Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endoscopy - : Brain Station Cases
Uploaded by
florenzo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesThis document provides information about various medical procedures and departments within a hospital. It describes emergency room procedures for common issues like heart attacks, asthma, accidents, and poisonings. It also outlines outpatient department cases involving ear, nose, throat and eye issues. Neurological procedures discussed include EEGs and treatments for seizures, Parkinson's disease, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis. Urological procedures like cystoscopy, ureteroscopy and meatoplasty are also summarized. Departments covered are the hemodialysis unit and day surgery unit.
Original Description:
Original Title
ISNAIRA-assignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about various medical procedures and departments within a hospital. It describes emergency room procedures for common issues like heart attacks, asthma, accidents, and poisonings. It also outlines outpatient department cases involving ear, nose, throat and eye issues. Neurological procedures discussed include EEGs and treatments for seizures, Parkinson's disease, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis. Urological procedures like cystoscopy, ureteroscopy and meatoplasty are also summarized. Departments covered are the hemodialysis unit and day surgery unit.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesEndoscopy - : Brain Station Cases
Uploaded by
florenzoThis document provides information about various medical procedures and departments within a hospital. It describes emergency room procedures for common issues like heart attacks, asthma, accidents, and poisonings. It also outlines outpatient department cases involving ear, nose, throat and eye issues. Neurological procedures discussed include EEGs and treatments for seizures, Parkinson's disease, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis. Urological procedures like cystoscopy, ureteroscopy and meatoplasty are also summarized. Departments covered are the hemodialysis unit and day surgery unit.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ISNAIRA A.
IMAM BSN-III Colonoscopy- is an exam used to detect
changes or abnormalities in the large intestine
EMERGENCY ROOM: (colon) and rectum.
ERs are hospital units where you can seek urgent Endoscopy - is the insertion of a long, thin
medical care and treatment. Most major public tube directly into the body to observe an
hospital EDs are open 24 hours a day and have internal organ or tissue in detail.
emergent doctors and other health professionals on Ultrasounds - scans, or sonography, they use
site to deal with emergencies. They assess, treat, sound waves or echoes to make an image,
stabilize and start the health management of people instead of radiation.
who have come to the ED with a serious illness or Transvaginal ultrasound- is a test used to look
injury. at a woman's uterus, ovaries, tubes, cervix and
The most common problem that need emergent pelvic area.
assistance and treatment: Pelvic exam- visual and
Myocardial Infarction- also known heart physical examination of a woman's
attack it occurs when blood flow decreases or reproductive organs.
stops to a part of the heart, causing damage to Pap smear- involves collecting cells from your
the heart muscle. cervix the lower, narrow end of your uterus
Asthma- is a condition in which your airways that's at the top of your vagina.
narrow and swell and may produce extra Enema- is an injection of fluid into the lower
mucus. Using Nebulizer medical equipment bowel by way of the rectum.
that a person with asthma or another TPN- is a method of feeding that bypasses the
respiratory condition it facilitate proper gastrointestinal tract.
breathing pattern. PEG- is an endoscopic medical procedure in
Vehicle Accident - (head trauma and fractures which a tube is passed into a patient's
accompanied by intense pain when the initial stomach through the abdominal wall, most
injury occurs.) commonly to provide a means of feeding
Stab wounds- specific form of penetrating when oral intake is not adequate.
trauma to the skin that results from a knife or Ophthalmoscope- allows you to look into the
a similar pointed object. Typically known to be back of the eye to look at the health of the
caused by knives, broken bottles and ice picks. retina, optic nerve, vasculature and vitreous
Poisoning- it can be chemically harmed humor
severely by a toxic substance or venom of an Otoscope- medical device which is used to
animal that might cause big problem. look into the ears.
Machines and equipment in ER Hearing aids and it types- is a small electronic
ECG- Records the electrical signal from your device that you wear in or behind your ear. It
heart to check for different heart conditions. makes some sounds louder so that a person
Defibrillators - are devices that restore a with hearing loss.
normal heartbeat by sending an electric pulse Weber’s test- is a screening test for
or shock to the heart. hearing performed with a tuning fork
Nebulizer - medical equipment that a person Audiometer - a machine used for evaluating
with asthma or another respiratory hearing acuity.
condition it facilitate proper breathing pattern. Rinne’s - is used primarily to evaluate loss of
Laryngoscopy - is a visual examination below hearing in one ear.
