Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Studies-I: (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)
Uploaded by
akshayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Studies-I: (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)
Uploaded by
akshayCopyright:
Available Formats
General Studies-I
(Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the
World and Society)
Indian Culture - Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from
ancient to modern times.
Modern Indian History from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the
present- significant events, personalities, issues.
The Freedom Struggle — its various stages and important
contributors/contributions from different parts of the country.
Post-independence Consolidation and Reorganization within the country.
History of the World will include events from 18th century such as Industrial
Revolution, world wars, Redrawal of National Boundaries, Colonization,
Decolonization, political philosophies like Communism, Capitalism, Socialism etc.
— their forms and effect on the society.
Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
Role of Women and Women’s Organization, Population and Associated Issues,
Poverty and Developmental issues, Urbanization, their problems and their
remedies.
Effects of Globalization on Indian society.
Social Empowerment, Communalism, Regionalism & Secularism.
Salient features of World’s Physical Geography.
Distribution of Key Natural Resources across the world (including South Asia
and the Indian sub-continent); factors responsible for the location of primary,
secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including
India).
Important Geophysical Phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic
activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location-changes in critical
geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna
and the effects of such changes.
General Studies-II
(Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relations)
Indian Constitution—Historical Underpinnings, Evolution, Features, Amendments, Significant
Provisions and Basic Structure.
Functions and Responsibilities of the Union and the States, Issues and Challenges Pertaining to
the Federal Structure, Devolution of Powers and Finances up to Local Levels and Challenges
Therein.
Separation of Powers between various organs Dispute Redressal Mechanisms and Institutions.
Comparison of the Indian Constitutional Scheme with that of Other Countries.
Parliament and State Legislatures—Structure, Functioning, Conduct of Business, Powers &
Privileges and Issues Arising out of these.
Structure, Organization and Functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary—Ministries and
Departments of the Government; Pressure Groups and Formal/Informal Associations and their Role
in the Polity.
Salient Features of the Representation of People’s Act.
Appointment to various Constitutional Posts, Powers, Functions and Responsibilities of various
Constitutional Bodies.
Statutory, Regulatory and various Quasi-judicial Bodies.
Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors and Issues arising
out of their Design and Implementation.
Development Processes and the Development Industry — the Role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups
and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders.
Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable Sections of the population by the Centre and States and the
Performance of these Schemes; Mechanisms, Laws, Institutions and Bodies constituted for the
Protection and Betterment of these Vulnerable Sections.
Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health,
Education, Human Resources.
Issues relating to Poverty and Hunger.
Important Aspects of Governance, Transparency and Accountability, E-governance-
applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; Citizens Charters, Transparency &
Accountability and institutional and other measures.
Role of Civil Services in a Democracy.
India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting
India’s interests.
Effect of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India’s interests,
Indian Diaspora.
Important International Institutions, agencies and fora - their Structure, Mandate.
General Studies-III (Technology, Economic Development, Bio-diversity, Environment,
Security and Disaster Management)
Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth,
Development and Employment.
Inclusive Growth and issues arising from it.
Government Budgeting.
Major Crops - Cropping Patterns in various parts of the country, - Different Types of
Irrigation and Irrigation Systems; Storage, Transport and Marketing of Agricultural Produce
and Issues and Related Constraints; E-technology in the aid of farmers.
Issues related to Direct and Indirect Farm Subsidies and Minimum Support Prices;
Public Distribution System - Objectives, Functioning, Limitations, Revamping; Issues of
Buffer Stocks and Food Security; Technology Missions; Economics of Animal-Rearing.
Food Processing and Related Industries in India- Scope’ and Significance, Location,
Upstream and Downstream Requirements, Supply Chain Management.
Land Reforms in India.
Effects of Liberalization on the Economy, Changes in Industrial Policy and their Effects
on Industrial Growth.
Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
Investment Models.
Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday
Life.
Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology; Indigenization of Technology and
Developing New Technology.
Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-technology, Bio-
technology and issues relating to Intellectual Property Rights.
Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact
Assessment.
Disaster and Disaster Management.
Linkages between Development and Spread of Extremism.
Role of External State and Non-state Actors in creating challenges to Internal Security.
Challenges to Internal Security through Communication Networks, Role of Media and
Social Networking Sites in Internal Security Challenges, Basics of Cyber Security; Money-
Laundering and its prevention.
