Professional Documents
Culture Documents
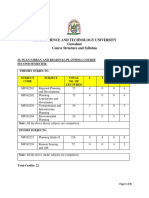
Course Code Course Name L-T-S Credits Year of AR6202 Planning Legislation & Governance 2-1-0 3 2016 Course Objectives
Uploaded by
Udayabhanu DM0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesThis document provides information on the course "Planning Legislation & Governance" including its objectives, syllabus, expected outcomes, and course plan. The course aims to make students aware of key planning laws and governance mechanisms in India. It will cover topics like the legislative process, important laws influencing planning and development, and government and governance systems at various levels. The course plan lists 6 modules that will examine concepts of law and legislation, critical planning laws in India, governance structures and institutions, and principles of good governance and participatory planning.
Original Description:
Original Title
Planning Legislation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on the course "Planning Legislation & Governance" including its objectives, syllabus, expected outcomes, and course plan. The course aims to make students aware of key planning laws and governance mechanisms in India. It will cover topics like the legislative process, important laws influencing planning and development, and government and governance systems at various levels. The course plan lists 6 modules that will examine concepts of law and legislation, critical planning laws in India, governance structures and institutions, and principles of good governance and participatory planning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesCourse Code Course Name L-T-S Credits Year of AR6202 Planning Legislation & Governance 2-1-0 3 2016 Course Objectives
Uploaded by
Udayabhanu DMThis document provides information on the course "Planning Legislation & Governance" including its objectives, syllabus, expected outcomes, and course plan. The course aims to make students aware of key planning laws and governance mechanisms in India. It will cover topics like the legislative process, important laws influencing planning and development, and government and governance systems at various levels. The course plan lists 6 modules that will examine concepts of law and legislation, critical planning laws in India, governance structures and institutions, and principles of good governance and participatory planning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
COURSE COURSE NAME L-T-S CREDITS YEAR OF
CODE INTRODUCTION
AR6202 Planning Legislation & 2-1-0 3 2016
Governance
Course To make the students aware of the concept of legislation as the
Objectives back-bone of any planned development.
To create awareness about the critical laws used in India and their
salient features.
To make the students aware of the governance mechanisms
involved in development planning, administration and
management.
Syllabus Introduction to Law and Legislation, significance of law and its relation
to planning, salient features and implications in development of
important laws, Concept of Government and Governance, Institutions
and processes followed in India, Good governance and new forms of
governance with best practices.
Expected
The students will have acquired knowledge about the process
Outcome
of planning and governance in India and the critical laws that
influence them.
Reference 1. A.Joshi, Town Planning Regeneration of Cities.
Books 2. Jain R B, Public Administration in India, 21st Century Challenges
for Good Governance, Deep and Deep Publications. PVT. LTD.,
2002
3. Manoj Sharma, Local Government Rural and Urban, Anmol
Publications Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2004
4. Mario Pinto, Metropolitan City Governance in India, Sage
Publications, New Delhi, 2000
5. Ministry of Health, Government of India - Report of the
Committee on Model Planning Legislation.
6. Mohammad Naseem, Environmental Law in India, Kluwer Law
International, 2011
7. Pai Panadiker V A, Governmental Systems and Development, S N
Mishra, Sweta Mishra, ChaitaliPai, Decentralised Planning and
Panchayati Raj Institutions, Mittal Publications, A-110, Mohan
Garden, New Delhi, 2000.
8. Tyagi R Public Administration, Principles and Practices, Atma
Ram & Sons
9. URDPFI Guidelines, Govt of India, Ministry of Urban
Development, www.moud.gov.in
10. Viswambar Nath, Administration and Development Planning in
India
COURSE PLAN
Module Contents Hours End
Sem.
Exam
Marks
Meaning of terms of law, legislation, ordinance,
bill, act, regulation and bye-laws.
Significance of law and its relationship to urban
planning - Benefits of statutory backing of schemes
- Law of eminent domain and police powers -
Evolution of planning legislation – A brief History
I of Planning Legislation in India and Abroad.