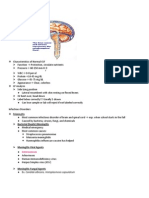
the back of the throat, where the voice box BRAIN STATION
(larynx) containing the vocal cords is located. They are the station who’s assigned in brain problem
OPD (OUT PATIENT DEPARTMENT) and cases.
A part of the hospital with allotted physical facilities Brain Station cases:
and medical and other staffs, with regularly scheduled Seizures- is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical
hours, to provide care for patients who are not disturbance in the brain. It can cause changes
registered as inpatients. A hospital department where in your behavior, movements or feelings, and
patients receive diagnosis and/ or treatment but do in levels of consciousness.
not stay overnight. Parkinson’s disease- is a brain disorder that
CASES IN OPD leads to shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with
EENT problem like cataract, glaucoma and walking, balance, and
hearing loss are common cases encountered in coordination. Parkinson's symptoms usually
OPD. begin gradually and get worse over time. As
OPD PROCEDURES the disease progresses, people may have
difficulty walking and talking.
Cerebral palsy (CP) - is a group of permanent Phosphorus binders. ...
movement disorders that appear in early B-complex Vitamin & folic acid. ...
childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among Topical creams & antihistamines. ...
people and over time. Cerebral palsy (CP) is a Vitamin E.
group of permanent movement disorders that Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney
appear in early childhood. Signs and failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function.
symptoms vary among people and over time. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your
Myasthenia diseases -is a chronic blood, which are then excreted in your urine.
autoimmune, neuromuscular disease that Acute kidney failure -happens when
causes weakness in the skeletal muscles that your kidneys suddenly lose the ability to eliminate
worsens after periods of activity and improves excess salts, fluids, and waste materials from the
after periods of rest. blood. This elimination is the core of your kidneys'
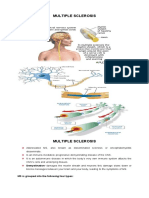
Multiple sclerosis- is a potentially disabling main function. Body fluids can rise to dangerous levels
disease of the brain and spinal cord (central when kidneys lose their filtering ability.
nervous system).the immune system attacks
Day Surgery
the protective sheath (myelin) that covers
The Day Surgery Unit is a standalone facility designed
nerve fibers and causes communication
specifically for patients who do not need to stay in
problems between your brain and the rest of
hospital overnight. All of our patients for general
your body.
anesthesia are carefully selected for suitability through
Guillain-Barre syndrome- is a rare disorder in
pre-assessment.
which your body's immune system attacks
your nerves. Weakness and tingling in your
GENITOURINARY CASES
extremities are usually the first symptoms.
URETEROSCOPY- uses an ureteroscope to look
These sensations can quickly spread,
inside the ureters and kidneys. Abnormal
eventually paralyzing your whole body.
tissue, polyps, tumors, or cancer in a ureter or
Procedure: in the lining of a kidney.
EEG- electroencephalogram is a test that detects CYSTOSCOPY- A procedure that allows to
electrical activity in your brain using small, metal discs examine the lining of your bladder and the
(electrodes) attached to your scalp. Your brain cells tube that carries urine out of your body
communicate via electrical impulses and are active all (urethra).
the time, even when you're asleep. Meatoplasty -This procedure is done when
HEMODIALYSIS UNIT the opening at the end of the penis is too
The Hemodialysis unit provides all of the necessary small or the shape of the hole distorts the
services required for the optimal management of the urinary stream, making it difficult for him to
patient with acute renal failure or End Stage Renal urinate.
Disease. Specialized services include the placement of Orchiopexy -A surgery to move an
vascular access for the conduct of therapeutic undescended testicle into the scrotum and
hemodialysis, hemoperfusion, plasmapheresis, or permanently fix it there.
hemofiltration. Scrotoplasty -Also known as oscheoplasty, is
HEMODIALYSIS PROCEDURES surgery to repair or create a scrotum.
There are three main components to a
Sclerotherapy -A medicine is injected into
hemodialysis machine - the hemodialysis
blood vessels or lymph vessels that causes
(artificial kidney), the dialysis membrane, and
them to shrink. It is commonly used to treat
the dialysate.
varicose veins or so-called spider veins.
Hemodiafiltration third technique is a
combination of the first two techniques - Septoplasty -is a procedure to fix a deviated
i.e. hemodialysis combined with septum. Often the result of trauma, a deviated
hemofiltration. There a various permutations septum is a misalignment of the nasal septum
of this combination, with recent evidence leading to impeded airflow into the nasal
suggesting that intermittent hemodiafiltration cavities.
gives better long term results in an outpatient Tonsillectomy -A surgical procedure that
setting, when compared with patients removes the tonsils to treat infection and
receiving regular hemodialysis. inflammation of the tonsils.