Security Challenges and their Management in Border Areas - Linkages of Organized
Crime with Terrorism.
Various Security Forces and Agencies and their Mandate.
Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
This paper will include questions to test the candidates’ attitude and approach to issues
relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem solving approach to various
issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilise the case
study approach to determine these aspects. The following broad areas will be covered:
Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, Determinants and Consequences of
Ethics in - Human Actions; Dimensions of Ethics; Ethics - in Private and Public
Relationships. Human Values - Lessons from the Lives and Teachings of Great
Leaders, Reformers and Administrators; Role of Family Society and Educational
Institutions in Inculcating Values.
Attitude: Content, Structure, Function; its Influence and Relation with Thought
and Behaviour; Moral and Political Attitudes; Social Influence and Persuasion.
Aptitude and Foundational Values for Civil Service, Integrity,
Impartiality and Non-partisanship, Objectivity, Dedication to Public Service,
Empathy, Tolerance and Compassion towards the weaker-sections.
Emotional Intelligence-Concepts, and their Utilities and Application in
Administration and Governance.
Contributions of Moral Thinkers and Philosophers from India and World.
Public/Civil Service Values and Ethics in Public Administration: Status and
Problems; Ethical Concerns and Dilemmas in Government and Private Institutions;
Laws, Rules, Regulations and Conscience as Sources of Ethical Guidance;
Accountability and Ethical Governance; Strengthening of Ethical and Moral Values
in Governance; Ethical Issues in International Relations and Funding; Corporate
Governance.
Probity in Governance: Concept of Public Service; Philosophical Basis of
Governance and Probity; Information Sharing and Transparency in Government,
Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work
Culture, Quality of Service Delivery, Utilization of Public Funds, Challenges of
Corruption.
Case Studies on above issues.
You might also like
- GS Mains SyllabusDocument8 pagesGS Mains SyllabusVivechan GunpalNo ratings yet
- Paper GSDocument3 pagesPaper GSshyamkattiNo ratings yet
- IAS Main General Studies Paper-I Syllabus Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument3 pagesIAS Main General Studies Paper-I Syllabus Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyGeetanshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mains SyllabusDocument4 pagesMains SyllabusChris HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Mains Detailed Syllabus UPSCDocument4 pagesMains Detailed Syllabus UPSCmanglish thongamNo ratings yet
- CSE Mains SyllabusDocument7 pagesCSE Mains SyllabusSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Upsc SyllabusDocument6 pagesUpsc Syllabusapoorvaraghuvanshi7No ratings yet
- Indian Culture, History, Geography, Constitution, Economy and EthicsDocument13 pagesIndian Culture, History, Geography, Constitution, Economy and EthicsManas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 General Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument4 pagesPaper 1 General Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Societyanon_56564465No ratings yet
- GS I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument9 pagesGS I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyShivani Snigdha N VNo ratings yet
- UPSC Mains Syllabus Guide for History, Geography, Polity & MoreDocument4 pagesUPSC Mains Syllabus Guide for History, Geography, Polity & MorePrabhat KusumaNo ratings yet
- CSE Mains General Studies Paper - I, II, III, IV and Economics SyllabusDocument21 pagesCSE Mains General Studies Paper - I, II, III, IV and Economics SyllabusMadhumitha PodishettyNo ratings yet
- CSE Mains General Studies SyllabusDocument5 pagesCSE Mains General Studies SyllabusSudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- UPSC Syllabus Guide for Civil Services Mains Exam Paper 1Document6 pagesUPSC Syllabus Guide for Civil Services Mains Exam Paper 1NaveenNo ratings yet
