Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Monoethanolamine Introduction
Uploaded by
Harish GojiyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Monoethanolamine Introduction
Uploaded by
Harish GojiyaCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION
1.1 GENERAL:
Amino alcohols have been prepared industrially since the 1930s. However large-
scale production started only after 1945. In industries amino alcohols are usually
designated as alkanolamines. Ethanolamines are the important compounds in this group.
ETHANOL AMINES:
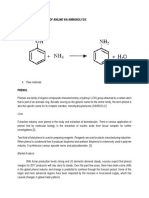
Monoethanolamine (MEA), diethanolamine (DEA) and triethanolamine (TEA)
can be regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one two or three hydrogen atoms
have been replaced by –CH2-CH2-OH group.
Ethanolamines were prepared in 1860 by Wurtz from ethylene chlorohydrin and
aqueous ammonia. It was only toward the end of the 19th century that an ethanolamine
mixture was separated into its mono, di and triethanolamine components. It was achieved
by fractional distillation.
Ethanol amine were not available commercially before 1930’s; they assumed
steadily growing commercial importance as intermediates only after 1945, because of the
large scale production of ethylene oxide. Since the mid-1970’s production of very pure,
colorless ethanolamine in industrial quantities has been possible. All the ethanol amine
now be obtained economically in very pure form.
The most important use of ethanolamines is in production of emulsifiers,
detergent raw materials and textile chemicals; in gas purification processes and in cement
production, as milling additives. Monoethanolamine is an important feedstock for the
production of ethylelediamines and ethylenimines.
You might also like
- Ethanol Fuel: Learn to Make and Use Ethanol to Power Your VehiclesFrom EverandEthanol Fuel: Learn to Make and Use Ethanol to Power Your VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of ( ) - Menthol: Industrial Synthesis Routes and Recent DevelopmentDocument15 pagesSynthesis of ( ) - Menthol: Industrial Synthesis Routes and Recent DevelopmentLucas LiraNo ratings yet
- Methanol: Chemical Process Industry (Ce1707) Mini-Project ReportDocument16 pagesMethanol: Chemical Process Industry (Ce1707) Mini-Project ReportakshayNo ratings yet
- Industrial Surfactants: An Industrial GuideFrom EverandIndustrial Surfactants: An Industrial GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- All About EthanolaminesDocument7 pagesAll About EthanolaminesVineeth Nair100% (1)
- AlcoholesDocument3 pagesAlcoholesDaniel ParraNo ratings yet
- PPDDocument79 pagesPPDEddie ChangNo ratings yet
- Flavour Fragrance J - 2022 - Dylong - Synthesis of Menthol Industrial Synthesis Routes and Recent DevelopmentDocument15 pagesFlavour Fragrance J - 2022 - Dylong - Synthesis of Menthol Industrial Synthesis Routes and Recent DevelopmentVinod SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Ethanolamines and Secondary Products: 15.1. Ethanolamine ProcessDocument8 pagesEthanolamines and Secondary Products: 15.1. Ethanolamine ProcessNetchanok BoontekNo ratings yet
- Property Grade A Grade A A: Table 1. Specifications For Pure MethanolDocument2 pagesProperty Grade A Grade A A: Table 1. Specifications For Pure MethanolDeneshVijayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - of - PETROCHEMICAL NEWDocument116 pagesChemistry - of - PETROCHEMICAL NEWvivaline AchiengNo ratings yet
- Uses of Alcohol (Ethanol)Document11 pagesUses of Alcohol (Ethanol)ettyoNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical: Petrochemicals AreDocument9 pagesPetrochemical: Petrochemicals AreprathapNo ratings yet
- Industrial Alcohol Production ProcessDocument24 pagesIndustrial Alcohol Production Processzekariyasa3No ratings yet
- Presentation For SaifulDocument13 pagesPresentation For SaifulBoier Sesh PataNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical - WikipediaDocument5 pagesPetrochemical - WikipediaDharmesh patelNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 Benceno y Sus DerivadosDocument44 pagesTema 2 Benceno y Sus DerivadosMARCONo ratings yet
- Petrochemical Industry: Eng/Bassem FathallaDocument45 pagesPetrochemical Industry: Eng/Bassem FathallaGalal Eldien GalalNo ratings yet
- Classification of PetrochemicalsDocument5 pagesClassification of PetrochemicalsMarvin Paras0% (1)
