Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sanitary Drinking Water Storage and Methods of Garbage Disposal
Uploaded by
clar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesnur
Original Title
CDX Health Implications
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnur
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesSanitary Drinking Water Storage and Methods of Garbage Disposal
Uploaded by
clarnur
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Bayani, Clarise M.
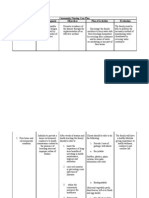
3.16 Status of Storage for Drinking Water
Covered- water has to be stored properly to prevent recontamination.
Safe storage means keeping your treated water away from sources of
contamination, and using a clean and covered container. It also means
that drinking from the container should be done in a way that cross-
contamination can be avoided. The container should prevent hands, cups
and dippers from touching the water, so that the water does not
get recontaminated.
Uncovered- Uncovered drinking water storage may be at risk of some
infections. Some vectors may leave bacteria and viruses to water if we
leave them uncovered in result Individuals may have a probability of
ingesting contaminated drinking water that may sometimes lead to
diseases. The growth of bacteria is even high when you store the
water in a warm area. You should avoid drinking water left open for a
very long time. The water left overnight or for a long period of time
in an open glass or container is home to numerous bacterias
and is not safe for drinking
3.17 Sanitary Condition of Storage for Drinking Water
Clean - Care should be taken to avoid using any container previously
used for transport of toxic materials (such as pesticides or petroleum
products) as a drinking water storage container. Lastly, locally
appropriate cleaning mechanisms – such as use of soap and brushes, or
dilute chlorine solution – should be developed and recommended to
clean the container on a regular basis.
Unclean- unclean water may be prone to water borne diseases like
diarrhea, typhoid fever, amoebiasis and cholera. People should be aware
on what should be the precautions and choice of drinking water that they
should select.
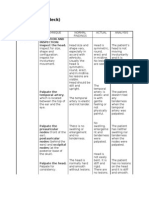
3.18 Method of Garbage Disposal
Compost Pit - Composting also creates a nutrient-rich soil enhancer that
can help plants grow. This final product, called compost or humus, is a
dark, soil-like substance that people can use in gardens, on farms, and
as mulch. Compost and potting mix often contain the bacteria
which cause legionellosis, also known as Legionnaires' disease.
Infection can occur when dust from compost and potting mixes is inhaled.
Legionnaires' disease can vary in severity from a flu-like illness to severe
pneumonia. Compost can be a breeding ground for dangerous
pathogens, some of which have killed or seriously harmed unsuspecting
gardeners. Inspectors should familiarize themselves with these illnesses,
some of which can be contracted in other parts of the house.
Burning - Smoke created by backyard garbage burning especially
affects people with sensitive respiratory systems, as well as children and
the elderly. Exposure to smoke can also increase the risk of heart
disease, cause rashes, nausea, and headaches. Among the
environmental and health risks posed by residential garbage burning,
dioxin is the key concern. Dioxin is a potent human carcinogen that is
especially harmful for pregnant women, children, and the elderly. Dioxin
is also an endocrine disrupter and can cause reproductive,
developmental, and immunological problems in humans and animals.
Unburned portions of the plastic become litter on the ground and in lakes
and rivers. As it disintegrates, animals may eat the plastic and get sick.
Larger pieces of plastic can become a breeding ground for diseases,
such as by trapping water that provides habitat for mosquitoes.
Open Dumping - Open dumping speads foul odous also provides a
place for germs, insect and other vectors to grow and spread different
health problems and also can contaminates groundwater that can
damages the plants and wildlife habitat. Its also can containates streams,
rivers and lake and even the soil and drinking water this type of dumping
also decreases the quality of life of the nearby areas and the local
communities.
Collected - Waste that is not properly managed, especially excreta and
other liquid and solid waste from households and the community, are a
serious health hazard and lead to the spread of infectious diseases.
Unattended waste lying around attracts flies, rats, and other creatures
that in turn spread disease. Garbage collectors never know what
hazardous materials and foraging animals they may come across in the
course of their duty. There are countless ways to be injured on the job
and all manner of toxic materials in the trash that garbage men carry and
transport every day.
Lifting heavy objects repeatedly can result in spinal damage, hernias or
any number of physical injuries. Proper lifting techniques help to reduce
the danger, as does the practice of asking a fellow trash collector for help
when lifting a particularly heavy or awkward item.
Garbage contains every type of hazardous material imaginable from
battery acid to bleach, from pesticides to hypodermic needles. Even
radioactive waste material has reportedly been found in normal
residential trash from time to time. The potential for injury, infection,
poisoning, burns or respiratory damage is high and unavoidable in many
cases. Sanitation workers should wear long pants, long sleeves, work
gloves and heavy boots in all weather to combat the danger and avoid
injury.
