Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4.1.5. Jacobian Matrix Theory Part A
Uploaded by
Nagamani ArumugamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4.1.5. Jacobian Matrix Theory Part A
Uploaded by
Nagamani ArumugamCopyright:
Available Formats
SNS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
16AE308 FEM UNIT – IV
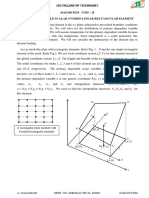
JACOBIAN MATRIX
What is a Jacobian matrix?
The Jacobian, J , relates an element length in the Global coordinate system to an element length in
Natural coordinate system. In general, J is a function of ξ ,η and depends on the numerical values
of the nodal coordinates.
It is a matrix that contains the derivatives of the global coordinates with respect to the natural
coordinates of a particular element.
Write the Jacobian for 1-D elements?
In one dimensional domain, the transformation from x-cordinate to ξ -coordinate is given by
L 1
∫ f ( x )dx = ∫ f (ξ ) J d ξ
0 −1
where J is the Jacobian.
In one-dimensional domain, the differential element dx in the global coordinate system x is related
dx
to the differential element d ξ in the natural coordinate system ξ by
= dx = d ξ Jd ξ where J is
dξ
dx d m m dN i
called the Jacobian of transformation.=
J =
d ξ=
∑ i i ∑
d ξ i 1 =
N =
x
i 1
xi
dξ
For a 1-D 2-noded linear bar element:
N1 =
(1 − ξ ) , N2 =
(1 + ξ ) , J = x1
dN1
+ x2
dN 2 1 1 1 L
= x1 − + x2 = ( x2 − x1 ) =
2 2 dξ dξ 2 2 2 2
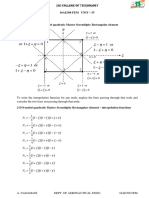
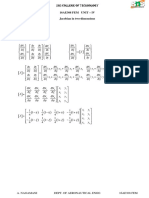
Jacobian for 2D elements
∂x ∂y m dN i dN i dN1 dN 2 dN m x1 y1
∑ ∑
m
xi y ... y2
∂ξ =
∂ξ 1 1=
dξ 1 1 i
dξ dξ dξ d ξ x2
=J = =
∂x ∂y m dN i dN i dN1 dN 2 dN m ... ...
∑ xi dη ∑1 1 yi dη
m
...
∂η 1 1 =
∂η =
dη
dη dη xm ym
What is the importance of Jacobian matrix?
Geometrically, the Jacobean J represents the ratio of an area element in the real element to the
corresponding area element in the master element, dA ≡ dx dy = J d ξ dη . If J is zero, then a non-
zero area element in the real element is mapped into zero area in the master element, which is
unacceptable. Also if J is negative, a right-handed coordinate system is mapped into a left-handed
coordinate system.
A. NAGAMANI DEPT. OF AERONAUTICAL ENGG 16AE308 FEM
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Fred Steckling - We Discovered Alien Bases On The Moon (Transl From German)Document166 pagesFred Steckling - We Discovered Alien Bases On The Moon (Transl From German)ethan01194% (18)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Online Food Ordering System MiniDocument11 pagesOnline Food Ordering System Minijwala reddy83% (47)
- 671 - BP Well Control Tool Kit 2002Document20 pages671 - BP Well Control Tool Kit 2002Uok Ritchie100% (1)
- Andrew KC Chan (2003) - Observations From Excavations - A ReflectionDocument19 pagesAndrew KC Chan (2003) - Observations From Excavations - A ReflectionMan Ho LamNo ratings yet
- 4 Eccentricity of TrajectoryDocument24 pages4 Eccentricity of TrajectoryNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Som Unit - 1.1.1 Prismatic BarDocument1 pageSom Unit - 1.1.1 Prismatic BarNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 3 Exact Numerical ValuesDocument23 pages3 Exact Numerical ValuesNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 4 Measurement of AirspeedDocument23 pages4 Measurement of AirspeedNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Som Unit - 1.1.2 Prismatic Bar With FosDocument1 pageSom Unit - 1.1.2 Prismatic Bar With FosNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Som Unit - 1.2.1 Stepped Bar 3 Regions ProblemDocument2 pagesSom Unit - 1.2.1 Stepped Bar 3 Regions ProblemNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 2 Pillar of ThermodynamicsDocument23 pages2 Pillar of ThermodynamicsNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- 2 Convenient Geometric InterpretationDocument15 pages2 Convenient Geometric InterpretationNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Elongation of Tapered BarDocument17 pagesElongation of Tapered BarNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Deformation of Springs 1Document18 pagesDeformation of Springs 1Nagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Ansys Workbench Basics ManualDocument75 pagesAnsys Workbench Basics ManualOmar Alzuabi90% (20)
- Ansys Workbench Shah Ruck TutorialsDocument25 pagesAnsys Workbench Shah Ruck TutorialsNagamani Arumugam0% (1)
- Unit 4.1.1 Xy To Zeta Eta and Vice VersaDocument3 pagesUnit 4.1.1 Xy To Zeta Eta and Vice VersaNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1.4 4-Node and 9-Node Master ElementsDocument1 pageUnit 4.1.4 4-Node and 9-Node Master ElementsNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.2.1 2D 3noded Single Variable Scalar Rectangular Element BDocument2 pagesUnit 3.2.1 2D 3noded Single Variable Scalar Rectangular Element BNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Dietmar Gross, Wolfgang Ehlers, Peter Wriggers, Jörg Schröder, Ralf Müller-Statics - Formulas and Problems - Engineering Mechanics 1-Springer-Verlag (2017) PDFDocument240 pagesDietmar Gross, Wolfgang Ehlers, Peter Wriggers, Jörg Schröder, Ralf Müller-Statics - Formulas and Problems - Engineering Mechanics 1-Springer-Verlag (2017) PDFĐào Hải Nam0% (1)
- Unit 3.2.2 2D 3noded Single Variable Scalar Rectangular Element Problem 2Document1 pageUnit 3.2.2 2D 3noded Single Variable Scalar Rectangular Element Problem 2Nagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1.3 2D 8-Noded Quadratic Rect ElementDocument1 pageUnit 4.1.3 2D 8-Noded Quadratic Rect ElementNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1.2 Jacobian in Two Dimensions BDocument1 pageUnit 4.1.2 Jacobian in Two Dimensions BNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.1.4 2D Torsion of Non-Circular BarDocument6 pagesUnit 3.1.4 2D Torsion of Non-Circular BarNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- A Practical Hindi-English Dictionary PrefaceDocument17 pagesA Practical Hindi-English Dictionary PrefaceNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Dietmar Gross, Wolfgang Ehlers, Peter Wriggers, Jörg Schröder, Ralf Müller-Statics - Formulas and Problems - Engineering Mechanics 1-Springer-Verlag (2017) PDFDocument240 pagesDietmar Gross, Wolfgang Ehlers, Peter Wriggers, Jörg Schröder, Ralf Müller-Statics - Formulas and Problems - Engineering Mechanics 1-Springer-Verlag (2017) PDFĐào Hải Nam0% (1)
- CMS WORKBOOK Complete BookDocument38 pagesCMS WORKBOOK Complete BookNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- A Practical Hindi-English Dictionary B-HDocument890 pagesA Practical Hindi-English Dictionary B-HNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Aero 4th Sem Ae6403 Aircraft Structures 1 Aprmay 2017 R 2013Document4 pagesAero 4th Sem Ae6403 Aircraft Structures 1 Aprmay 2017 R 2013Nagamani Arumugam100% (1)
- A Practical Hindi English Dictionary A DH PDFDocument461 pagesA Practical Hindi English Dictionary A DH PDFBobby Khalsa100% (1)
- Anna University - 2007: B.E/B.Tech Model Examination (Aeronautical Engineering) Time-3Hour MARK-100 Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnna University - 2007: B.E/B.Tech Model Examination (Aeronautical Engineering) Time-3Hour MARK-100 Answer All QuestionsNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Arcturus - Huge Book of Puzzles (2008, Arcturus Publishing LTD) PDFDocument386 pagesArcturus - Huge Book of Puzzles (2008, Arcturus Publishing LTD) PDFNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Aero Elasticity 1Document6 pagesAero Elasticity 1b1165367No ratings yet
