Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Summary 7 World
Chapter Summary 7 World
Uploaded by
evertCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Summary 7 World
Chapter Summary 7 World
Uploaded by
evertCopyright:
Available Formats
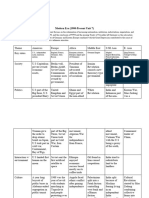
NAME DATE CLASS
Chapter Summary
The Reach of Imperialism
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the causes and effects of imperialism? How do some groups resist
control by others?
A new wave of Western colonial expansion in Southeast Asia and Africa began in the nineteenth century as
countries sought access to industrial raw materials and new markets for European products. Though some
Europeans believed it was their moral duty to preach Christianity and civilize primitive people, imperialism
was tied to Social Darwinism and racism. Native efforts to break free of colonial rule met with varying
degrees of success. The United States controlled the economies of Latin America and used military force to
protect its investments.
Colonial Rule in Southeast Asia British Rule in India
• European nations exploited natural resources in • Indians challenged British rule with the Sepoy
Asia and sought new markets for European Great (Mutiny Rebellion); the revolt was crushed,
goods; rivalries spurred nations to increase their but it fueled Indian nationalism.
prestige by dominating colonies in Southeast
Asia. • British introduced political stability to India but
harmed India’s local industries and demeaned
• European countries controlled the governments the Indian people and their culture.
and economies of their colonies in Southeast Asia
through direct and indirect rule. • Mohandas Gandhi led India’s independence
movement.
• Some native rulers and peasants resisted colonial
rule in Southeast Asia, but their efforts often • Rabindranath Tagore promoted national pride in
failed. Indian culture.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
Empire Building in Africa Imperialism in Latin America
• Europeans exploited West Africa’s resources and • U.S. involvement in Latin America resulted in the
controlled North Africa, where the Suez Canal Spanish-American War, the independence of
linked the Mediterranean and Red Seas, providing Panama, and the building of the Panama Canal.
access to India.
• The U.S. sent military forces to Cuba, Mexico,
• Searching for a navigable river, David Livingstone Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama,
explored Africa’s interior, and King Leopold II Colombia, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic to
opened up the Congo to Belgium. protect American investments.
• Germany’s interest in East Africa was political, • The Mexican Revolution led to the Constitution
whereas Britain wanted a route from South Africa of 1917; it set up a government led by a
to Egypt. president, created land reform policies, and
established limits on foreign investors.
• With British troops, the Boers defeated the native
Zulu, but later the British defeated the Boers and • Latin America experienced some prosperity
established the independent Union of South through exporting foodstuffs and raw materials,
Africa. which led to the growth of a middle class.
• Africans educated in Western schools sought the
end of colonial rule and promoted African
nationalism.
You might also like
- Final Fraud ReportDocument27 pagesFinal Fraud Reportpvchandu100% (1)
- Rwandan GenocideDocument28 pagesRwandan GenocideZoltan NagyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 21 - The Height of ImperialismDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 21 - The Height of ImperialismJonathan Daniel KeckNo ratings yet
- Fiat Justitia Ruat CaelumDocument4 pagesFiat Justitia Ruat Caelumarsene wenNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Suzanne Wakim & Mandeep GrewalDocument731 pagesHuman Biology: Suzanne Wakim & Mandeep GrewalevertNo ratings yet
- Social Studies 7th Grade Southern Eastern Asia Teacher Notes PDFDocument32 pagesSocial Studies 7th Grade Southern Eastern Asia Teacher Notes PDFDavid BriggsNo ratings yet
- Exam Form 2Document23 pagesExam Form 2Didi Gump EddieNo ratings yet
- The Age of Imperialism (1800-1914)Document21 pagesThe Age of Imperialism (1800-1914)shikhaNo ratings yet
- Scramble For AfricaDocument20 pagesScramble For AfricaColton McKeeNo ratings yet
- MCQ - PC 21 - Civil Accounts Manual (CAM)Document13 pagesMCQ - PC 21 - Civil Accounts Manual (CAM)DEVI SINGH MEENANo ratings yet
- Corporate Restructuring For Value CreationDocument10 pagesCorporate Restructuring For Value CreationKrishna Vyas100% (4)
- Imperialism: HistoryDocument7 pagesImperialism: HistorysandhyaNo ratings yet
