Professional Documents
Culture Documents
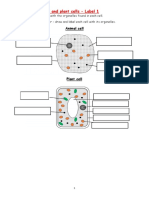
1 Parts and Function of Eye Ws
Uploaded by
aastha dograOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Parts and Function of Eye Ws
Uploaded by
aastha dograCopyright:
Available Formats
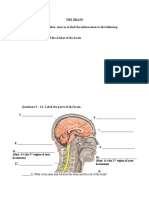
SCIENCE 8 – PARTS OF THE EYE WORKSHEET
NAME:
Use the vocabulary words in the box below to label the parts of the eye.
Place the correct letter on the line next to each part of the eye. Not all letters will be used.
Vocabulary
a. Iris
b. Blind spot
c. Vitreous humour
d. Sclera
e. Pupil
f. Cornea
g. Retina
h. Aqueous humour
i. Optic nerve
j. Lens
Use your notes from pages 23 – 26 and the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks for the
following ten questions.
1) Light rays are first refracted by the .
2) Surrounding the cornea is an opaque white tissue called the .
3) Light enters the eye through an opening in the centre called the .
4) The is the fluid that nourishes the cornea
since it does not have a blood supply of its own.
5) The is the coloured circle of muscle surrounding the pupil. It controls
the amount of light entering the eye.
6) Light then passes through the flexible, convex which can change its
shape.
7) Once light is refracted by the lens, it is focussed on the at the back of
the eye, where an image is formed.
8) Light-sensitive cells detect the image and an electric message is sent to the brain through the
.
9) The is the fluid found between the lens
and the retina and provides support for the eyeball.
10) No image is formed at the since this is the location
where the optic nerve attaches to the retina and therefore lacks receptors for light.
11) Describe how the eye adapts to the following changes in conditions:
(a) Sudden increase in brightness:
(b) Gradual dimming of light until it is almost dark:
(c) Looking at a kite, then down at your hand to let out string:
Read the statements given below. If the statement is true, write “T” on the line in front of the statement.
If it is false, write “F” and rewrite the statement to make it true.
12) The lens does most of the focussing of the light rays that pass through the eye.
13) The light rays that pass through the eye diverge.
14) In bright light, the iris makes the pupil larger to allow more light to enter.
15) The human eye has a concave lens.
16) Light rays are sent to the brain through the optic nerve.
17) The vitreous humour provides nourishment for the retina.
18) The ciliary muscles adjust the shape of the lens.
You might also like
- S1l1-Animals-Lesson 2Document4 pagesS1l1-Animals-Lesson 2api-371196243100% (1)
- 5th Grade Cells Lesson PlanDocument5 pages5th Grade Cells Lesson Planapi-255511422No ratings yet
- (Z65.ebook) Dental Decks Part 2 2013 2014Document3 pages(Z65.ebook) Dental Decks Part 2 2013 2014aastha dogra0% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson Planapi-272708709100% (1)
- Ict Miscroscope Lesson ThreeDocument2 pagesIct Miscroscope Lesson Threeapi-280941862100% (1)
- Floating-Sinking Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesFloating-Sinking Lesson Planapi-336350504No ratings yet
- Cells Lesson 1Document7 pagesCells Lesson 1api-372328325No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Lesson Plan 1Document11 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lesson Plan 1api-207974201100% (2)
- Animal Cell Lesson Plan TeachingDocument3 pagesAnimal Cell Lesson Plan Teachingapi-272315601No ratings yet
- Draft e Proceeding PDFDocument547 pagesDraft e Proceeding PDFHerdy VeristianNo ratings yet
- Case Report CataractDocument12 pagesCase Report Cataractbelly sutopo88% (8)
- Shyla Jennings Ebook FinalDocument17 pagesShyla Jennings Ebook FinalChye Yong HockNo ratings yet
- Animal Habitats: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAnimal Habitats: Learning ObjectivesGRose SolisNo ratings yet
- Habitats Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesHabitats Lesson Planapi-335363324No ratings yet
- Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesChoose The Letter of The Correct AnswerJoseph ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Worksheet (7) - 0Document4 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Worksheet (7) - 0Yatish TiwariNo ratings yet
- A Welcoming Letter To The ParentsDocument5 pagesA Welcoming Letter To The Parentsapi-238189917No ratings yet
- Grade 3 Skeletal SystemDocument41 pagesGrade 3 Skeletal SystemVanny Gimotea BaluyutNo ratings yet
- BBC - KS2 Bitesize - Science - LightDocument2 pagesBBC - KS2 Bitesize - Science - LightJeminah Grace Lopez TelewikNo ratings yet
- Class 8: Subject: Science Chapter 2-Microorganism: Friend and Foe WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass 8: Subject: Science Chapter 2-Microorganism: Friend and Foe Worksheetazwin hasyanaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Particle Theory of MatterDocument1 page5.1 Particle Theory of Matterjohn doeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Class 2 - CH 7 (EVS) - Jharna - PramilaDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - Class 2 - CH 7 (EVS) - Jharna - PramilaVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- CH 1: LEAF-The Food Factory of Plant: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument3 pagesCH 1: LEAF-The Food Factory of Plant: Very Short Answer QuestionsAruba100% (1)
- Butterfly Life Cycle Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesButterfly Life Cycle Lesson PlanPeter GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Holiday Assignment-Grade 7Document3 pagesHoliday Assignment-Grade 7aryan10No ratings yet
- Science Lesson For ElDocument3 pagesScience Lesson For Elapi-279742832No ratings yet
- Calculating Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument1 pageCalculating Kinetic and Potential EnergySietina Villanueva100% (1)
- Mixtures and Solutions Lesson Plan AssignmentDocument14 pagesMixtures and Solutions Lesson Plan AssignmentDonn NiñoNo ratings yet
- Transparent Translucent Opaque Window Brochure Lesson Plan March 20Document2 pagesTransparent Translucent Opaque Window Brochure Lesson Plan March 20api-361291175No ratings yet
- Weather Worksheets For Lesson 3Document3 pagesWeather Worksheets For Lesson 3api-345589648No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument9 pagesCell OrganellesariaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Cardinal DirectionDocument2 pagesLesson Plan For Cardinal Directionapi-235824394No ratings yet
- So Lesson Plan Reflection 2Document4 pagesSo Lesson Plan Reflection 2api-309886906No ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesNervous System WorksheetaNo ratings yet
- Gulzar Hina 5 6 Lesson Plan AnalysisDocument8 pagesGulzar Hina 5 6 Lesson Plan Analysisapi-300665697No ratings yet
- Respiratory System WorksheetDocument4 pagesRespiratory System WorksheetAsheka TenzinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Class 5Document3 pagesChapter 21 Class 5SuvashreePradhan100% (1)
- Year 7 HassDocument15 pagesYear 7 Hassapi-496451435No ratings yet
- Animal Classification LessonDocument7 pagesAnimal Classification Lessonapi-269984318No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Cells-1Document3 pagesLesson Plan Cells-1api-371640211No ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell - Docx YuvenDocument8 pagesPlant Cell and Animal Cell - Docx YuvenVikneswaran Gunahlan NeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson Note On IrritabilityDocument3 pagesBiology Lesson Note On IrritabilityJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Natural Sciences Resource Pack on Energy and ChangeDocument41 pagesGrade 8 Natural Sciences Resource Pack on Energy and Changendodana SibandaNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 What Is LightDocument7 pagesACTIVITY 1 What Is LightLuka Sepulveda SermenoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Nervous System PPT DiscDocument60 pagesGrade 5 Nervous System PPT DiscScience Teacher100% (1)
- Cell Organelles 10 Day Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesCell Organelles 10 Day Lesson PlanRandi Lines100% (2)
