Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Quarterly Exam Review Guide: Principle Example
Uploaded by
Austin WilliamsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Quarterly Exam Review Guide: Principle Example
Uploaded by
Austin WilliamsCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Quarterly Exam Review Guide
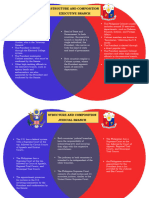
1. What are the principles of the Constitution? Provide examples for each from the executive branch. Fill in
the blanks
Principle Definition Example
Checks and Balances The ability of each branch of government to The Senate can choose to not confirm
check the actions of the others so that power is the President’s appointments.
balanced.
Judicial Review The courts have the power to declare acts The Supreme Court can rule an
unconstitutional executive order unconstitutional
Separation of Powers The powers of the national government are The legislative branch, the executive
divided branch, and the judicial branch.
Federalism Powers are shared and divided between a National government maintains a
national and state governments military, states est. & maintain
schools.
National Supremacy The national government supersedes state State governments can’t tax the
powers national government.
Limited Government A way to prevent and/or punish abuse of power The President can only be elected to 2
in government. terms
Popular Sovereignty Authority of government is created and The people elect the state legislatures
sustained by the consent of its PEOPLE, who chose the electors who elect the
through elected representatives. President
Rule of Law That all people and institutions are subject to Presidents can be charged with
and accountable to law that is fairly applied crimes
and enforced regardless of your status or
position.
Due Process Government must treat everyone fairly The FBI must follow procedural due
process when arresting those accused
of committing federal crimes.
2. What is the primary role of the legislative branch?
To draft and pass proposed laws.
3. Identify TWO ways Congress can check the power of the President
○ The House of Representatives can:
Can override a veto with ⅔ vote.
○ The Senate can:
Confirm or Deny Appointments.
4. What are three ways that interest groups influence lawmaking?
5. How does population influence representation in Congress?
The more people in a state, the more representatives, with at least one for each state.
6. In the Supreme Court case of Baker v. Carr what precedent setting opinion did the court make in regards to
redistricting congressional districts?
It decided that redistricting cases are justiciable.
7. What are three powers RESERVED to the states?
Ownership of property
Maintaining a judicial system.
Education of Inhabitants
8. What is the job of the office of planning and zoning in Anne Arundel County?
To plan the overall physical development and growth of the County, update and enforce the zoning
code, and administer the subdivision and development regulations.
9. What is the primary role of the executive branch?
The executive branch carries out and enforces laws
10. What are the roles of the President? Fill in the blanks
Role of the Description of Role Example of action in this role
President
Formal Chief Executive The president manages the Executive
Branch, deciding how the laws of the
Roles
United States are to be enforced and
appointing officials and advisers to help run
the Executive Branch.
Chief Diplomat The president decides what American Traveling to London to meet with
diplomats and ambassadors shall say to British leaders.
foreign governments. With the help of
advisers, the president makes the foreign
policy of the United States. Negotiating a treaty or a trade deal.
Commander in The president runs the military. Deciding, in wartime, whether to
bomb foreign cities, where to station
Chief
troops, or how to use weapons.
11. Identify FOUR FORMAL powers of the President outlined in Article II of the Constitution. Highlight the powers that
can influence foreign policy once identified.
12. What might constitute a circumstance where the President would need to write an executive order?
When immediate action is needed and time can not be wasted to wait to make it a law.
13. How did the War Powers Act of 1973 impact the President’s war making power?
It prevented them from entering a conflict with troops without first getting legislative approval
14. Who is the head of the executive branch at the state level?
The Governor
15. What is the area of expertise of each cabinet department?
Name of Department Area of Expertise
State The primary goal of the Secretary of State and the U.S. Department of State is to
shape a freer, more secure, and more prosperous world through formulating and
implementing the President's foreign policy, while supporting and protecting
American interests abroad.
Defense The Department of Defense's enduring mission is to provide combat-credible
military forces needed to deter war and protect the security of our nation.
Justice To enforce the law and defend the interests of the United States according to the
law.
16. What types of regulations do the following agencies make?
Full Name Example of Regulation
Food and Drug Administration Approve a OTC drug
FDA
Federal Trade Commission Identity Theft Act
FTC
Federal Communication Commission Give out licences to products that transmit.
