Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment of Pulse Sites
Uploaded by
choobiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment of Pulse Sites
Uploaded by
choobiCopyright:
Available Formats
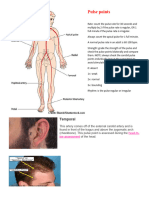
Assessment of Pulse Sites*
Temporal Found over the temporal bone above and lateral to the eye; easily
accessible, used often in children
Apical Best found between the fourth and fifth intercostals space,
midclavicular line; used to auscultate heart sounds and before the
administration of digoxin
Carotid Found on either side of the neck over the carotid artery; used to
assess circulation during shock or cardiac arrest and when other peripheral
pulses are poor
Brachial Found in the antecubital area of the arm; used to auscultate blood
pressure and to assess circulation of the lower arm
Radial Found on the thumb side of the forearm at the wrist; used to assess
circulation of the head and peripheral circulation
Ulnar Found at the wrist on the opposite side of the radius; used to assess
circulation of the hand and in Allen’s assessment test
Femoral Found below the inguinal ligament midway between the
symphysis pubis and the anterosuperior iliac spine; used to assess circulation
of the leg; can be used to assess circulation during shock or cardiac arrest or
when other peripheral pulses are poor
Popliteal Found behind the knee; used to assess lower leg circulation
Posterior tibial Found on the inner side of each ankle; used to assess foot
circulation
Dorsalis pedis Found along the top of the foot between extension tendons of
the great and first toes; used to assess the circulation of the foot
Normal Breath Sounds
Vesicular Soft, low-pitched sighing over bronchiole and alveoli base on
inspiration
Bronchial Moderate, high-pitched sound over trachea
Bronchovesicular Moderate sound over first and second intercostal spaces
Tracheal Loudest and highest pitched of normal breath sounds, harsh and
tubular
You might also like
- Pulse PointsDocument4 pagesPulse PointsZnieh ZniehNo ratings yet
- Assessing the Pulse: Factors, Sites, and AlterationsDocument22 pagesAssessing the Pulse: Factors, Sites, and AlterationsMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesChapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemSandra GabasNo ratings yet
- Cardiothoraxic and Vascular ExaminationDocument4 pagesCardiothoraxic and Vascular ExaminationPreetha PANo ratings yet
- Approach To The Cardiovascular Examination567 160120085414 PDFDocument22 pagesApproach To The Cardiovascular Examination567 160120085414 PDFHNINNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment: The Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular SystemsDocument18 pagesPhysical Assessment: The Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular Systemsmalyn1218No ratings yet
- Pulse Points Nursing Assessment PDFDocument8 pagesPulse Points Nursing Assessment PDFERANo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument53 pagesCardiovascular Systemmehakapoor29No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANDocument122 pagesCardiovascular System: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANClifford Subagan Patil-aoNo ratings yet
- PulseDocument13 pagesPulseArdi EroNo ratings yet
- Arterial Pulse Sites PDFDocument1 pageArterial Pulse Sites PDFRigor MortisNo ratings yet
- Abdomen exam guide under 40 charsDocument5 pagesAbdomen exam guide under 40 charsdidutza91No ratings yet
- CVS Examination InstructionsDocument5 pagesCVS Examination Instructionsmagdy balahaNo ratings yet
- Heart & Neck Vessel AssessmentDocument46 pagesHeart & Neck Vessel AssessmentLouise Nathalia VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisOlga RevalinaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of CvsDocument70 pagesAssessment of CvsTouseeq ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Examination TechniquesDocument36 pagesCardiovascular Examination TechniquesRUTUJA HARISH KSHIRSAGAR100% (1)
- Presentation B. INGGRIS FIKS BUK PUPUTDocument52 pagesPresentation B. INGGRIS FIKS BUK PUPUTRosy OktaridaNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Institute of NursingDocument9 pagesFar Eastern University: Institute of NursingAmira VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chest Xray 2Document39 pagesChest Xray 2sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemCallie ParkNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document1 pageModule 13A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Heart AuscultationDocument17 pagesHeart AuscultationshadabNo ratings yet
- Pulseandheartsound 181202083753Document21 pagesPulseandheartsound 181202083753Akanksha LahaseNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: DiaphragmDocument18 pagesVital Signs: DiaphragmLenjoy CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular BigDocument37 pagesCardiovascular Bigfaiz nasirNo ratings yet
- Cardiac AssessmentDocument48 pagesCardiac AssessmentRatheesh NathNo ratings yet
- Combat Life Saver: Lesson 18 Measure and Monitor A Casualty'S PulseDocument24 pagesCombat Life Saver: Lesson 18 Measure and Monitor A Casualty'S PulseMark CheneyNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument1 pageCardiovascularshellstyneyenyenNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) Is ADocument14 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) Is APaul John HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Topics:: 1. The Heart 2. Peripheral Vascular System 3. Abnormal FindingsDocument18 pagesTopics:: 1. The Heart 2. Peripheral Vascular System 3. Abnormal FindingsAya CalauToNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Vital SignsDocument7 pagesAssessment of Vital SignsFloriza de LeonNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Caridovascular SysDocument36 pagesAssessment of Caridovascular Syssceince with EZNo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck AssessmentDocument3 pagesHeart and Neck AssessmentKiara Ash BeethovenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physical Examination GuideDocument59 pagesCardiovascular Physical Examination GuideSheila Jessica AndavaniaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument38 pagesCardiovascular SystemShyn BaldostamonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment (1)Document73 pagesCardiovascular Assessment (1)matthewsarfrazbhattiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Cardiovascular Examination, ECG and BPDocument43 pagesLab 5 Cardiovascular Examination, ECG and BP202310446No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument47 pagesUntitledJi CaratNo ratings yet
