Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Chapter 21 (Britain Inter War)
Uploaded by
Sally MoynihanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Chapter 21 (Britain Inter War)
Uploaded by
Sally MoynihanCopyright:
Available Formats
Niamh Cremin 5D
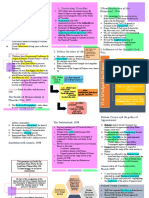
Economic and Social Problems in Britain during the Inter-War Years 1920-39
What Do You Need to Know? - Coal Mines; shovels + picks vs
mechanical mining (Germany & US).
Causes of British economic depression in Competition from petrol, oil,
1920’s/30’s electricity. Difficulties brought owners
& miners into conflict/ lockouts 2. Government Policy- Laissez Faire
Social conditions in Britain in inter-war
years (General Strike of 1926) Government policy of ‘Laissez-Faire’
Role of John Maynard Keyes (intervening very little in the economy) also
CASE STUDY; Jarrow March Location of Industry- Depressed areas; contributed to economic depression
Clydesdale (shipbuilding & engineering) Concerned with large national debt & needed
Effects of WWI Tyneside (shipbuilding & coal mining) to balance the budget- did not want to
Lancashire (cotton & engineering) South borrow more money
Wales (coal mining) Churchill (Chancellor of the Exchequer)
High unemployment, Low woman’s labor, decided in 1925 to fix value of £ to Gold
750,000 ↑ Taxation Social problems e.g. high infant mortality Standard
soliders Inflation & Hoped to control inflation by fixing
killed Borrowing In contrast, Greater London area &
exchange rate
Kept interest rates high but this damaged
Midlands were prosperous
PM Llyod George investing & spending
Referred to as ‘Inner Britain’ (new
Causes
Unemployment promised 'Land fit
industries, not dependent on export) VS These changes only made British exports
for Heroes'
‘Outer Britain’ (depressed) dearer, further damaging trade & slowing
1. Decline of British trade & staple industries; economic growth
- C19th & early C20th- British prosperity
depended on export trade TheJune
Dole1921,
& WageNational
Cuts Insurance
- A general decline in world trade after unemployment Act=
WWI (impacted shipbuilding & export increased to >2 unemployment
million benefit
markets for cotton & coal) Decline of
Britain’s Staple Industries;
- Caused structural unemployment Govt allowed workers to
Scheme was get additional payments
- Shipbuilding; ↓ world trade= surplus ineffective from the Poor Law
ships. Shipyards fell behind in advances- Guardians- DOLE
effected iron & steel production
Those who kept their
- Cotton: Britain had been the leading jobs in the affected After WWI, Trade
cotton producer but after WWI faced industries also suffered unions in a stronger
(particularly coal
competition & lost traditional markets position
industry)
(China/ India)
- Workers wanted
Owners of industry nationalisation
wanted wage cuts (government
& longer working ownership), higher
hours wages & shorter
working hours
TUC membership fell by over 2 million
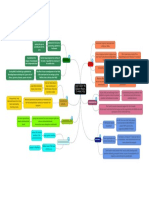
general strikes
Effects of
Condition of the
the Strikes
people- Social Problems
The General
` Strike, 1926
Mine owners looked for further wage cuts Unions moved towards negotiation & Unemployment benefit looked on as a charity, not a
cooperation over conflict right & affected the esteem & self-respect of the
A.J. Cook, leader of the workers responded- ‘not a workers
penny off the pay, not a minute on the day’ Unemployment was the main cause of poverty
Samuel Commission set up to enquire into the issues Poverty contributed to disease & death among the
Increased class & social tensions due to Prosperity
facing the coal industry role of the middle class volunteers poorer classes
Found mines should be modernised, agreed that wages Many of the employed were on such low wages that
should be cut & they did not have enough money for food after
The TUC (Trade Union Congress) supported the miners spending on rent, clothing, fuel, light
& on 3 May 1926, a General Strike began Govt policy of
HungerFree
Marchestrade ended &
About 2 million workers went on strike in support of and The Great Depression in Britain Laissez Faire
protectionism
questioned - govt
in addition to the 1 million miners brought
Series When in during
the
of marches NYtoStocktheExchange
highlight crashed
long-term in Oct
unemployment
should take a more
Strike only lasted 9 days as govt plans to counter it in depressed 30s
1929, itsareas,
effects spread worldwide-
organised by the activeWall
National
role
worked Street Crash
Unemployed Workers’ Movement (NUWM) in 1932,
J. International
1934, 1936
M. trade fell, factories closed &
Keynes advocated
OMS (organisation for the Maintenance of Supplies) set
govt intervention to rose
unemployment create(3.4 million)- most in the
People demanded govt
up full employment-
industries take greater care of its
already in difficulty
Churchill oversaw the publication of the British Gazette Keyensian
Government economic
action citizens -creation of
so govt got its message across despite strikes in policy put in place after the Welfare State
1931 financial
WWII crisis - budget deficit
newspapers
New Gov - the National Government - PM:
TUC leaders called off the strike leaving miners on their Ramsay McDonald made some difficult
own decisions which all contributed to ending the
