Professional Documents
Culture Documents
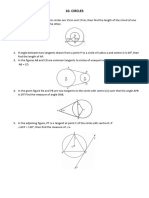
Circles
Uploaded by
Akshita KambojOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circles
Uploaded by
Akshita KambojCopyright:
Available Formats
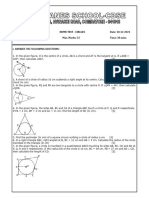
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
PRACTICE PAPER 09 (2023-24)
CHAPTER 10 CIRCLES
SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS MAX. MARKS : 40
CLASS : X DURATION : 1½ hrs
General Instructions:
(i). All questions are compulsory.
(ii). This question paper contains 20 questions divided into five Sections A, B, C, D and E.
(iii). Section A comprises of 10 MCQs of 1 mark each. Section B comprises of 4 questions of 2 marks
each. Section C comprises of 3 questions of 3 marks each. Section D comprises of 1 question of 5
marks each and Section E comprises of 2 Case Study Based Questions of 4 marks each.
(iv). There is no overall choice.
(v). Use of Calculators is not permitted
SECTION – A
Questions 1 to 10 carry 1 mark each.
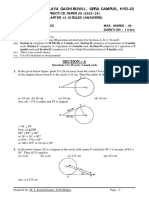
1. In the given below figure, point P is 26 cm away from the centre O of a circle and the length PT
of the tangent drawn from P to the circle is 24 cm. Then the radius of the circle is
(a) 25 cm (b) 26 cm (c) 24 cm (d) 10 cm
2. In the figure AT is a tangent to the circle with centre O such that OT = 4 cm and OTA = 30°.
Then AT is equal to
(a) 4 cm (b) 2 cm (c) 2√3 cm (d) 4√3 cm
3. In figure if O is centre of a circle, PQ is a chord and the tangent PR at P makes an angle of 50°
with PQ, then POQ is equal to
(a) 100° (b) 80° (c) 90° (d) 75°
4. In figure, O is the centre of a circle, AB is a chord and AT is the tangent at A. If AOB = 100°,
then BAT is equal to
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
(a) 100° (b) 40° (c) 50° (d) 90°
5. In the figure PA and PB are tangents to the circle with centre O. If APB = 60°, then OAB is
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 90° (d) 15°
6. In the given figure, TP and TQ are two tangents to a circle with centre O, such that POQ =
110°. Then PTQ is equal to
(a) 55° (b) 70° (c) 110° (d) 90°
7. In figure, AP, AQ and BC are tangents to the circle. If AB = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm and BC = 4 cm,
then the length of AP (in cm) is
(a) 7.5 (b) 15 (c) 10 (d) 9
8. In figure, PQ and PR are tangents to a circle with centre A. If QPA = 27°, then QAR equals to
(a) 63° (b) 153° (c) 126° (d) 117°
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
In the following questions 9 and 10, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of
reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
9. Assertion (A): From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of
Q from the centre is 25 cm then the radius of the circle is 7 cm.
Reason (R): A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact
10. Assertion (A): In the below figure, AB and CD are common tangents to circles which touch
each other at D. If AB = 8 cm, then the length of CD is 4 cm
Reason (R): A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact
SECTION – B
Questions 11 to 14 carry 2 marks each.
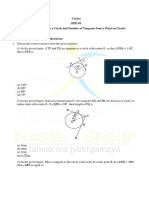
11. In the below figure, there are two concentric circles, with centre O and of radii 5 cm and 3 cm.
From an external point P, tangents PA and PB are drawn to these circles. If AP = 12 cm, find the
length of BP.
12. In figure, a circle touches the side BC of ∆ABC at P and touches AB and AC produced at Q and
R respectively. If AQ = 5 cm, find the perimeter of ∆ABC.
13. Two tangents PA and PB are drawn to the circle with centre O, such that APB = 120°. Prove
that OP = 2AP.
14. In figure, AP and BP are tangents to a circle with centre O, such that AP = 5 cm and APB =
60°. Find the length of chord AB.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
SECTION – C
Questions 15 to 17 carry 3 marks each.
15. Prove that the intercept of a tangent between two parallel tangents to a circle subtends a right
angle at the centre.
16. In figure, from an external point P, two tangents PT and PS are drawn to a circle with centre O
and radius r. If OP = 2r, show that OTS = OST = 30°.
17. In figure, two equal circles, with centres O and O′, touch each other at X. OO′ produced meets
the circle with centre O′ at A. AC is tangent to the circle with centre O, at the point C. O′D is
DO '
perpendicular to AC. Find the value of .
CO
SECTION – D
Questions 18 carry 5 marks.
18. In figure, the sides AB, BC and CA of triangle ABC touch a circle with centre O and radius r at
P, Q and R respectively.
