Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bolts and Threaded Parts Strength and Design
Uploaded by
sh4kesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bolts and Threaded Parts Strength and Design
Uploaded by
sh4kesCopyright:
Available Formats
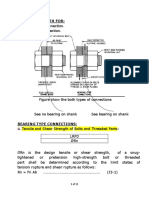
16.1–120 BOLTS AND THREADED PARTS [Sect. J3.
TABLE J3.2
Nominal Strength of Fasteners and
Threaded Parts, ksi (MPa)
Nominal Shear Strength in
Nominal Tensile Strength, Bearing-Type Connections,
Description of Fasteners Fnt , ksi (MPa)[a] Fnv , ksi (MPa)[b]
A307 bolts 45 (310) 27 (188) [c] [d]
Group A (e.g., A325) bolts,
when threads are not excluded 90 (620) 54 (372)
from shear planes
Group A (e.g., A325) bolts,
when threads are excluded 90 (620) 68 (457)
from shear planes
Group B (e.g., A490) bolts,
when threads are not excluded 113 (780) 68 (457)
from shear planes
Group B (e.g., A490) bolts,
when threads are excluded 113 (780) 84 (579)
from shear planes
Threaded parts meeting the
requirements of Section A3.4,
when threads are not excluded 0.75Fu 0.450Fu
from shear planes
Threaded parts meeting the
requirements of Section A3.4,
when threads are excluded 0.75Fu 0. 563Fu
from shear planes
[a]
For high-strength bolts subject to tensile fatigue loading, see Appendix 3.
[b]
For end loaded connections with a fastener pattern length greater than 38 in. (965 mm), Fnv shall be
reduced to 83.3% of the tabulated values. Fastener pattern length is the maximum distance parallel to the
line of force between the centerline of the bolts connecting two parts with one faying surface.
[c]
For A307 bolts the tabulated values shall be reduced by 1% for each 1/16 in. (2 mm) over 5 diameters of
length in the grip.
[d]
Threads permitted in shear planes.
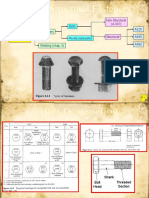
2. Size and Use of Holes
The maximum sizes of holes for bolts are given in Table J3.3 or Table J3.3M, except
that larger holes, required for tolerance on location of anchor rods in concrete foun-
dations, are permitted in column base details.
Standard holes or short-slotted holes transverse to the direction of the load shall be
provided in accordance with the provisions of this specification, unless oversized
holes, short-slotted holes parallel to the load, or long-slotted holes are approved
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, June 22, 2010
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Sect. J3.] BOLTS AND THREADED PARTS 16.1–125
6. Tensile and Shear Strength of Bolts and Threaded Parts
The design tensile or shear strength, φRn, and the allowable tensile or shear
strength, Rn /Ω, of a snug-tightened or pretensioned high-strength bolt or threaded
part shall be determined according to the limit states of tension rupture and shear
rupture as follows:
Rn = Fn Ab (J3-1)
φ = 0.75 (LRFD) Ω = 2.00 (ASD)
where
Ab = nominal unthreaded body area of bolt or threaded part, in.2 (mm2)
Fn = nominal tensile stress, Fnt, or shear stress, Fnv, from Table J3.2, ksi (MPa)
The required tensile strength shall include any tension resulting from prying action
produced by deformation of the connected parts.
User Note: The force that can be resisted by a snug-tightened or pretensioned
high-strength bolt or threaded part may be limited by the bearing strength at the
bolt hole per Section J3.10. The effective strength of an individual fastener may
be taken as the lesser of the fastener shear strength per Section J3.6 or the bear-
ing strength at the bolt hole per Section J3.10. The strength of the bolt group is
taken as the sum of the effective strengths of the individual fasteners.
7. Combined Tension and Shear in Bearing-Type Connections
The available tensile strength of a bolt subjected to combined tension and shear
shall be determined according to the limit states of tension and shear rupture as
follows:
Rn = F′nt Ab (J3-2)
φ = 0.75 (LRFD) Ω = 2.00 (ASD)
where
F′nt = nominal tensile stress modified to include the effects of shear stress,
ksi (MPa)
Fnt
F′nt = 1.3Fnt − frv ≤ Fnt (LRFD) (J3-3a)
φFnv
ΩFnt
F′nt = 1.3Fnt − frv ≤ Fnt (ASD) (J3-3b)
Fnv
Fnt = nominal tensile stress from Table J3.2, ksi (MPa)
Fnv = nominal shear stress from Table J3.2, ksi (MPa)
frv = required shear stress using LRFD or ASD load combinations, ksi (MPa)
The available shear stress of the fastener shall equal or exceed the required shear
stress, frv.