- Jordias Jeffries - Imperialism Digital Interactive NotebookDocument11 pagesJordias Jeffries - Imperialism Digital Interactive NotebookJordias JeffriesNo ratings yet
- Food UnscrambleDocument6 pagesFood UnscrambleKevin CollierNo ratings yet
- Catherine The GreatDocument7 pagesCatherine The GreatHyona NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Rocha v. PratsDocument1 pageRocha v. PratsJose Edmundo DayotNo ratings yet
- Global-Tourism Midterm ReviewerDocument15 pagesGlobal-Tourism Midterm ReviewerRose Ann AsnaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Unit 6Document2 pagesStudy Guide Unit 6Charlie WalkerNo ratings yet
- Anthropology NotesDocument6 pagesAnthropology Notesaishareyjumawan29No ratings yet
- Imperialism and ColonialismDocument41 pagesImperialism and ColonialismSaad AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Indian National MovementDocument218 pagesLecture 13 - Indian National MovementShyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 BookDocument27 pagesChapter 27 Bookmwero6030No ratings yet
- Nationalism in Africa and Latin AmericaDocument12 pagesNationalism in Africa and Latin AmericaRaghav GoelNo ratings yet
- History Mini Lesson Causes of Modern ImperialismDocument5 pagesHistory Mini Lesson Causes of Modern Imperialismim fineNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Test Review Social StudiesDocument4 pagesCH 1 Test Review Social Studiesapi-365454115No ratings yet
- Study Guide: Western Dominance in Southeast Asia Empire Building in AfricaDocument1 pageStudy Guide: Western Dominance in Southeast Asia Empire Building in AfricaevertNo ratings yet
- Territorial Division of The WorldDocument17 pagesTerritorial Division of The WorldJasmine LopezNo ratings yet
- Key Concept 4Document9 pagesKey Concept 4Joel PeteNo ratings yet
- The Quest For Empire, 1885-1914 VocabDocument6 pagesThe Quest For Empire, 1885-1914 VocabashleyNo ratings yet
- Civilizations of Southeast Asia: PreviewDocument17 pagesCivilizations of Southeast Asia: PreviewMao SamphasNo ratings yet
- Asian Political Philosophers, Brief HistoryDocument14 pagesAsian Political Philosophers, Brief HistorySofia CornejoNo ratings yet
- APWH UNIT 6 Cheat Sheet-1Document6 pagesAPWH UNIT 6 Cheat Sheet-1josephchaiteaNo ratings yet
- The High Tide O-WPS OfficeDocument28 pagesThe High Tide O-WPS OfficeRandom Bll ShTNo ratings yet
- British Imperialism in IndiaDocument27 pagesBritish Imperialism in IndiaSaad AliNo ratings yet
- Apwh 2018Document11 pagesApwh 2018api-345337486No ratings yet
- Classical Civilizations: Africa, America and The Islands in The PacificDocument40 pagesClassical Civilizations: Africa, America and The Islands in The PacificRichmond Jake AlmazanNo ratings yet
- PeriodDocument37 pagesPeriodNinaNo ratings yet
- Modern Era SPICE Chart Unit 8Document3 pagesModern Era SPICE Chart Unit 8chrisbaffour48No ratings yet
- Unit 6.1 & 6.2 Notes - Rationales For State ExpansionDocument23 pagesUnit 6.1 & 6.2 Notes - Rationales For State ExpansionnutulateNo ratings yet
- Ceylon: Burning of The Widow.Document6 pagesCeylon: Burning of The Widow.LoveAlwaysHopes137No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Southeast Asia in Cold War & Post Cold War 2017Document83 pagesChapter 2 Southeast Asia in Cold War & Post Cold War 2017sumi yatiNo ratings yet
- DecolonizationDocument11 pagesDecolonizationapi-294034727No ratings yet
- Cape Unit 1 LessonDocument6 pagesCape Unit 1 LessonShauntea MooreNo ratings yet
- European Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Document12 pagesEuropean Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Oyon Nur newazNo ratings yet
- Sample ResumeDocument14 pagesSample ResumeasdfNo ratings yet
- Socialism in Europe and The Russian Revolution CBSE Grade 9Document30 pagesSocialism in Europe and The Russian Revolution CBSE Grade 9Anagha Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- HISTORY CHAPTER 10 Struggle For Freedom - IDocument8 pagesHISTORY CHAPTER 10 Struggle For Freedom - Iagrim.jain2790No ratings yet
- Origins of American ImperialismDocument26 pagesOrigins of American ImperialismAbigail ArreolaNo ratings yet
- Imperialism in Victorian EraDocument14 pagesImperialism in Victorian Eramstanton2000No ratings yet
- The British in IndiaDocument66 pagesThe British in IndiaSidra SulmanNo ratings yet
- Imperialism Social DarwinismDocument17 pagesImperialism Social DarwinismMuhamamd Khan Muneer100% (1)
- British Rule in IndiaDocument12 pagesBritish Rule in IndiaAkash kadapaNo ratings yet
- CNI Answer TemplatesDocument12 pagesCNI Answer TemplatesRajjnishNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Pg. 325 and 329Document5 pagesReview Questions Pg. 325 and 329Eamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- BritishDocument23 pagesBritishSaba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Nort Lect 28 America Claims An Empire, 1890-1920Document26 pagesNort Lect 28 America Claims An Empire, 1890-1920Michelle MtzNo ratings yet