- Iohexol USP42NF37Document5 pagesIohexol USP42NF37John Alejandro Restrepo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Alcatel 4029 EngDocument31 pagesAlcatel 4029 Engafsanto2000No ratings yet
- Calibration of The Continuous Surface Cap Model For ConcreteDocument19 pagesCalibration of The Continuous Surface Cap Model For ConcreteAbhijit KulkarniNo ratings yet
- LANTUS XR Label InformationDocument17 pagesLANTUS XR Label InformationMichaelJonatanNo ratings yet
- Handheld Vital Signs Monitor: XH-30 SeriesDocument4 pagesHandheld Vital Signs Monitor: XH-30 SeriesTopan AssyNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic SteelDocument18 pagesCryogenic SteelMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- 20-F201007-SC-010 R0 - Design Calculation of Foam Tank and Fire Pump ShedDocument187 pages20-F201007-SC-010 R0 - Design Calculation of Foam Tank and Fire Pump ShedSaravan KumarNo ratings yet
- DNV RP F401Document23 pagesDNV RP F401Christopher BlevinsNo ratings yet
- Abb Sas GeneralDocument43 pagesAbb Sas Generalsabill arasyidNo ratings yet
- HCL McQs SET-3Document8 pagesHCL McQs SET-3ThorNo ratings yet
- Mds Ti-Alloy Ta15 0720 enDocument3 pagesMds Ti-Alloy Ta15 0720 enshahin_723No ratings yet
- Production of Hard Grade Bitumen For Using in High Modulus Asphalt ConcreteDocument18 pagesProduction of Hard Grade Bitumen For Using in High Modulus Asphalt ConcretePanjiNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: DPS 232 Differential Positioning SystemDocument154 pagesInstallation Manual: DPS 232 Differential Positioning SystemVladimirs Arzeninovs100% (3)
- L011375 - MT4434TE Spec SheetDocument2 pagesL011375 - MT4434TE Spec SheetJunior BautistaNo ratings yet
- 1 - A Biomechanical Model To Predict Hand-Arm Vibration When UsingDocument7 pages1 - A Biomechanical Model To Predict Hand-Arm Vibration When Usingkamel atiiaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Utility Impact Assessment For Local Roads in Developed Areas MME 2012 Cross-SectionDocument81 pagesGuidelines For Utility Impact Assessment For Local Roads in Developed Areas MME 2012 Cross-Sectionirfan mohammedNo ratings yet
- C ValueDocument2 pagesC ValuePadmanabh Shetty0% (1)
- ME361 - Manufacturing Science Technology: Measurements and MetrologyDocument20 pagesME361 - Manufacturing Science Technology: Measurements and MetrologyKartikeyaNo ratings yet
- Competition Systems IGN1A Inductive Smart Coil - IGN1ADocument2 pagesCompetition Systems IGN1A Inductive Smart Coil - IGN1AJoão Lucas ZaionsNo ratings yet
- Elasticity Measurement of Local Taxes and Charges in Forecast of Own-Source Revenue (PAD) of Provincial Government in IndonesiaDocument27 pagesElasticity Measurement of Local Taxes and Charges in Forecast of Own-Source Revenue (PAD) of Provincial Government in Indonesiaayu desiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-JavaDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank-Javarachana saiNo ratings yet
- Practical Exercise 2 - SolutionDocument5 pagesPractical Exercise 2 - SolutionmidoriNo ratings yet
- Wrong Number Series 23 June by Aashish AroraDocument53 pagesWrong Number Series 23 June by Aashish AroraSaurabh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Statistial Process Control (SPC)Document22 pagesChapter 4 Statistial Process Control (SPC)Yousab CreatorNo ratings yet
- Transportation ModelDocument20 pagesTransportation ModelRaj UpadhyayNo ratings yet