Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 La
Uploaded by
Dindin Lou Mendoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesLA
Original Title
CHAPTER 3 LA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesChapter 3 La
Uploaded by
Dindin Lou MendozaLA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
CHAPTER 3 Vasoconstrictor actions so resembles the
PHARMACOLOGY IN VASOCONSTRICTOR response of adrenergic nerves to
stimulation that they are classified as
Most LA are vasodilators sympathomimetic, or adrenergic drugs.
Vaso – blood vessels
Dilate – opens up Catecholamines
The degree of vasodilation varies: (OH & NH2) Hydroxyl and Amine group
Procaine – the most potent vasodilatory Sympathetic “fight or flight” hormones
properties released by adrenal glands in response to
Prilocaine & Mepivacaine – the least stress
potent vasodilatory properties Naturally occurring catecholamines of
The degree of dilation depends on: sympathetic nervous system:
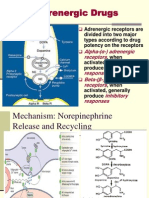
The particular anesthetic Epinephrine (Adrenalin) – stress
The injection site (is it high vascular?) hormone and neurotransmitter
Individual patient response Norepinephrine – stress
hormone & neurotransmitter
Dilation of the blood vessels cause an increase in Dopamine – neurotransmitter,
blood flow to the site of injection (perfusion – precursor to Epi and Norepi “feel
huge increase in blood flow into the site) which in good and focus”
turn causes: Sympathomimetic drugs are Direct-Acting
An increase rate of anesthetic absorption on adrenergic receptors Alpha & Beta
into the bloodstream increasing toxicity
A decrease in the duration of the Adrenergic Receptors
anesthetics action Epinephrine, Norepinephrine &
Increase bleeding in the area due to the Levonordephrine activate adrenergic
increase flow of blood into the area receptors
Higher blood/plasma levels These receptors are found in most body
tissues and divided into 2 types of
These advantage can be overcome to a certain adrenergic receptors:
extent by adding vasoconstrictors Alpha – excitatory & inhibitory
Vasoconstrictors are called vasopressors actions (constriction of blood
Helpful in dentistry where long duration vessels – heart)
& more profound anesthesia are required Beta – inhibitory and excitatory
Vasoconstrictors are drugs that constrict actions (dilation of blood vessels
blood vessels and thereby control tissue and lungs and heart stimulation
perfusion Epinephrine acts directly on both alpha & beta
They added to LA’s to oppose the natural Epinephrine activates alpha receptors –
vasodilatory action of the LA’s vasoconstriction
Vasoconstrictors used with injected LA Activates beta receptors – vasodilation
are chemically identical or similar to the “epinephrine reaction” – apprehension.
sympathetic nervous system mediators Tachycardia, sweating, and pounding in
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine the chest. Epi: Direct effect on CNS
The 2 vasoconstrictors routinely are stimulation
found in the dental local anesthetic in
North America: Alpha – vasoconstriction of blood vessels smooth
Epinephrine (2% Lidocaine w/ 1:50,000 & muscles
1:20,000) a1 - receptors are excitatory
Levonordefrin ( 2% Mepivacaine w/ Levo (constriction) heart
1:20,000) a2 - receptors are inhibitory
Beta – actions predominate MRD = maximum recommended dose
B1 - heart muscles constriction uses mg’s
(stimulation) 1:1000 means 1 gram (1000 mg) of solute
B2 - smooth muscle relaxation (drug) is contained in 1000 ml
(vasodilation & bronchodilation) lungs; Therefore, a 1:1000 means
dilation of coronary arteries
“You have 1 heart and 2 lungs” 1000 mg = 1.0mg/ml (0.3 mg of 1:1000
Beta 1 receptors – primarily on the heart 1000 ml in epi pen)
Beta 2 receptors – primarily on the lungs
ml added to 9 ml of sterile H2O
Vasoconstrictor Drugs: (this would be too highly concentrated for
Benefits versus Risks LA so they would need to diluted further.