- GS Paper 1-5: Complete Guide to Indian Civil Services ExamDocument3 pagesGS Paper 1-5: Complete Guide to Indian Civil Services ExamPradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: Essay (250 Marks) Paper 2: General Studies Paper 1 (250 Marks)Document3 pagesPaper 1: Essay (250 Marks) Paper 2: General Studies Paper 1 (250 Marks)Pradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- General Studies General Studies-IDocument4 pagesGeneral Studies General Studies-IDeepanker TewariNo ratings yet
- Upsc Main SyllabusDocument8 pagesUpsc Main SyllabusPayel SenNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of General Studies Paper - I General Studies Paper - I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument22 pagesSyllabus of General Studies Paper - I General Studies Paper - I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyAnonymous tLP4Ow6GmNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusParameswari SarakamNo ratings yet
- Indian Culture For Ias MainsDocument5 pagesIndian Culture For Ias MainsMehar ChandNo ratings yet
- MPSC MAINS Goooh ToDocument4 pagesMPSC MAINS Goooh ToShrau ShrauNo ratings yet
- Indian Heritage, Governance, Technology, EthicsDocument5 pagesIndian Heritage, Governance, Technology, EthicsJohnny PrinceNo ratings yet
- Upsc Mains SyllabusDocument4 pagesUpsc Mains Syllabusnitish chahalNo ratings yet
- Upsc Mains SyllabusDocument5 pagesUpsc Mains SyllabusAbhi RajNo ratings yet
- Numbered UPSC CSM 2013 Syllabus For GS PDFDocument7 pagesNumbered UPSC CSM 2013 Syllabus For GS PDFSushant PatilNo ratings yet
- General Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument4 pagesGeneral Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyKedar BhasmeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Thematic DivideDocument4 pagesSyllabus Thematic DivideMUHASIN KTNo ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Preliminary Exam PapersDocument7 pagesUPSC CSE Preliminary Exam PapersBuajsnNo ratings yet
- CSP Syllabus PDFDocument10 pagesCSP Syllabus PDFmaverickvivekNo ratings yet
- 4 Draft3Document5 pages4 Draft3ashwin kumarNo ratings yet
- Gs Mains SyllabiDocument6 pagesGs Mains SyllabiNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- CSE Mains General Studies Syllabus - 2016-2017 - UPSCsyllabusDocument9 pagesCSE Mains General Studies Syllabus - 2016-2017 - UPSCsyllabusShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- UPSC Exam Syllabus 2017 For Mains - Subjects & PapersDocument5 pagesUPSC Exam Syllabus 2017 For Mains - Subjects & Paperssaurav chandanNo ratings yet
- 3 Draft2Document3 pages3 Draft2ashwin kumarNo ratings yet
- Part-A Preliminary Examination Paper I - (200 Marks) Duration: Two HoursDocument7 pagesPart-A Preliminary Examination Paper I - (200 Marks) Duration: Two HoursHarsha DeepakNo ratings yet
- Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument12 pagesIndian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyManas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus and SourceDocument12 pagesSyllabus and SourceAyushNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs: History of India Indian and World GeographyDocument10 pagesCurrent Affairs: History of India Indian and World GeographySam JoseNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Public Service Commission Ukpsc Syllabus State Pcs EnglishDocument5 pagesUttarakhand Public Service Commission Ukpsc Syllabus State Pcs EnglishpreetiNo ratings yet
- Upsc SyllabusDocument5 pagesUpsc SyllabusPsp Flying beast fanNo ratings yet
- General Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument10 pagesGeneral Studies-I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyGraduate IndianNo ratings yet
- Main Exam Assesses Candidates' Intellectual TraitsDocument12 pagesMain Exam Assesses Candidates' Intellectual Traitsneodoc16No ratings yet
- Part-B Main Examination Qualifying Papers On Indian Languages and EnglishDocument6 pagesPart-B Main Examination Qualifying Papers On Indian Languages and EnglishAmoghNo ratings yet
- Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietyDocument4 pagesIndian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and SocietysamvikasNo ratings yet
- UpscDocument11 pagesUpscSanskriti NaithaniNo ratings yet
- Civil Services Mains Examination New PatternDocument5 pagesCivil Services Mains Examination New PatternKaran SharmaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Mains Exam GuideDocument9 pagesUPSC Mains Exam Guideca_maneeshNo ratings yet