FCC
17. EXPLAIN the difference between isolationism and interventionism.
18. What are the five GOALS of foreign policy? Provide an example of each.
19. DESCRIBE five TOOLS of foreign policy.
20. Why are tariffs considered beneficial? Why are tariffs considered harmful?
You might also like
- Summary of Steven Rab's The Founders' Speech to a Nation in CrisisFrom EverandSummary of Steven Rab's The Founders' Speech to a Nation in CrisisNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Unit - III - Study - Guide - Branches - of - Government PDFDocument3 pagesKami Export - Unit - III - Study - Guide - Branches - of - Government PDFOdwin Gonzalez PachecoNo ratings yet
- Powers of The US PresidentDocument11 pagesPowers of The US PresidentSohail NasirNo ratings yet
- The Powers of The President: The Constitution and The PresidencyDocument2 pagesThe Powers of The President: The Constitution and The PresidencySasha VermaNo ratings yet
- AP Government Chapter 13 Notes: The PresidencyDocument10 pagesAP Government Chapter 13 Notes: The PresidencyAllen GuNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Organs of GovernmentDocument56 pagesUnit I: Organs of GovernmentAditi ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- The United States Political SystemDocument14 pagesThe United States Political SystemRUTH HUAMAN LOZADANo ratings yet
- Social Studies 16:02:2024Document11 pagesSocial Studies 16:02:2024152956No ratings yet
- Local GovernmentDocument55 pagesLocal GovernmentElaiza RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vietnamese Legal SystemDocument60 pagesIntroduction To Vietnamese Legal Systemanon_355962815No ratings yet
- Study GuideMar16Document2 pagesStudy GuideMar16Jaylen CarringtonNo ratings yet
- POL 101 ProjectDocument16 pagesPOL 101 ProjectOlivia HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Political Law Reviewer (Midterms)Document19 pagesPolitical Law Reviewer (Midterms)Joel TabiraraNo ratings yet
- Created by Article II of The Constitution: Presidential Roles Presidential Powers QualificationsDocument34 pagesCreated by Article II of The Constitution: Presidential Roles Presidential Powers QualificationsJemaicaNo ratings yet
- Three Branches of The GovernmentDocument12 pagesThree Branches of The Governmententengp22No ratings yet
- MISBAH PATEL - APGovUnit1StudyGuidewwwultimatereviewpacketcom-230109-104332Document3 pagesMISBAH PATEL - APGovUnit1StudyGuidewwwultimatereviewpacketcom-230109-104332misbahpatel0919No ratings yet
- Constitutional PrinciplesDocument8 pagesConstitutional Principlesapi-264755370No ratings yet
- Intro To Am Law OutlineDocument11 pagesIntro To Am Law OutlineArk Joseph NdulueNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument4 pagesConstitutionapi-329620206No ratings yet
- Unit5masterytake2 1Document3 pagesUnit5masterytake2 1api-295725781No ratings yet
- Retail Trade ReviewerDocument83 pagesRetail Trade ReviewerIRA YSABEL AZULNo ratings yet
- Created by Article II of The Constitution: Presidential Roles Presidential Powers QualificationsDocument34 pagesCreated by Article II of The Constitution: Presidential Roles Presidential Powers QualificationsMel Froilan ArregloNo ratings yet
- PILDocument4 pagesPILJoselle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9Document5 pagesAssignment 9Margarita SánchezNo ratings yet
- Q2 UcspDocument8 pagesQ2 UcspYancey LucasNo ratings yet
- 3.3.5 Practice - Comparing The BranchesDocument7 pages3.3.5 Practice - Comparing The Branchesjvillarreal489No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Indian Constitution: What Is A Constitution?Document4 pagesIntroduction To The Indian Constitution: What Is A Constitution?Jaspreet TandaNo ratings yet
- Legal Research Mikee Louise Q. Mirasol JD 1E-BDocument5 pagesLegal Research Mikee Louise Q. Mirasol JD 1E-BMikee BornforThis MirasolNo ratings yet
- LAW ReviewerDocument13 pagesLAW ReviewerMontecer, Donnalyn S. BSE SOCIAL STUDIES 2ENo ratings yet
- Features of Us ConstitutionDocument7 pagesFeatures of Us ConstitutionnaheedNo ratings yet
- 9.systems of Check and BalancesDocument3 pages9.systems of Check and BalancesAmee MemonNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Elements of Public LawDocument5 pagesTopic 3 Elements of Public LawMalon KipkoechNo ratings yet
- Branches If USgoverment TareaDocument2 pagesBranches If USgoverment Tareagenshin teodioNo ratings yet