Prove that
(i) AB + CQ = AC + BQ
1
(ii) Area ( ABC) = (perimeter of ABC) × r
2
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
SECTION – E (Case Study Based Questions)
Questions 19 to 20 carry 4 marks each.
19. The discus throw is an event in which an athlete attempts to throw a discus. The athlete spins
anti-clockwise around one and a half times through a circle, then releases the throw. When
released, the discus travels along tangent to the circular spin orbit.
In the given figure, AB is one such tangent to a circle of radius 75 cm. Point O is centre of the
circle and ∠ABO = 30°. PQ is parallel to OA.
Based on the above, information:
(a) Find the length of AB. (1)
(b) Find the length of OB. (1)
(c) Find the length of AP. (2)
OR
(c) Find the length of PQ. (2)
20. Circles play an important part in our life. When a circular object is hung on the wall with a cord
at nail N, the cords NA and NB work like tangents. Observe the figure, given that ∠ANO = 30°
and OA = 5 cm.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
Based on the above, answer the following questions:
(a) Find the distance AN.
(b) Find the measure of ∠AOB.
(c) Find the total length of cords NA, NB and the chord AB.
OR
(c) If ∠ANO is 45°, then name the type of quadrilateral OANB.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 6 -
You might also like
- Chemical Formulas List For Class 10Document5 pagesChemical Formulas List For Class 10Akshita Kamboj91% (35)
- Geomtery II AssignmentDocument20 pagesGeomtery II AssignmentHimanshu Chahar100% (1)
- Ioqm FST 5Document7 pagesIoqm FST 5Shakir MommandNo ratings yet
- BMTSC Exam Reference Problems GeometryDocument13 pagesBMTSC Exam Reference Problems GeometryAloma Fonseca100% (1)
- 21 Cyclic Quadrilaterals: 21.1 Angles in A CircleDocument14 pages21 Cyclic Quadrilaterals: 21.1 Angles in A CircleAndre Swaggerific PickettNo ratings yet
- Exemplar CirclesDocument12 pagesExemplar CirclesnNo ratings yet
- (A) Plane SailingDocument11 pages(A) Plane SailingKaren DavilaNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Document22 pagesSine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Rudi Berlian100% (2)
- Geometry II AssignmentDocument102 pagesGeometry II Assignmentkoushik reddyNo ratings yet
- Asia International Mathematical Olympiad Union: Senior SecondaryDocument4 pagesAsia International Mathematical Olympiad Union: Senior SecondaryNguyen MinhThanhNo ratings yet
- Python Content ManualDocument95 pagesPython Content Manualakashsinha_2004No ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Cbse Circles NotesDocument11 pagesClass 9 Maths Cbse Circles Notesdinesh_kp7647No ratings yet
- 3 - Angle PropertiesDocument4 pages3 - Angle PropertiesbuurningNo ratings yet
- Important Questions on Circles from Class IX Mathematics Assignments (Term 2Document25 pagesImportant Questions on Circles from Class IX Mathematics Assignments (Term 2sshoeburrahman100% (1)
- CIMCO CNC-Calc 2 - User Guide With Tutorials 1-10Document156 pagesCIMCO CNC-Calc 2 - User Guide With Tutorials 1-10Alexandru IancuNo ratings yet
- Arihant All in One Science PDFDocument565 pagesArihant All in One Science PDFAkshita Kamboj63% (16)
- Artificial Intelligence - Intro History Adv Disad and TypesDocument44 pagesArtificial Intelligence - Intro History Adv Disad and TypesAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Finding Unkown Angle Measures 3 KEYDocument2 pagesFinding Unkown Angle Measures 3 KEYKim Tae20% (5)
- Revision Worksheet (39 Pages)Document39 pagesRevision Worksheet (39 Pages)Amudha LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Final Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesMath 4 Final Lesson PlanJuvy Anne Dacara100% (1)
- CirclesDocument6 pagesCircleskumarm78No ratings yet
- Maths-Class-X-Holiday Homework Autumn Break CircleDocument6 pagesMaths-Class-X-Holiday Homework Autumn Break CirclecuriousnavinNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 11Document5 pagesMaths Class Ix Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 11neetikagupta990No ratings yet
- Maths Class x Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 09 AnswersDocument11 pagesMaths Class x Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 09 AnswersPaarvathy RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- CH 9 (26 2 2009) .PMDDocument10 pagesCH 9 (26 2 2009) .PMDRaj palNo ratings yet
- 10. Circles worksheetDocument4 pages10. Circles worksheetpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Mathematics Part 2 of 2Document58 pagesClass 10 Mathematics Part 2 of 2Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleDarkNo ratings yet
- PT-2, Maths, Class-X, 2022-23, RKSDocument6 pagesPT-2, Maths, Class-X, 2022-23, RKScuriousnavinNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-10 CircleDocument21 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-10 Circlefunson123No ratings yet
- S Classes 9811284214: Choose The Correct Answer From The Given Four OptionsDocument6 pagesS Classes 9811284214: Choose The Correct Answer From The Given Four OptionsJitu AtwalNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Impq Sa 2 5 CircleDocument14 pages10 Mathematics Impq Sa 2 5 CircleJesse SandersNo ratings yet