Endogenous release of epinephrine – 1:100,000, means 1 gram (1000 mg) of
release of epinephrine from within solute (drug) is contained in 100,000 ml
Meaning that a stressed or unhappy patient has a Therefore a 1:100,000 meas
greater release of epinephrine than those a
normal patient who receives an injection of LA 1000 mg = 1 = .01 mg/ml
plus epinephrine as a vasoconstrictor. 100,000 ml 100
In such a case of stress, the patient’s
blood level of epinephrine is already 1 ml of a 10,000 solution is added to 9 ml
higher than normal, then we added a of solvent
local anesthetic with epi making the 2% Lidocaine with epi/ 1:50,000 – strong
blood level even higher. 2% Lidocaine with epi/ 1:100,000
However, at a 1:100,000 epi amount, the blood
pressure and heart rate are minimally affected Vasoconstrictor used in LA sol.
Cardiac dose (2 catridges of epi with EPINEPHRINE – adrenalin
1:100,00) Concentrations
Elevation of epinephrine plasma levels is 1:50,000
dose dependent and persists from several 1:100,000
minutes to a half hour so we don’t leave 1:200,000
patient alone after giving a local
anesthetic Levonordefrin – Neo-Cobefrin
New evidence supports that epinephrine Concentrations
levels are equal to moderate to heavy 1:20,000
exercise after an oral injection.
Those who should NOT receive an anesthetic with Epinephrine aka: Adrenalin
vasoconstrictor include: The most useful & best example of a
Patients with recent myocardial drug mimicking the activities of the
infarction, coronary bypass surgery, or sympathetic discharge
cerebrovascular accident within the past Actions of other drug are compared to
6 months Epinephrine – used as the “benchmark”
Patients with uncontrolled hypertension, Is an acid salt & highly soluble in water –
angina, arrhythmias, diabetes, and acid/base
hyperthyroidism Slightly acidic solutions are relatively
Possibly can have a cardiac dose stable & protected from air
Sodium Bisulfite is added to epi to delay
Dilution of Vasoconstrictors deterioration (oxidation) – longer shelf
stated as Ratio i.e, 1:1000 life
1 gram = 1000 mg LA solution w/ no vasoconstrictor = 36
months
LA solution w/ vasoconstrictor = 18 Above calculation are for an epi 1:100,000
months dosage
use lowest possible dose
Epinephrine Actions on Specific System proper aspiration
Epinephrine acts directly on both a & B inject slowly
receptors Proper technique!!
B effects predominate – vasodilation of
heart (coronary arteries) & Hemostatsis: decreasing the bleeding at the site
bronchodilation (lungs) of injection
Cardiac: both alpha and beta (1&2) 1:50,000 epi is more effective than
Stimulate beta 1 receptors = 1:100,000
increase heart rate. Stroke 1:100,000 more effective than no
volume, and cardiac output and vasoconstrictor and sufficient enough SRP
also beta 2 effects that dilate 1:100,000 for pts who are sensitive to
blood vessels and lungs catecholamines
Blood pressure
Small doses = increase systolic & decrease Levonordefrin – Neo-Cobefrin
diastolic pressure Synthetic vasoconstrictor
High doses = increase diastolic pressure Man made
Cardiovascular system: Beta 1 effects – Approx. one sixth (15%) as potent as
stimulation epinephrine
Increase cardiac output, heart rate, stroke Manufactured in higher concentrations
volume, contraction , & increase Vailable ONLY with 2% Mepivacaine in
systolic/diastolic w/ 1 to 2 cartridges 1:20,000 mg/ml to achieve same effect
Overall decrease in cardiac efficiency as Epi 1:100,000
Metabolic: inhibits insulin secretion (the Contains sodium bisulfite
diabetic) Provides significantly less hemostasis
than Epi
Respiratory System Can be used in dentistry as alternative to
Beta 2 effects epi if epi cant be used
Bronchial dilator
Tx acute asthmatic attacks and Norepinephrine – Levartenerol
anaphylactic reactions CNS NOT recommended for used in dentistry
Normal dose: does NOT stimulate CNS & not sold in USA. Authors should
Overdose: CNS stimulation – anxiety, eliminated all together