- The Development of Systems of ProductionDocument4 pagesThe Development of Systems of ProductionkayannaNo ratings yet
- African Americans Help Create A New NationDocument51 pagesAfrican Americans Help Create A New NationAnanya Varahabhatla Student - PantherCreekHSNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Indigenous Responses To Imperialism.: Carolina MontillaDocument7 pages6.3 Indigenous Responses To Imperialism.: Carolina MontillacarolinaNo ratings yet
- 3 - EmpireDocument2 pages3 - EmpireshaneagcaintNo ratings yet
- Three Theories Explaining ImperialismDocument3 pagesThree Theories Explaining ImperialismMussadiq RehmanNo ratings yet
- What Are The Roles of Great Power inDocument10 pagesWhat Are The Roles of Great Power inJeffery MillefioreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 - Southeast Asia: Section Notes Video MapsDocument45 pagesChapter 28 - Southeast Asia: Section Notes Video Mapsaireen cloresNo ratings yet
- American Imperialism in The 19TH CenturyDocument5 pagesAmerican Imperialism in The 19TH CenturyAustin TropNo ratings yet
- Vs 4 2015Document2 pagesVs 4 2015api-297727492No ratings yet
- ImperialismDocument48 pagesImperialismddzq57xz9hNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document9 pagesModule 3Laynie Gaspar DampogNo ratings yet
- The Pre Modern World: InstagramDocument10 pagesThe Pre Modern World: InstagramHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contact Information For Sheldon Coaches 2020-2021: Title Name E-MailDocument1 pageContact Information For Sheldon Coaches 2020-2021: Title Name E-MailevertNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Western Dominance in Southeast Asia Empire Building in AfricaDocument1 pageStudy Guide: Western Dominance in Southeast Asia Empire Building in AfricaevertNo ratings yet
- Guided Reading Activity: The Reach of ImperialismDocument2 pagesGuided Reading Activity: The Reach of ImperialismevertNo ratings yet
- Guided Reading Activity: The Reach of ImperialismDocument2 pagesGuided Reading Activity: The Reach of ImperialismevertNo ratings yet
- Oregon DMV Driver's ManualDocument2 pagesOregon DMV Driver's ManualBardicNo ratings yet
- Airprep 00 A4P006EDocument196 pagesAirprep 00 A4P006EcivodulNo ratings yet
- TVM Buy Vs Rent Decision CaseDocument3 pagesTVM Buy Vs Rent Decision CaseNowshinNo ratings yet
- Demo 30 Banking Awareness (English) - Arihant ExpertsDocument35 pagesDemo 30 Banking Awareness (English) - Arihant Expertsmalik mohsinNo ratings yet
- Reading 5 - Health RequirementsDocument8 pagesReading 5 - Health RequirementsHani MasriNo ratings yet
- DC-DC BoostDocument21 pagesDC-DC BoostvinaykumaarNo ratings yet
- ADMINISTRATIVE ACCOUNTABILITY of Public OfficersDocument9 pagesADMINISTRATIVE ACCOUNTABILITY of Public OfficersMarjorie Canteras TejanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Money MarketDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Money MarketJuanito Dacula Jr.No ratings yet
- Free ConsentDocument6 pagesFree ConsentMadhu Mahesh RajNo ratings yet
- Franjo I KlaraDocument22 pagesFranjo I KlaramaliciosusNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument293 pagesUntitledStu D HD hgNo ratings yet
- Price 770: Appart'City Confort Nantes CentreDocument2 pagesPrice 770: Appart'City Confort Nantes CentreJithendra BhattiproluNo ratings yet
- Costaccounting 170209080426Document33 pagesCostaccounting 170209080426Samayak JainNo ratings yet
- Issues and Redemption LiabilitiesDocument75 pagesIssues and Redemption LiabilitiesOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Pension RulesDocument79 pagesPension Rulesnit111No ratings yet
- Role Play Script Group 2Document13 pagesRole Play Script Group 2Gelyn GabianeNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 CoverageDocument20 pagesQuiz 1 Coveragekristeen yumangNo ratings yet
- DoT Letter On CBuD - MergedDocument5 pagesDoT Letter On CBuD - Mergedramarao.maramesiNo ratings yet
- Pepsi ProspectusDocument229 pagesPepsi ProspectusJemely BagangNo ratings yet
- Vicarious Liability - Torts and DamagesDocument11 pagesVicarious Liability - Torts and DamagesFRANCIS PATRAYNo ratings yet
- Auf-Related Questions (Yellow) 1. What Does The Acronym JLEA Stands For? Ans. Junior Law EnforcersDocument3 pagesAuf-Related Questions (Yellow) 1. What Does The Acronym JLEA Stands For? Ans. Junior Law EnforcersmarlondomingoNo ratings yet
- Charge Account Setups - Ebiz Integration TechnicsDocument3 pagesCharge Account Setups - Ebiz Integration TechnicsSandip SinghNo ratings yet