6 10%
Constitutional basis and provisions relating to land
its development and its use – Statutory powers and
responsibilities of Central Government, State
Governments, Union Territories, Local Bodies and
Local Authorities with respect to urban
development and their legal structure.
Town and Country Planning Act - Its implication on
preparation and implementation of regional plans,
development plans, town planning schemes, area
plans etc.
Critical Appraisal of Improvement Trust Act,
Development Authorities Act, Land Acquisition
Act 1986, Urban Land (Ceiling and Regulation) Act
1976, Slum Clearance/Slum Improvement Act,
Rent Control Act, legislations on conservation of
natural and manmade resources including Coastal
Zone regulations, Air and Water (Prevention and
II
Control) of Pollution Act, Mining and Forestry act, 8 20%
Conservation and management of ancient
monuments and archeological sites and remains
Act, 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts,
Legislations for public-private partnerships in urban
development and infrastructure projects.
Implications of the Acts on development.
Overview of development control regulations –
zoning, sub division regulations, building
regulations and bye-laws.
FIRST INTERNAL TEST
Governance: Definition, concepts and components,
Government and governance, salient provisions in
the Constitution of India.
Governance systems in India - Overview of urban
III and rural governance structure in India, evolution,
processes and the role of - The Planning 8 20%
Commission, National Development Council, NITI
Ayog and their role in framing development
policies.
Role of states in planning processes: facilitative,
regulatory and other powers, decentralization of
powers after the 73rd and 74th CAA, Local
institutions in the governance process. Post 73 rd
and 74 th Constitution Amendment Act
environment and the modified role and functions of
local bodies, local authorities, district authorities
and state level agencies, case examples.
Institutional framework for urban and rural
development planning, TCPO and various national
level committees and commissions on urbanisation,
IV state level institutions like metropolitan/urban
6 10%
development authorities, regional planning and
district level organisations
SECOND INTERNAL TEST
Participatory governance, people’s participation,
role of people’s participation in the planning
process, other stakeholders like NGO’s, civil
V society, private sector, scientific network,
international institutions etc. process of inclusion 6 20%
and exclusion in governance, access to government
by various stakeholders
Principles of good governance and practices, new
forms of governance, effectiveness of E-
governance mechanisms, role of advanced locality
management, resident welfare associations and
VI other such agencies in urban governance system.
International and National best practices on 8 20%
participatory governance and development
planning.
END SEMESTER EXAM
You might also like
- Arroyo Vs de Venecia Case DIgestDocument3 pagesArroyo Vs de Venecia Case DIgestAlvin Hilario100% (1)
- Manotok Realty, Inc V CADocument2 pagesManotok Realty, Inc V CAAgz Macalalad100% (2)
- General Studies New SyllabusDocument4 pagesGeneral Studies New SyllabusmykhaulujjhjNo ratings yet
- NLSIUDocument9 pagesNLSIUchandni babunuNo ratings yet
- Public Administration MmainDocument3 pagesPublic Administration MmainsuryabonagiriNo ratings yet
- Public AdministrationDocument4 pagesPublic AdministrationnitvivekNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Template - DR WASI AHMADDocument4 pagesSyllabus Template - DR WASI AHMADanushka vermaNo ratings yet