nausea, restlessness, weakness, tremor, Side effect are nine times potent than
headache, hyperventilation those of Epi
Hemostasis: high doses stimulate alpha Pain control is only ¼ (25%) potent as Epi
receptors resulting in vasoconstriction Can cause necrosis is tissue w/ excessive
use (hardpalate)
Max Doses of Epinephrine
1cc = 1ml Phenylephrine – (Neo-Synephrine)
1 cartridge = 1.8 ml No loner used in dentistry; Tachyphylaxis
Healthy patient 0.2 mg (1.8ml X .01 mg/ml = .018 noted
mg) Still in use nose spray etc
.018 X 11 cartridges = 0.198 or 0.2 mg rounded
Felypressin
Med. compromised patient 0.04 mg (1.8 X .01 Not available
mg/ml = .018
.018 X 2 cartridges = .036 or .04 mg rounded Hemostasis
Concentrated epi, 1:50,000 provides Vasoconstriction must be deposited
greatest hemostasis; used for surgery locally into the surgical site to provide
Studies shows effective hemostasis with hemostasis
1:100,000 for SRP procedure Vasoconstrictors acts directly on a
No difference in pain control between receptors in the vascular smooth muscle
1:50,000 and 1:100,000 dilution so use Only small volume of LA solutions with
1:100,000 which is less concentrated vasoconstrictors are required to achieve
Epi is rapidly diluted inactivated in blood hemostasis
stream
Diluted Epi, 1:200,000 is safer for Medical Status of the Patient
cardiovascularly compromised patients Few contraindications are known to
vasoconstrictor concentrations that are
Selection of a Vasoconstrictor used in today’s dentistry
Factors to be considered The benefits and risks of including a
1. Length of the procedure vasopressor in the LA must be weighed
2. Need for hemostasis & after the against using a plain LA
procedure Establishing the degree of severity of
Need for postop pain control condition is the key
Medical status of the patient
Length of the procedure Concern
The addition of any vasoactive drug to LA Minimal dosage: patients with non-
prolongs the duration (&depth) of pulpal cardiovascular disease (ASA 2 or 3);
and soft tissue anesthesia of most controlled hyperthyroid dysfunction (no
anesthetic clinical symptoms) controlled diabetes,
Ex: 2% Lidocaine HCL (plain) provides sulfite surgery
pulpal and hard tissue approx. 5-10 min. Minimal dosage: patients receiving MAO
the addition of Epi increases to approx. 60 inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressant,
min. (6 times longer) phenothiazines (antipsychotic) shows no
The addition of vasoconstrictor to great risk with only minimal dosage
Prilocaine does not significantly increase Controlled ASA 2or 3: vasoconstrictors –
the duration just relative contraindication if
The typical pt is scheduled for a 1 hour administered minimally (2 cartridges) and
apt. duration of actual tx is 47 – 48 min slowly even with mild to moderate
cardiovascular disease
Requirements for Hemostasis >200/115 blood pressure should NOT
Epi prevents or minimizes blood loss receive elected dental care until condition
during surgical procedures is treated
Epi possesses both a and b actions ASA 3 or 4 with poorly controlled severe
Epi produces a ‘rebound’ vasodilatory cardio disease is too great od risk for
effect as the tissue level of epi declines; elective dental care
possible post op bleeding which may Myocardial infarction within last 6
interfere w/ wound healing months
Used in 1:50,000 concentration, Epi Daily or unstable angina episodes
produces vasoconstriction through it’s a Refractory cardiac dysrhythmias
effect Poorly controlled and clinically evident
Once the a constriction effect has ceased, hyperthyroidism (bulging eyes, tremors,
epi produces a definite rebound b effect high temp, etc
Lesser effects w/ 1:100,000 concentration Use 1:100,000 sensitive to
catecholamines
Medical status of the patient
Vasoconstrictors contain Sodium Bisulfite
Sodium bisulfite is an acidic antioxidant to
prolong shelf life of the vasoconstrictor to
18 months
Can produce a slightly slower onset
Sodium bisulfite is the most frequently
used antioxidant used in LA.