- SyllDocument7 pagesSyllsuryaNo ratings yet
- Civil Services Mains Exam SyllabusDocument3 pagesCivil Services Mains Exam SyllabusPuran SinghNo ratings yet
- Structure and Plan of Civil Services Examination: Paper I: General Studies Paper II: Aptitude TestDocument13 pagesStructure and Plan of Civil Services Examination: Paper I: General Studies Paper II: Aptitude TestVikas LatherNo ratings yet
- GS Syllabus Topic WiseDocument7 pagesGS Syllabus Topic WiseborudeabhiNo ratings yet
- UPSC MainsDocument2 pagesUPSC MainsNisha KumariNo ratings yet
- Detailed SyllabusDocument3 pagesDetailed Syllabusdummyem1234No ratings yet
- SNM Academy - IAS Coaching in ChandigarhDocument21 pagesSNM Academy - IAS Coaching in ChandigarhsnmacademyNo ratings yet
- CSE Mains General Studies PaperDocument9 pagesCSE Mains General Studies Paperbpsharmab1p1No ratings yet
- General Studies 1 Paper Syllabus: Indian Culture Will Cover The Salient Aspects of Art Forms, Literature andDocument5 pagesGeneral Studies 1 Paper Syllabus: Indian Culture Will Cover The Salient Aspects of Art Forms, Literature anddiwakars_18No ratings yet
- General Studies-I 250 Marks (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)Document16 pagesGeneral Studies-I 250 Marks (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)Venugopal ShettyNo ratings yet
- Global Politics: Exploring Diverse Systems and Ideologies: Understanding Political Systems, Ideologies, and Global Actors: Global Perspectives: Exploring World Politics, #1From EverandGlobal Politics: Exploring Diverse Systems and Ideologies: Understanding Political Systems, Ideologies, and Global Actors: Global Perspectives: Exploring World Politics, #1No ratings yet
- Diversity Management:: Global and Interdisciplinary PerspectivesFrom EverandDiversity Management:: Global and Interdisciplinary PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Scrib 3Document3 pagesScrib 3akshayNo ratings yet
- Scribe 7Document1 pageScribe 7akshayNo ratings yet
- IRDocument2 pagesIRakshayNo ratings yet
- Scribe 9Document1 pageScribe 9akshayNo ratings yet
- Scribe 10Document1 pageScribe 10akshayNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledakshayNo ratings yet
- Scribe 6Document1 pageScribe 6akshayNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument2 pagesAir PollutionakshayNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution, Governance, Polity & Social JusticeDocument2 pagesIndian Constitution, Governance, Polity & Social JusticeakshayNo ratings yet
- GS Module Details IDocument1 pageGS Module Details IakshayNo ratings yet
- Ge Al Studies-I: (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)Document1 pageGe Al Studies-I: (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of The World and Society)akshayNo ratings yet
- Security and Disaster Management)Document2 pagesSecurity and Disaster Management)akshayNo ratings yet
- Scribe 5Document1 pageScribe 5akshayNo ratings yet
- India's Diverse Architectural Styles Spanning Thousands of YearsDocument1 pageIndia's Diverse Architectural Styles Spanning Thousands of YearsakshayNo ratings yet
- For ScribdDocument1 pageFor ScribdakshayNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1akshayNo ratings yet
- Foreign DiplomacyDocument1 pageForeign DiplomacyakshayNo ratings yet
- Why There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaDocument1 pageWhy There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaakshayNo ratings yet
- Thank You ScribdDocument1 pageThank You ScribdakshayNo ratings yet
- OrganizationDocument1 pageOrganizationakshayNo ratings yet
- Thank You ScribdDocument1 pageThank You ScribdakshayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document9 pagesLecture 4akshayNo ratings yet
- Why There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaDocument1 pageWhy There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaakshayNo ratings yet
- AM14M028 - Mid Semester Exam - Akshay Bhagwan PawarDocument10 pagesAM14M028 - Mid Semester Exam - Akshay Bhagwan PawarakshayNo ratings yet
- Why There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaDocument1 pageWhy There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaakshayNo ratings yet
