Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assets
Uploaded by
Melanie SamsonaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assets
Uploaded by
Melanie SamsonaCopyright:
Available Formats
INVESTMENTS
Assertions:
● Existence, occurrence, and completeness of transactions related to
investments
● Valuation of investments
● Presentation and disclosure
Objectives:
● Determine the existence of investments and that the hospital entity
has rights to the investments
● Consider internal control over the investments held by the hospital
entity
● Determine that all investments of the entity are reported and
transactions affecting the investments are properly accounted for
● Establish the proper measurements of investments
● Establish accuracy of the amounts recognized relating to investments
● Determine that the presentation and disclosure of the investments are
adequate
Audit Procedure:
● Reading custody agreements
● Reviewing control and safeguarding procedures
● Confirming or examining securities
● Testing authorization and documentation supporting transactions
● Reviewing the basis of valuation and reporting income
● Verifying the investments like shares, debentures, bonds, and security
certificates
Specific Audit Procedure
The auditor confirms balances with the trustee or broker if the investments
are in the custody of an independent outside entity. Confirmations should be as of the same
date to obtain a reasonable assurance that there is no switching of securities to conceal a
shortage. The confirmation should include the description of each investment held for the
hospital entity, as well as the number of shares and the total amount of investment. If the
hospital entity keeps custody of the investments, the auditor should physically inspect and
count all securities on hand simultaneously. The auditor may also verify them with the
investment register.
The proper measurement of investments is validated by referring to
published price quotations for securities that are measured at fair value. If the securities do
not have published price quotations, the auditor shall consider obtaining estimates of fair
value from security dealers/brokers or other third party sources. Lastly, the auditor should
also determine whether investments are properly classified and the disclosure guidelines in
the accounting standards are observed in the financial statements. In doing so, the auditor
has to obtain an understanding of management’s process for classifying securities.
ACCOUNT RECEIVABLES
Assertions:
● Completeness and existence of information regarding accounts eceivables in
the financial statments
● Appropriate use of measurement bases and appropriate presentation and
disclosure of financial statement account receivable
Objectives:
● Consider internal control over receivables
● Determine the existence of receivables, that the hospital entity has
rights to these assets
● Establish the completeness of recorded receivables
● Determine that the receivables are measured at appropriate amounts
● Establish that the presentation and disclosure of receivables are
appropriate
Audit Procedure:
● Confirmation with the third-party payors
● Reviewing the adequacy of provision made for differences between
contractual interim billing rates and full-rate charges
● Reviewing the computation made to estimate the amount of
retroactive adjustments provided for in the accounts
● Reviewing related contracts to determine whether required
adjustments have been reflected in the accounts
● Reviewing of cost-reimbursement reports to determine that they were
prepared based on the principles of reimbursement of the third-party
payor
Specific Audit Procedure
The auditor has to update information on the hospital entity’s
business risk and analyze potential motivation to or circumstances
that misstate account receivables. The auditor must understand the
hospital entity’s operations and identify the proper recognition and
measurement of account receivables.
To establish the correctness of the balance of accounts
receivables in the general ledger, it is necessary for the auditor to
obtain a list of the accounts receivable from the subsidiary ledgers and
reconcile the total to the balance in the general ledger. As a standard
audit procedure, accounts receivable must be confirmed. Confirmation
with the debtors must be done to assure that no lapping or any other
form of manipulation has been resorted to by the entity’s employees.
The auditing firm must mail directly the confirmation request, with
attached business reply envelope, to the hospital entity’s
patients/customers.
INVENTORIES
Assertions:
● Completeness and accuracy of inventory records
Objectives:
● Establish the completeness of the inventories
● Establish the clerical accuracy of records and supporting schedules
for inventories
Audit Procedure:
● Reviewing the independent organization’s procedures
● Observing physical counts
● Testing pricing
Specific Audit Procedure
Hospitals frequently employ independent organizations to inventory and price
drugs, medicines, and medical supplies. This is done because the quality of these items can
usually be determined more readily and accurately by these organizations than by the
hospital’s staff. Thus, the auditor must participate in the hospital entity’s physical inventory
and review the written instructions prepared by management for the employees who will
make the counts. The auditor must also perform a test of prices applied to inventories to
determine whether the inventory costing procedure used by the hospital entity has been
properly applied.
