Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 4: Apply Your Knowledge Decision Case 4-1: Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual 392
Uploaded by
Loany MartinezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 4: Apply Your Knowledge Decision Case 4-1: Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual 392
Uploaded by
Loany MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch 4: Apply Your Knowledge
Decision Case 4-1
The way to solve this case is to:
Prepare the income statement to determine net income.
2
Compare net income to drawing. If net income exceeds
drawing, Collins’ capital increased. But if drawing exceed net
income, the company’s owner’s equity decreased.
Collins Consignment Sales Company
Income Statement
Year Ended December 31, 20XX
Revenues:
Service revenue ($80,700 + $1,000 + $800) $82,500
Expenses:
Salary expense ($17,000 + $1,200) $18,200
Depreciation expense 7,000
Advertising expense 2,400
Supplies expense 2,100
Utilities expense 800
Total expenses 30,500
Net income $52,000
392 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
(continued) Decision Case 4-1
Net income ($52,000) exceeded Drawing ($50,000), so owner’s
equity grew during the year. Collins can expect to get the loan.
Ethical Issue 4-1
Req. 1
The journal entry to record the revenue is:
Dec Accounts receivable.............. 10,000
Service revenue............... 10,000
The debit to Accounts receivable will increase total current
assets and, as a result, increase (improve) the current ratio.
Req. 2
To record this transaction in December violates the revenue
principle. At December 31, the business has not performed the
service for the client and, therefore, has not yet earned the
revenue. Revenue should not be recorded before it is earned.
This action is unethical because it deliberately misrepresents
the facts.
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 393
Fraud Case 4-1
Req. 1
When a customer pays for product received, there will be a
debit to cash and a credit to accounts receivable, which has
zero net effect on current assets, and on the current ratio. In
this case, however, no cash is received. The accounts
receivable is reduced which in turn reduces current assets
and also reduces the current ratio. Note: ratio analysis is
sometimes used to identify accounting irregularities.
Req. 2
A manager may receive a bonus for reaching income targets;
a manager may wish to conceal the fact that the company is
having problems with product quality; a manager who has an
equity interest (capital investment) in this company may wish
to hide bad news to keep stakeholders (creditors) happy.
394 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
Financial Statement Case 4-1
Req. 1 Report format of balance sheet
Req. 2 Largest current asset = Cash and cash equivalents
$3,444 M Corrected to reflect 2009 and 2008 data from
annual report (pts 2, 3, and 5)
Largest current liability = Accounts payable $5,605 M
Req. 3 Current ratio:
December 31, December 31,
2009 2008
Corrected to
show data for
2009 and 2008
Total current
assets 9,797 = 1.33 6,157 = 1.30
Total current
liabilities 7,364 4,746
The current ratio went up (improved slightly) from 2008 to 2009.
Req. 4 Fixed assets
Req. 5
Cost…………………………………………………. $1,905
Accumulated depreciation…………................... (625)
Book value…………………………………………. $1,290
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 395
Team Project 4-1
Req. 1
Wintz Lawn Service
Income Statement
Four Months Ended August 31, 20XX
Service revenue: ($5,500 + $750) $6,250
Expenses:
Wage expense ($1,800 + $300) $2,100
Equipment rent expense ($600 u 4/6) 400
Supplies expense ($400 – $50) 350
Repair expense 300
Depreciation expense ($300 u 1/3) 100
Total expenses 3,250
Net income $3,000
Wintz Lawn Service
Statement of Owner’s Equity
Four Months Ended August 31, 20XX
Wintz, capital, May 1, 20XX $ 0
Owner investment 400
Net income 3,000
3,400
Drawing (500)
Wintz, capital, August 31, 20XX $ 2,900
396 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
(continued) Team Project
Req. 2
Wintz Lawn Service
Balance Sheet
August 31, 20XX
ASSETS LIABILITIES
Current assets: Current:
Cash $2,000 Wages payable $ 300
Accounts receivable 750 Total current liabilities 300
Prepaid equipment rent 200
Supplies 50
Total current assets 3,000
Long-term: OWNER’S EQUITY
Trailer $ 300
Acc. depr. (100) 200 Wintz, capital 2,900
Total liabilities and
Total assets $3,200 owner’s equity $3,200
Req. 3
Wintz’s summer work was successful. She earned net income of
$3,000.