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, June 22, 2010
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Sect. J3.] BOLTS AND THREADED PARTS 16.1–127
(ii) Where bolts have not been added to distribute the load in the filler:
(a) For one filler between connected parts
hf = 1.0
(b) For two or more fillers between connected parts
hf = 0.85
ns = number of slip planes required to permit the connection to slip
9. Combined Tension and Shear in Slip-Critical Connections
When a slip-critical connection is subjected to an applied tension that reduces the net
clamping force, the available slip resistance per bolt, from Section J3.8, shall be mul-
tiplied by the factor, ksc, as follows:
Tu
ksc = 1 − (LRFD) (J3-5a)
DuTb nb
1.5Ta
ksc = 1 − (ASD) (J3-5b)
DuTb nb
where
Ta = required tension force using ASD load combinations, kips (kN)
Tu = required tension force using LRFD load combinations, kips (kN)
nb = number of bolts carrying the applied tension
10. Bearing Strength at Bolt Holes
The available bearing strength, φRn and Rn/Ω, at bolt holes shall be determined for
the limit state of bearing as follows:
φ = 0.75 (LRFD) Ω = 2.00 (ASD)
The nominal bearing strength of the connected material, Rn, is determined as
follows:
(a) For a bolt in a connection with standard, oversized and short-slotted holes, inde-
pendent of the direction of loading, or a long-slotted hole with the slot parallel to
the direction of the bearing force
(i) When deformation at the bolt hole at service load is a design consideration
Rn = 1.2lc tFu ≤ 2.4dtFu (J3-6a)
(ii) When deformation at the bolt hole at service load is not a design considera-
tion
Rn = 1.5lc tFu ≤ 3.0dtFu (J3-6b)
(b) For a bolt in a connection with long-slotted holes with the slot perpendicular to
the direction of force
Rn = 1.0lc tFu ≤ 2.0dtFu (J3-6c)
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, June 22, 2010
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
16.1–128 BOLTS AND THREADED PARTS [Sect. J3.
(c) For connections made using bolts that pass completely through an unstiffened
box member or HSS, see Section J7 and Equation J7-1;
where
Fu = specified minimum tensile strength of the connected material, ksi (MPa)
d = nominal bolt diameter, in. (mm)
lc = clear distance, in the direction of the force, between the edge of the hole and
the edge of the adjacent hole or edge of the material, in. (mm)
t = thickness of connected material, in. (mm)
For connections, the bearing resistance shall be taken as the sum of the bearing resist-
ances of the individual bolts.
Bearing strength shall be checked for both bearing-type and slip-critical connections.
The use of oversized holes and short- and long-slotted holes parallel to the line of
force is restricted to slip-critical connections per Section J3.2.
User Note: The effective strength of an individual fastener is the lesser of the fas-
tener shear strength per Section J3.6 or the bearing strength at the bolt hole per
Section J3.10. The strength of the bolt group is the sum of the effective strengths
of the individual fasteners.
11. Special Fasteners
The nominal strength of special fasteners other than the bolts presented in Table J3.2
shall be verified by tests.
12. Tension Fasteners
When bolts or other fasteners in tension are attached to an unstiffened box or HSS
wall, the strength of the wall shall be determined by rational analysis.
J4. AFFECTED ELEMENTS OF MEMBERS AND CONNECTING
ELEMENTS
This section applies to elements of members at connections and connecting elements,
such as plates, gussets, angles and brackets.
1. Strength of Elements in Tension
The design strength, φRn, and the allowable strength, Rn /Ω, of affected and con-
necting elements loaded in tension shall be the lower value obtained according to the
limit states of tensile yielding and tensile rupture.