PROPERTY, PLANT, AND EQUIPMENT
Assertions:
● Existence of transactions that result in PPE account
● Correctness and accuracy of depreciation during the period
● VAluation of PPE
Objectives:
● Substantiate the existence of property, plant, and equipment
● Determine the correctness and accuracy of recorded depreciation
● Determine that the measurement of PPE is in accordance with
accounting standards
Audit Procedure:
● Evaluating depreciation policy
● Verify the changes in acquisition and retirements of PPE during the
current period
Specific Audit Procedure
The auditor considers the internal control procedures adopted by the hospital
entity for fixed assets. The auditor examines the invoices, deeds, and title insurance
policies.
The auditor has to prepare a summary of the amounts of accumulated
depreciation for various groups of assets at the beginning of the year, the amounts
provided for depreciation during the year, the amounts removed because of asset
retirements, and the ending balances. Computations may then be reviewed for a
representative number of units and traced to both the expense accounts and
accumulated depreciation accounts. Then, the auditor makes inquiries of executives
and supervisors regarding retired assets and examines the auditor must obtain
retirement work orders prepared during the year.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Samsona-Case-Act 122 5 - 3GDocument4 pagesSamsona-Case-Act 122 5 - 3GMelanie Samsona100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis ExerciseDocument5 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis ExerciseMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Hockey Camp-CvpDocument2 pagesCase Analysis - Hockey Camp-CvpMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Hockey Camp-CvpDocument2 pagesCase Analysis - Hockey Camp-CvpMelanie Samsona100% (1)
- CASE ANALYSIS - Don Masters and Assoicates Law OfficeDocument1 pageCASE ANALYSIS - Don Masters and Assoicates Law OfficeMelanie Samsona0% (1)
- Specialized Industry HospitalDocument55 pagesSpecialized Industry HospitalMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- AMS 48 - 2000-n - D0114354 - 055 - 00Document116 pagesAMS 48 - 2000-n - D0114354 - 055 - 00wanhall100% (1)
- Chapter 13Document11 pagesChapter 13Christine GorospeNo ratings yet
- Asian MedicalDocument124 pagesAsian MedicalMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- SAMSONA C Lab2Document11 pagesSAMSONA C Lab2Melanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Time On Students' Academic PerformanceDocument14 pagesImpact of Time On Students' Academic PerformanceMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Specialized Industry HospitalDocument44 pagesSpecialized Industry HospitalMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- AssetsDocument4 pagesAssetsMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- 5TH ActivityDocument15 pages5TH ActivityMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- SAMSONA C Lab3Document9 pagesSAMSONA C Lab3Melanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Deferred Revenue, and Accruals For Salaries, Interest, Vacations, and Taxes. Included Also Are Liabilities ToDocument6 pagesDeferred Revenue, and Accruals For Salaries, Interest, Vacations, and Taxes. Included Also Are Liabilities ToMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument3 pagesCombinepdfMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- ABE058 Lab2b SamsonaDocument1 pageABE058 Lab2b SamsonaMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Double Acting Air CylinderDocument1 pageDouble Acting Air CylinderMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
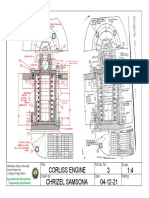
- Corliss EngineDocument1 pageCorliss EngineMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11-TVL 3 Aviso 2018-2019Document42 pagesGrade 11-TVL 3 Aviso 2018-2019Melanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
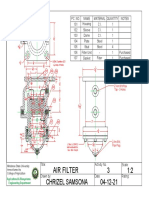
- Air FilterDocument1 pageAir FilterMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Basic Commands For 2-D ModellingDocument1 pageBasic Commands For 2-D ModellingMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Time On StudentsDocument10 pagesImpact of Time On StudentsMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- ENS 164 SyllabusDocument1 pageENS 164 SyllabusMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Stress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressDocument79 pagesStress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressMelanie Samsona100% (1)
