Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vakharia Academy: 10 (English)
Uploaded by
Rohan MehtaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vakharia Academy: 10 (English)
Uploaded by
Rohan MehtaCopyright:
Available Formats
VAKHARIA ACADEMY DATE:
10 (English)
TIME: 1hr
Maths – Circles
MARKS: 20
SEAT NO:
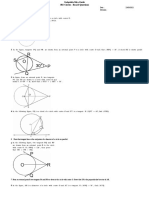
1. From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is
25 cm. The radius of the circle is (1 mark)
(A) 7 cm (B) 12 cm (C) 15 cm (D) 24.5 cm
2. If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at angle of 80°,
then Ð POA is equal to (1 mark)
(A) 50° (B) 60° (C) 70° (D) 80°
3. Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
(2 marks)
4. A quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle. Prove that
AB + CD = AD + BC (2 marks)
5. Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus. (2 marks)
6. In two concentric circles, a chord of length 24 cm of larger circle becomes a tangent to the smaller circle
whose radius is 5 cm. Find the radius of the larger circle. (2 marks)
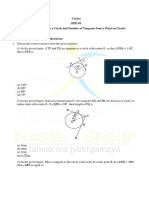
7. A circle touches the side BC of a ∆ABC at a point P and touches AB
and AC when produced, at Q & R respectively.
Show that AQ = ½ (perimeter of ∆ABC). (3 marks)
8. Tangents AP and AQ are drawn to circle with centre O, from an
external point A. Prove that ∠PAQ=2∠OPQ (3 marks)
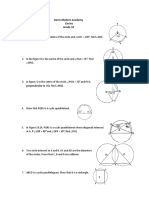
9. In the adjoining Fig, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle
with centre O and
another tangent AB with point of contact C intersecting XY at A
and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90°. (4 marks)
You might also like
- Bergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsFrom EverandBergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Areas Related To CirclesDocument1 pageAreas Related To CirclesRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- 10. Circles worksheetDocument4 pages10. Circles worksheetpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Ski-hill Graph Pedagogy Meter Fundamentals: Mathematical Music Theory for BeginnersFrom EverandSki-hill Graph Pedagogy Meter Fundamentals: Mathematical Music Theory for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Circles AssignmentDocument4 pagesCircles Assignmentaahaan.handaNo ratings yet
- Cs 1Document4 pagesCs 1Teereg VINo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-10 CircleDocument21 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-10 Circlefunson123No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Circles Worksheet Set ADocument6 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Circles Worksheet Set AAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Circles Test 02Document1 page10 Mathematics Circles Test 02ImranHashmiNo ratings yet
- Geometry 9 TH STDDocument3 pagesGeometry 9 TH STDsnehalrgawali455No ratings yet
- CirclesDocument6 pagesCirclesAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- class 10 Maths Mark type Questions Chapter 10Document105 pagesclass 10 Maths Mark type Questions Chapter 10ashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Class 10 Mathematics Part 2 of 2Document58 pagesClass 10 Mathematics Part 2 of 2Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 9th Maths Circle Test Paper SolvedDocument4 pages9th Maths Circle Test Paper SolvedStephen GreenNo ratings yet
- Math-CirclesDocument10 pagesMath-Circlesigptyfklm9199rsNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry - Tangents: ProblemsDocument1 pagePlane Geometry - Tangents: ProblemsevkrishnaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 CirclesDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 CirclesArpitNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 10 Circles SolutionsDocument12 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 10 Circles Solutionsrai venugopalNo ratings yet
- Subject-Mathematics, Class-Ix Circles: Worksheet (Basic)Document7 pagesSubject-Mathematics, Class-Ix Circles: Worksheet (Basic)sanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument6 pagesCircleskumarm78No ratings yet
- Circles Class 10th MCQ - 1Document15 pagesCircles Class 10th MCQ - 1Melissa CouthinoNo ratings yet
- MATHS TEST PAPER - KeyDocument3 pagesMATHS TEST PAPER - KeyDeepanshu ThakurNo ratings yet
- Q C1 NER9 Ifs RDvxdeq MWVDocument5 pagesQ C1 NER9 Ifs RDvxdeq MWVtgaryangamerzsNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 - X - CBSE - (C.W-120) - 31.01.2024 (Geometry)Document5 pages2023-24 - X - CBSE - (C.W-120) - 31.01.2024 (Geometry)shivaNo ratings yet
- CIRCLESDocument3 pagesCIRCLESAswinNo ratings yet
- Solutions to Mathematics Questions from Class XI & XII O-Caps -3Document12 pagesSolutions to Mathematics Questions from Class XI & XII O-Caps -3Honey ChunduruNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Maths Circles Test Paper 01Document2 pagesCBSE Class X Maths Circles Test Paper 01AvianaNo ratings yet
- Circle Most Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesCircle Most Important QuestionsVino PrabaNo ratings yet
- Cs 2Document4 pagesCs 2Teereg VINo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CirclesDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Circlesmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- X-M-Midterm-QP-A-E-21-22Document2 pagesX-M-Midterm-QP-A-E-21-22tmsssk23No ratings yet
- Geometry 123Document4 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28No ratings yet
- Maths-Class-X-Holiday Homework Autumn Break CircleDocument6 pagesMaths-Class-X-Holiday Homework Autumn Break CirclecuriousnavinNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument3 pagesCirclesAlvina ShakirNo ratings yet
- 1 3 1 1 5Document16 pages1 3 1 1 5Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument14 pagesMathsjaishreeNo ratings yet
- Geometry 123Document3 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28No ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Cbse Circles NotesDocument11 pagesClass 9 Maths Cbse Circles Notesdinesh_kp7647No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Worksheet - CirclesDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Worksheet - CirclesmrudulaNo ratings yet
