NCPKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Rle 101Document15 pagesRle 101Fea Marielle MacapayadNo ratings yet
- Red Paper Texture With PNG Cutout Student Internship Actor Resume PresentationDocument18 pagesRed Paper Texture With PNG Cutout Student Internship Actor Resume PresentationMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Sto: DX: DX: STO: Goal MetDocument3 pagesSubjective: Sto: DX: DX: STO: Goal MetFaith BugtongNo ratings yet
- 2.B .Ndera CaseDocument9 pages2.B .Ndera CaseNsengimana Eric MaxigyNo ratings yet
- Anam Sardar (DBT Presentation)Document37 pagesAnam Sardar (DBT Presentation)Anam SardarNo ratings yet
- Impact of Sensory Deprivation On Health OutcomeDocument4 pagesImpact of Sensory Deprivation On Health OutcomeNitu GodaraNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Involuntary Movement ScaleDocument3 pagesAbnormal Involuntary Movement Scalemaria putriNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument10 pagesActual NCPRouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- "Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" AsDocument4 pages"Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" Ashanna caballoNo ratings yet
- VIDEO 2 - CHAPTER 2. Code of Ethics (COE) For RN'sDocument3 pagesVIDEO 2 - CHAPTER 2. Code of Ethics (COE) For RN'sBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Video 1: Ethico Legal Considerations: The Ethical Principles or Bio-Ethical PrinciplesDocument9 pagesVideo 1: Ethico Legal Considerations: The Ethical Principles or Bio-Ethical PrinciplesBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Video 10 Magna Carta For Public Health WorkersDocument8 pagesVideo 10 Magna Carta For Public Health WorkersBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Video 12 Patients Bill of Rights DohDocument8 pagesVideo 12 Patients Bill of Rights DohBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Video 4 - Chapter 4: Ethical Decision-Making Process: BioethicsDocument6 pagesVideo 4 - Chapter 4: Ethical Decision-Making Process: BioethicsBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Video 4 - Chapter 4: Ethical Decision-Making Process: BioethicsDocument6 pagesVideo 4 - Chapter 4: Ethical Decision-Making Process: BioethicsBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Video 11 AccountabilityDocument9 pagesVideo 11 AccountabilityBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- VIDEO 1: Neurologic SystemDocument9 pagesVIDEO 1: Neurologic SystemBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice: VIDEO 7 - Chapter 7: Standards ofDocument10 pagesNursing Practice: VIDEO 7 - Chapter 7: Standards ofBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureDocument6 pagesMnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- B. Immunosuppressive Therapy: Video 11Document9 pagesB. Immunosuppressive Therapy: Video 11Bianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Soapie Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Progress NotesDocument3 pagesSoapie Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Progress NotesBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Iris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballDocument8 pagesIris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Peri-Orbital Hematoma Sub-Conjunctiva Hemorrhage On Left EyeDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Peri-Orbital Hematoma Sub-Conjunctiva Hemorrhage On Left EyeBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Soapie Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Progress NotesDocument3 pagesSoapie Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Progress NotesBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Nurse-Patient Interaction Process Recording: College of NursingDocument3 pagesNurse-Patient Interaction Process Recording: College of NursingBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Deep Breathing and Coughing ExercisesDocument5 pagesTeaching Deep Breathing and Coughing ExercisesBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Suctioning The Nasopharygeal and Oropharyngeal AirwaysDocument7 pagesSuctioning The Nasopharygeal and Oropharyngeal AirwaysBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeDocument5 pagesName: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument6 pagesMental Status ExaminationKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of ThinkingDocument11 pagesDisorders of Thinkingjahanavi12No ratings yet
- MSE 2 - Binu Mam PDFDocument6 pagesMSE 2 - Binu Mam PDFMeenakshi Antil100% (1)
- Case Study PsychiatricDocument29 pagesCase Study PsychiatricSimran Josan100% (3)
- PSYCHE Mental Health Concepts N2018 Ans KeyDocument5 pagesPSYCHE Mental Health Concepts N2018 Ans KeyJo Hn Vengz100% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing TerminologiesDocument56 pagesPsychiatric Nursing TerminologiesJasmin Jacob95% (22)
- Sign and Symptoms of Mental Illness (2) : A-Disturbance in The Form and Process (Organization) of ThoughtDocument13 pagesSign and Symptoms of Mental Illness (2) : A-Disturbance in The Form and Process (Organization) of ThoughtWani GhootenNo ratings yet
- Terms in The Field of Psychiatry and NeurologyDocument25 pagesTerms in The Field of Psychiatry and NeurologyMarlon SigfredNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Note Taking GuideDocument26 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Note Taking GuideJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Status Exam Cheat Sheet ICANotesDocument7 pagesMental Health Status Exam Cheat Sheet ICANotesSanober Memon100% (1)
- Victorian Aod Comprehensive Assessment FormDocument20 pagesVictorian Aod Comprehensive Assessment FormMadNo ratings yet
- Typical Signs and Symptoms of Psychiatric IllnessesDocument52 pagesTypical Signs and Symptoms of Psychiatric IllnessesmejammbatoonNo ratings yet
- Mental Assessment StatusDocument14 pagesMental Assessment StatusPretty Grace Jumalon Anes100% (1)
- Obj Questions 19.03.2018Document2 pagesObj Questions 19.03.2018Eli Zza KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Case StudyDocument14 pagesSchizophrenia Case Studykristinanicole47100% (3)
- Disorders of Thought & Speech (Psychopathology)Document21 pagesDisorders of Thought & Speech (Psychopathology)Upasana Baruah100% (2)
- Patterns of BehaviorDocument8 pagesPatterns of BehaviorKeith AquinoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Dysfunctions in Patients With Obsessive-Compulsive DisordersDocument8 pagesCognitive Dysfunctions in Patients With Obsessive-Compulsive DisordersmmimcNo ratings yet
- Combinepdf 2Document96 pagesCombinepdf 2Dexter John CarpioNo ratings yet
- AbPsy HandoutDocument14 pagesAbPsy HandoutJona AddatuNo ratings yet
- The Spychiatrists, by Frater PyramidatusDocument76 pagesThe Spychiatrists, by Frater PyramidatusBrian Adam Newman (Frater Pyramidatus)100% (1)
- PsychiatryDocument23 pagesPsychiatryharpalmehanNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument5 pagesMental Status ExaminationNhelia Santos Bañaga100% (3)
- PsychoEducation Mental Illness. 1Document13 pagesPsychoEducation Mental Illness. 1Sathyanarayanan MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Sims A Etal. Descriptive Phenomenology. New Oxford Textbook of PsychiatryDocument30 pagesSims A Etal. Descriptive Phenomenology. New Oxford Textbook of PsychiatryCíntia BragaNo ratings yet
- Neral PractitionersDocument216 pagesNeral PractitionersSudhir Tyagi100% (1)
- Young Mania Rating Scale (Ymrs) : Guide For Scoring ItemsDocument7 pagesYoung Mania Rating Scale (Ymrs) : Guide For Scoring ItemsAsepDarussalamNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Patient AssessmentDocument3 pagesPsychiatric Patient AssessmentmichaelurielNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing: Alma Trinidad R. Taragua RN, RM, MANDocument63 pagesPsychiatric Nursing: Alma Trinidad R. Taragua RN, RM, MANShy Dela PuertaNo ratings yet