7 Common Drugs Prescribed for Dialysis Patients Vasectomy -is usually completed within 30
Erythropoietin. Nearly all patients with end minutes. After a short period of rest, the
stage renal disease (ESRD) who are on dialysis, patient can return home and resume normal
have anemia. activity, including typical sexual behavior,
Iron. within a week.
Active Vitamin D. EXCISION OF LUMPS
Excision of lumps and bumps refers to any minor the size and location. The tissue is often
procedure for skin or subdermal lesions, such as warts, completely detached.
moles, cysts or lipomas. Amputation- The loss of a distinct body part
such as a limb, finger, toe or ear. Often very
Excision of sebaceous cyst-A sebaceous or
severe with profuse bleeding. In the cases of
epidermoid cyst is an intradermal lesion
limb loss this is a medical emergency.
caused by a blocked sebaceous duct.
Excision of lipoma- A lipoma is a benign fatty WOUND DRESSING
tumor that usually occurs superficially in the Cleansing a wound or incision and apply sterile
subcutaneous tissue. Other sites include protective covering using aseptic technique.
deeper planes with attachment to fascial TYPES OF DRESSING
layers and in the retro peritoneum.
-Superficial lipomas can occur anywhere on Dry to dry- Used primarily for wounds closing
the body but are often found on contact areas by primary intention. Layer of wide mesh
over extensor surfaces. cotton gauze lies next to the wound surface.
-Lipomas can grow to a considerable size; they Second layer of dry absorbent cotton to
are usually encapsulated and lobulated with protect the wound.
fibrous attachments. Wet to dry- These are particularly useful for
-Multiple lipomata can occur in rare familial untidy or infected wounds that must be
conditions such as Dercum's disease although debrided and closed by secondary intention.
malignant change is rare. Wet to Wet- Used in clean open wounds.
Layer of wide mesh gauze saturated with
SUTURING
antibacterial solution next to the wound
The surgical suture is used to hold body tissues
surface, second layer of absorbent material
together after injury or surgery. Suturing a wound is an
saturated with the same solution to dilutes
important surgical skill to learn and become
viscous exudates
competent in.
Wet to damp- Variation of wet to dry dressing.
SUTURING TECHNIQUES
Interrupted Suture CATHETER
Continuous Suture
Indwelling Catheter-An indwelling
Simple Continuous
catheter is similar to an intermittent
Locking Continuous
catheter but remains in place for a period
Continuous over & over suture
of days or weeks.
Vertical Mattress Suture
- Urethral catheter- Also called a Foley
Horizontal Mattress Suture
catheter, the healthcare provider inserts
Figure of 8 Suture
this type through a person’s urethra.
Subcuticular Suture
- Suprapubic catheter- A doctor will
surgically insert the suprapubic catheter
TYPES OF WOUND
through a small hole a few inches below
Incised wound- A clean, straight cut caused by the patient’s navel.
a sharp edge. Tends to bleed heavily as - External Catheter- Some males have the
multiple vessels may be cut directly across. option of using an external catheter. This
Laceration -A messy looking wound caused by is a condom-like device that fits over the
a tearing or crushing force. Doesn’t tend to penis. A tube attached to the catheter
bleed as much as incised wounds but often collects urine into a drainage bag.
causes more damage to surrounding tissues. - External Catheter- Doctors usually
Abrasion- An abrasion is a type of open wound recommend external catheters for males
that's caused by the skin rubbing against a with incontinence who do not experience
rough surface. It may be called a scrape or a urinary blockages or retention and can use
graze. When an abrasion is caused by the skin the catheter themselves.
sliding across hard ground, it may be called - Intermittent Catheter- The intermittent
road rash. catheter, or a standard catheter, is a thin,
Puncture- A deep wound caused by a sharp, flexible tube that a person temporarily
stabbing object (i.e. a nail). May appear small inserts into their bladder through the
from the outside but may damage deep urethra.
tissues. URINOMETER- The urinometer, a type of
Avulsion- A wound caused by a tearing force hydrometer, was used for measuring the
in which tissue is torn away from its normal specific gravity of urine. Specific gravity is
position. May bleed profusely depending on a function of the number, density and
weight of the solute particles present in
the urine, and is used as a measure of the
concentrating power of the kidney.