Can produce an allergic reaction
Sodium bisulfite leaves LA slightly more
acidic (the pH drops) than w/out a
vasoconstrictor
2% Lidocaine HCL is already slightly acidic.
Sodium bisulfite in the vaso causes the pH
to drop even further
Sodium bisulfite contains more RNH+
than RN molecules so diffusion into
axoplasm is slower resulting in slightly
slower onset
In dentistry today, adequate pain control of
sufficient clinical duration and depth is difficult to
achieve without inclusion of vasoconstrictors in
the LA solution
Inclusion of a vasoconstrictor should be
considered routine unless specifically
contraindicated by a pt medical status (ASA 4 or
above) or by the short treatment duration
Hyper-responders
(tremor of arms and legs, drowsiness
etc). Overly responders with duration of
anesthesia longer than normal. 70 – 80
min. adverse reaction with less than
normal doses
Hypo-responders
Under responders with duration of
anesthesia shorter than normal.
Lidocaine with a vasoconstrictor only
lasting 45, 30 or 15 minutes or even less.
Need much higher doses of LA to show
adverse reactions
Hypersensitivity
Refers to an allergic process that involves
antigen-antibody responses
True allergic response are NOT dose
related
You might also like
- SympathomimeticDocument56 pagesSympathomimeticvarish0% (1)
- Epinephrine Sympthomimic AdrenergicDocument19 pagesEpinephrine Sympthomimic AdrenergicAlee Iz HarNo ratings yet
- Acosta, Joyce Ara T. Week 7 & 8 Drug StudyDocument11 pagesAcosta, Joyce Ara T. Week 7 & 8 Drug StudyJoyce Ara Tumbaga AcostaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic& Antiadrengeic DrugsDocument39 pagesAdrenergic& Antiadrengeic DrugsAsif Ali LashariNo ratings yet
- I. Adrenergic Nervous System: OverviewDocument71 pagesI. Adrenergic Nervous System: OverviewPravita BalijepalliNo ratings yet
- By: Professor Emiliano Z. Sison JRDocument40 pagesBy: Professor Emiliano Z. Sison JRT Z BenNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat VasopresorDocument25 pagesFarmakologi Obat Vasopresorhendrik taufikNo ratings yet
- FARMAKOLOGI OBAT VASOPRESOR-dr DjujukDocument25 pagesFARMAKOLOGI OBAT VASOPRESOR-dr DjujukjavajavuNo ratings yet
- The Use of Vasopressor and Inotropes in The Emergency Departement For The Treatment of ShockDocument36 pagesThe Use of Vasopressor and Inotropes in The Emergency Departement For The Treatment of ShockAndre Eka Putra PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of VasoconstrictorsDocument35 pagesPharmacology of VasoconstrictorsAlice HuiiNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat VasopresorDocument25 pagesFarmakologi Obat VasopresorNudyan BetharinaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medications: Hamdan Al HarbiDocument7 pagesEmergency Medications: Hamdan Al Harbijohn72decNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 - Pharmacology of VasoconstrictorsDocument27 pagesLECTURE 3 - Pharmacology of VasoconstrictorsKIH 20162017No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D.Document25 pagesAdrenergic Drugs: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D.Zakaria salimNo ratings yet
- Lec 16Document3 pagesLec 16Abdullahayad farouqNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Adrenergic ReceptorDocument13 pagesAssignment On Adrenergic ReceptoryannaingNo ratings yet
- Internet Book of Critical Care (IBCC) : Rapid ReferenceDocument1 pageInternet Book of Critical Care (IBCC) : Rapid Referenceian porterNo ratings yet
- Vasoconstrictors: Anesthesia For DentstyDocument7 pagesVasoconstrictors: Anesthesia For DentstyJarrikyu MestayaNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat VasopresorDocument25 pagesFarmakologi Obat Vasopresoralex_christian1992No ratings yet
- 3adrenomimetic DrugsDocument26 pages3adrenomimetic DrugsSolomon H.No ratings yet
- INOTROPESDocument8 pagesINOTROPESessevyNo ratings yet
- L18 - Adrenergics IIIDocument10 pagesL18 - Adrenergics IIIyasaira707No ratings yet
- P Harm Lab NotesDocument3 pagesP Harm Lab NotesaapjennNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY of ANS (Synopsis For Students)Document16 pagesPHARMACOLOGY of ANS (Synopsis For Students)JIEHASMARTNo ratings yet
