Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LQ SW and Ugw
LQ SW and Ugw
Uploaded by
Sophie BaromanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LQ SW and Ugw
LQ SW and Ugw
Uploaded by
Sophie BaromanCopyright:
Available Formats
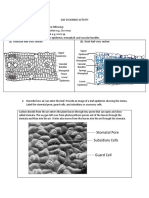
1. The unending circulation of the earth’s water supply is called ___. 1.
1. The unending circulation of the earth’s water supply is called ___.
2-3. What happens to the precipitation once it has fallen on land? 2-3. What happens to the precipitation once it has fallen on land?
4-5. What is the formula of porosity (%)? 4-5. What is the formula of porosity (%)?
6-7. What is meant by water balance? 6-7. What is meant by water balance?
7-8. What will happen when water balance is upset? 7-8. What will happen when water balance is upset?
9-11. List down three factors that influence the amount of water 9-11. List down three factors that influence the amount of water
that runs off rather than infiltration? that runs off rather than infiltration?
12-15. Enumerate the four main types of four spaces. 12-15. Enumerate the four main types of four spaces.
16. What will happen to the water flow as the river reaches the 16. What will happen to the water flow as the river reaches the
ocean or sea? ocean or sea?
17. What type of stream flow exhibits whirlpools and water rapids? 17. What type of stream flow exhibits whirlpools and water rapids?
18-20. What is the difference between the zone of aeration and 18-20. What is the difference between the zone of aeration and
zone of saturation? zone of saturation?
21-22. Give two factors that influences the change in the amount of 21-22. Give two factors that influences the change in the amount of
water discharge by a river over time? water discharge by a river over time?
23. What part of the river system contributes water to the main 23. What part of the river system contributes water to the main
stream, hence, increasing discharge of water downstream? stream, hence, increasing discharge of water downstream?
24. The coarse particles that make up the bed load move by 24. The coarse particles that make up the bed load move by
(dissolution, suspension, saltation). (dissolution, suspension, saltation).
25. It is a kind of stream that signifies that the elevation of the water 25. It is a kind of stream that signifies that the elevation of the water
table must be higher that the elevation of the stream surface. table must be higher that the elevation of the stream surface.
26. The material deposited by a stream are called ______ 26. The material deposited by a stream are called ______
(aggregates, meanders, ore deposits) (aggregates, meanders, ore deposits)
27. This unconfined runoff flow eventually develops threads of 27. This unconfined runoff flow eventually develops threads of
current that form tiny channels called _________. current that form tiny channels called _________.
28-29. (T/F) The number of tributaries increases upstream. 28-29. (T/F) The number of tributaries increases upstream.
30-31. What is the difference between aquitards and aquifers? 30-31. What is the difference between aquitards and aquifers?
32. (T/F) The stream channels become progressively shallower and 32. (T/F) The stream channels become progressively shallower and
wider downstream. wider downstream.
33-36. Sketch the difference between the four stream patterns. 33-36. Sketch the difference between the four stream patterns.
37-38. What are the 2 factors necessary to store water in the water 37-38. What are the 2 factors necessary to store water in the water
table? table?
39. (T/F) All rivers run towards the sea. 39. (T/F) All rivers run towards the sea.
40. (T/F) The stream velocity increases as you move into the deeper 40. (T/F) The stream velocity increases as you move into the deeper
part of the channel. part of the channel.
1. The unending circulation of the earth’s water supply is called ___. 1. The unending circulation of the earth’s water supply is called ___.
2-3. What happens to the precipitation once it has fallen on land? 2-3. What happens to the precipitation once it has fallen on land?
4-5. What is the formula of porosity (%)? 4-5. What is the formula of porosity (%)?
6-7. What is meant by water balance? 6-7. What is meant by water balance?
7-8. What will happen when water balance is upset? 7-8. What will happen when water balance is upset?
9-11. List down three factors that influence the amount of water 9-11. List down three factors that influence the amount of water
that runs off rather than infiltration? that runs off rather than infiltration?