- Participatory Planning Processes in Indian CitiesDocument17 pagesParticipatory Planning Processes in Indian CitiesAnkitaVermaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus A3Document1 pageSyllabus A3Nikhil KondapalliNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission, Ajmer: Syllabi of The Paper/Subjects Prescribed For The Main ExaminationDocument3 pagesRajasthan Public Service Commission, Ajmer: Syllabi of The Paper/Subjects Prescribed For The Main ExaminationamangabbarNo ratings yet
- Numbered UPSC CSM 2013 Syllabus For GS PDFDocument7 pagesNumbered UPSC CSM 2013 Syllabus For GS PDFSushant PatilNo ratings yet
- General Studies-II: Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International RelationsDocument1 pageGeneral Studies-II: Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International RelationsdongfengJudahNo ratings yet
- Public - Administration - Mains IGNOU BA MADocument19 pagesPublic - Administration - Mains IGNOU BA MAjaytrips988150% (2)
- Upsc SyllabusDocument6 pagesUpsc Syllabusapoorvaraghuvanshi7No ratings yet
- Manipur Public Service Commission SyllabusDocument9 pagesManipur Public Service Commission SyllabusJohn LoukrakpamNo ratings yet
- Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument12 pagesIndian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyManas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Public Administration (Paper-I) Section-A:: Budget - Concepts, Forms, Formulation, ExecutionDocument2 pagesPublic Administration (Paper-I) Section-A:: Budget - Concepts, Forms, Formulation, ExecutionAshok BehuriaNo ratings yet
- UPSC MainsDocument2 pagesUPSC MainsNisha KumariNo ratings yet
- General Studies 3 Upsc SyllabusDocument2 pagesGeneral Studies 3 Upsc SyllabusManoj AvhadNo ratings yet
- Casesyllabus Sarkariresult ComDocument3 pagesCasesyllabus Sarkariresult ComHimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusParameswari SarakamNo ratings yet
- Upsc Syllabus For Paper I - (200 Marks) Duration: Two Hours (Counted For The Merit Rank in The Prelims)Document6 pagesUpsc Syllabus For Paper I - (200 Marks) Duration: Two Hours (Counted For The Merit Rank in The Prelims)NaveenNo ratings yet
- Urban Development PlanningDocument5 pagesUrban Development Planningnikhil saiNo ratings yet
- Public Admin SyllabusDocument4 pagesPublic Admin Syllabusananth83inNo ratings yet
- Syllabus UPSCDocument4 pagesSyllabus UPSCAshish MeshramNo ratings yet
- UPSC Exam Syllabus 2017 For Mains - Subjects & PapersDocument5 pagesUPSC Exam Syllabus 2017 For Mains - Subjects & Paperssaurav chandanNo ratings yet
- UPSC Mains Syllabus UPSC Mains Syllabus For IAS Exam 2019: GS Paper 1Document5 pagesUPSC Mains Syllabus UPSC Mains Syllabus For IAS Exam 2019: GS Paper 1Siva PethakamsettyNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Public Service Commission Ukpsc Syllabus State Pcs EnglishDocument5 pagesUttarakhand Public Service Commission Ukpsc Syllabus State Pcs EnglishpreetiNo ratings yet
- UPSC SylubusDocument10 pagesUPSC SylubusDany PaulbabyNo ratings yet
- IAS Main General Studies Paper-I Syllabus Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument3 pagesIAS Main General Studies Paper-I Syllabus Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyGeetanshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- General Studies 2 Upsc SyllabusDocument2 pagesGeneral Studies 2 Upsc SyllabusManoj AvhadNo ratings yet
- Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society. Literature and Architecture From Ancient To Modern TimesDocument13 pagesIndian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society. Literature and Architecture From Ancient To Modern TimesManas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mains SylabusDocument4 pagesMains SylabusBhaiya KamalenduNo ratings yet
- General Studies-I: (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)Document5 pagesGeneral Studies-I: (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)akshayNo ratings yet