- Inotropic Agents: Submitted ToDocument87 pagesInotropic Agents: Submitted Toraman kumariNo ratings yet
- By: Mary Lloyd, MSN, RN, CNE: NervousDocument42 pagesBy: Mary Lloyd, MSN, RN, CNE: Nervousmystery126No ratings yet
- Vas Opressor 233Document55 pagesVas Opressor 233songsokalinNo ratings yet
- Adrenoceptor Agonist and Antagonist Drugs-2014.10.7pptDocument83 pagesAdrenoceptor Agonist and Antagonist Drugs-2014.10.7pptking_gold100% (1)
- Chapter - 015 Adrenergic Agonists and AntagonistsDocument52 pagesChapter - 015 Adrenergic Agonists and AntagonistsMaureen CuartoNo ratings yet
- Specific MedicationsDocument10 pagesSpecific MedicationsMico Adrian Depositario Dema-alaNo ratings yet
- 41.5A: Epinephrine and Norepinephrine: Key PointsDocument2 pages41.5A: Epinephrine and Norepinephrine: Key PointsAshley MudzingwaNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine Vs Norepinephrine: Advanced Pharmacology Dr. Sana' Al Aqqad by Students: Ali Ghanem Ismael Bani MatarDocument15 pagesEpinephrine Vs Norepinephrine: Advanced Pharmacology Dr. Sana' Al Aqqad by Students: Ali Ghanem Ismael Bani MatarSabrina ShalhoutNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetic - AdrenergicDocument3 pagesSympathomimetic - AdrenergicRohit GodaseNo ratings yet
- Vaso Pressors and InotropesDocument18 pagesVaso Pressors and InotropesBabu RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgonistsDocument52 pagesAdrenergic AgonistsTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Application of Drugs Acting On Autonomic Nervous System in HospitalsDocument58 pagesApplication of Drugs Acting On Autonomic Nervous System in HospitalsTama Fara ChiNo ratings yet
- Adrenrgic AgonistsDocument35 pagesAdrenrgic Agonistssamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Medical Pharmacology Ovidius 2014 1st TestDocument19 pagesMedical Pharmacology Ovidius 2014 1st TestWissam DadiNo ratings yet
- Zalameda ANSDocument32 pagesZalameda ANSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis&Manajemen ShockDocument8 pagesDiagnosis&Manajemen ShockHJKIMNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Inotropes and VasopressorsDocument51 pagesPharmacology of Inotropes and VasopressorsApen Silaban100% (1)
- T: Time: 1. Lidocaine Toxicity: "SAMS"Document9 pagesT: Time: 1. Lidocaine Toxicity: "SAMS"Cleo Robien DamesNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics 2005Document31 pagesLocal Anesthetics 2005Ioana DănilăNo ratings yet
- Reading C. Vasoactive Therapies.2015Document5 pagesReading C. Vasoactive Therapies.2015Mohamed AinacheNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - MidtermDocument35 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - MidtermHeizmaebrizNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and VasopressorsDocument56 pagesInotropes and VasopressorsMuhammad Ali Yousuf100% (6)
- Penggunaan Vasopresor Dan Inotropik Dalam Penanganan Darurat SYOK - .Document25 pagesPenggunaan Vasopresor Dan Inotropik Dalam Penanganan Darurat SYOK - .Habibullah AlNo ratings yet
- SympatheticDocument10 pagesSympatheticSharneeshriyaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System PharmacologyDocument7 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Pharmacologydonordarah93No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonist and AntagonistDocument35 pagesAdrenergic Agonist and AntagonistFirjat AfiataNo ratings yet
- LOCAL ANESTHETICS and EMERGENCY DRUGSDocument7 pagesLOCAL ANESTHETICS and EMERGENCY DRUGSrosheanne0913No ratings yet
- Chapter 30 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 30 NotesMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Oral SurgeryDocument6 pagesOral SurgeryShahd ShehabNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument20 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistssireesha valluriNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic DrugsbezaleeljonelNo ratings yet
- Obat SimpatomimetikDocument42 pagesObat SimpatomimetiknatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocument120 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Agentscoosa liquors100% (1)
