Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 Vocab
Uploaded by
Cassidy Nalband0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 4 vocab
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesChapter 4 Vocab
Uploaded by
Cassidy NalbandCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chapter 4 vocab
1. Sensation- any concrete, conscious experience resulting from stimulation of a specific
sense organ, sensory nerve, or sensory area in the brain.
2. Perception- the ability to see, hear, or become aware of something through the senses.
3. White light- a brilliant light reported to be experienced by some people when dying or
undergoing near-death experiences
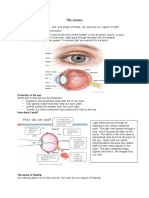
4. Cornea-the transparent layer forming the front of the eye.
5. Iris- a flat, colored, ring-shaped membrane behind the cornea of the eye, with an
adjustable circular opening (pupil) in the center.
6. Lens- a nearly transparent biconvex structure suspended behind the iris of the eye, the
sole function of which is to focus light rays onto the retina.
7. Pupil- the opening within the iris through which light passes before reaching the lens
and being focused onto the retina
8. Retina- layer of nervous tissue that covers the inside of the back two-thirds of the
eyeball, in which stimulation by light occurs, initiating the sensation of vision
9. Blind spot-an obscuration of the visual field
10. Rod- a type of photoreceptor cell in the retina, they are sensitive to light levels and help
give us good vision in low light, they are concentrated in the outer areas of the retina
and give us peripheral vision
11. Cone- a type of photoreceptor cell in the retina, give us our color vision, cones are
concentrated in the center of our retina in an area called the macula and help us see
fine details, the retina has approximately 120 million rods and 6 million cones
12. Color blindness- can happen when one or more of the color cone cells are absent, not
working, or detect a different color than normal. Severe color blindness occurs when all
three cone cells are absent
13. Afterimage-visual illusion in which retinal impressions persist after the removal of a
stimulus, believed to be caused by the continued activation of the visual system
14. Audition- formal phrase for hearing
15. Pitch- the subjective attribute that permits sounds to be ordered on a musical scale
16. Timbre- the perceptual attribute relating to the quality of a sound
17. Intensity-the quantitative value of a stimulus or sensation
18. Decibels- a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of acoustic or electric power
19. Eardrum- a thin flap of skin at the end of the ear canal
20. Cochlea- a bony, spiral-shaped, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound
waves travel and trigger nerve impulses
21. Hair cells- any of the sensory receptors for hearing, located in the organ of Corti within
the cochlea of the inner ear, they respond to vibrations of the basilar membrane via
movement of the fine hair-like structures that protrude from them
22. Auditory nerve-is a sensory nerve, it is found in the head and transmits information
from the inner ear to the brain in the form of sound (energy that impinges on
the ear drum
23. Cutaneous receptors- the types of sensory receptor found in the dermis or epidermis
24. Olfaction- the sense of smell, involving stimulation of receptor cells in
the olfactory epithelium (located in the nasal passages) by airborne volatile substances
called odorants
25. Cilia-microscopic, hair-like structures on the surface of cells that beat in unison to create
movement
26. Olfactory bulbs- brain structure responsible for our sense of smell
27. Pheromones- a chemical signal that is released outside the body by members of a
species and that influences the behavior of other members of the same species
28. Taste receptors- chemically react with food molecules and saliva to produce taste
29. Size constancy- the ability to perceive an object as being the same size despite the fact
that the size of its retinal image changes depending on its distance from the observer.
30. Color constancy- a process that allows the brain to recognize a familiar object as being a
consistent color regardless of the amount or wavelengths of light reflecting from it at a
given moment.