- Paper 2, General Studies I Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument4 pagesPaper 2, General Studies I Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyC.V. RajendraNo ratings yet
- CSE Mains SyllabusDocument7 pagesCSE Mains SyllabusSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Flow of Things For Next Nine (9) MonthsDocument4 pagesFlow of Things For Next Nine (9) MonthsAshok VenkatNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: Essay (250 Marks) Paper 2: General Studies Paper 1 (250 Marks)Document3 pagesPaper 1: Essay (250 Marks) Paper 2: General Studies Paper 1 (250 Marks)Pradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: Essay (250 Marks) Paper 2: General Studies Paper 1 (250 Marks)Document3 pagesPaper 1: Essay (250 Marks) Paper 2: General Studies Paper 1 (250 Marks)Pradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- CSP Syllabus PDFDocument10 pagesCSP Syllabus PDFmaverickvivekNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusZafar KhanNo ratings yet
- GS Syllabus Topic WiseDocument7 pagesGS Syllabus Topic WiseborudeabhiNo ratings yet
- Ignou Ba IndexDocument7 pagesIgnou Ba IndexreadingthehinduNo ratings yet
- Paper GSDocument3 pagesPaper GSshyamkattiNo ratings yet
- Mpa - 104Document242 pagesMpa - 104Kanhu ChslNo ratings yet
- ChandigarhDocument42 pagesChandigarhPrashant SeenuNo ratings yet
- GS Mains SyllabusDocument8 pagesGS Mains SyllabusVivechan GunpalNo ratings yet
- Public Administration (Vi Sem)Document3 pagesPublic Administration (Vi Sem)AayushNo ratings yet
- General Studies PapersDocument2 pagesGeneral Studies Papersnimish sharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 General Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument4 pagesPaper 1 General Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Societyanon_56564465No ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Mains SyllabusDocument7 pagesUPSC CSE Mains Syllabusalisha112888No ratings yet
- SyllDocument7 pagesSyllsuryaNo ratings yet
- Assam Science and Technology University Guwahati Course Structure and SyllabusDocument8 pagesAssam Science and Technology University Guwahati Course Structure and SyllabusGirindra KonwarNo ratings yet
- Upsc Mains Syllabus: I: EssayDocument4 pagesUpsc Mains Syllabus: I: EssayPrabhat KusumaNo ratings yet
- Part A-Preliminary ExaminationDocument5 pagesPart A-Preliminary ExaminationPranshu MalikNo ratings yet
- Mains SyllabusDocument4 pagesMains SyllabusChris HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Government Strives To Have A Workforce Which Reflects Gender Balance and Women Candidates Are Encouraged To ApplyDocument7 pagesGovernment Strives To Have A Workforce Which Reflects Gender Balance and Women Candidates Are Encouraged To ApplyBuajsnNo ratings yet
- Mains Detailed Syllabus UPSCDocument4 pagesMains Detailed Syllabus UPSCmanglish thongamNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission, AjmerDocument4 pagesRajasthan Public Service Commission, AjmerjujofegiNo ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Mains SyllabusDocument4 pagesUPSC CSE Mains Syllabusrodagab903No ratings yet
- State Consultation Report of RajasthanDocument15 pagesState Consultation Report of Rajasthankritikasinghk20No ratings yet
- Land Information System: Ar. Nahlah BasheerDocument29 pagesLand Information System: Ar. Nahlah BasheerUdayabhanu DMNo ratings yet
- Guide To Preliminary Planning Surveys of Urban Areas Including Land Use ClassificationDocument38 pagesGuide To Preliminary Planning Surveys of Urban Areas Including Land Use ClassificationUdayabhanu DMNo ratings yet
- Data Collection TechniquesDocument13 pagesData Collection TechniquesUdayabhanu DMNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Base Maps: Planning Techniques - 2021-2022Document4 pagesPreparation of Base Maps: Planning Techniques - 2021-2022Udayabhanu DMNo ratings yet
- Road AccidentsDocument11 pagesRoad AccidentsUdayabhanu DMNo ratings yet