(a) For tensile yielding of connecting elements
Rn = Fy Ag (J4-1)
φ = 0.90 (LRFD) Ω = 1.67 (ASD)
(b) For tensile rupture of connecting elements
Rn = Fu Ae (J4-2)
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, June 22, 2010
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
You might also like
- Steel Design - LRFD Bolted Connections TutorialDocument4 pagesSteel Design - LRFD Bolted Connections TutorialFernando PizarroNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Sandy SoilDocument1 pageMathcad - Sandy SoillsatchithananthanNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing Using Mathcad PrimeDocument6 pagesCombined Footing Using Mathcad PrimeYan YanNo ratings yet
- RectangularTanks 25-3-2015Document98 pagesRectangularTanks 25-3-2015Sary LimNo ratings yet
- Effective Length Factor For DiscontinuousDocument7 pagesEffective Length Factor For Discontinuoussaber javidNo ratings yet
- Division III-WIND DESIGN Section 1615 - General Section 1617 - Symbols and NotationsDocument13 pagesDivision III-WIND DESIGN Section 1615 - General Section 1617 - Symbols and NotationsjirongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 BoltDocument38 pagesChapter 7 BoltRamesh P KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Plate Stresses in STAADDocument7 pagesPlate Stresses in STAADARYANo ratings yet
- POLEFDN.xls Pole Foundation Analysis ProgramDocument10 pagesPOLEFDN.xls Pole Foundation Analysis ProgramANGEL .No ratings yet
- Foundation Design Philosophy For Horizontal VesselDocument6 pagesFoundation Design Philosophy For Horizontal VesselKeaten ClaneyNo ratings yet
- 10 Stability of SlopesDocument18 pages10 Stability of Slopesامين الزريقيNo ratings yet
- CALCULO de Pullout de Pernos en ConcretoDocument10 pagesCALCULO de Pullout de Pernos en ConcretoJuan Carlos VillalbaNo ratings yet
- AISC 13th - Table J3.3 Nominal Hole Dimensions PDFDocument1 pageAISC 13th - Table J3.3 Nominal Hole Dimensions PDFmuathNo ratings yet
- Column Design AnalysisDocument18 pagesColumn Design AnalysisSurya FahmiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Tank Seismic OCRDocument35 pagesBasics of Tank Seismic OCRmario_gNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Structures - Concrete Ductile Moment Resisting Space FrameDocument34 pagesSeismic Analysis of Structures - Concrete Ductile Moment Resisting Space FrameEmmanuel LazoNo ratings yet
- COMPRESS Saddle DesignDocument2 pagesCOMPRESS Saddle Designarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Tank DesignDocument4 pagesChapter 3: Tank Designevrim77No ratings yet
- 6.5 Design of Precast Protection Slab 6.5.1 Materials: Job: Made by Sheet No. Total Sh. Set No. Date Rev. No. Job NoDocument47 pages6.5 Design of Precast Protection Slab 6.5.1 Materials: Job: Made by Sheet No. Total Sh. Set No. Date Rev. No. Job NobalaramNo ratings yet
- Sand Heap AnalogyDocument23 pagesSand Heap AnalogyTatyGendadeReynosoNo ratings yet
- RC COLUMN CAPACITY CALCULATIONDocument6 pagesRC COLUMN CAPACITY CALCULATIONnicolaemariusNo ratings yet
- Foundation Calculation Sheet: Title DescriptionDocument22 pagesFoundation Calculation Sheet: Title Descriptionvananhlt18No ratings yet
- Table J3.2 Nominal Strength of Fasteners and Threaded Parts, Ksi (Mpa)Document1 pageTable J3.2 Nominal Strength of Fasteners and Threaded Parts, Ksi (Mpa)rcNo ratings yet
- Blind ThicknessDocument1 pageBlind ThicknessRizwan Waheed KhanNo ratings yet
- M11 Bor Pile Load Lateral 15257 0Document28 pagesM11 Bor Pile Load Lateral 15257 0Yusril RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Trunnion Check - Node 710Document13 pagesTrunnion Check - Node 710Prashant ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - 06-Loads On StaircaseDocument2 pagesMathcad - 06-Loads On Staircasedinu69inNo ratings yet
- Calculo de Brida Segun ASMEDocument29 pagesCalculo de Brida Segun ASMEakarcz6731No ratings yet
- Table J2.4 Minimum Size of Fillet Welds: 2b. LimitationsDocument2 pagesTable J2.4 Minimum Size of Fillet Welds: 2b. LimitationsJen Tan100% (2)