- 10TH Cbse - CirclesDocument40 pages10TH Cbse - Circlesrizwan farhanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Document21 pagesNcert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Shivam EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument9 pagesCircles PDFbansallove2008No ratings yet
- Class 10th 40 Marks Test.3Document3 pagesClass 10th 40 Marks Test.3Jasmeet singhNo ratings yet
- Cat 16-19 Geomerty Questions, Answers and SolutionsDocument8 pagesCat 16-19 Geomerty Questions, Answers and SolutionsAditya Nath ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- UDAAN 2024: CirclesDocument2 pagesUDAAN 2024: CirclesRatnendra Shivendra VikramNo ratings yet
- Mastermind English Medium School Class Ix Cambridge Mathematics-D Practice Worksheet - 04 3/5/2020 - 7/5/2020Document5 pagesMastermind English Medium School Class Ix Cambridge Mathematics-D Practice Worksheet - 04 3/5/2020 - 7/5/2020Aditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- ch10 Extra QuestionsDocument5 pagesch10 Extra Questionsdrallanushka79No ratings yet
- Assignment On CirclesDocument3 pagesAssignment On CirclesVACHAN L ANo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 3 Mathematics Class XDocument15 pagesModel Test Paper 3 Mathematics Class XPRIYANKA ROYNo ratings yet
- Exercise 16.1 Page No: 16.5: RD Sharma Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 16 CirclesDocument36 pagesExercise 16.1 Page No: 16.5: RD Sharma Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 16 CircleskeerthuhariNo ratings yet
- 1 3 1 1 5Document16 pages1 3 1 1 5Naveen ShankarNo ratings yet
- Circles Class 10th MCQ - 1 TestDocument6 pagesCircles Class 10th MCQ - 1 TestMelissa CouthinoNo ratings yet
- 10.circles PYQsDocument9 pages10.circles PYQsAtharv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Geomtery II AssignmentDocument20 pagesGeomtery II AssignmentHimanshu Chahar100% (1)
- Circles Basic QuestionsDocument7 pagesCircles Basic QuestionsMd AkramNo ratings yet
- Exemplar CirclesDocument12 pagesExemplar CirclesnNo ratings yet
- 1st and 2nd July-Geometry-Day17&18Document6 pages1st and 2nd July-Geometry-Day17&18Pradeep PanwarNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleDarkNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument60 pagesCircleShivani Ekant YadavNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsAyushi ghosh100% (1)
- 10th CBSE - Science - Chemical Reaction, Reflection of Light, Life Process (Set II)Document2 pages10th CBSE - Science - Chemical Reaction, Reflection of Light, Life Process (Set II)Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Letter WritingDocument1 pageLetter WritingRohan Mehta100% (2)
- 8 DMT Mix MN - Gundecha (10!1!24) School Portion Retest (Chapters - Playing With Numbers, Sets & Algebraic Identities)Document1 page8 DMT Mix MN - Gundecha (10!1!24) School Portion Retest (Chapters - Playing With Numbers, Sets & Algebraic Identities)Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFDocument118 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFSayan Dutta100% (1)
- The Sermon at Benares: Betty RenshawDocument14 pagesThe Sermon at Benares: Betty RenshawRohan Mehta100% (2)
- Important Questions (Maths) ICSE Class 10Document15 pagesImportant Questions (Maths) ICSE Class 10Sagnik85% (13)
- Physics Formula ICSE 10 Class Standard Chapter-WiseDocument11 pagesPhysics Formula ICSE 10 Class Standard Chapter-WiseRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Marriage Proposal: by Anton ChekhovDocument15 pagesThe Marriage Proposal: by Anton ChekhovRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - GST (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - GST (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- The NecklaceDocument29 pagesThe NecklaceRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Chapter-8 The Hack DriverDocument10 pagesClass - X: Chapter-8 The Hack DriverRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- JD's Private Tutorials: RevisionDocument12 pagesJD's Private Tutorials: RevisionRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - GST (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - GST (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Linear Inequation (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinDocument1 pageChapter 4 - Linear Inequation (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Banking Chapter QuestionsDocument5 pagesBanking Chapter QuestionsRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- GST SolutionDocument7 pagesGST SolutionRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- GST SolutionDocument7 pagesGST SolutionRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Amphibians Revision 1Document25 pagesAmphibians Revision 1Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Banking Chapter QuestionsDocument5 pagesBanking Chapter QuestionsRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Linear Inequation (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinDocument1 pageChapter 4 - Linear Inequation (30 Marks) Time: 1hr 15 MinRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Marginal CostingDocument4 pagesMarginal CostingRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Vakharia Academy: 10 (English)Document1 pageVakharia Academy: 10 (English)Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- 03 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsDocument3 pages03 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Vakharia Academy: 10 (English)Document1 pageVakharia Academy: 10 (English)Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- JD's Private Tutorials: Building "Neev" For FutureDocument7 pagesJD's Private Tutorials: Building "Neev" For FutureRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- JD's Private Tutorials: Contact: 7303781863 / 9920564563 IX CBSE Prelim 1Document7 pagesJD's Private Tutorials: Contact: 7303781863 / 9920564563 IX CBSE Prelim 1Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- JD's Private Tutorials: Contact: 7303781863 / 9920564563 IX CBSE Prelim (Narayana)Document7 pagesJD's Private Tutorials: Contact: 7303781863 / 9920564563 IX CBSE Prelim (Narayana)Rohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenFrom EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)