Dangerous materials like broken glass and light bulbs are a common
cause of injury for sanitation workers The broken shards are typically
placed into plastic garbage bags, which are then lifted and carried to the
truck for removal. During lifting or moving, glass or metal blades can cut
the hands or body of a garbage collector and result in serious injury.
You might also like
- Family Nursing Care Plan for the Tactay FamilyDocument26 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan for the Tactay FamilyDALE DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Community Health Analysis of Brgy. 628Document79 pagesCommunity Health Analysis of Brgy. 628YongNo ratings yet
- University of Baguio Nursing Students Assess Health of Purok 3Document61 pagesUniversity of Baguio Nursing Students Assess Health of Purok 3Maria MercedesNo ratings yet
- Community Diagnosis NCM 113 2Document63 pagesCommunity Diagnosis NCM 113 2Jewenson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument4 pagesDischarge Plan of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDenise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching RabiesDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching RabiesMeryl Encarnacion100% (1)
- Impact of Pandemic To The Psychological Aspects of Nursing StudentsDocument25 pagesImpact of Pandemic To The Psychological Aspects of Nursing StudentsBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Hivaids Related Knowledge Attitude Risk Perception and Sexual BehaviorDocument5 pagesHivaids Related Knowledge Attitude Risk Perception and Sexual BehaviorIJARP PublicationsNo ratings yet
- COPAR Tally SheetDocument3 pagesCOPAR Tally SheetAnna SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Natural remedies for chronic cough from ancient textsDocument4 pagesNatural remedies for chronic cough from ancient textsLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Fatima 121 ThesisDocument144 pagesFatima 121 ThesisNecesario BanaagNo ratings yet
- CDXDocument6 pagesCDXMaridel SulbianoNo ratings yet
- Community Diagnosis Sample PDFDocument2 pagesCommunity Diagnosis Sample PDFLisaNo ratings yet
- X. Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesX. Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeErvina Luisa Delias CampusNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Assessment Sitaca Tan Viedor Yap BSN 2cDocument9 pagesUnit 3 Assessment Sitaca Tan Viedor Yap BSN 2capi-532152575No ratings yet
- Involving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialDocument10 pagesInvolving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialAngel MayNo ratings yet
- Health Education Plan For PTBDocument2 pagesHealth Education Plan For PTBSheena ClaireNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERDocument6 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERCarla LimNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeDocument1 pageBlood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeMir MirNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument8 pagesGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Factors: AffectingDocument23 pagesFactors: AffectingAmeerah Mousa KhanNo ratings yet
- Cultural Beliefs On Disease Causation in The PhilippinesDocument19 pagesCultural Beliefs On Disease Causation in The PhilippinesDexter ReyesNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Immersion in Northville 2BDocument18 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Immersion in Northville 2BKath Mendoza ÜNo ratings yet
- LaryngitisDocument5 pagesLaryngitisAngeliqueNo ratings yet
- 1st Level AssessmentDocument2 pages1st Level AssessmentRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- FNCP Figueroa and de GuzmanDocument3 pagesFNCP Figueroa and de GuzmanDANIELA DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- You Dont Know JackDocument7 pagesYou Dont Know JackSunaira MalikNo ratings yet
- Ethical ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesEthical ConsiderationsBern NerquitNo ratings yet
- Aquino Health AgendaDocument41 pagesAquino Health AgendaJannine Mae Zaragosa MosquisaNo ratings yet
- Elec 121Document14 pagesElec 121MARITONI MEDALLANo ratings yet
- Case 1-Clinical Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase 1-Clinical Case StudyRachel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyAdelle SmithNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study-Chapter 6Document6 pagesFamily Case Study-Chapter 6Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- COPAR or Community Organizing Participatory Action Research Is A Vital Part ofDocument5 pagesCOPAR or Community Organizing Participatory Action Research Is A Vital Part ofPrei BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Framework For Prevention: Nancy MilioDocument9 pagesFramework For Prevention: Nancy MilioBrenlei Alexis NazarroNo ratings yet