- Assignment On OrganicDocument12 pagesAssignment On OrganicHasan ShahriarNo ratings yet
- ALCOHOL Report KODocument3 pagesALCOHOL Report KORhaine Miejoy PenaNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument14 pagesBenzeneTaraPanNo ratings yet
- IAFT Presentation Ethanol & MethanolDocument24 pagesIAFT Presentation Ethanol & MethanolTech RulerNo ratings yet
- 1 Procesos OlefinasDocument19 pages1 Procesos OlefinasBethzabe Campos HijarNo ratings yet
- Ethanolamines From Ethylene Oxide and AmmoniaDocument1 pageEthanolamines From Ethylene Oxide and AmmoniaBramJanssen76100% (1)
- Process OutlineDocument39 pagesProcess Outlinezekariyasa3No ratings yet
- ChE EL 3 - 1. IntroductionDocument7 pagesChE EL 3 - 1. IntroductionEfraim AbuelNo ratings yet
- Process 2Document5 pagesProcess 2Mika PelagioNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals PresentationDocument27 pagesPetrochemicals PresentationVarunKumarNo ratings yet
- Cap 4 Petroleo - CompressedDocument44 pagesCap 4 Petroleo - CompressedYulieth CastilloNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals2 5Document41 pagesPetrochemicals2 5Patricia Jane Perey100% (1)
- Alcohol ProductionDocument85 pagesAlcohol Productiondebjani kundu100% (1)
- Petchem Industry SnapshotDocument1 pagePetchem Industry SnapshotsmithsvaultNo ratings yet
- Systematic Name Chemical Compound Hydrocarbon Alkyne: Acetylene/ethyne - (Document2 pagesSystematic Name Chemical Compound Hydrocarbon Alkyne: Acetylene/ethyne - (Golden SunriseNo ratings yet
- Azo and Diazo Dyes: ProductionDocument5 pagesAzo and Diazo Dyes: ProductionAhmed ElabdNo ratings yet
- Ethylene ProductionDocument7 pagesEthylene ProductionCharles Amiel DionisioNo ratings yet
- Modern Petrochemicals PDFDocument179 pagesModern Petrochemicals PDFmanojkp33No ratings yet
- MethanolDocument6 pagesMethanolelenabalicaNo ratings yet
- Ethanol and Its HistoryDocument6 pagesEthanol and Its HistoryAlgin Mark DaquioagNo ratings yet
- مشروعDocument2 pagesمشروعAhmed NasrNo ratings yet
- Amines in The Chemical Industry: Prepared By: Eugene Benito O. RusianaDocument35 pagesAmines in The Chemical Industry: Prepared By: Eugene Benito O. RusianaKim Lloyd A. BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Application of Aromatic Compounds: Student Name: Student Number: Student Level: Course Name: Course CodeDocument12 pagesApplication of Aromatic Compounds: Student Name: Student Number: Student Level: Course Name: Course Code1828298 1828298No ratings yet
- Tema 2. - Benceno y Sus DerivadosDocument44 pagesTema 2. - Benceno y Sus Derivadosrobbyroken100% (1)
- Nitrogen Products: Production and ConsumptionDocument2 pagesNitrogen Products: Production and ConsumptionJeff Gomez PerezNo ratings yet
- Monoethanolamine Pollution 2520control&safetyDocument2 pagesMonoethanolamine Pollution 2520control&safetySanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Ethanol:: Do Not Confuse Ethanol With Methanol Which Will Probably Make You Go Blind or Die If You Drink ItDocument4 pagesEthanol:: Do Not Confuse Ethanol With Methanol Which Will Probably Make You Go Blind or Die If You Drink ItRajib SarkarNo ratings yet
- Ethylamine 30.07.2020Document2 pagesEthylamine 30.07.2020HARSH VERMANo ratings yet
- صناعات بتروكيمياويةDocument146 pagesصناعات بتروكيمياويةدنيا ثامر حاجي عبدNo ratings yet
- Report MegDocument17 pagesReport MegKrishnamoorthy VijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Survey of Industrial Chemestry - Chenier - 3edDocument25 pagesSurvey of Industrial Chemestry - Chenier - 3edBiain A SecasNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical OverviewDocument8 pagesPetrochemical OverviewAtish NandanwarNo ratings yet
- PROCESS - 3 - Chemical and Process Design HandbookDocument4 pagesPROCESS - 3 - Chemical and Process Design HandbookEdrian A. MañalongNo ratings yet
- Aminas - ETHANOLAMINAS PDFDocument6 pagesAminas - ETHANOLAMINAS PDFFidel Flores CaricariNo ratings yet
- AND Salts: Unit Amino Compounds DiazoniumDocument26 pagesAND Salts: Unit Amino Compounds DiazoniumKhatiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Petrochemicals: OverviewDocument9 pagesLecture 1: Petrochemicals: Overviewمرتضى كاظم غانمNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals AreDocument7 pagesPetrochemicals Areapurv123456789No ratings yet
