Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 - Forecasting Dalam Perencanaan IWK
03 - Forecasting Dalam Perencanaan IWK
Uploaded by
svernav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views11 pagesThis document discusses forecasting techniques used in infrastructure planning. It outlines two main steps:
1. Using baseline data and judgmental or numerical techniques like extrapolation or econometrics to project key variables like population, housing, and employment.
2. Generating scenarios and alternative plans by varying input assumptions within realistic limits. Scenarios are then used to make predictions about outcomes like transportation or infrastructure needs. The goal is exploratory scenarios based on trends to facilitate infrastructure planning.
Original Description:
Original Title
03 - Forecasting dalam Perencanaan IWK
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses forecasting techniques used in infrastructure planning. It outlines two main steps:
1. Using baseline data and judgmental or numerical techniques like extrapolation or econometrics to project key variables like population, housing, and employment.
2. Generating scenarios and alternative plans by varying input assumptions within realistic limits. Scenarios are then used to make predictions about outcomes like transportation or infrastructure needs. The goal is exploratory scenarios based on trends to facilitate infrastructure planning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views11 pages03 - Forecasting Dalam Perencanaan IWK
03 - Forecasting Dalam Perencanaan IWK
Uploaded by
svernavThis document discusses forecasting techniques used in infrastructure planning. It outlines two main steps:
1. Using baseline data and judgmental or numerical techniques like extrapolation or econometrics to project key variables like population, housing, and employment.
2. Generating scenarios and alternative plans by varying input assumptions within realistic limits. Scenarios are then used to make predictions about outcomes like transportation or infrastructure needs. The goal is exploratory scenarios based on trends to facilitate infrastructure planning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
FORECASTING DALAM PERENCANAAN
INFRASTRUKTUR WILAYAH DAN KOTA
Parkin and Sharma, Infrastructure Planning, Chapter 5, Thomas
Thelford, 1999
“
Building the right infrastructure depends on good
forecasting, and the accuracy of this forecasting
will depend on the degree control over future
events that can be exercised by the planner
Baseline data
Judgemental and numerical
techniques
Projections:
Population
Housing
Employment
Scenario generation and design
of alternatives
Predictions:
Land travel
Air travel
Electricity demand
Civil engineering
infrastructure
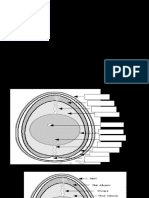
Typical Infrastructure forecasting Process (p. 66)
1.
Judmental and Numerical Techniques
Judgement MEthods
▷ The use of expert to predict the future
conforms to common sense
▷ To See what They Want To See, overly
conservative, consistently overconfidence
▷ Try to avoid your judges together in a group
▷ Combine forecast derived by different
methods
Extrapolation
▷ The extrapolation of historical data : reliable and the
social environment is stable
▷ Steps in extrapolation methods:
1. Cleaning data (outliers, combining measures)
2. Deseasonalizing data
3. Selecting smooting factors
4. Calculating new starting point for the forecast curve
5. Calculating a new trend
6. Estimating the current status, correcting for lag
7. Calculating the forecast
8. Updating seasonal factors, returning to step iv and repeating
Econometric Method
▷ When causal relationship are well understood
▷ Predictable changes are anticipated in the causal variables
▷ Regression analysis is the best known
▷ The key: to keep the regression equation as simple as possible,
complexity leads to confusion, no increase the accuracy
▷ Mitigation for causal variables
▷ Sensitivity testing
Segmentation
▷ When the phenomenon being forecast can be broken down
into discrete parts
▷ Segment to be independent, equal importance, good database
▷ The relationship between segments must be understood
▷ Segment may be chosen because of their relevance to the
prediction of changes in the variable or because of similarity of
causal variables (marketing research and trip forecasting)
▷ A form of simulation sometimes used in regional planning
studies is input-output analysis
▷ Accuracy improved by combining method: subjective,
segmentation, extrapolation or econometric method
Examples of projections
▷ Population projections
Segmentation component methods
Migration between regions significant factors
▷ Housing projections
Little control over the mechanism of supply (unless state)
Space for housing and the adequacy of this provision
Household, headship rates: proportion of a population groups :
household heads
The type of housing depend on the range of household sizes
▷ Employment projections
Needs comprehensive knowledge of the past and present economic
activities in the target region
Surveys, census data or from surveys
Manufacturing non manufacturing, traffic analysis zone, commuting trip
between zones
Complexity of market motivation, sitting of small to medium
enterprises; choice of people make when they choose housing
2.