12-15. Enumerate the four main types of four spaces. 12-15. Enumerate the four main types of four spaces.
16. What will happen to the flow of water as the river reaches the 16. What will happen to the flow of water as the river reaches the
ocean or sea? ocean or sea?
17. What type of stream flow exhibits whirlpools and water rapids? 17. What type of stream flow exhibits whirlpools and water rapids?
18-20. What is the difference between the zone of aeration and 18-20. What is the difference between the zone of aeration and
zone of saturation? zone of saturation?
21-22. Give two factors that influences the change in the amount of 21-22. Give two factors that influences the change in the amount of
water discharge by a river over time? water discharge by a river over time?
23. What part of the river system contributes water to the main 23. What part of the river system contributes water to the main
stream, hence, increasing discharge of water downstream? stream, hence, increasing discharge of water downstream?
24. The coarse particles that make up the bed load move by 24. The coarse particles that make up the bed load move by
(dissolution, suspension, saltation). (dissolution, suspension, saltation).
25. It is a kind of stream that signifies that the elevation of the water 25. It is a kind of stream that signifies that the elevation of the water
table must be higher that the elevation of the stream surface. table must be higher that the elevation of the stream surface.
26. The material deposited by a stream are called ______ 26. The material deposited by a stream are called ______
(aggregates, meanders, ore deposits) (aggregates, meanders, ore deposits)
27. This unconfined runoff flow eventually develops threads of 27. This unconfined runoff flow eventually develops threads of
current that form tiny channels called _________. current that form tiny channels called _________.
28-29. (T/F) The number of tributaries increases upstream. 28-29. (T/F) The number of tributaries increases upstream.
30-31. What is the difference between aquitards and aquifers? 30-31. What is the difference between aquitards and aquifers?
32. (T/F) The stream channels become progressively shallower and 32. (T/F) The stream channels become progressively shallower and
wider downstream. wider downstream.
33-36. Sketch the difference between the four stream patterns. 33-36. Sketch the difference between the four stream patterns.
37-38. What are the 2 factors necessary to store water in the water 37-38. What are the 2 factors necessary to store water in the water
table? table?
39. (T/F) All rivers run towards the sea. 39. (T/F) All rivers run towards the sea.
40. (T/F) The stream velocity increases as you move into the deeper 40. (T/F) The stream velocity increases as you move into the deeper
part of the channel. part of the channel.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- TALISAY (Terminalia Catappa) LEAF FIBERS AS A Wood-Free Paper SubstituteDocument63 pagesTALISAY (Terminalia Catappa) LEAF FIBERS AS A Wood-Free Paper SubstituteSophie Baroman100% (1)
- Dams: Parts, PakistanDocument22 pagesDams: Parts, PakistanEnigmatic Yousafzai100% (1)
- Flood Management Master Plan For Metro Manila and Surrounding AreasDocument21 pagesFlood Management Master Plan For Metro Manila and Surrounding AreasArangkada Philippines100% (1)
- MSC LiUDocument43 pagesMSC LiUMoksadur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Cogon GrassDocument15 pagesThe Feasibility of Cogon GrassSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Brief Survey of Philippine ArtDocument14 pagesBrief Survey of Philippine ArtSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- The Picture Between Mirror and Mind: From Phenomenology To Empirical Studies in Pictorial SemioticsDocument51 pagesThe Picture Between Mirror and Mind: From Phenomenology To Empirical Studies in Pictorial SemioticsSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Does Existence Precede Essence? Existentialism and AvicennaDocument20 pagesDoes Existence Precede Essence? Existentialism and AvicennaSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Manila To Re-Implement Curfew For MinorsDocument4 pagesManila To Re-Implement Curfew For MinorsSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- 29345-Article Text-77642-1-10-20171211Document4 pages29345-Article Text-77642-1-10-20171211Sophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Philippine StudiesDocument11 pagesPhilippine StudiesSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Deserts Subtropical DesertsDocument2 pages4 Types of Deserts Subtropical DesertsSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Groundsurface WaterDocument1 pageGroundsurface WaterSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - BioDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 - BioSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Quality Improvement of Corn Husk As Raw Material For Textile ProductsDocument5 pagesQuality Improvement of Corn Husk As Raw Material For Textile ProductsSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport ActivityDocument3 pagesPlant Transport ActivitySophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Development LAB EXERCISEDocument6 pagesReproduction and Development LAB EXERCISESophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange ActivityDocument3 pagesGas Exchange ActivitySophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Phil Sci ResultsDocument105 pagesPhil Sci ResultsSophie Baroman0% (1)
- Dam Safety Activity ReportDocument67 pagesDam Safety Activity Reportramkumar121No ratings yet
- Ok Weir (Constant Head)Document3 pagesOk Weir (Constant Head)Homer Batalao0% (2)
- Mcqs On Rivers of India ImpDocument30 pagesMcqs On Rivers of India ImpTawseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- IbisDocument4 pagesIbisAbrar AfzaNo ratings yet
- Private Islands For Sale Worldwide 3Document1 pagePrivate Islands For Sale Worldwide 3Angelina SinglaNo ratings yet
- The Journey of A RiverDocument4 pagesThe Journey of A Riverleon daveyNo ratings yet
- Chennai: WaterbodiesDocument34 pagesChennai: WaterbodiesLekshmi ShunnmaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo FluidosDocument7 pagesTrabajo FluidosJaneth Lopez ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Tujunga USGS PaperDocument37 pagesTujunga USGS Paperenrico66No ratings yet
- 2 Erosional Development of Streams (Horton, 1945)Document96 pages2 Erosional Development of Streams (Horton, 1945)alvlaroNo ratings yet
- Hydarulic Structures-Ii (G5-C) River Training WorksDocument15 pagesHydarulic Structures-Ii (G5-C) River Training WorkshailishNo ratings yet
- List of Famous Cities On River Banks in The WorldDocument2 pagesList of Famous Cities On River Banks in The WorldDiptangshu DeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 FLOODS AND ROUTINGDocument18 pagesUnit 4 FLOODS AND ROUTINGPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Rock Irrigation Weir Project: Xyz: Profile ViewDocument1 pageRock Irrigation Weir Project: Xyz: Profile ViewAnonymous MAQrYFQDzVNo ratings yet
- Dam and RiverDocument6 pagesDam and Riverjkl manNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TopographyDocument26 pagesChapter 1 TopographyPU BG100% (2)
- Rainage Ystem: Geography - Part IDocument11 pagesRainage Ystem: Geography - Part IChithra ThambyNo ratings yet
- Kalyan Sir - Indian River System PDFDocument14 pagesKalyan Sir - Indian River System PDFR Aditya Vardhana Reddy100% (1)
- Deposit: Bihar GK For BPSC Bihar Drainage SystemDocument4 pagesDeposit: Bihar GK For BPSC Bihar Drainage SystemAnkul RanjanNo ratings yet
- National Register of Large Dams 2015Document207 pagesNational Register of Large Dams 2015Thapa S100% (1)
- Cusec To LitersDocument8 pagesCusec To LitersPrakash J VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- December KGS ReportDocument38 pagesDecember KGS ReportTessa VanderhartNo ratings yet
- Braided ChannelsDocument9 pagesBraided ChannelsFebrian Rahmana Putra100% (1)
- The Great LakesDocument20 pagesThe Great LakesAmra Talić-ČikmišNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary EnvironmentDocument67 pagesSedimentary EnvironmentElfi Agustini RNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Gi Dan Tpi GabunggDocument1 pagePerbandingan Gi Dan Tpi GabunggVaiiErlanggaGeoNo ratings yet
- Rivers OdishaDocument3 pagesRivers OdishaJason Hugh100% (1)
- Chap 5 River TrainingDocument28 pagesChap 5 River Traininghaile gidey100% (1)