6 months later they accepted defeat with less pay & Great Depression in Britain from 1934
longer hours Introduced means test for unemployment
benefit
Wages cut for civil servants, soldiers &
teachers
Bank interest rate lowered (people could
borrow to buy cars etc)
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NSS Exploring Economics 1 (3 Edition) : Answers To ExercisesDocument14 pagesNSS Exploring Economics 1 (3 Edition) : Answers To Exercisesrrrrr88888No ratings yet
- Hotel Booking PDFDocument2 pagesHotel Booking PDFferuzbekNo ratings yet
- LCHL Indices and Logs NotesDocument8 pagesLCHL Indices and Logs NotesSally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- Leaving Cert History Past Papers Essay Questions: Europe and The Wider World: Topic 3Document3 pagesLeaving Cert History Past Papers Essay Questions: Europe and The Wider World: Topic 3Sally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- Hitler'S Foreign Policy 1. Destroying Versailles 3.remilitarisation of The Rhineland, 1936Document3 pagesHitler'S Foreign Policy 1. Destroying Versailles 3.remilitarisation of The Rhineland, 1936Sally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- Jarrow Assessment : Case Study: The Jarrow March, October 1936Document1 pageJarrow Assessment : Case Study: The Jarrow March, October 1936Sally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 12Document42 pagesSolutions Chapter 12Sally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- The Chieftains: Paddy MoloneyDocument1 pageThe Chieftains: Paddy MoloneySally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- 03 Miche+íl +ô S+ Illeabh+íinDocument1 page03 Miche+íl +ô S+ Illeabh+íinSally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- 01 Collectors of Irish MusicDocument1 page01 Collectors of Irish MusicSally MoynihanNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction in The RestaurantDocument14 pagesCustomer Satisfaction in The RestaurantAyesha SiddiquaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics & Business Strategy: The Theory of Individual BehaviorDocument15 pagesManagerial Economics & Business Strategy: The Theory of Individual BehaviorMalat DiemNo ratings yet
- Quiz In-Class June 8Document2 pagesQuiz In-Class June 8Đạt Hồ Sĩ ThànhNo ratings yet
- Cirrus (Interbank Network) - WikipediaDocument2 pagesCirrus (Interbank Network) - WikipediaSamNo ratings yet
- TheContemporaryWorld ReviewerDocument8 pagesTheContemporaryWorld ReviewerRyzajane DalingNo ratings yet
- UK Land LawDocument12 pagesUK Land LawLuminita OlteanuNo ratings yet
- PDF Sales Midterm Reviewer by Article 1530 1593pdfDocument43 pagesPDF Sales Midterm Reviewer by Article 1530 1593pdfsoyoung kimNo ratings yet
- Importanceand Roleof Entrepreneurshipin EconomicDocument5 pagesImportanceand Roleof Entrepreneurshipin EconomicSasquarch VeinNo ratings yet
- Cement February2021Document25 pagesCement February2021Adarsh PoojaryNo ratings yet
- Seminar Analysis 8 Key Elements of Shopee E-Commerce: University of Economics & Finance TP - HCMDocument17 pagesSeminar Analysis 8 Key Elements of Shopee E-Commerce: University of Economics & Finance TP - HCMHiền LêNo ratings yet
- Top Fintech Payment Trends 2023 WhitepaperDocument15 pagesTop Fintech Payment Trends 2023 Whitepaperemanuele.deangelisNo ratings yet
- Procedure For MaintenanceDocument2 pagesProcedure For MaintenanceSharif KhanNo ratings yet
- Declining Oil Rev NigeriaDocument12 pagesDeclining Oil Rev NigeriaAltay KalpakNo ratings yet
- Hussen Nuri Adem Import and Export TradeDocument2 pagesHussen Nuri Adem Import and Export Tradehaymanot fuadNo ratings yet
- My Current Portfolio SahamDocument1 pageMy Current Portfolio Sahamshahfiq95 1210No ratings yet
- Environment Threat and Opportunity Profile (Etop) : A VIEW FROM:-AnishDocument11 pagesEnvironment Threat and Opportunity Profile (Etop) : A VIEW FROM:-Anishgmbhuvaneswari100% (2)
- Staff Working Paper No. 899: The Central Bank Balance Sheet As A Policy Tool: Past, Present and FutureDocument52 pagesStaff Working Paper No. 899: The Central Bank Balance Sheet As A Policy Tool: Past, Present and FutureJohnyMacaroniNo ratings yet
- Mahesh Resume-MaintenanceDocument3 pagesMahesh Resume-MaintenanceskodeNo ratings yet
- Tbchap 016 Test BankDocument30 pagesTbchap 016 Test BankTRUC NGUYEN THI THANHNo ratings yet
- Guesstimates: by ICON-Consulting Club of IIM-BDocument9 pagesGuesstimates: by ICON-Consulting Club of IIM-BPratyush GoelNo ratings yet
- MAnRep Ch02 Job Order CostingDocument70 pagesMAnRep Ch02 Job Order CostingAlexandra NicoleNo ratings yet
- ParCor Notes 5Document9 pagesParCor Notes 5Noreen DelizoNo ratings yet
- IBAÑEZ - O1 Graphic Organizer or Table MappingDocument2 pagesIBAÑEZ - O1 Graphic Organizer or Table MappingBen Aldrian IbañezNo ratings yet
- JFC 2021 SEC Sustainability ReportDocument83 pagesJFC 2021 SEC Sustainability Reportgjana4179No ratings yet
- CA Vijay Patidar ResumeDocument1 pageCA Vijay Patidar Resumevijay patidarNo ratings yet
- Consolated Balance Sheet: Advance Accounting-II (Chapter-3.4)Document8 pagesConsolated Balance Sheet: Advance Accounting-II (Chapter-3.4)Md Shah AlamNo ratings yet
- Detailed Supply Chain of Lenskart 1Document10 pagesDetailed Supply Chain of Lenskart 1contactme251198No ratings yet
- QTMKT TN (CLC)Document152 pagesQTMKT TN (CLC)chowchowdangiiuNo ratings yet