- Koronadal National Comprehensive High School-Senior High SchoolDocument60 pagesKoronadal National Comprehensive High School-Senior High SchoolMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11-Abm 3 HamiltonDocument45 pagesGrade 11-Abm 3 HamiltonMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- FilmmakingDocument10 pagesFilmmakingMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Electronic Class Record: InstructionsDocument39 pagesSenior High School Electronic Class Record: InstructionsMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Stress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressDocument23 pagesStress: Normal Stress Shearing Stress Bearing StressMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- 2133 Rla RlvaDocument2 pages2133 Rla RlvaAgung SubangunNo ratings yet
- High Speed DoorsDocument64 pagesHigh Speed DoorsVadimMedooffNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper-RprDocument6 pagesReaction Paper-Rprapi-543457981No ratings yet
- Task 5 Banksia-SD-SE-T1-Hazard-Report-Form-Template-V1.0-ID-200278Document5 pagesTask 5 Banksia-SD-SE-T1-Hazard-Report-Form-Template-V1.0-ID-200278Samir Mosquera-PalominoNo ratings yet
- Women and ViolenceDocument8 pagesWomen and ViolenceStyrich Nyl AbayonNo ratings yet
- Ec Declaration of Conformity: W1/35 KEV KIRK - Protective Gloves - Cathegory IIDocument3 pagesEc Declaration of Conformity: W1/35 KEV KIRK - Protective Gloves - Cathegory IICrystal HooverNo ratings yet
- Lichens - Naturally Scottish (Gilbert 2004) PDFDocument46 pagesLichens - Naturally Scottish (Gilbert 2004) PDF18Delta100% (1)
- Bacterial Genome Assembly IlluminaDocument49 pagesBacterial Genome Assembly IlluminadksaNo ratings yet
- Outlook 2Document188 pagesOutlook 2Mafer Garces NeuhausNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Unfinished RRLDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Unfinished RRLGM XylerNo ratings yet
- Epo-Fix Plus: High-Performance Epoxy Chemical AnchorDocument3 pagesEpo-Fix Plus: High-Performance Epoxy Chemical Anchormilivoj ilibasicNo ratings yet
- Quality Factor of Inductor and CapacitorDocument4 pagesQuality Factor of Inductor and CapacitoradimeghaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Project ListDocument25 pagesEngineering Project ListSyed ShaNo ratings yet
- PEOPLE V JAURIGUE - Art 14 Aggravating CircumstancesDocument2 pagesPEOPLE V JAURIGUE - Art 14 Aggravating CircumstancesLady Diana TiangcoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Packet KeyDocument21 pagesUnit 8 Packet KeyHiddenNo ratings yet
- ReliabilityDocument5 pagesReliabilityArmajaya Fajar SuhardimanNo ratings yet
- NORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For HearingDocument146 pagesNORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For Hearingcaod1712100% (1)
- 107 2021 High Speed Rail Corridor RegDocument3 pages107 2021 High Speed Rail Corridor Rega siva sankarNo ratings yet
- Soil SSCDocument11 pagesSoil SSCvkjha623477No ratings yet
- Drug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForDocument7 pagesDrug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForRafika DitaNo ratings yet
- Iomm VFD-3 030112Document100 pagesIomm VFD-3 030112Alexander100% (1)
- As ISO 9919-2004 Pulse Oximeters For Medical Use - RequirementsDocument10 pagesAs ISO 9919-2004 Pulse Oximeters For Medical Use - RequirementsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Rooftop Rain Water Harvesting in An Educational CampusDocument9 pagesRooftop Rain Water Harvesting in An Educational CampusAkshay BoratiNo ratings yet
- United States v. Victor Vallin-Jauregui, 4th Cir. (2013)Document4 pagesUnited States v. Victor Vallin-Jauregui, 4th Cir. (2013)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Topic of Assignment: Health Wellness and Yoga AssignmentDocument12 pagesTopic of Assignment: Health Wellness and Yoga AssignmentHarsh XNo ratings yet
- Electri RelifDocument18 pagesElectri Relifsuleman247No ratings yet
- Given The Simulation Area For Room ServiceDocument3 pagesGiven The Simulation Area For Room ServiceRico EsponillaNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts of Enzyme Histochemistry in Modern PathologyDocument11 pagesCurrent Concepts of Enzyme Histochemistry in Modern PathologyRosa AquinoNo ratings yet
- Flame Retardant and Fire Resistant Cable - NexansDocument2 pagesFlame Retardant and Fire Resistant Cable - NexansprseNo ratings yet