- I. Overview of United States Form of Government: Concept of Federal Constitutional RepublicDocument19 pagesI. Overview of United States Form of Government: Concept of Federal Constitutional RepublicAnonymous kzucg21MeNNo ratings yet
- Aws 7 Ocr Government and PoliticsDocument28 pagesAws 7 Ocr Government and PoliticsIntroer GratisNo ratings yet
- Comparative Law - Lecture 1Document14 pagesComparative Law - Lecture 1Amlan DeNo ratings yet
- T o P I CDocument14 pagesT o P I CReen Zaza ZareenNo ratings yet
- COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS - Module 3.activity 1Document2 pagesCOMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS - Module 3.activity 1Cee Bagat PadillaNo ratings yet
- Pa1 Chapter 3Document2 pagesPa1 Chapter 3Paulo NarvajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Constitutional Authority To Regulate BusinessDocument1 pageChapter 5: Constitutional Authority To Regulate BusinessNic Satur Jr.No ratings yet
- 2018 Civic Education Study Kit - Second Edition Final - Kitwe D PDFDocument127 pages2018 Civic Education Study Kit - Second Edition Final - Kitwe D PDFBricious Mulimbi84% (37)
- Constitutional Law 1 Quiz Jeffrey M. GenitaDocument3 pagesConstitutional Law 1 Quiz Jeffrey M. Genitalionroarlaw.infoNo ratings yet
- Democracy, Government and Constitution (Part Ii)Document10 pagesDemocracy, Government and Constitution (Part Ii)Chardii PuthNo ratings yet
- KARIS ENCHELMAYER - (Template) Six Big Ideas OutlineDocument2 pagesKARIS ENCHELMAYER - (Template) Six Big Ideas OutlineKARIS ENCHELMAYERNo ratings yet
- Amgov ActivityDocument12 pagesAmgov Activity202210028No ratings yet
- Chapter3 QACDocument4 pagesChapter3 QACnighatparveen00786No ratings yet
- Politics and GovernanceDocument7 pagesPolitics and GovernanceMarilyn BasaNo ratings yet
- Powers of The American PresidentDocument2 pagesPowers of The American Presidentrajbakhtiyar11No ratings yet
- Us: Governance and Policy-Making: Presented By: Seerat Gul (006) Course Title: Comparative PoliticsDocument17 pagesUs: Governance and Policy-Making: Presented By: Seerat Gul (006) Course Title: Comparative Politicssafaasim62No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Executive BranchDocument50 pagesUNIT 3 Executive BranchJoebert ArcuenoNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Constitutional LawDocument32 pages1-Introduction To Constitutional LawAlyea IwaniNo ratings yet
- MOOCs-Separation of Powers-E TextDocument13 pagesMOOCs-Separation of Powers-E TextPulakNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law-Harvard OutlineDocument82 pagesConstitutional Law-Harvard OutlineJosh Critselous100% (8)
- Executive Organ of The GovernmentDocument7 pagesExecutive Organ of The Governmentjay kumarNo ratings yet
- LEGISLATIVE DEPARTMENT ReviewerDocument7 pagesLEGISLATIVE DEPARTMENT ReviewerJica Rose Antog ParokNo ratings yet
- A System of Checks and BalancesDocument4 pagesA System of Checks and Balancesregie odiamarNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Government NotesDocument6 pagesThe Philippine Government Noteswoman in stemNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law: Reporter of Group 1Document23 pagesAdministrative Law: Reporter of Group 1Mary Grace LadiosNo ratings yet
- PHILIPPINE CONSTITUTION de Leon Personal NotesDocument15 pagesPHILIPPINE CONSTITUTION de Leon Personal NotesMarionne GNo ratings yet
- Week 011-Module The LegislativeDocument7 pagesWeek 011-Module The LegislativeDoty AcasioNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab Physical or Chemical ChangeDocument2 pagesVirtual Lab Physical or Chemical ChangeAustin Williams83% (6)
- Notes On Parenting StylesDocument2 pagesNotes On Parenting StylesAustin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Austin Williams - 5.4 Practice Amplitude and MidlineDocument2 pagesAustin Williams - 5.4 Practice Amplitude and MidlineAustin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Rafael Caro Quintero Most Wanted Poster 20M USD Reward 4.12.18Document1 pageRafael Caro Quintero Most Wanted Poster 20M USD Reward 4.12.18Chivis MartinezNo ratings yet
- Jimenez English CleanDocument1 pageJimenez English CleanKevin LiNo ratings yet