- 9th Maths Circle Test Paper SolvedDocument4 pages9th Maths Circle Test Paper SolvedStephen GreenNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 CirclesDocument15 pagesNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 CirclesJayant KumarNo ratings yet
- Circles AssignmentDocument4 pagesCircles Assignmentaahaan.handaNo ratings yet
- Circles Class 10th MCQ - 1Document15 pagesCircles Class 10th MCQ - 1Melissa CouthinoNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10Document15 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10Aaryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Subject-Mathematics, Class-Ix Circles: Worksheet (Basic)Document7 pagesSubject-Mathematics, Class-Ix Circles: Worksheet (Basic)sanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Document21 pagesNcert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10Shivam EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Test 47 - AP, Circles, Areas Related To CirclesDocument9 pagesTest 47 - AP, Circles, Areas Related To CirclessghkkNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument14 pagesMathsjaishreeNo ratings yet
- Solutions to Mathematics Questions from Class XI & XII O-Caps -3Document12 pagesSolutions to Mathematics Questions from Class XI & XII O-Caps -3Honey ChunduruNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 CirclesDocument15 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circlesausome.2289No ratings yet
- ch10 Extra QuestionsDocument5 pagesch10 Extra Questionsdrallanushka79No ratings yet
- X - Maths (041) Q. STANDARDDocument18 pagesX - Maths (041) Q. STANDARDektachawla203No ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 On Circles GRD 10Document3 pagesWorksheet 1 On Circles GRD 10RakshithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CirclesDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Circlesmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 10 Circles SolutionsDocument12 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 10 Circles Solutionsrai venugopalNo ratings yet
- Q C1 NER9 Ifs RDvxdeq MWVDocument5 pagesQ C1 NER9 Ifs RDvxdeq MWVtgaryangamerzsNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure - HL MathDocument13 pagesCircular Measure - HL MathPrakash PhilipNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Circles Test 02Document1 page10 Mathematics Circles Test 02ImranHashmiNo ratings yet
- Circles & TrianglesDocument5 pagesCircles & TrianglestheskygaurdianNo ratings yet
- Geometry 123Document4 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-01 at 9.00.03 PMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-01 at 9.00.03 PMdevanand.r.mahesh123No ratings yet
- Circle Geometry: Euclid Eworkshop # 6Document6 pagesCircle Geometry: Euclid Eworkshop # 6Dhananjay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- In QDocument11 pagesIn QGurupreetNo ratings yet
- Circle Most Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesCircle Most Important QuestionsVino PrabaNo ratings yet
- Geometry 123Document3 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28No ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of CirclesDocument17 pagesExercise Solution of CirclesiTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- 10.CirclesDocument20 pages10.CirclesMp SunilNo ratings yet
- Maths 10 Prep Exam2Document7 pagesMaths 10 Prep Exam2chandanNo ratings yet
- SA-II-2010-2011 Mathematics Class-X: Section-A (1 Mark Each)Document4 pagesSA-II-2010-2011 Mathematics Class-X: Section-A (1 Mark Each)Saayuj Bosseade ShanmughanNo ratings yet
- ojQab5DwVGhSXUvWFcTn PDFDocument94 pagesojQab5DwVGhSXUvWFcTn PDFtejas nandaniNo ratings yet
- class 10 Maths Mark type Questions Chapter 10Document105 pagesclass 10 Maths Mark type Questions Chapter 10ashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Lines, Angles, Triangles. Quadrilaterals, CircleDocument4 pagesLines, Angles, Triangles. Quadrilaterals, Circledarshanasawant8476No ratings yet
- 18-12-2021 HOME TESTDocument1 page18-12-2021 HOME TESTsaapldesign1 1No ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths SA2Document6 pagesClass 10 Maths SA2mahboobtandaNo ratings yet
- 1 3 1 1 5Document16 pages1 3 1 1 5Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hacker CrackdownDocument223 pagesHacker CrackdownMayank ParekhNo ratings yet
- Practical File Artificial Intelligence Class 10 For 2023-24Document26 pagesPractical File Artificial Intelligence Class 10 For 2023-24Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- MI circular Grade 3 & 4 -2024-25-1Document3 pagesMI circular Grade 3 & 4 -2024-25-1Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Class X Cartoon Based Questions Unique Study PointDocument23 pagesClass X Cartoon Based Questions Unique Study Pointmushrraf.hakimNo ratings yet