Scenario Generation and Design
Alternatives
Scenario generation
▷ Scenario are plans generated to facilitate predictions
▷ Descriptions of possible plans situated on the planning horizon
▷ Input assumption (population, housing, or employment projections) are varied between
realistic limits, typical sketch plans creation combination of values
▷ Different types of transport modes or variation in funding
▷ Prediction, based on modeling, derived for each of the scenarios
▷ Axes in scenarios:
○ Exploratory – anticipatory : present and explore what consequences may result. Anticipatory: final state and speculate
on what events are required to create it
○ Descriptive – normative: descriptive take no account desirability of the future; normative: social values and desirable
goals
○ Trend – peripheral: projections based on past events; peripheral : low probability futures
▷ Infrastructure planning study: exploratory, descriptive, trends
▷ Community group: anticipatory, normative, peripheral “imagination and hope”
▷ Number of scenario: avoid 5-6
You might also like
- HPLC Calculator MTSDocument13 pagesHPLC Calculator MTSNguyễn Văn MinhNo ratings yet
- 8.7 Case StudyDocument2 pages8.7 Case StudymaddisonNo ratings yet
- Can Foresight Studies Strengthen Strategic Planning Processes at The Urban and Regional Level?Document21 pagesCan Foresight Studies Strengthen Strategic Planning Processes at The Urban and Regional Level?Venu KailashNo ratings yet
- PPA 691 - Seminar in Public Policy Analysis: Lecture 5 - Forecasting Policy FuturesDocument21 pagesPPA 691 - Seminar in Public Policy Analysis: Lecture 5 - Forecasting Policy FuturesAira KatongNo ratings yet
- Dare To Plan An Essay On The Future in Planning Practice and EducationDocument11 pagesDare To Plan An Essay On The Future in Planning Practice and EducationYogma Noor Dinara G.No ratings yet
- Robust Plans and Contingent PlansDocument17 pagesRobust Plans and Contingent PlanstaliagcNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Backcasting For Strategic Sustainable City PlanningDocument32 pagesCase Study On Backcasting For Strategic Sustainable City PlanningMisaj SNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Demand For ServicesDocument14 pagesForecasting Demand For ServicesCHRISTY LINNo ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument29 pagesRemote Sensingjie ZhangNo ratings yet
- House Price Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument6 pagesHouse Price Prediction Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- The Application of Space Syntax Analysis in Project Identification: A Special Reference To The MoratuwaDocument9 pagesThe Application of Space Syntax Analysis in Project Identification: A Special Reference To The MoratuwaaveendraNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument6 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityuditNo ratings yet
- Bond Risk Premia With Machine LearningDocument73 pagesBond Risk Premia With Machine LearningVictor MaiaNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument11 pagesForecastingJeremias Pangisban Jr.No ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument6 pagesForecastingNambi RajanNo ratings yet
- Settlement Pattern in Regional Plan: Case Study of Pune DistrictDocument2 pagesSettlement Pattern in Regional Plan: Case Study of Pune DistrictBhuvanaNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Analyzing Quantitative Da PDFDocument5 pagesStrategies For Analyzing Quantitative Da PDFwinda ahmadNo ratings yet
- Forecasting State and Household Populations Evaluating The Forecast Accuracy and Bias of Alternative Population Projections For StatesDocument14 pagesForecasting State and Household Populations Evaluating The Forecast Accuracy and Bias of Alternative Population Projections For StatesEugenio MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2.importance of Data in Geographical Studies-1Document3 pages2.importance of Data in Geographical Studies-1Zubair AnsariNo ratings yet
- PPA 691 - Seminar in Public Policy Analysis: Lecture 5 - Forecasting Policy FuturesDocument21 pagesPPA 691 - Seminar in Public Policy Analysis: Lecture 5 - Forecasting Policy Futureskuldip singhNo ratings yet
- 2 Ijeefusjun20182Document14 pages2 Ijeefusjun20182TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ee PBLDocument15 pagesEe PBLAnekant ManthanNo ratings yet