- KTU UrbanPlanning CurriculumwithSyllabusof34semDocument34 pagesKTU UrbanPlanning CurriculumwithSyllabusof34semUdayabhanu DMNo ratings yet
- Pillars of StateDocument5 pagesPillars of StateAmara ArshadNo ratings yet
- Amended Notice of Taking The Video Deposition of Darin EvavoldDocument2 pagesAmended Notice of Taking The Video Deposition of Darin EvavoldmikekvolpeNo ratings yet
- Ernest Hemingway FBI File PDFDocument129 pagesErnest Hemingway FBI File PDFAlan Jules WebermanNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law Course OutlineDocument21 pagesAdministrative Law Course Outlineidko2wNo ratings yet
- Regulating Act of 1773 - WikipediaDocument11 pagesRegulating Act of 1773 - WikipediaTorque MasterNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 92403 April 22, 1992 VICTOR A. AQUINO, Petitioner, Civil Service Commission and Leonarda D. DE LA PAZ, RespondentsDocument6 pagesG.R. No. 92403 April 22, 1992 VICTOR A. AQUINO, Petitioner, Civil Service Commission and Leonarda D. DE LA PAZ, RespondentsKeepy FamadorNo ratings yet
- Eo 277Document4 pagesEo 277Legal CaapNo ratings yet
- Articles of ARSONDocument4 pagesArticles of ARSONChristopher PjunatasNo ratings yet
- 2021 UPS Rate and Service Guide: Daily RatesDocument3 pages2021 UPS Rate and Service Guide: Daily RatesJDS JICENo ratings yet
- Hayes v. USA - Document No. 5Document5 pagesHayes v. USA - Document No. 5Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Qualities and Recalling of DiplomatsDocument16 pagesQualities and Recalling of DiplomatsraymondNo ratings yet
- TheDose Election Watch - Region 1 - DAGUPAN CITY An Official Tally RESULTSDocument12 pagesTheDose Election Watch - Region 1 - DAGUPAN CITY An Official Tally RESULTSKeith Giomeer PetrolaNo ratings yet
- The Draconian-Saurian War ConspiracyDocument94 pagesThe Draconian-Saurian War ConspiracyTracy Mx Li100% (1)
- Issuance of Writ of PossessionDocument2 pagesIssuance of Writ of Possessionstaircasewit4100% (1)
- Albanian HomophobiaDocument4 pagesAlbanian HomophobiaSasa MilosevicNo ratings yet
- DodatakDocument122 pagesDodatakmilos_vuckovic_4No ratings yet
- Aboriginal Australia 2Document28 pagesAboriginal Australia 2Jade Wang100% (1)
- Career Service Examination, Pen and Paper Test (Cse-Ppt) For Professional and Subprofessional Levels For Cy 2019Document11 pagesCareer Service Examination, Pen and Paper Test (Cse-Ppt) For Professional and Subprofessional Levels For Cy 2019MojaahedNo ratings yet
- US Code 1182 Chapter 12 - Immigration and NationalityDocument234 pagesUS Code 1182 Chapter 12 - Immigration and NationalityBarbara EspinosaNo ratings yet
- SBGR SampleDocument54 pagesSBGR SampleGeen Abrasado0% (1)
- Director Trade Compliance in USA Resume John McElroyDocument2 pagesDirector Trade Compliance in USA Resume John McElroyJohnMcElroy100% (1)
- Search Warrant Face PageDocument2 pagesSearch Warrant Face PageShawn FreemanNo ratings yet
- Essay 6 - The MediaDocument5 pagesEssay 6 - The MediaHìnhxămNơigóckhuấtTimAnhNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Constitution 1956, Military Coup in 1958 and Ayub Khan' Basic DemocracyDocument15 pagesPakistan Constitution 1956, Military Coup in 1958 and Ayub Khan' Basic DemocracyKhandaker Fazla Elahe Sheam 1812561642No ratings yet
- Housing and Land Use Regulatory BoardDocument2 pagesHousing and Land Use Regulatory BoardmralexisabinesNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Service Related A.C.R.O.N.Y.M.S: Atty. Danilo N. Dividina, REB, READocument90 pagesReal Estate Service Related A.C.R.O.N.Y.M.S: Atty. Danilo N. Dividina, REB, REARhuejane Gay MaquilingNo ratings yet
- Julius CaesarDocument17 pagesJulius CaesarMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- HUD - NHLP-04 Reasonable Accommodations OutlineDocument18 pagesHUD - NHLP-04 Reasonable Accommodations Outlinekiannyc100% (1)