- Milio's Framework TheoryDocument1 pageMilio's Framework TheorySANDRINO RAFAEL RONAN RYANNo ratings yet
- Nurses Notes Soapie Day 2Document3 pagesNurses Notes Soapie Day 2Sunny Al asadiNo ratings yet
- Bioethical Components of CareDocument2 pagesBioethical Components of CarekeiitNo ratings yet
- Post-abortion pain relief guideDocument7 pagesPost-abortion pain relief guideABDULRAHMAN MISHARI AL-THABITNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community Health Nursing ExposureDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Community Health Nursing ExposureRay LaderaNo ratings yet
- Examining root causes of poor health and diseaseDocument1 pageExamining root causes of poor health and diseaseDONITA DALUMPINESNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument10 pagesFNCPgracielue1120100% (1)
- The Omaha System-FinalDocument21 pagesThe Omaha System-FinalerajanejNo ratings yet
- Table 4Document3 pagesTable 4dave_castañedaNo ratings yet
- Legal and Ethical Issues Affecting End-Of-Life Care: Advance DirectivesDocument12 pagesLegal and Ethical Issues Affecting End-Of-Life Care: Advance Directiveserwin kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Perspective of AgingDocument21 pagesPerspective of AgingMarianne Joyce ManzoNo ratings yet
- IMCI LectureDocument161 pagesIMCI LectureNaveen PandeyNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPapi-3728995No ratings yet
- Understanding Cirrhosis of the LiverDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Cirrhosis of the LiverAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gastric UlcerDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Gastric UlcerNielArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Management of The Sick Child Aged 2 Months Up To 5 YearsDocument3 pagesManagement of The Sick Child Aged 2 Months Up To 5 Yearstiban_07No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5 ThesisDocument54 pagesChapter 1 5 ThesisJarda julie DacuagNo ratings yet
- COPAR EditedDocument4 pagesCOPAR EditedNiko MendozaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument2 pagesTheoretical FrameworkLisette CastilloNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument34 pagesFamily Nursing Care Planjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Sample Family Case Study 1 1 - CompressDocument55 pagesSample Family Case Study 1 1 - CompressGladys JhayeNo ratings yet
- P.A. 1Document6 pagesP.A. 1SamSarah BongolanNo ratings yet
- What is Littering and its EffectsDocument12 pagesWhat is Littering and its EffectsNandaa MuhmaliaaNo ratings yet
- RRL ResearchDocument3 pagesRRL ResearchJess Marie D. GodinNo ratings yet
- Group 2-CSTDocument3 pagesGroup 2-CSTclarNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Drinking Water Storage and Methods of Garbage DisposalDocument2 pagesSanitary Drinking Water Storage and Methods of Garbage DisposalclarNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Drinking Water Storage and Methods of Garbage DisposalDocument2 pagesSanitary Drinking Water Storage and Methods of Garbage DisposalclarNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterm QuizzesDocument6 pagesNCM 109 Midterm QuizzesclarNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterm QuizzesDocument6 pagesNCM 109 Midterm QuizzesclarNo ratings yet
- Bayani, Clarise M. NUR04ADocument1 pageBayani, Clarise M. NUR04AclarNo ratings yet
- Assignment BayaniDocument1 pageAssignment BayaniclarNo ratings yet
- Bayani, Clarise M. NUR04ADocument1 pageBayani, Clarise M. NUR04AclarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument11 pagesDrug Study PediaclarNo ratings yet
- NCM Ob Ward Rot EvalDocument5 pagesNCM Ob Ward Rot EvalclarNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument16 pagesQuestionsclarNo ratings yet
- NCM Ob Ward Rot EvalDocument5 pagesNCM Ob Ward Rot EvalclarNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF THE SICK CHILDDocument6 pagesMANAGEMENT OF THE SICK CHILDclarNo ratings yet
- Assignment BayaniDocument1 pageAssignment BayaniclarNo ratings yet
- Name: Course/Section:: An Assessment of The Current National SituationDocument1 pageName: Course/Section:: An Assessment of The Current National SituationclarNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF THE SICK CHILDDocument6 pagesMANAGEMENT OF THE SICK CHILDclarNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Case 1Document47 pagesPost Partum Case 1clarNo ratings yet
- Problems and RecommendationDocument8 pagesProblems and RecommendationclarNo ratings yet
- Informatio N Age Informatio N AgeDocument35 pagesInformatio N Age Informatio N AgeclarNo ratings yet
- PBL1Document3 pagesPBL1clarNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument34 pagesClimate ChangeclarNo ratings yet