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 397
Communication Activity 4-1
Closing zeroes out the score keeping (revenue and expense)
accounts as well as the drawing account and updates owner’s
capital.
398 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
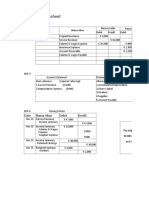
Chapter 4: Appendix A
Reversing Entries: An Optional Step
Appendix Problem
(20 min.) P 4A-1A
Req. 1
Unadjusted balance at the end of October 31, 2012:
Salary payable Salary expense
Oct 31 0 Oct 31 2,500
At the end of month Adjusting and Journal entries:
Journal
POST.
DATE ACCOUNTS AND EXPLANATIONS REF. DEBIT CREDIT
Oct 31 Adjusting Entry
e. Salary expense 200
Salary payable 200
Closing Entry
Oct 31 Income summary 2,700
Salary expense 2,700
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 399
(continued) P 4A-1A
Req. 2
Adjusting and Closing entries
Salary payable Salary expense
Oct 31 0 Oct 31 2,500 Clo 2,700
Adj 200 Adj (e) 200
Bal 200 Bal 0
Req. 3
The following month, November, 2012:
Journal
POST.
DATE ACCOUNTS AND EXPLANATIONS REF. DEBIT CREDIT
Cash payment entry
Nov 5 Salary payable 200
Salary expense 700
Cash 900
Cash payment for salary expense:
Cash Salary payable
Nov 5 900 Nov 5 200 Nov 1 200
Bal 0
Salary expense
Nov 1 0
Nov 5 700
Bal 700
400 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
(continued) P 4A-1A
Req. 4
Situation: Using Reversing entry, repeat Req. 1 - 3
Journal
POST.
DATE ACCOUNTS AND EXPLANATIONS REF. DEBIT CREDIT
Oct 31 Adjusting Entry
e. Salary expense 200
Salary payable 200
Closing Entry
Oct 31 Income summary 2,700
Salary expense 2,700
Nov 1 Salary payable 200
Salary expense 200
5 Salary expense 900
Cash 900
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 401
(continued) P 4A-1A
Req. 4
Salary payable Salary expense
Oct 31 200 Oct 31 2,500 Clo 2,700
Nov 1 Rev. 200 Adj (e) 200
Bal 0 Nov 5 900 Nov 1 Rev. 200
Bal 700
The balance of the Salary payable account after using a
reversing entry is the same as the balance computed without the
reversing entry (as it appears in the answer to requirement 3).
The balance of the Salary expense account after using a
reversing entry is the same as the balance computed without the
reversing entry (as it appears in the answer to requirement 3).
402 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
(20 min.) P 4A-2B
Req. 1
Unadjusted balance at the end of January 31, 2012:
Salary payable Salary expense
Jan 31 0 Jan 31 2,500
Req. 2
At the end of month Adjusting and Journal entries:
Journal
POST.
DATE ACCOUNTS AND EXPLANATIONS REF. DEBIT CREDIT
Jan 31 Adjusting Entry
e. Salary expense 500
Salary payable 500
Closing Entry
Jan 31 Income summary 3,000
Salary expense 3,000
Adjusting and Closing entries
Salary payable Salary expense
Jan 31 0 Jan 31 2,500 Clo 3,000
Adj(e) 500 Adj (e) 500
Bal 500 Bal 0
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 403
(continued) P 4A-2B
Req. 3
The following month, February, 2012:
Journal
POST.
DATE ACCOUNTS AND EXPLANATIONS REF. DEBIT CREDIT
Cash payment entry
Feb 5 Salary payable 500
Salary expense 100
Cash 600
Cash payment for salary expense:
Cash Salary payable
Feb 5 600 Feb 5 500 Feb 1 500
Bal 0
Salary expense
Feb 1 0
Feb 5 100
Bal 100
404 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
(continued) P 4A-2B
Req. 4
Situation: Using Reversing entry, repeat Req. 1 - 3
Journal
POST.