- Why There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaDocument1 pageWhy There Are High Antibiotic Resistance Cases in IndiaakshayNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Akshay Pawar (AM14M028)Document7 pages3D Printing of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Akshay Pawar (AM14M028)akshayNo ratings yet
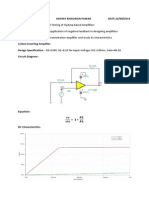
- To Build An Instrumentation Amplifier and Study Its CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesTo Build An Instrumentation Amplifier and Study Its CharacteristicsakshayNo ratings yet
- 3D Printed Tissue Scaffolds for EngineeringDocument1 page3D Printed Tissue Scaffolds for EngineeringakshayNo ratings yet
- Career Profile: Nidhi PathakDocument4 pagesCareer Profile: Nidhi PathaknidhipathakNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Defends Wife's InnocenceDocument6 pagesAffidavit Defends Wife's InnocenceGreggy LawNo ratings yet
- SPE Estimating Fracture Gradient in Gulf of Mexico Deepwater, Shallow, Massive Salt SectionsDocument9 pagesSPE Estimating Fracture Gradient in Gulf of Mexico Deepwater, Shallow, Massive Salt SectionsTHiago LOpesNo ratings yet
- Osha CFR 1910Document16 pagesOsha CFR 1910CI Amilcar100% (3)
- Henry FordDocument18 pagesHenry Fordsonabeta07No ratings yet
- Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security Midterm 1: (Last) (First)Document7 pagesWagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security Midterm 1: (Last) (First)Ahsan RamzanNo ratings yet
- Advance Corporate StrategyDocument2 pagesAdvance Corporate StrategyPassionate_to_LearnNo ratings yet
- The Difficult Patient' As Perceived by Family Physicians: Dov Steinmetz and Hava TabenkinDocument6 pagesThe Difficult Patient' As Perceived by Family Physicians: Dov Steinmetz and Hava TabenkinRomulo Vincent PerezNo ratings yet
- Sjzl20061019-ZXC10 BSCB (V8.16) Hardware ManualDocument69 pagesSjzl20061019-ZXC10 BSCB (V8.16) Hardware ManualAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- DENR CC 2022 1st - Edition FIN 25 - March - 2022Document234 pagesDENR CC 2022 1st - Edition FIN 25 - March - 2022CENRO BANGUED PLANNINGNo ratings yet
- ClassifiedrecordsDocument23 pagesClassifiedrecordsChetana SJadigerNo ratings yet
- Water Quality For Irrigation Free PPT - Google SearchDocument3 pagesWater Quality For Irrigation Free PPT - Google SearchJames NeoNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy, PerformanceDocument20 pagesBusiness Strategy, Performance6oktoberday2023No ratings yet
- CRAPAC Monthly JanDocument4 pagesCRAPAC Monthly JanJasonMortonNo ratings yet
- Arduino ProjectsDocument584 pagesArduino ProjectsJoão Francisco83% (12)
- Ir 2101Document14 pagesIr 2101Willard DmpseyNo ratings yet
- In Millions USD: Balance Sheet 2020 2021 2022Document4 pagesIn Millions USD: Balance Sheet 2020 2021 2022Trần Ngọc Quỳnh ChiNo ratings yet
- Uti MF v. Ito 345 Itr 71 - (2012) 019taxmann - Com00250 (Bom)Document8 pagesUti MF v. Ito 345 Itr 71 - (2012) 019taxmann - Com00250 (Bom)bharath289No ratings yet
- Polity by LaxmikantDocument3 pagesPolity by LaxmikantJk S50% (6)
- Cebu Oxygen Acetylene Co., vs. Drilon, G.R. No. 82849, August 2, 1989Document6 pagesCebu Oxygen Acetylene Co., vs. Drilon, G.R. No. 82849, August 2, 1989JemNo ratings yet
- PACiS GTW EN O C80Document170 pagesPACiS GTW EN O C80paradiseparasNo ratings yet
- Dhi-Ehs-Hsm-028 Work Over Water Rev0Document5 pagesDhi-Ehs-Hsm-028 Work Over Water Rev0Phạm Đình NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Pilkington Profilit Techn Info enDocument12 pagesPilkington Profilit Techn Info enSalmonelo Abdul RamosNo ratings yet
- Market Profiling, Targeting and PositioningDocument16 pagesMarket Profiling, Targeting and PositioningMichelle RotairoNo ratings yet
- 266DSH Differential Pressure TransmittersDocument36 pages266DSH Differential Pressure TransmittersSibabrata ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Autoencoder Asset Pricing ModelsDocument22 pagesAutoencoder Asset Pricing ModelsEdson KitaniNo ratings yet
- Bhushan Steel LTD (BHUS IN) - Balance SheetDocument4 pagesBhushan Steel LTD (BHUS IN) - Balance SheetVamsi GunturuNo ratings yet
- Tender Status Report Delhi-Mumbai Expressway 10.01.19Document66 pagesTender Status Report Delhi-Mumbai Expressway 10.01.19chtrp100% (2)
- Communicate With S7-1200 Via EhernetDocument6 pagesCommunicate With S7-1200 Via EhernetRegisNo ratings yet