- 5134-Saqlain Babar2 (For Question 2)Document5 pages5134-Saqlain Babar2 (For Question 2)Faris AhmadNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals GeneralDocument6 pagesPetrochemicals GeneralPiyush AmbulgekarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Fccu Operation: Bhupesh MishraDocument44 pagesPresentation On Fccu Operation: Bhupesh MishraHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Reforming Unit (Cru/Ccru)Document60 pagesCatalytic Reforming Unit (Cru/Ccru)Harish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing OF Ethanolamine: BY Tony Mathew Aditya Damle Nikit NairDocument12 pagesManufacturing OF Ethanolamine: BY Tony Mathew Aditya Damle Nikit NairHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- The Use of Galena As Weighting Material in Drilling Mud: Journal of Scientific Research & ReportsDocument11 pagesThe Use of Galena As Weighting Material in Drilling Mud: Journal of Scientific Research & ReportsHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Ethyl 2520hexanol BibliographyDocument2 pages2 Ethyl 2520hexanol BibliographyHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Fire & Safety Management in Refinery by - AK SINGH GM (F&S)Document80 pagesFire & Safety Management in Refinery by - AK SINGH GM (F&S)Harish Gojiya100% (3)
- 2 Ethyl 2520hexanol BibliographyDocument2 pages2 Ethyl 2520hexanol BibliographyHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Mud 2 .Drilling Mud Additives 3 .Drilling Fluid Types 4 .Drilling Mud Properties 5. Drilling Fluid Selection 6 .Drilling Mud Problems 7. Solids Control 8.fluid Pumping EquipmentDocument22 pagesFunctions of Mud 2 .Drilling Mud Additives 3 .Drilling Fluid Types 4 .Drilling Mud Properties 5. Drilling Fluid Selection 6 .Drilling Mud Problems 7. Solids Control 8.fluid Pumping EquipmentHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Crude Distillation & Desalting-IICHE Online Summer Training-05.06.2020 7 PMDocument30 pagesCrude Distillation & Desalting-IICHE Online Summer Training-05.06.2020 7 PMHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- (RPE4) Assignment 1Document4 pages(RPE4) Assignment 1Harish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Processing Operations in Refinery: Online Summer, Iiche ForDocument86 pagesHydro-Processing Operations in Refinery: Online Summer, Iiche ForHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- DCU-IICHE Online Summer Training-05.09.2020 - 07 PMDocument28 pagesDCU-IICHE Online Summer Training-05.09.2020 - 07 PMHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Refinery Overview & ConfigurationDocument51 pagesWelcome: Refinery Overview & ConfigurationHarish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Application No: Regular: Fatehgunj, Vadodara-390 002, Gujarat (India) Academic Year: 2020-2021Document2 pagesApplication No: Regular: Fatehgunj, Vadodara-390 002, Gujarat (India) Academic Year: 2020-2021Harish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Monoethanolamine: CHEMTREC: (800) 424-9300Document9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Monoethanolamine: CHEMTREC: (800) 424-9300Harish GojiyaNo ratings yet
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaFrom EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNo ratings yet
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureFrom EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (125)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyFrom EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNo ratings yet
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceFrom EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (588)
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreFrom EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyFrom EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerFrom EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeFrom EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (99)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterFrom EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchFrom EverandThe Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (133)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)From EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)No ratings yet
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (242)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)