DATE ACCOUNTS AND EXPLANATIONS REF. DEBIT CREDIT
Jan 31 Adjusting Entry
e. Salary expense 500
Salary payable 500
Closing Entry
Jan 31 Income summary 3,000
Salary expense 3,000
Feb 1 Salary payable 500
Salary expense 500
5 Salary expense 600
Cash 600
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 405
(continued) P 4A-2B
Req. 4
Salary payable Salary expense
Jan 31 500 Jan 31 2,500 Clo 3,000
Feb1 Rev 500 Adj (e) 500
Bal 0 Feb 5 600 Feb1 Rev 500
Bal 100
The balance of the Salary payable account after using a
reversing entry is the same as the balance computed without the
reversing entry (as it appears in the answer to requirement 3).
The balance of the Salary expense account after using a
reversing entry is the same as the balance computed without the
reversing entry (as it appears in the answer to requirement 3).
406 Accounting 9/e Solutions Manual
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Problems and Solutions EnglishDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Problems and Solutions EnglishyandaveNo ratings yet
- Worksheet AdjustmentsDocument3 pagesWorksheet AdjustmentsAlche MistNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises 4-35 Closing EntriesDocument1 pagePractice Exercises 4-35 Closing EntriesTalionNo ratings yet
- Final Exam QuestionDocument4 pagesFinal Exam QuestionHồng XuânNo ratings yet
- CH 005 AIA 5eDocument20 pagesCH 005 AIA 5eNadine MillaminaNo ratings yet
- (ASSIGNMENT 3) Eslam Mahmoud MohamedDocument4 pages(ASSIGNMENT 3) Eslam Mahmoud MohamedAmira OkashaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Process With AnsDocument6 pagesAccounting Process With AnsMichael BongalontaNo ratings yet
- 4 Completing The Accounting Cycle PartDocument1 page4 Completing The Accounting Cycle PartTalionNo ratings yet
- E3-5 (LO 3) Adjusting Entries: InstructionsDocument6 pagesE3-5 (LO 3) Adjusting Entries: InstructionsAntonios Fahed0% (1)
- Financial Accounting Seminar3 Accrual and IncomeDocument4 pagesFinancial Accounting Seminar3 Accrual and IncomeThomas ShelbyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Tutorial Worksheet (Session 1)Document15 pagesUnit 3 Tutorial Worksheet (Session 1)MingxNo ratings yet
- CH 3 HomeworkDocument6 pagesCH 3 HomeworkAxel OngNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 4 Summer 22Document4 pagesProblem Sheet 4 Summer 22Md Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document5 pagesCH 02Tien Thanh Dang0% (1)
- Accounting Assignment 04A 207Document10 pagesAccounting Assignment 04A 207Aniyah's RanticsNo ratings yet
- POADocument7 pagesPOAjohnnyNo ratings yet
- Ahsan Saleem 18-Arid-2445 Finn..Document11 pagesAhsan Saleem 18-Arid-2445 Finn..HumnaZaheer muhmmadzaheerNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AdjustmentsDocument5 pagesFinancial Statement AdjustmentsHasan NajiNo ratings yet
- P4-1A Prepare A Worksheet, Financial Statements, and Adjusting and Closing EntriesDocument7 pagesP4-1A Prepare A Worksheet, Financial Statements, and Adjusting and Closing EntriesDidan EnricoNo ratings yet
- PART B - SET A (Odd groups - 1,3,5,7,9)Document4 pagesPART B - SET A (Odd groups - 1,3,5,7,9)ngocanhhlee.11No ratings yet
- CHAPTER-3-Bai-tap (1)Document19 pagesCHAPTER-3-Bai-tap (1)Phuong Anh HoangNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Assignment 2Document6 pagesFinancial Accounting Assignment 2kirubelNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements & Accounting Cycle OverviewDocument5 pagesFinancial Statements & Accounting Cycle OverviewmikeNo ratings yet
- 2021-11 ICMAB FL 001 PAC Year Question CMA Special Examination November 2021Document4 pages2021-11 ICMAB FL 001 PAC Year Question CMA Special Examination November 2021Mohammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment - Questions - RevisedDocument6 pagesGroup Assignment - Questions - Revised31231023949No ratings yet