- House Price Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument10 pagesHouse Price Prediction Using Machine Learningphani phaniiiNo ratings yet
- Predictions in Soil Engineering: Gpotechnique 23, No. 2, 149-202Document52 pagesPredictions in Soil Engineering: Gpotechnique 23, No. 2, 149-202grf06No ratings yet
- Report Real EstateDocument8 pagesReport Real Estateshelkevaibhav218No ratings yet
- Fuzzy Versus Probabilistic Benefit/Cost Ratio Analysis For Public Work ProjectsDocument14 pagesFuzzy Versus Probabilistic Benefit/Cost Ratio Analysis For Public Work ProjectsTatik HandayaniNo ratings yet
- ES205 ResearchpaperDocument17 pagesES205 ResearchpaperBushra KhanNo ratings yet
- Syeda Saba Ali Asghar AbediDocument10 pagesSyeda Saba Ali Asghar AbedikomalNo ratings yet
- Geot 1973 23 2 151Document52 pagesGeot 1973 23 2 151znawcaduszkobietNo ratings yet
- Scenario Analysis in Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument14 pagesScenario Analysis in Environmental Impact AssessmentYnandar NandarNo ratings yet
- PT 1 DataDocument39 pagesPT 1 DataSHASHIKANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tourism Forecasting - 19M805, 19M811Document23 pagesTourism Forecasting - 19M805, 19M811Shreya GoyalNo ratings yet
- Best PDF in FPFDocument16 pagesBest PDF in FPFmanish kashyapNo ratings yet
- Predictions in Soil EngineeringDocument52 pagesPredictions in Soil Engineeringxieyn100% (1)
- A Prototype Method For Future Event Prediction Based On Future Reference Sentence ExtractionDocument8 pagesA Prototype Method For Future Event Prediction Based On Future Reference Sentence ExtractionnisaNo ratings yet
- Geographical Big Data Analysis of House Price in Shenzhen For Adaptation in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesGeographical Big Data Analysis of House Price in Shenzhen For Adaptation in Malaysiaindex PubNo ratings yet
- PT 2 MappingDocument35 pagesPT 2 MappingSHASHIKANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- A Visual Landscape Assessment Approach For Highdensity Urban DevelopmentDocument10 pagesA Visual Landscape Assessment Approach For Highdensity Urban DevelopmentNadiaFatimahAz-ZahrahNo ratings yet
- Topic - Mini Research Project (CIA 4)Document4 pagesTopic - Mini Research Project (CIA 4)MUDIT CHOPRA 2020224No ratings yet
- Lecture No.1Document8 pagesLecture No.1MUHAMMAD USMANNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Technology ForecastingDocument23 pagesUnit 3: Technology ForecastingNiharica SohalNo ratings yet
- A Free, Open-Source Tool For Identifying Urban Agglomerations Using Polygon DataDocument21 pagesA Free, Open-Source Tool For Identifying Urban Agglomerations Using Polygon DataJefferson WidodoNo ratings yet
- SpatialAnalysis&Modeling 2Document327 pagesSpatialAnalysis&Modeling 2henokmisaye23No ratings yet
- Cost Prediction Model For Building Construction ProjectsDocument2 pagesCost Prediction Model For Building Construction ProjectsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Crime Rate PredictionDocument26 pagesCrime Rate PredictionbsdrinkuNo ratings yet
- Use of Artificial Intelligence To Predict The Accuracy of Pre-Tender Building Cost EstimateDocument17 pagesUse of Artificial Intelligence To Predict The Accuracy of Pre-Tender Building Cost EstimateleeNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 1Document10 pages06 Chapter 1srisaidegree collegeNo ratings yet
- "Scenarios": Quality Tools LeanDocument3 pages"Scenarios": Quality Tools LeanAhmed M. HashimNo ratings yet
- Types of Survey Used in Urban PlanningDocument19 pagesTypes of Survey Used in Urban PlanningAshNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method For Rainfall Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument6 pagesA Novel Method For Rainfall Prediction Using Machine Learningvechalapu bhargaviNo ratings yet
- Berkhout Foresight PDFDocument16 pagesBerkhout Foresight PDFMiranda081No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Contextual Analysis - Rev00Document46 pagesLecture 1 - Contextual Analysis - Rev00Syee KhorNo ratings yet
- Operational Management POMG2710: Chapter OutlineDocument17 pagesOperational Management POMG2710: Chapter OutlineلبليايلاNo ratings yet
- Krithika HeheeeDocument17 pagesKrithika HeheeeNaveen Kumar R.S.No ratings yet