- Class X - Maths Test (ch-1-4)Document2 pagesClass X - Maths Test (ch-1-4)Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Test-1 ElectricityDocument2 pagesTest-1 ElectricityAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- His Darkest DevotionDocument682 pagesHis Darkest DevotionAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Wa0088.Document18 pagesWa0088.Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Relief Features of India Assignment - 1.5.22Document3 pagesCh.2 Relief Features of India Assignment - 1.5.22Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Cbse - Department of Skill Education Curriculum For Session 2023-2024Document20 pagesCbse - Department of Skill Education Curriculum For Session 2023-2024Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 71Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 71Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Cir 06 RT Schedule - IX-XDocument2 pagesCir 06 RT Schedule - IX-XAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 71Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 71Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 75Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 75Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Management - Akshita KambojDocument6 pagesWater Resource Management - Akshita KambojAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 71Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 71Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 71Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 71Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 75Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 75Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Unit 5,6 and 7Document24 pagesUnit 5,6 and 7Akshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Water Resource ManagementDocument3 pagesWater Resource ManagementAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course for Class IX-X Students to Connect ConceptsDocument1 pageBridge Course for Class IX-X Students to Connect ConceptsAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Types of AI: Reactive, Limited Memory & Theory of MindDocument11 pagesTypes of AI: Reactive, Limited Memory & Theory of MindAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Value of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseDocument11 pagesValue of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus From JAMB - MyschoolDocument1 pageMathematics Syllabus From JAMB - Myschooljanebaldore48No ratings yet
- 10th Intro To TrigoDocument11 pages10th Intro To TrigoDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- CBSE 9, Math, CBSE - Lines and Angles, HOTS QuestionsDocument2 pagesCBSE 9, Math, CBSE - Lines and Angles, HOTS QuestionsADITI RANJANNo ratings yet
- EG Unit 1-1Document79 pagesEG Unit 1-1SundraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - TrigonometryDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - TrigonometryDamon LeongNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 6 Math Q4Document3 pagesSummative Test 6 Math Q4Jann Christian P. PonganNo ratings yet
- WEEK 14 - The Central Angle-Intercepted Arc PostulateDocument39 pagesWEEK 14 - The Central Angle-Intercepted Arc PostulateCedrick Nicolas ValeraNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics June 1983 P2Document8 pagesCSEC Mathematics June 1983 P2zarzsultan12No ratings yet
- Httpstrial Spmpaper Me2022matematik20 (Maths) Perak202220Perak20Maths20K1 PDFDocument21 pagesHttpstrial Spmpaper Me2022matematik20 (Maths) Perak202220Perak20Maths20K1 PDFxinyunnNo ratings yet
- Al-Faiz Model School Multan: Q1. MCQ'sDocument1 pageAl-Faiz Model School Multan: Q1. MCQ'sAley ShahNo ratings yet
- Refresher2015.MathDocument11 pagesRefresher2015.MathBlanche Iris Estrel SiapnoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 2Document1 pageTrigonometry 2ArShad0% (1)
- Ailles RectangleDocument1 pageAilles Rectangleultimate3No ratings yet
- Crossword YEDvISe0QYDocument1 pageCrossword YEDvISe0QYOLIVIA BRANDON-PICKENSNo ratings yet
- Maths Lesson on NumbersDocument72 pagesMaths Lesson on NumbersPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Solving Problems Involving CirclesDocument16 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Solving Problems Involving CirclesJay Vincent MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- 05 Locus NotesDocument9 pages05 Locus NotesmNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Engineering DrawingDocument11 pagesComputer Aided Engineering DrawingSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Mathematics, Paper-I & Ii: InstructionsDocument9 pagesMathematics, Paper-I & Ii: Instructionssirichowdhary82No ratings yet
- IIT JEE Formula PCMDocument83 pagesIIT JEE Formula PCMCOOLTEX YTNo ratings yet
- Projection of PlaneDocument33 pagesProjection of PlaneSamitShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document16 pagesChapter 7Pyae Sone KyawNo ratings yet
- CBSE Worksheets For Class 12 Maths Application of Derivatives PDFDocument2 pagesCBSE Worksheets For Class 12 Maths Application of Derivatives PDFvimalNo ratings yet
- Undefined Terms in Geometry From HTTPS://WWW - Mcckc.edu/tutoring/docs/bt/geometry/basic - Geometric - Terms PDFDocument12 pagesUndefined Terms in Geometry From HTTPS://WWW - Mcckc.edu/tutoring/docs/bt/geometry/basic - Geometric - Terms PDFLilybeth Agno100% (1)