- Prepare financial statements and adjusting entries for Warren RoofingDocument8 pagesPrepare financial statements and adjusting entries for Warren RoofingJulian Lukman SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Quiz # 2 NewsDocument20 pagesQuiz # 2 NewsSaram NadeemNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment On Fundamentals of Accounting IDocument6 pagesGroup Assignment On Fundamentals of Accounting IKaleab ShimelsNo ratings yet
- Tevis Company Inventory Costing MethodsDocument6 pagesTevis Company Inventory Costing MethodsMinh HiềnNo ratings yet
- Accounting ExamDocument14 pagesAccounting ExamSally SalehNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan CH 3 4 5Document30 pagesPembahasan CH 3 4 5bella0% (1)
- Use Perpetual Inventory System For P6.3Document15 pagesUse Perpetual Inventory System For P6.3Giang LinhNo ratings yet
- Accounting Homework AdjustmentsDocument5 pagesAccounting Homework AdjustmentsHasan NajiNo ratings yet
- Mock 1 mid-term exam (answers and explanations)Document8 pagesMock 1 mid-term exam (answers and explanations)100519554No ratings yet
- Brief ExercisesDocument13 pagesBrief ExercisesPhuong Ngo Tran QuynhNo ratings yet
- Item (A) Type of Adjustment (B) Accounts Before AdjustmentDocument11 pagesItem (A) Type of Adjustment (B) Accounts Before Adjustmentsuci monalia putriNo ratings yet
- 201.AFA IP.L II December 2020Document4 pages201.AFA IP.L II December 2020leyaketjnuNo ratings yet
- Adjusting EntriesDocument5 pagesAdjusting EntriesM Hassan BrohiNo ratings yet
- Accounting information system chapter 3 trial balanceDocument14 pagesAccounting information system chapter 3 trial balanceMutiara MahuletteNo ratings yet
- PA-HW Chap3 + 4Document8 pagesPA-HW Chap3 + 4Hà Anh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On AdjustmentsDocument8 pagesTutorial On AdjustmentsPushpa ValliNo ratings yet
- Eco & Actg for Engineers Assignment SolutionsDocument6 pagesEco & Actg for Engineers Assignment SolutionsNayeem HossainNo ratings yet
- Acc101 - Chapter 2: Accounting For TransactionsDocument16 pagesAcc101 - Chapter 2: Accounting For TransactionsMauricio AceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, AccountingDocument13 pagesChapter 4, AccountingIyadAitHou100% (1)
- Midterm Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesMidterm Practice QuestionsGio RobakidzeNo ratings yet
- CMA Exam Questions on Accounting Principles and Business CommunicationDocument51 pagesCMA Exam Questions on Accounting Principles and Business Communicationzia4000100% (1)
- Prepare financial statementsDocument27 pagesPrepare financial statementsMohammed AkramNo ratings yet
- Preparing financial statements and adjusting entriesDocument27 pagesPreparing financial statements and adjusting entriesTrisha Monique VillaNo ratings yet
- Adjustment ProcessDocument19 pagesAdjustment ProcessDarwin Dionisio ClementeNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements and Accounting Concepts/Principles: Category Financial Statement(s)Document7 pagesFinancial Statements and Accounting Concepts/Principles: Category Financial Statement(s)cialeeNo ratings yet
- Nerissa Mae L. Santos Activity On Completing The Accounting Cycle 1Document3 pagesNerissa Mae L. Santos Activity On Completing The Accounting Cycle 1Mica Mae Correa100% (1)
- ACT301 (Final), Spring-21Document4 pagesACT301 (Final), Spring-21Papon SarkerNo ratings yet
- RTM 2 Pa 1Document3 pagesRTM 2 Pa 1Mega UrjuwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 ExercisesChoco PieNo ratings yet
- Unadjusted Trial BalanceDocument10 pagesUnadjusted Trial BalanceMingxNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 04Document23 pagesExercises Chapter 04vintcs181892No ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI NLKT - ĐỀ 5Document4 pagesĐỀ THI NLKT - ĐỀ 5Hợp BáchNo ratings yet