- ELEVATION AND PIPE STRESS CALCULATIONSDocument14 pagesELEVATION AND PIPE STRESS CALCULATIONSDidik AhmadiNo ratings yet
- CR4 - Thread - How To Calculate Flat Plate Thickness of Flat Bottom Storage Tank - PDFDocument3 pagesCR4 - Thread - How To Calculate Flat Plate Thickness of Flat Bottom Storage Tank - PDFInamullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 7-12-0024 Rev 7Document1 page7-12-0024 Rev 7cynideNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Rules For Flat Bottom Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tanks PDFDocument35 pagesSeismic Design Rules For Flat Bottom Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tanks PDFJose Felix AcevedoNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-05 Wind LoadsDocument31 pagesASCE 7-05 Wind LoadsSebastián Ignacio Pajarito VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Cargas de Viento en Edificios y Estructuras de Acuerdo Al Código Asce 7-02Document2 pagesCargas de Viento en Edificios y Estructuras de Acuerdo Al Código Asce 7-02Michele SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Add any change made in the sheet with new revision NoDocument16 pagesAdd any change made in the sheet with new revision Nochenfs27531No ratings yet
- Differential Settlement Bh7Document9 pagesDifferential Settlement Bh7Zhi Ming CheahNo ratings yet
- Sample Shear ConnectionDocument1 pageSample Shear ConnectionmaheshbandhamNo ratings yet
- Vertical Equation Foundation-Spread Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesVertical Equation Foundation-Spread Sheet PDFmassive85No ratings yet
- IBC 2006 SEISMIC PARAMETER For StaadDocument22 pagesIBC 2006 SEISMIC PARAMETER For Staadutoy032367No ratings yet
- Aisc Shapes Database v15.0hDocument432 pagesAisc Shapes Database v15.0hGuyNo ratings yet
- Shear Lug Verification Example 2Document1 pageShear Lug Verification Example 2Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Shear Key or Shear Lug Design - US AISC SectionDocument3 pagesShear Key or Shear Lug Design - US AISC SectionYash PaulNo ratings yet
- Import and Analyze SAP2000 Models in AFESDocument12 pagesImport and Analyze SAP2000 Models in AFESFauzankalibataNo ratings yet
- Calculating Wind Load on a Dish AntennaDocument1 pageCalculating Wind Load on a Dish AntennadovermanNo ratings yet
- Tedds Foundation DesignDocument7 pagesTedds Foundation DesignMasaba SolomonNo ratings yet
- SP by CantileverDocument18 pagesSP by CantileverPaldexNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pile-Soil Interaction Under Lateral Loading Using Infinite and Finite ElementsDocument32 pagesAnalysis of Pile-Soil Interaction Under Lateral Loading Using Infinite and Finite Elementsaln123No ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Elevated TanksDocument59 pagesSeismic Design of Elevated Tankstuky10No ratings yet
- Foundations For Vibrating Machines: Shamsher Prakash Vijay K. PuriDocument53 pagesFoundations For Vibrating Machines: Shamsher Prakash Vijay K. PuriAliNo ratings yet
- Block+Shear+Equations+Revisited AgainDocument8 pagesBlock+Shear+Equations+Revisited AgainSergioAlcantaraNo ratings yet
- AISC Design Guide 1 Table 3.2 PDFDocument1 pageAISC Design Guide 1 Table 3.2 PDFamine ayari100% (1)
- Bolt Shear SF - AISC360-2010Document1 pageBolt Shear SF - AISC360-2010sh4kesNo ratings yet
- Connections 2Document11 pagesConnections 2E. Ibrahim SalemNo ratings yet
- Bolts Non-Structural (A-307) A325 A449 A490 Rivets (Obsolete)Document40 pagesBolts Non-Structural (A-307) A325 A449 A490 Rivets (Obsolete)claudio perez prietoNo ratings yet
- CIVDES2 Lecture Notes - 13 Bolted ConnectionDocument26 pagesCIVDES2 Lecture Notes - 13 Bolted ConnectionVivian RositaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bolted Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 13 Ed. (Old)Document3 pagesChapter 4 - Bolted Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 13 Ed. (Old)perdhana2000No ratings yet