- Pharmacology Module For FinalsDocument11 pagesPharmacology Module For FinalsCarlo GaradoNo ratings yet
- Ephinephrine NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesEphinephrine NorepinephrineTendyAustinChristianNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The HeadDocument8 pagesMuscles of The HeadDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The HeadDocument17 pagesBones of The HeadDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 LaDocument5 pagesChapter 2 LaDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 LaDocument4 pagesChapter 4 LaDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Armamentarium LaDocument10 pagesThe Armamentarium LaDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Shock: 23 September 2016Document10 pagesNeurogenic Shock: 23 September 2016royNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behavior NotesDocument15 pagesBiological Bases of Behavior NoteslcjenleeNo ratings yet
- Case Study SchizopreniaDocument21 pagesCase Study SchizopreniaRay-ann Sorilla100% (1)
- " The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotDocument7 pages" The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotNargess OsmanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Final Answers 2012 3 DhudahDocument96 pagesPharma Final Answers 2012 3 DhudahSaif AlzameliNo ratings yet
- Deception DetectionDocument22 pagesDeception DetectionFelix Geromo100% (1)
- Psy Chapter 2Document146 pagesPsy Chapter 2OceanNo ratings yet
- Medical SurgicalDocument177 pagesMedical SurgicalShannon Mitch Kelly SantosNo ratings yet
- PBL MCDDocument15 pagesPBL MCDMustafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Test Bank PatrickDocument41 pagesChapter 19 Test Bank PatrickAmir ali WalizadehNo ratings yet
- 3 Nervous SystemDocument33 pages3 Nervous SystemSusan ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Mod10Document8 pagesUnderstanding The Self Mod10Asher Sarceno100% (1)
- Function Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesFunction Autonomic Nervous SystemSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Progressive and NonprogressiveDocument2 pagesProgressive and NonprogressiveEryll Joy AgojoNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument8 pagesHeartAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia, Analgesia, and The Surgical Stress ResponseDocument8 pagesAnesthesia, Analgesia, and The Surgical Stress Responsejannatin aliya indrinaNo ratings yet
- 267 Impulses Serving Pain Sensation in The Left Foot Are RelayedDocument12 pages267 Impulses Serving Pain Sensation in The Left Foot Are RelayedNathanNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AnatomyDocument10 pagesAutonomic Nervous System AnatomyghalyNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument15 pagesSpinal Cordsimi y100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System DrugsDocument128 pagesAutonomic Nervous System DrugsMubashra Habib100% (1)
- HHBS1HBB Workshop Activities Wk8 2022Document5 pagesHHBS1HBB Workshop Activities Wk8 2022Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- 1974 Axelrod-NEUROTRANSMITTERSDocument15 pages1974 Axelrod-NEUROTRANSMITTERScortizmenNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter ExamDocument5 pagesThird Quarter ExamTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet
- 4 Ob ExamDocument9 pages4 Ob ExamKim Ramos100% (1)
- Nervous System-WPS OfficeDocument36 pagesNervous System-WPS OfficeShubhendu Chattopadhyay100% (1)
- Answer Key in Pharmacology Pink PacopDocument139 pagesAnswer Key in Pharmacology Pink PacopJoslin Roz GalileaNo ratings yet
- Elib - Tips - Performing Neurological AssessmentDocument34 pagesElib - Tips - Performing Neurological AssessmentTcx YivcNo ratings yet
- Posterior and Anterior MediastinumDocument6 pagesPosterior and Anterior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- GTP BookDocument113 pagesGTP BookEDUARDOLOBOX100% (1)
- Gorniak 2016Document12 pagesGorniak 2016Soraia Rosa CoelhoNo ratings yet