31. Brightness constancy- the tendency to perceive a familiar object as having the
same brightness under different conditions of illumination
32. Space constancy-the ability to keep objects in the environment steady by perceiving
either. ourselves or outside objects as moving
33. Depth perception- the visual ability to perceive the world in three dimensions, coupled
with the ability to gauge how far away an object is
34. Visual cliff-involves an apparent, but not actual drop from one surface to another,
originally created to test babies' depth perception
35. Binocular disparity- refers to the difference in image location of an object seen by the
left and right eyes, resulting from the eyes' horizontal separation
36. Visual texture- an attribute of a two-dimensional figure or a two-dimensional rendering
of a three-dimensional object that describes its surface characteristics
37. Gestalt-an organized whole that is perceived as more than the sum of its parts.
38. Similarity-degree of identity of two mental representations
39. Closure- when you see an image that has missing parts, your brain will fill in the blanks
and make a complete image so you can still recognize the pattern
40. Proximity-how close an object or person is physically to you
41. Illusion- a distortion of the senses, which can reveal how the human brain normally
organizes and interprets sensory stimulation
42. Muller-Lyer illusion- a well-known optical illusion in which two lines of the same length
appear to be of different lengths
43. Reversible figure- an ambiguous figure in which the perspective easily shifts, so that at
certain times specific elements appear to make up a distinct figure while at others those
same elements appear as an indistinct background
44. Subliminal perception- the registration of stimuli below the level of awareness,
particularly stimuli that are too weak for an individual to consciously perceive them
You might also like
- Printable Iq Test With Answers PDFDocument2 pagesPrintable Iq Test With Answers PDFBiniam Nega25% (12)
- TIPPS Psychiatric Evaluation ProformaDocument7 pagesTIPPS Psychiatric Evaluation Proformaknvr2001100% (1)
- Psychology Terms Chapt. 5Document3 pagesPsychology Terms Chapt. 5Meghan HanlonNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception HandoutsDocument3 pagesSensation and Perception HandoutsMariaMirandaJrNo ratings yet
- Sensing and PerceivingDocument38 pagesSensing and Perceivingsaba naheedNo ratings yet
- Zimmerman Becoming A Self Regulated Learner PDFDocument7 pagesZimmerman Becoming A Self Regulated Learner PDFIra Metariana100% (3)
- Basic Personality Inventory (Bpi)Document14 pagesBasic Personality Inventory (Bpi)Roxanne Forbes100% (1)
- Sensory ExaminationDocument4 pagesSensory ExaminationAthena BorjaNo ratings yet
- VIII. Special SensesDocument21 pagesVIII. Special SensesSkyNayvieNo ratings yet
- Ranga SNC PDFDocument287 pagesRanga SNC PDFcoolathea100% (1)
- Module 11 - Special SensesDocument6 pagesModule 11 - Special SensesAngela FelixNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Perceptual Process NotesDocument10 pagesSensory and Perceptual Process NotesSarah KimNo ratings yet
- KUSSNER MVI 24 Questions 2019 PDFDocument11 pagesKUSSNER MVI 24 Questions 2019 PDFChristian JaiderNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Through Clinical CasesDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomy Through Clinical CasesRomanescu Miruna0% (1)
- Stress ManagementDocument26 pagesStress Managementjune jaguarNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument72 pagesNeurophysiologyRaihan LuthfiNo ratings yet
- Heather Hardman Chapter 3 Terms 1. 2. 3. Sensory Receptors-4. 5. 6Document6 pagesHeather Hardman Chapter 3 Terms 1. 2. 3. Sensory Receptors-4. 5. 6Heather HardmanNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument2 pagesVocabularyapi-430903239No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sensation & Perception (A)Document13 pagesChapter 3 Sensation & Perception (A)Sidra.kNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Psychology Vocabulary (Part 1)Document3 pagesChapter 5 Psychology Vocabulary (Part 1)Annette MalysaNo ratings yet
- 9.00 Exam 1 Notes: KOSSLYN CHAPTER 3 - Sensation and Perception: How The World Enters The MindDocument13 pages9.00 Exam 1 Notes: KOSSLYN CHAPTER 3 - Sensation and Perception: How The World Enters The MindVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument14 pagesSensation and PerceptionJohn Kenneth Lopez BarritaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Visual Perception: Cognitive PsychologyDocument4 pagesChapter 3: Visual Perception: Cognitive PsychologyMicaella TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Document35 pages6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument14 pagesSensation and PerceptionStef FieNo ratings yet
- Psychology 201 Participation Questions Week 5Document1 pagePsychology 201 Participation Questions Week 5dina26633No ratings yet
- Special Senses HandoutDocument3 pagesSpecial Senses HandoutClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Olfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESDocument23 pagesOlfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESTida TpNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Nes-Grade 9 - Unit 1: Edited By: Aliaa MuhammedDocument25 pagesNes-Grade 9 - Unit 1: Edited By: Aliaa MuhammedMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Eyes Notes BiologyDocument5 pagesEyes Notes Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Special Senses: Part I: The Eye and VisionDocument8 pagesSpecial Senses: Part I: The Eye and VisionJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Visual and AuditoryDocument7 pagesVisual and AuditoryChristi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Guide 4Document6 pagesGuide 4Gabriela GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Crash Course VisionDocument2 pagesCrash Course VisionReem SleemNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Sensation & PerceptionDocument6 pagesWEEK 3 Sensation & PerceptionCHEN, KEYINGNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument1 pageHuman EyeLaksh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Sensory SystemDocument10 pagesSensory System- Cata Villalba -No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PerceptionDocument121 pagesChapter 3 PerceptionCHIQUI JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Human Visual System (Disowner)Document4 pagesHuman Visual System (Disowner)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 16 HANDOUTS Special SensesDocument6 pagesMODULE 16 HANDOUTS Special SensesMichaela PoNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument7 pagesNarrative ReportAndre DueñasNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EyeDocument17 pagesPhysiology of EyeHanna ShibuNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument3 pagesSensation and PerceptionjdmacatuladNo ratings yet