- Vitalsignslecturenewbatch 160211000037Document8 pagesVitalsignslecturenewbatch 160211000037faityneoNo ratings yet
- Pericardium & HeartDocument52 pagesPericardium & HeartShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Respiratory AssessmentDocument3 pagesPulse and Respiratory AssessmentYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign: PulseDocument29 pagesVital Sign: PulsedanielNo ratings yet
- Pulse sites for upper limb, lower limb, head, neck and torso assessmentDocument1 pagePulse sites for upper limb, lower limb, head, neck and torso assessmentArnel AlmazanNo ratings yet
- PulseDocument15 pagesPulseapi-391911357No ratings yet
- 2. Human BodyDocument2 pages2. Human Bodypoweryou403No ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular Assessment: Manali H Solanki F.Y.M.Sc - Nursing J G College of NursingDocument46 pagesCardio Vascular Assessment: Manali H Solanki F.Y.M.Sc - Nursing J G College of NursingmeghanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: By: S@JDocument35 pagesCardiovascular System: By: S@JD TekNo ratings yet
- Examining the Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesExamining the Cardiovascular SystemPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of CVSDocument33 pagesClinical Examination of CVSmahnoorNo ratings yet
- Semi CoaDocument19 pagesSemi Coa31 PASION, ROCHELLE C.No ratings yet
- L7 - Locomotion and Movement - Oct 8, 2019 PDFDocument47 pagesL7 - Locomotion and Movement - Oct 8, 2019 PDFKent WellsNo ratings yet
- Cardio AuscultationDocument19 pagesCardio AuscultationshadabNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs or Cardinal SignsDocument5 pagesVital Signs or Cardinal SignsMadelaine Mary Rose GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Thorax and The Lungs: Group 11 FMPDocument27 pagesThe Thorax and The Lungs: Group 11 FMPTisha TancongcoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory LabDocument4 pagesCirculatory LabKyla NicoleNo ratings yet
- CVS Clinical Mark Sheet: Adel HasaninDocument19 pagesCVS Clinical Mark Sheet: Adel HasaninDrShamshad Khan100% (1)
- Procedure of The Heart and Lungs Heart DiseasesDocument19 pagesProcedure of The Heart and Lungs Heart DiseasesKristin ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- DopplerDocument5 pagesDopplerGwyneth GuintuNo ratings yet
- CIP Com Dev 2018Document4 pagesCIP Com Dev 2018choobiNo ratings yet
- Research NursingDocument3 pagesResearch NursingchoobiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Concepts in Critical Care NursingDocument3 pagesAdvanced Concepts in Critical Care Nursingchoobi100% (1)
- NEW BSN CURRICULUM - CMO 15 RevisedDocument2 pagesNEW BSN CURRICULUM - CMO 15 RevisedchoobiNo ratings yet
- Universal Prec QuestionsDocument8 pagesUniversal Prec QuestionschoobiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy: CannulaDocument3 pagesOxygen Therapy: CannulachoobiNo ratings yet
- DR Case SlipDocument1 pageDR Case SlipchoobiNo ratings yet
- ACCOMPLISHMENT REPORT On FAC. DEVDocument3 pagesACCOMPLISHMENT REPORT On FAC. DEVchoobiNo ratings yet
- Common Lung Disorders: Asthma Atelectasis BronchiectasisDocument2 pagesCommon Lung Disorders: Asthma Atelectasis BronchiectasischoobiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation ExamDocument2 pagesEvaluation ExamchoobiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal and Adventitious Sounds: Assessment Questions Regarding Respiratory StatusDocument1 pageAbnormal and Adventitious Sounds: Assessment Questions Regarding Respiratory StatuschoobiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System TumorsDocument1 pageNervous System TumorschoobiNo ratings yet
- Coronary ArteriesDocument2 pagesCoronary ArterieschoobiNo ratings yet
- Nres 1 Instructional PlanDocument10 pagesNres 1 Instructional PlanchoobiNo ratings yet
- level-of-disaster-preparedness-EDITED 1Document16 pageslevel-of-disaster-preparedness-EDITED 1choobiNo ratings yet
- Seizure Terminology: Without ShakingDocument1 pageSeizure Terminology: Without ShakingchoobiNo ratings yet
- Assessing Patient's Use of Sensory AidsDocument2 pagesAssessing Patient's Use of Sensory AidschoobiNo ratings yet
- Breast CaDocument1 pageBreast CachoobiNo ratings yet
- Types of Synovial JointsDocument2 pagesTypes of Synovial JointschoobiNo ratings yet
- Use of Cold: Local EffectsDocument2 pagesUse of Cold: Local EffectschoobiNo ratings yet
- Do We Really Need Theor1Document1 pageDo We Really Need Theor1choobiNo ratings yet
- Self AwarenessDocument1 pageSelf AwarenesschoobiNo ratings yet
- Types of FracturesDocument2 pagesTypes of FractureschoobiNo ratings yet
- Levels of ConsciousnessDocument1 pageLevels of ConsciousnesschoobiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories in The UkDocument1 pageNursing Theories in The UkchoobiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Problems TypologyDocument8 pagesNursing Problems TypologyClifford Ogad0% (1)
- Your Time Is LimitedDocument1 pageYour Time Is LimitedchoobiNo ratings yet
- TimeDocument1 pageTimechoobiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories in The United StatesDocument1 pageNursing Theories in The United StateschoobiNo ratings yet