- Answers Practical Assignments Week 46 2022/2023 Name ... Student Number .... . Assignment 1 FastprintDocument5 pagesAnswers Practical Assignments Week 46 2022/2023 Name ... Student Number .... . Assignment 1 FastprintT.F. EvansNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Using Economic Indicators to Improve Investment AnalysisFrom EverandUsing Economic Indicators to Improve Investment AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (1)
- BSA 1101 Fundamentals of Basic Accounting 1 and 2 FinalsDocument16 pagesBSA 1101 Fundamentals of Basic Accounting 1 and 2 FinalsJohn AcunaNo ratings yet
- Direct Materials For Conversion WorkshopDocument3 pagesDirect Materials For Conversion WorkshopAsiq MahbubNo ratings yet
- Taking Charge What To Do If Your Identity Is StolenDocument68 pagesTaking Charge What To Do If Your Identity Is StolenthdatumNo ratings yet
- Managing Retainage in Oracle Apps R12Document4 pagesManaging Retainage in Oracle Apps R12KarthikRamaswamyNo ratings yet
- General Ledger in ExcelDocument7 pagesGeneral Ledger in ExcelTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet AccountingDocument7 pagesBalance Sheet AccountingGauravNo ratings yet
- Locker Rentals Corp LRC Operates Locker Rental Services at SeveralDocument1 pageLocker Rentals Corp LRC Operates Locker Rental Services at SeveralHassan JanNo ratings yet
- BBP GST Implementation - Draft - V1.3 LorealDocument103 pagesBBP GST Implementation - Draft - V1.3 LorealBina Bisht100% (1)
- Q1w5fabm2 JournalizingDocument39 pagesQ1w5fabm2 JournalizingHanissandra Franz V. DalanNo ratings yet
- COGS and DCOGS Workflow Example of A Revenue COGS Matching For A Sales OrderDocument3 pagesCOGS and DCOGS Workflow Example of A Revenue COGS Matching For A Sales OrderNauman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Accounting Q&ADocument6 pagesAccounting Q&AIftikharNo ratings yet
- AP - Audit of CashDocument4 pagesAP - Audit of CashRose CastilloNo ratings yet
- College Commerce Business Accounting Principles Financial AssignmentDocument11 pagesCollege Commerce Business Accounting Principles Financial AssignmentDr. Mohammad Noor AlamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 WorksheetDocument4 pagesChapter 13 WorksheetSy HimNo ratings yet
- Mohsin Hassan Bba Iib BUS-19F-044 Principle of AccountingDocument7 pagesMohsin Hassan Bba Iib BUS-19F-044 Principle of AccountingMohsin HassanNo ratings yet
- Session 7Document109 pagesSession 7Tram AnhhNo ratings yet
- End To End Configuration of AR in R12Document19 pagesEnd To End Configuration of AR in R12강태민No ratings yet
- Mock Test Qe1 1Document31 pagesMock Test Qe1 1Ma. Fatima H. FabayNo ratings yet
- Insurance - Companies Problems TYBAFDocument12 pagesInsurance - Companies Problems TYBAFsmit9993No ratings yet
- TB CHDocument77 pagesTB CHg202301230No ratings yet
- P 2-1 (Cash and Net Assets Contributions)Document7 pagesP 2-1 (Cash and Net Assets Contributions)pjmerinNo ratings yet
- ACCT 312 - Exam 2 (Part 1) - Spring 2022 FinalDocument8 pagesACCT 312 - Exam 2 (Part 1) - Spring 2022 FinalMercy Jerop KimutaiNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Finance For Bankers-Jaiib-Module D: SBLC RanchiDocument41 pagesAccounting & Finance For Bankers-Jaiib-Module D: SBLC RanchiAmit MakwanaNo ratings yet
- General Ledger (Fusion)Document142 pagesGeneral Ledger (Fusion)srikar valluNo ratings yet
- 0452 m19 Ms 22Document11 pages0452 m19 Ms 22Tan Ai LingNo ratings yet
- E3 (ANS) - Depreciation of Non-Current AssetsDocument18 pagesE3 (ANS) - Depreciation of Non-Current AssetsansonNo ratings yet
- Canara Bank's Management of NPAsDocument84 pagesCanara Bank's Management of NPAsKiran Chandrashekar100% (1)
- Auto Invoice InterfaceDocument16 pagesAuto Invoice Interfacedeba11sarangi100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Answers Key Millan Financial Accounting and Reporting (3rd Edition)Document6 pagesChapter 5 Answers Key Millan Financial Accounting and Reporting (3rd Edition)Terese Pingol100% (1)
- Assessing Bookkeeping Practices of Pottery BusinessesDocument10 pagesAssessing Bookkeeping Practices of Pottery BusinessesElinet AldovinoNo ratings yet