- Data Science For Finance Class 1Document12 pagesData Science For Finance Class 1PHAT NGUYENNo ratings yet
- 3 43 62 MCA03920 EditedDocument20 pages3 43 62 MCA03920 EditedPratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Câu 7.2Document5 pagesCâu 7.2Nguyễn Huỳnh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Budgeting of Infrastructure ProjectsDocument10 pagesRisk Based Budgeting of Infrastructure ProjectsAshimolowo BabatundeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of KNN and C5.0 Algorithm For Smart City ClassificationDocument3 pagesComparative Analysis of KNN and C5.0 Algorithm For Smart City Classificationanil kasotNo ratings yet
- Load Forecasting Methods and Techniques by Dr. Chandrasekhar Reddy Atla Dr. Chandras PDFDocument32 pagesLoad Forecasting Methods and Techniques by Dr. Chandrasekhar Reddy Atla Dr. Chandras PDFmarab12No ratings yet
- Fuzzy Criteria InfrastructureDocument12 pagesFuzzy Criteria InfrastructureAldi Martino HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Artificial intelligence: AI in the technologies synthesis of creative solutionsFrom EverandArtificial intelligence: AI in the technologies synthesis of creative solutionsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09. 28122020 E&MEDocument41 pagesLecture 09. 28122020 E&MEMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- ETABS To Builder Conversion WorkflowDocument24 pagesETABS To Builder Conversion Workflowchhay longNo ratings yet
- 2012 Topics On The Dynamics of Civil StructuresDocument435 pages2012 Topics On The Dynamics of Civil Structuresaion_rebNo ratings yet
- HIST 1010 EXAM 3 TEST PREP (With Answers)Document2 pagesHIST 1010 EXAM 3 TEST PREP (With Answers)Ophelia ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion: DR Vishwabharathi TDocument28 pagesBlood Transfusion: DR Vishwabharathi TSuma0% (1)
- Peachey: Knives and Bookbinding ToolsDocument30 pagesPeachey: Knives and Bookbinding ToolsRodrigo_La_Ros_1525No ratings yet
- CITDocument12 pagesCITAnu PartheeNo ratings yet
- Quantech Origin Averages - 1Document2 pagesQuantech Origin Averages - 1MAHESH VNo ratings yet
- Understanding Stress and StrainDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Stress and StrainYunus KhanNo ratings yet
- List of Measuring DevicesDocument8 pagesList of Measuring DevicesSajid SheikhNo ratings yet
- Barley Saturday in PicturesDocument2 pagesBarley Saturday in PicturesDigital MediaNo ratings yet
- Class Prefixes Suffixes and Present Perfect Continuous 2021Document22 pagesClass Prefixes Suffixes and Present Perfect Continuous 2021Angelo Jorge ParedesNo ratings yet
- RidgeBot - AI Driven Pen TestDocument1 pageRidgeBot - AI Driven Pen TestMuhammed Asif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Cataract SurgeryDocument19 pagesAnaesthesia For Cataract SurgeryRido Banar EkaputraNo ratings yet
- Linearization Techniques in Power AmplifiersDocument22 pagesLinearization Techniques in Power AmplifiersSalma KhanNo ratings yet
- Durastar DS1910HFDocument2 pagesDurastar DS1910HFEvelyn SigoliNo ratings yet
- Structure of An EggDocument29 pagesStructure of An EggsheilaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Economy, Hydrogen Storage and Fuelcell StackDocument20 pagesHydrogen Economy, Hydrogen Storage and Fuelcell StackpolysourceNo ratings yet
- GFL-LX Datasheet 150422Document1 pageGFL-LX Datasheet 150422AHMAD AMMEIRNo ratings yet
- Bulk Cargo GrainDocument7 pagesBulk Cargo GrainMayura RanatungaNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text DocumentsasgaatwilliamsNo ratings yet
- Delta Airlines and SummaryDocument39 pagesDelta Airlines and Summaryeissa alesayiNo ratings yet
- Maquette Des Enseignements: GGC 3eme ANNEE (GGC3)Document56 pagesMaquette Des Enseignements: GGC 3eme ANNEE (GGC3)aliabdalghafourNo ratings yet
- Belt Tracking in General: Light Belt Conveyor Installations - Engineering GuidelinesDocument1 pageBelt Tracking in General: Light Belt Conveyor Installations - Engineering Guidelines9964355812No ratings yet
- 2305-01-101 Proposal Attn Ms. Camille PDFDocument11 pages2305-01-101 Proposal Attn Ms. Camille PDFJohn Eduard De LeonNo ratings yet
- Alg 9.1 PacketDocument5 pagesAlg 9.1 PacketAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Acme Juicer ManualDocument12 pagesAcme Juicer Manualmilesdzyn100% (1)
- My Custom Review-ProblemsDocument11 pagesMy Custom Review-ProblemsHân BảoNo ratings yet