Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patho HFdocx
Uploaded by
JrBong SemaneroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patho HFdocx
Uploaded by
JrBong SemaneroCopyright:
Available Formats
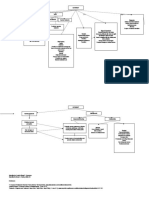
Nursing Diagnosis:
- Decreased cardiac output related to increased heart size as evidence by x-ray
- Activity intolerance related to dyspnea as evidence by body malaise
Nursing interventions:
- Palpate peripheral pulse
- Monitor blood pressure
- Assess for abnormal heart sound and lungs
- Monitor results of laboratory and diagnostic test
- Monitor oxygen level
- Administer cardiac glycoside agents, as ordered, for signs of left heart failure and monitor for toxicity
- Position patient to high fowler position
Medications:
- Vasodilators such as nitrates
- ACE inhibitors
- Beta blockers
Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
Non-Modifiable:
Modifiable: - Age
- Lifestyle - Genetics
- Diet - Congenital
- environment - Diabetes
- Gender
S/Sx:
Dyspnea -increase the use of
accessory muscles
-increase heart rate
Hypertension -Paleness
Valvular Disease Myocardial Infarction
-Body malaise
Increase cardiac workload
-Increase heart size and mass
Increase wall stress
-increase protein synthesis
-Abnormal proteins
-Fibrosis Test:
-Inadequate vasculature Muscles stretch Ripening of cardiac -X-Ray
muscles -ECG
Hypertrophy
Cardiac dysfunction
Cardiomegaly Cardiomyopathy
-Heart Failure Compensated cardiac
-Arrhythmias output Anemia
-Neurohumonal stimulation S/Sx:
-abnormal heart rhythm
-swelling
-Dyspnea Pulmonary
-Fainting hypertension
-Chest Pain
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Case Study - CvaDocument3 pagesCase Study - CvaJrBong Semanero50% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Case Study - Cardio FunctionDocument3 pagesCase Study - Cardio FunctionJrBong Semanero100% (1)
- Fitness ChartDocument18 pagesFitness ChartBayAreaNewsGroup100% (1)
- Intubation EquipmentDocument4 pagesIntubation EquipmentJrBong Semanero100% (1)
- Histrionic Personality Disorder: Effects of HPDDocument2 pagesHistrionic Personality Disorder: Effects of HPDJrBong Semanero100% (1)
- C. Radiation Is Very Irritating To The Lining of GI Tract, Which Caused DiarrheaDocument5 pagesC. Radiation Is Very Irritating To The Lining of GI Tract, Which Caused DiarrheaJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis HTNDocument22 pagesCase Analysis HTNJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- PersonalityDocument1 pagePersonalityJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Case Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockDocument3 pagesCase Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument2 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study01Document6 pagesDrug Study01JrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Known To Self Not Known To SelfDocument1 pageKnown To Self Not Known To SelfJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Advance Cardiac Life Support With CQIDocument2 pagesAdvance Cardiac Life Support With CQIJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Charting CraniotomyDocument1 pageCharting CraniotomyJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Part Four - L&MDocument18 pagesPart Four - L&MJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CATARACTDocument2 pagesConcept Map CATARACTJrBong Semanero100% (1)
- Heart Failure COncept MapDocument2 pagesHeart Failure COncept MapJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Disorder3Document43 pagesConnective Tissue Disorder3thapan87No ratings yet
- Rethinking Lockdowns Joffe COMMENTARY FWebDocument12 pagesRethinking Lockdowns Joffe COMMENTARY FWebGllauber Marlon RibeiroNo ratings yet
- MINDMAPDocument2 pagesMINDMAPrayzaoliveira.ausNo ratings yet
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF) Is Commonly A Birth DefectDocument18 pagesTracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF) Is Commonly A Birth Defectboni_paguiganNo ratings yet
- Wang2015 1 PDFDocument10 pagesWang2015 1 PDFAdriani HartantoNo ratings yet
- Optic Disc Abnormalities - Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesOptic Disc Abnormalities - Cheat SheetPaula EmyNo ratings yet
- Traveller GreeceDocument2 pagesTraveller GreeceElefteriosNo ratings yet
- Retina SlidesDocument70 pagesRetina SlidesMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- CHF LapsusDocument27 pagesCHF Lapsuseno46No ratings yet
- Head Injury EciDocument29 pagesHead Injury EciYullytia Galaksi MharyatiNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument5 pagesHistoryrawan.sharari0911No ratings yet
- Project Proposal DiabetesDocument3 pagesProject Proposal DiabetesShayne Cabotaje Delos Santos - BorlingNo ratings yet
- Nipah Virus Infection-GuidelinesDocument7 pagesNipah Virus Infection-GuidelinesSIVAPRASADNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan CriteriaDocument7 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan CriteriaAnonymous K99UIf1No ratings yet
- Synopsis of Kent'S 12 Observations: TH THDocument3 pagesSynopsis of Kent'S 12 Observations: TH THIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Consent For HIV TestingDocument2 pagesConsent For HIV TestingRaviraj PisheNo ratings yet
- Ramsay Hunt SyndromeDocument3 pagesRamsay Hunt SyndromeAnish RajNo ratings yet
- Contoh Daftar Target KompetensiDocument14 pagesContoh Daftar Target KompetensiSiti MaulidiyaNo ratings yet
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionJea Joel Mendoza100% (1)
- Does Parkinson's Begin in The Gut - Scientific AmericanDocument5 pagesDoes Parkinson's Begin in The Gut - Scientific AmericanCarl MacCordNo ratings yet
- Framingham Data Famous Cohort Study of 5209 Subjects From Framingham MADocument2 pagesFramingham Data Famous Cohort Study of 5209 Subjects From Framingham MAEdwin Johny Asnate SalazarNo ratings yet
- Ivy Tagotoc NCPDocument2 pagesIvy Tagotoc NCPIvy Grace TagotocNo ratings yet
- Emerging: and Reemerging DiseasesDocument40 pagesEmerging: and Reemerging DiseasesReg LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Diseases With Diarrhea SyndromeDocument19 pagesDiseases With Diarrhea SyndromeManishNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy & SLE: by Mahmoud BaqerDocument9 pagesPregnancy & SLE: by Mahmoud BaqerMahmoud BaqerNo ratings yet
- Department of Education School Form 8 Learner's Basic Health and Nutrition Report (SF8)Document12 pagesDepartment of Education School Form 8 Learner's Basic Health and Nutrition Report (SF8)Jeff HambreNo ratings yet
- Acute-Bacterial-Meningitis - in ChildrenDocument49 pagesAcute-Bacterial-Meningitis - in ChildrenMitulNo ratings yet
- 01 Data ICD 10 Diagnosis Di ICUDocument4 pages01 Data ICD 10 Diagnosis Di ICUady suciptoNo ratings yet
- The Comorbidity of Conduct Problems and Depression in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument21 pagesThe Comorbidity of Conduct Problems and Depression in Childhood and AdolescencefitryerlinNo ratings yet