UROFLOWMETER- Uroflowmetry is a
simple, diagnostic screening procedure
used to calculate the flow rate of urine
over time. The test is noninvasive and may
be used to assess bladder and sphincter
function.
You might also like
- Spinal Stenosis And Pinched Nerve A Simple Guide to These conditionsFrom EverandSpinal Stenosis And Pinched Nerve A Simple Guide to These conditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Diagnostic Table 11Document9 pagesDiagnostic Table 11api-404185844No ratings yet
- Iicp 1Document5 pagesIicp 1Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Medical Health Terms A-CDocument19 pagesMedical Health Terms A-CKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Special Sensors PDFDocument45 pagesSpecial Sensors PDFSwarna JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- EXPOSEEDocument9 pagesEXPOSEEMind BlowerNo ratings yet
- ANSWERSDocument4 pagesANSWERSShyn MargarethNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic EvaluationDocument67 pagesDiagnostic EvaluationMyzing OraaNo ratings yet
- Medical Term PQRSTDocument37 pagesMedical Term PQRSTTika Arizon R NNo ratings yet
- Complete Physical Examination Eyes, Ears, Nose, ThroatDocument103 pagesComplete Physical Examination Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throatjennylyn guadalupe100% (3)
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument16 pagesMeniere's DiseaseKarina BundaNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSYDocument37 pagesEPILEPSYPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Human Development Psy. 127 4W2 Instructor Aileen Mccabe by Earl R. Lofland AUGUST 30, 2018Document14 pagesHuman Development Psy. 127 4W2 Instructor Aileen Mccabe by Earl R. Lofland AUGUST 30, 2018EarlNo ratings yet
- Ściąga AnfDocument1 pageŚciąga AnfKasia ManżukNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemVinDiesel Balag-eyNo ratings yet
- English Class 1Document9 pagesEnglish Class 1Jose RamirezNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy EpilepsyDocument8 pagesEpilepsy EpilepsyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Neurology: Michael R. EncisoDocument171 pagesNeurology: Michael R. EncisoKristine BautistaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Bullets FoundationsDocument10 pagesSupplemental Bullets FoundationsrayneamgNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis. OCENA AUBREYDocument26 pagesMultiple Sclerosis. OCENA AUBREYCHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAONo ratings yet
- Chronic Open-Angle GlaucomaDocument8 pagesChronic Open-Angle GlaucomaDon AzagraNo ratings yet
- Neurological Alterations NotesDocument12 pagesNeurological Alterations NotesAnna TaylorNo ratings yet
- Park Inso N'S Dise ASEDocument132 pagesPark Inso N'S Dise ASEGrace Dela Rosa MelecioNo ratings yet
- Natural - History - of - Disease - Enriquez-FernandezDocument5 pagesNatural - History - of - Disease - Enriquez-FernandezPatrick EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve Palsy: Dr. Saud AlromaihDocument74 pagesFacial Nerve Palsy: Dr. Saud AlromaihChandra ManapaNo ratings yet
- Adhesive CapsulitisDocument7 pagesAdhesive CapsulitisMariane GumbanNo ratings yet
- PonstanDocument5 pagesPonstanYou know whoNo ratings yet
- Phrenic Nerve DamageDocument15 pagesPhrenic Nerve DamageIzza Mae Ferrancol PastranaNo ratings yet
- Vertigo Vertigo: Pembimbing: Dr. Nella, Sp. SDocument40 pagesVertigo Vertigo: Pembimbing: Dr. Nella, Sp. SAbdil AbdelNo ratings yet
- Neuro CH 14 Study GuideDocument9 pagesNeuro CH 14 Study GuideMichael J MillerNo ratings yet
- Principles of Emergency NursingDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Emergency NursingShamera MahabassalNo ratings yet
- Vestibular NeuronitisDocument3 pagesVestibular NeuronitisAnish RajNo ratings yet
- Dizziness: Presented By: Rawan Shaher Al-AssafDocument47 pagesDizziness: Presented By: Rawan Shaher Al-AssafRazan Shaher Al Assaf100% (1)
- Fundamentals TerminologiesDocument10 pagesFundamentals TerminologiesupuanNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Medical Terms - Pathology and Laboratory Medicine - Western UniversityDocument13 pagesGlossary of Medical Terms - Pathology and Laboratory Medicine - Western UniversitymusatiiNo ratings yet
- Eye AnatomyDocument18 pagesEye AnatomySteph VistalNo ratings yet
- Cetebella Lesion TestDocument19 pagesCetebella Lesion TestMadhura Pushpa kumaraNo ratings yet
- Pupillary Responses - Stanford Medicine 25 - Stanford Medicine - Https - Stanfordmedicine25.stanford - Edu - The25 - Pupillary - HTMLDocument8 pagesPupillary Responses - Stanford Medicine 25 - Stanford Medicine - Https - Stanfordmedicine25.stanford - Edu - The25 - Pupillary - HTMLMatthew PrestonNo ratings yet