- Community Case Study PaperDocument10 pagesCommunity Case Study Paperapi-355433171No ratings yet
- Primary Health Care PrinciplesDocument44 pagesPrimary Health Care PrinciplesBianca de Guzman83% (6)
- Human Flourishing Group ReportDocument12 pagesHuman Flourishing Group ReportclarNo ratings yet
- The Negative Effects of Overconsumption of SugarDocument11 pagesThe Negative Effects of Overconsumption of SugarHermilinda Orenze100% (5)
- Adacel Tdap VaccineDocument1 pageAdacel Tdap VaccineclarNo ratings yet
- Community Nursing DiagnosisDocument38 pagesCommunity Nursing DiagnosisclarNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy GuideDocument27 pagesEctopic Pregnancy GuideuunuunuunNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - NifedipineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - NifedipineSharlene Agcanas100% (10)
- The Seveso Disaster: A Deadly Chemical Leak in 1976Document29 pagesThe Seveso Disaster: A Deadly Chemical Leak in 1976mkkamarajNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart of The Production Chain of Soya (Bean) Meal and Oil Products For Feed Application in The EUDocument31 pagesFlow Chart of The Production Chain of Soya (Bean) Meal and Oil Products For Feed Application in The EUJoelCariazNo ratings yet
- LCA Sanitary PadsDocument24 pagesLCA Sanitary PadsMaria Angelica Arteta Molina100% (2)
- Risk Assessment Oils & Fats PDFDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment Oils & Fats PDFFlutura NurediniNo ratings yet
- Tsunoda, Humio - Tsunoda, Masashi - Yu, Ming-Ho-Environmental Toxicology - Biological and Health Effects of Pollutants, Third Edition-CRC PresDocument373 pagesTsunoda, Humio - Tsunoda, Masashi - Yu, Ming-Ho-Environmental Toxicology - Biological and Health Effects of Pollutants, Third Edition-CRC PresEğitim ParaylaNo ratings yet
- Animal FeedDocument19 pagesAnimal FeedOrfi AmirNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Module 16-1 Incineration of Healthcare WasteDocument36 pagesDay 2 Module 16-1 Incineration of Healthcare WasteikkaapriliasetiariniNo ratings yet
- Dioxins: An Overview: Arnold Schecter, Linda Birnbaum, John J. Ryan, John D. ConstableDocument10 pagesDioxins: An Overview: Arnold Schecter, Linda Birnbaum, John J. Ryan, John D. ConstableANISA FITRIANINo ratings yet
- Flow chart of the soya meal and oil production processDocument25 pagesFlow chart of the soya meal and oil production processadesuyan yomiNo ratings yet
- Polyvinyl ChlorideDocument6 pagesPolyvinyl ChlorideMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- 12 English Core Sp02Document17 pages12 English Core Sp02farhaNo ratings yet
- PVC As Pharmaceutical Packaging MaterialDocument10 pagesPVC As Pharmaceutical Packaging Materialave123ization100% (1)
- Automated Sample Preparation For Dioxins and Pcbs DextechtmDocument2 pagesAutomated Sample Preparation For Dioxins and Pcbs DextechtmMas EboyNo ratings yet
- State Soil Dioxin FinalDocument199 pagesState Soil Dioxin FinalVu NguyenNo ratings yet
- TES-AMM Analysis Pyrometallurgy Vs Hydrometallurgy April 2008Document6 pagesTES-AMM Analysis Pyrometallurgy Vs Hydrometallurgy April 2008papiloma753100% (1)
- Safavi 2022 - Dioxin Formation in Biomass Gasification A ReviewDocument17 pagesSafavi 2022 - Dioxin Formation in Biomass Gasification A ReviewChristiaan RichterNo ratings yet
- Chemical Hazards and Foodborne ToxinsDocument22 pagesChemical Hazards and Foodborne ToxinsDharanibalan PNo ratings yet
- Da QJQKK de O0 VM GZM B7 V GQN V45Document114 pagesDa QJQKK de O0 VM GZM B7 V GQN V45IsmaelMendozaNo ratings yet
- Fire Characteristics of Styropor FoamsDocument4 pagesFire Characteristics of Styropor FoamsRosman Al-QadriNo ratings yet
- Unseen Passages e TextDocument10 pagesUnseen Passages e TextKuber PatidarNo ratings yet
- PVC properties and uses for pipes, wire insulation, and moreDocument13 pagesPVC properties and uses for pipes, wire insulation, and morejbertralNo ratings yet
- Assignment/ TugasanDocument13 pagesAssignment/ TugasanFAEZAL HAZLY B. MOHD NAJIB STUDENT0% (1)
- Soil ContaminationDocument181 pagesSoil ContaminationNaya Septri HanaNo ratings yet
- Omni 1983 01 PDFDocument82 pagesOmni 1983 01 PDFMatthew Levi StevensNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health at Work: Kyung-Taek RimDocument8 pagesSafety and Health at Work: Kyung-Taek RimAkbarNo ratings yet
- Pre Animal FeedDocument47 pagesPre Animal FeedrohishaakNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Palm OilDocument22 pagesRisk Assessment Palm Oilanniq141100% (1)
- LCTech Dioxin BrochureDocument16 pagesLCTech Dioxin BrochureYoosu NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Precautionary Principle in ActionDocument26 pagesThe Precautionary Principle in ActionBaxter ValNo ratings yet
- Walking The Talk Duponts Untold Safety FailuresDocument28 pagesWalking The Talk Duponts Untold Safety Failuressl1828No ratings yet