- Inherited Traits and Learning BehavioursDocument3 pagesInherited Traits and Learning BehavioursSabha HamadNo ratings yet
- 1 3 Specialized Cells and Tissues Lesson PlanDocument4 pages1 3 Specialized Cells and Tissues Lesson Planapi-310312979100% (3)
- Year 11 General Human Biology - Lesson 3Document3 pagesYear 11 General Human Biology - Lesson 3api-345120999No ratings yet
- Food Chain Stage 3 Draft 1Document5 pagesFood Chain Stage 3 Draft 1api-281198656No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - WavesDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 - WavesMary BakhoumNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2007 Paper 1 Level 5-7Document28 pagesKS3 Science 2007 Paper 1 Level 5-7Illy GuissNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanKevin Paul DeañoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis ExperimentDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis ExperimentstjustinsNo ratings yet
- Light and ShadowsDocument4 pagesLight and Shadowsapi-311797972No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell ComparisonDocument16 pagesPlant and Animal Cell ComparisonSandWich TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument3 pagesCell StructuresKatherine DenisNo ratings yet
- "Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)Document1 page"Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)SusanAngDíaz0% (2)
- Lesson Plan 5 - Deforestation-So WhatDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 5 - Deforestation-So Whatapi-547106143No ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesCovalent Bonding Practice ProblemsGerryNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ExampleDocument2 pagesLesson Plan ExampleDaniela Ayala100% (1)
- Specialised Cell Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSpecialised Cell Lesson PlanMelissa Maas Richardson67% (3)
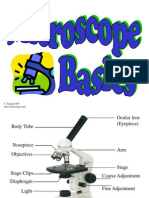
- Microscope BasicsDocument6 pagesMicroscope Basicsmaniiiiiiii100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper: General InstructionsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper: General Instructionsaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Describe What Is Happening in These PicturesDocument9 pagesDescribe What Is Happening in These Picturesaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: How Do You Grow From A Where Do TheDocument32 pagesCell Division: How Do You Grow From A Where Do Theaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Fun With Water Potential WorksheetDocument1 pageFun With Water Potential Worksheetaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves KS3Document13 pagesSound Waves KS3aastha dograNo ratings yet
- Ezy Math Tutoring - Year 6Document93 pagesEzy Math Tutoring - Year 6Clinton3011100% (3)
- Chemistry CBSE Class 10Document5 pagesChemistry CBSE Class 10aastha dograNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Science & Technology 1Document16 pagesScience & Technology 1hussainamini100% (1)
- Make The Grade As and A2 Chemistry Chemistry Revision Guide Edexcel As A2 Modular Nelson Advanced ScienceDocument147 pagesMake The Grade As and A2 Chemistry Chemistry Revision Guide Edexcel As A2 Modular Nelson Advanced Scienceareyouthere92100% (3)
- Year 3 Maths - Number - Multiplication - Division - Questions (Ch1 Ex3)Document4 pagesYear 3 Maths - Number - Multiplication - Division - Questions (Ch1 Ex3)aastha dograNo ratings yet
- Lebo106 PDFDocument31 pagesLebo106 PDFakhil_reddy7352No ratings yet
- Moneran (Bacteria), Animalia, Plantae, Fungi: - Conglomerate of Organisms Which Do Not Fit Into Other 4 KingdomsDocument36 pagesMoneran (Bacteria), Animalia, Plantae, Fungi: - Conglomerate of Organisms Which Do Not Fit Into Other 4 Kingdomsaastha dograNo ratings yet
- BioDocument24 pagesBioBenes Salamanca BolascoNo ratings yet
- Calculating Magnification WorksheetDocument3 pagesCalculating Magnification Worksheetaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of A PoemDocument45 pagesBasic Elements of A Poemaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Denture ConversionDocument11 pagesDenture Conversionaastha dogra100% (1)
- iGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1Document44 pagesiGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1aastha dograNo ratings yet
- Triquilar PM en PDFDocument54 pagesTriquilar PM en PDFElii LechmanNo ratings yet
- Train at Home PDFDocument2 pagesTrain at Home PDFaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus DENTAL PharmacologyDocument6 pagesCourse Syllabus DENTAL Pharmacologyaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Denture ConversionDocument11 pagesDenture Conversionaastha dogra100% (1)
- Extrovert Yourself How To Become Extrovert Confident and Overcome Shyness Extrovert Introvert Ambivert Become ExtrovertDocument2 pagesExtrovert Yourself How To Become Extrovert Confident and Overcome Shyness Extrovert Introvert Ambivert Become Extrovertaastha dogra0% (1)
- How To Take A Good Impression (Crown and Bridge)Document3 pagesHow To Take A Good Impression (Crown and Bridge)mutuora100% (1)
- 30284a Affinis BrochureDocument4 pages30284a Affinis Brochureaastha dograNo ratings yet
- BVM-X300 V2: 30-Inch 4K TRIMASTER EL™ OLED Critical Reference MonitorDocument11 pagesBVM-X300 V2: 30-Inch 4K TRIMASTER EL™ OLED Critical Reference MonitorJuanNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument31 pagesRetinal DetachmentEko KunaryagiNo ratings yet
- 30 06Document254 pages30 06pavel ionutNo ratings yet
- MANUAL MODE GUIDEDocument1 pageMANUAL MODE GUIDEKnbNo ratings yet
- Street Photography Short Guide by Kent DufaultDocument21 pagesStreet Photography Short Guide by Kent DufaultPinaki Ghosh100% (1)
- Color HarmonyDocument120 pagesColor HarmonyAlexandra Tutu100% (6)
- Understanding RAL colours and choosing colour samplesDocument47 pagesUnderstanding RAL colours and choosing colour samplesRosu VladNo ratings yet
- United Knit Wears (PVT) LTD: Must Be Delivery DateDocument1 pageUnited Knit Wears (PVT) LTD: Must Be Delivery DateShifatNo ratings yet
- The Way of The Eye: Jan KoenderinkDocument406 pagesThe Way of The Eye: Jan KoenderinkJoseph WhiteNo ratings yet
- Intro To Art SyllabusDocument3 pagesIntro To Art Syllabusapi-256719816No ratings yet
- Goldfish GraphingDocument1 pageGoldfish GraphingAlison SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Photography CompositionDocument10 pagesBasic Photography Compositionleslie sabateNo ratings yet
- Bat ManualDocument5 pagesBat ManualVadyan Haz KamalNo ratings yet
- Gaoler SlidesCarnivalDocument14 pagesGaoler SlidesCarnivalJoshua ZhangNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Black & White Photography PDFDocument196 pagesAdvanced Digital Black & White Photography PDFGiovanni el magnifico100% (1)
- Cad MCQDocument8 pagesCad MCQPlacements-helpNo ratings yet
- Principles of Design (Grade 8)Document31 pagesPrinciples of Design (Grade 8)Pilar VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CONTOH Klikbabylove - Catalog Mommy N Me 2022Document12 pagesCONTOH Klikbabylove - Catalog Mommy N Me 2022monika andianNo ratings yet
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument27 pagesRetinopathy of PrematurityTeoness JoyNo ratings yet
- Pastel Color: Color 1 Color 2 Color 3 Color 4 Color 5Document4 pagesPastel Color: Color 1 Color 2 Color 3 Color 4 Color 5throwawayyyyyNo ratings yet
- Fall Color by Number Printable PDFDocument2 pagesFall Color by Number Printable PDFMadelNo ratings yet
- Portfolio FormatDocument24 pagesPortfolio FormatJasmin Rose LazarraNo ratings yet
- Specifications in Detail-Canon 2000d: Image SensorDocument11 pagesSpecifications in Detail-Canon 2000d: Image SensornisarahmedgfecNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art: Arta Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesElements of Art: Arta Midterms ReviewerJendeuk KimNo ratings yet
- Act - Lenses Activity 5 1Document4 pagesAct - Lenses Activity 5 1Jhon carlo CastroNo ratings yet
- Rubric PanoramaDocument2 pagesRubric PanoramajcecilNo ratings yet
- Color 1 Color 2 Color 3 Color 4 Color 5Document4 pagesColor 1 Color 2 Color 3 Color 4 Color 5Jo MaNo ratings yet