- PHN Health TeachingDocument3 pagesPHN Health TeachingJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Disease Information SheetDocument2 pagesNote Taking Disease Information SheetRotem ShenkmanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Title PDFDocument20 pagesCase Study Title PDFZerimar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Neuro EquilibriumDocument6 pagesNeuro EquilibriumNeuro EquilibriumNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument10 pagesBrainurbanistasNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-19 at 4.56.02 PMDocument29 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-19 at 4.56.02 PMmiss latteNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis: Demyelination-Damages The Myelin Sheath and Neurons This Damage Slows Down orDocument6 pagesMultiple Sclerosis: Demyelination-Damages The Myelin Sheath and Neurons This Damage Slows Down orNorhana ManasNo ratings yet
- MECA Student Manual Rev 1.0Document82 pagesMECA Student Manual Rev 1.0Larche PalmaNo ratings yet
- Seizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaDocument4 pagesSeizure Dsiorder: University of Nueva Caceres College of Nursing City of NagaEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- What Is An Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) ? How Should I Prepare?Document4 pagesWhat Is An Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) ? How Should I Prepare?MarcelitaTaliaDuwiriNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Disorder and Rehab PDFDocument15 pagesVestibular Disorder and Rehab PDFMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Disorders and Rehabilitations: 1. AnatomyDocument15 pagesVestibular Disorders and Rehabilitations: 1. AnatomyMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Mineire'sDocument16 pagesMineire'sShaykh Evangelista BacualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Neurologic Examination: Section 3Document15 pagesChapter 1 - The Neurologic Examination: Section 3gus_lionsNo ratings yet
- Prefix and Meaning Medical Term (Site 2 - Preferably Terms Used in Surgery)Document6 pagesPrefix and Meaning Medical Term (Site 2 - Preferably Terms Used in Surgery)RAFNo ratings yet
- EpilepsyDocument29 pagesEpilepsyepeydenfajardoNo ratings yet
- HA LEC Module 8 and 9 1Document30 pagesHA LEC Module 8 and 9 1Althea Sachi CruzNo ratings yet
- Ingles - 1° AñoDocument43 pagesIngles - 1° AñoRox Sof100% (1)
- Acoustic Neuromas: Information For Patients and FamiliesDocument8 pagesAcoustic Neuromas: Information For Patients and FamiliesMrgNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Daga, Joel Andrew BSN 3DDocument17 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Daga, Joel Andrew BSN 3DJoel Andrew Java Daga100% (2)
- A Medical DictionaryDocument8 pagesA Medical DictionaryAdi CretuNo ratings yet
- Talley NervusDocument47 pagesTalley NervusChoga ArlandoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Semi-Final ExamDocument1 pageThe Contemporary World Semi-Final ExamflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Assessment RationaleDocument16 pagesNeurologic Assessment RationaleflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Crutchwalking QuizDocument2 pagesCrutchwalking QuizflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Some Flowers Are Not Fragrant - TrueDocument2 pagesSome Flowers Are Not Fragrant - TrueflorenzoNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionflorenzoNo ratings yet
- NCP - SamontinaDocument5 pagesNCP - SamontinaflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Problem: Pain at 6/10 For A "Sore Right Shoulder" Date Evaluated: December 14, 2020Document2 pagesProblem: Pain at 6/10 For A "Sore Right Shoulder" Date Evaluated: December 14, 2020florenzoNo ratings yet
- Presentation of The Situation Por Cristo Final VersionDocument4 pagesPresentation of The Situation Por Cristo Final VersionflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Assignment #5 - SamontinaDocument2 pagesAssignment #5 - SamontinaflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument2 pagesRequest LetterflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Histo 1Document4 pagesHisto 1florenzoNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY 11 411 5 and 12 2 12 3Document6 pagesCASE STUDY 11 411 5 and 12 2 12 3Florenz JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document5 pagesChapter 15florenzo100% (3)
- DEFINITIVE HOSTS para LecDocument2 pagesDEFINITIVE HOSTS para LecflorenzoNo ratings yet
- Application and ResumeDocument3 pagesApplication and ResumeflorenzoNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (20)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)