- Update 031618 FBI10MWF8.5x13 Alejandro Castillo 02Document1 pageUpdate 031618 FBI10MWF8.5x13 Alejandro Castillo 02Fábio Dantas CostaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Graphing PracticeDocument2 pages5.4 Graphing PracticeAustin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems (Matching)Document1 pagePractice Problems (Matching)Austin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Transformations of Powers and RootsDocument2 pages6.3 Transformations of Powers and RootsAustin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems (Matching)Document1 pagePractice Problems (Matching)Austin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Codal Revised Penal Code and Special Penal LawsDocument201 pagesCodal Revised Penal Code and Special Penal LawsCharmine AngaraNo ratings yet
- 12 Angry Men - HypothesisDocument3 pages12 Angry Men - HypothesisRavi ParekhNo ratings yet
- Rashomon FilmDocument2 pagesRashomon FilmNasreen HakimNo ratings yet
- 367308171-Uy-v-Capulong With Synospis and DoctrineDocument2 pages367308171-Uy-v-Capulong With Synospis and DoctrineJESSIE JAMES YAPAONo ratings yet
- UP Police Directory 2012Document82 pagesUP Police Directory 2012Pranay KumarNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Kidnapping in NigeriaDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Kidnapping in Nigeriaea844bbvNo ratings yet
- Questions 1-7 of 26:: LAW 3210 Family Law I (Husband & Wife) Domestic ViolenceDocument8 pagesQuestions 1-7 of 26:: LAW 3210 Family Law I (Husband & Wife) Domestic ViolenceIqbal CheverriaNo ratings yet
- Interim Order in Civil CasesDocument7 pagesInterim Order in Civil CasesRadheyNo ratings yet
- Case Digests For Constitutional Law 2 Review 2020: (List of Cases Based On Dean Joan S Largo'S Syllabus)Document14 pagesCase Digests For Constitutional Law 2 Review 2020: (List of Cases Based On Dean Joan S Largo'S Syllabus)MirafelNo ratings yet
- Alabama Governor's Office Public Records Request FormDocument3 pagesAlabama Governor's Office Public Records Request FormDeadspinNo ratings yet
- Carriage by AirDocument21 pagesCarriage by AirRoland LeongNo ratings yet
- DHS NotificationDocument3 pagesDHS NotificationYahoo NewsNo ratings yet
- People Vs TuandaDocument1 pagePeople Vs TuandahalleybackNo ratings yet
- Week 4 of Company LawDocument4 pagesWeek 4 of Company LawlowericaNo ratings yet
- قرارات منظمة الأمم المتحدة و المنظمات الدولية المتخصصة ودورها في مكافحة الجريمة المنظمة عبر الوطنية Resolutions of the United Nations and specialized international organizations and their role in combating the trDocument22 pagesقرارات منظمة الأمم المتحدة و المنظمات الدولية المتخصصة ودورها في مكافحة الجريمة المنظمة عبر الوطنية Resolutions of the United Nations and specialized international organizations and their role in combating the trﺗﺴﻨﻴﻢ بن مهيديNo ratings yet
- V2 DRAFT Audi Car ComplaintDocument7 pagesV2 DRAFT Audi Car ComplaintAmbience LegalNo ratings yet
- Living Testimony TemplateDocument6 pagesLiving Testimony TemplateCody100% (1)
- Grandparent Appeal BriefDocument21 pagesGrandparent Appeal BriefJodi Silbermann100% (1)
- Criminal Law QuestionsDocument6 pagesCriminal Law QuestionsSaurabhNo ratings yet
- GUION ModificadoDocument6 pagesGUION ModificadoSonia CastilloNo ratings yet
- Security Bank Corp V Great Wall Commercial Press CoDocument17 pagesSecurity Bank Corp V Great Wall Commercial Press CoTweetie TuazonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Section 3 Cause of Contracts 1350-1355Document6 pagesChapter 2 - Section 3 Cause of Contracts 1350-1355LawStudent101412No ratings yet
- (Candia Emmanuel V Attorney General, Miscellaneous Cause No 158 of 2018Document11 pages(Candia Emmanuel V Attorney General, Miscellaneous Cause No 158 of 2018Edgar OkitoiNo ratings yet
- BANAT v. COMELEC, G.R. No. 177508, August 7, 2009, 595 SCRA 477 PDFDocument13 pagesBANAT v. COMELEC, G.R. No. 177508, August 7, 2009, 595 SCRA 477 PDFanthony magandaNo ratings yet
- Investigation Data Form 1Document1 pageInvestigation Data Form 1Jossa ReyesNo ratings yet
- Rule 128 - General ProvisionsDocument14 pagesRule 128 - General ProvisionsJoshua CustodioNo ratings yet
- (Antonio - Cassese - and - Paola - Gaeta) - International - Cr. PP 20 - 48Document31 pages(Antonio - Cassese - and - Paola - Gaeta) - International - Cr. PP 20 - 48LIZETH EULALIA CORAS CARDENASNo ratings yet
- SABLAS V SABLAS - Partition NO DECLARATION OF DEFAULT IF NO MOTIONDocument4 pagesSABLAS V SABLAS - Partition NO DECLARATION OF DEFAULT IF NO MOTIONJade Palace TribezNo ratings yet
- Appointment Setter Agreement: 1-12-22 December Devansh SinghDocument3 pagesAppointment Setter Agreement: 1-12-22 December Devansh SinghDevansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Law Abiding Citizen (2009) BluRayExt HighDocument25 pagesLaw Abiding Citizen (2009) BluRayExt HighdamiloakinyemiNo ratings yet