- The SensesDocument6 pagesThe SensesDANNA MARCELA MENDEZ QUIROZNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Sensory System Vision AND Perception NOTESDocument12 pagesUNIT 6 Sensory System Vision AND Perception NOTESKristine Nicole FloresNo ratings yet
- Chp.5 Sensation & PerceptionDocument7 pagesChp.5 Sensation & PerceptionEmma MahoneyNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument25 pagesSense OrgansSalma LabaranNo ratings yet
- Bionic Eye EB KNS 2019Document58 pagesBionic Eye EB KNS 2019Lalitaditya DivakarlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5Document3 pagesLecture Notes 5Carol RiveraNo ratings yet
- Hassan Nawaz - 202321192010Document15 pagesHassan Nawaz - 202321192010hassanNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFDocument4 pagesFact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFWy TeayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 9-Senses SensationDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Chapter 9-Senses SensationRonnie De Vera IINo ratings yet
- Sense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaDocument35 pagesSense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaNamulondo Mwajib Bogere100% (1)
- Unit 3Document16 pagesUnit 3sanoopsrajNo ratings yet
- Special Senses TranscriptDocument10 pagesSpecial Senses TranscriptLuis Gatchalian LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Sensorysystem Lesson 6.1: Sense of SightDocument6 pagesLesson 6: Sensorysystem Lesson 6.1: Sense of SightGlessy AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception 1Document2 pagesSensation and Perception 1mohamedsadiolaNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination and ResponseDocument5 pagesCo-Ordination and Responseapi-3723991No ratings yet
- Ch5 - 6 AP PsychDocument5 pagesCh5 - 6 AP PsychShan MoluNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 SensationDocument32 pagesLec 7 SensationSyed Ifran EjazNo ratings yet
- Special Senses KIUTDocument35 pagesSpecial Senses KIUTAnnette MhenggaNo ratings yet
- $@! ( (&9999Document8 pages$@! ( (&9999DANNA MARCELA MENDEZ QUIROZNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Perceptual ProcessesDocument8 pagesSensory and Perceptual ProcessesKika EspejoNo ratings yet
- U6 - Sensory Organs and Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesU6 - Sensory Organs and Nervous Systempovad44811No ratings yet
- Module 8 Sensory SystemDocument11 pagesModule 8 Sensory SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Special Senses EYEDocument4 pagesSpecial Senses EYEDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Coordination: NotesDocument6 pagesCoordination: Notesyuki soraNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The EyeDocument1 pageVocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The EyeOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 VocabDocument2 pagesChapter 3 VocabCassidy NalbandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter 7 ReviewCassidy NalbandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 VocabDocument2 pagesChapter 6 VocabCassidy NalbandNo ratings yet
- At What Age Should Kids Start Playing Competitive SportsDocument1 pageAt What Age Should Kids Start Playing Competitive SportsCassidy NalbandNo ratings yet
- Integrating Gay Issues Into Mainstream PsychDocument12 pagesIntegrating Gay Issues Into Mainstream PsychEmmieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-Sociocultural Theory & Contextual PerspectivesDocument5 pagesChapter 11-Sociocultural Theory & Contextual PerspectivesEmmanuel YuNo ratings yet
- Bab 2-08211141014Document38 pagesBab 2-08211141014Bunga frzNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Weight Assignment Scheme For Multi-Task LearningDocument6 pagesAdaptive Weight Assignment Scheme For Multi-Task LearningIAES IJAINo ratings yet
- Specify The Specific Intoxicant (I.e., Amphetamine-Type Substance, Cocaine, or Other Specify IfDocument4 pagesSpecify The Specific Intoxicant (I.e., Amphetamine-Type Substance, Cocaine, or Other Specify IfAnyaNo ratings yet
- Animal PerceptionDocument11 pagesAnimal PerceptionDanaGrujićNo ratings yet
- ENG Motivation in OrganizastionDocument31 pagesENG Motivation in OrganizastionMajaMitrovićNo ratings yet
- Neuro MEP Micro en To ReadDocument7 pagesNeuro MEP Micro en To Readzakarya alkubatiNo ratings yet
- Membrane PotentialsDocument40 pagesMembrane PotentialsdehaNo ratings yet
- Kyambogo University: Faculty of Engineering Depertment of Civil and Building EngineeringDocument4 pagesKyambogo University: Faculty of Engineering Depertment of Civil and Building Engineeringskalema34No ratings yet
- Listening StrategiesDocument10 pagesListening StrategiesElma PaseraNo ratings yet
- Nola Pender - Wikipedia PDFDocument11 pagesNola Pender - Wikipedia PDFAvhie ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Thesis Proposal AssumptionsDocument6 pagesThesis Proposal Assumptionsafbtbegxe100% (1)
- Speech AudiometryDocument17 pagesSpeech AudiometryPero Kvržica100% (1)
- Background Info-Benefits of Many LanguagesDocument1 pageBackground Info-Benefits of Many LanguagesRashmie MamondiongNo ratings yet
- Bernadette A. Divinagracia: Bloom's TaxonomyDocument9 pagesBernadette A. Divinagracia: Bloom's TaxonomydenizsadayNo ratings yet
- Learning TargetsDocument1 pageLearning TargetsCarlos Leo SantosNo ratings yet
- LIDZ THEODORE - A Psicosocial Orientation To Schizophrenic DisordersDocument9 pagesLIDZ THEODORE - A Psicosocial Orientation To Schizophrenic DisordersRodrigo G.No ratings yet
- Muscle ContractionDocument21 pagesMuscle ContractionMarilyn GumeyiNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument21 pagesPersonal Developmentjessica.padilla01No ratings yet