- Advanced Design of Steel Structure: Civil Engineering Department, NUCES, Lahore PakistanDocument23 pagesAdvanced Design of Steel Structure: Civil Engineering Department, NUCES, Lahore Pakistansyed muneeb haiderNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structure - Steel Design Tension MembersDocument24 pagesDesign of Steel Structure - Steel Design Tension MembersshingkeongNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Flanges Dimensions and WeightsDocument3 pagesCarbon Steel Flanges Dimensions and WeightsChandan AulakhNo ratings yet
- Bolt Shear SF - AISC360-2010Document1 pageBolt Shear SF - AISC360-2010sh4kesNo ratings yet
- Table 2 - AISC 316Document1 pageTable 2 - AISC 316sh4kesNo ratings yet
- Table J3.2 - AISC 316Document1 pageTable J3.2 - AISC 316sh4kesNo ratings yet
- Section 6 PRM Carbon Stee Pipe and Fittings PDFDocument10 pagesSection 6 PRM Carbon Stee Pipe and Fittings PDFThefairman UnkownNo ratings yet
- FittingsDocument3 pagesFittingssh4kesNo ratings yet
- Section 6 PRM Carbon Stee Pipe and Fittings PDFDocument10 pagesSection 6 PRM Carbon Stee Pipe and Fittings PDFThefairman UnkownNo ratings yet
- Gasket Design BrochureDocument70 pagesGasket Design BrochurepandiangvNo ratings yet
- API Catalog EN PDFDocument56 pagesAPI Catalog EN PDFDarioPioliNo ratings yet
- API Catalog EN PDFDocument56 pagesAPI Catalog EN PDFDarioPioliNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Interaction Distance PDFDocument1 pageNozzle Interaction Distance PDFsh4kesNo ratings yet
- Ipenz PN 19 - SeismicDocument148 pagesIpenz PN 19 - Seismicsh4kesNo ratings yet
- MW Kellogg TrunnionDesign PDFDocument31 pagesMW Kellogg TrunnionDesign PDFtilsidNo ratings yet
- Stress Iso BlocksDocument1 pageStress Iso Blockssh4kesNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Interaction DistanceDocument1 pageNozzle Interaction Distancesh4kesNo ratings yet
- Resampling VB CodeDocument1 pageResampling VB Codesh4kesNo ratings yet
- BuhlerDocument2 pagesBuhlersh4kesNo ratings yet
- NozzlePRO PDFDocument185 pagesNozzlePRO PDFIan CarrNo ratings yet
- CV Replacement - ManualDocument8 pagesCV Replacement - Manualsh4kesNo ratings yet
- DowtyDocument1 pageDowtysh4kesNo ratings yet
- Main CharacteristicsDocument1 pageMain CharacteristicsAlex OngNo ratings yet
- Fuji Electric France S.A.S.: 2-Wire Universal Temperature TransmitterDocument4 pagesFuji Electric France S.A.S.: 2-Wire Universal Temperature Transmittersh4kesNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic SafetyDocument9 pagesIntrinsic Safetyfebri_bontangNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco - CompressorDocument1 pageAtlas Copco - Compressorsh4kes100% (1)
- Druck - 920-099BDocument4 pagesDruck - 920-099Bsh4kesNo ratings yet
- DowtyDocument1 pageDowtysh4kesNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco - CompressorDocument1 pageAtlas Copco - Compressorsh4kes100% (1)
- The Edge of Space: Revisiting The Karman LineDocument10 pagesThe Edge of Space: Revisiting The Karman LineAlpin AndromedaNo ratings yet
- Netprobe 2000Document351 pagesNetprobe 2000Jordon CampbellNo ratings yet
- The Future of Power Systems: Challenges, Trends, and Upcoming ParadigmsDocument16 pagesThe Future of Power Systems: Challenges, Trends, and Upcoming ParadigmsAndres ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Teach Empathy With LiteratureDocument3 pagesTeach Empathy With LiteratureSantiago Cardenas DiazNo ratings yet
- BPSM Strategic Management ProcessDocument4 pagesBPSM Strategic Management ProcessFaiyaz panchbhayaNo ratings yet
- 722.6 Transmission Conductor Plate Replacement DIYDocument3 pages722.6 Transmission Conductor Plate Replacement DIYcamaro67427100% (1)
- Free Fall ExperimentDocument31 pagesFree Fall ExperimentLeerzejPuntoNo ratings yet
- FS2-EP-12 - LanceDocument9 pagesFS2-EP-12 - LanceLance Julien Mamaclay MercadoNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging - Seminar Topics Project Ideas On Computer ...Document52 pagesMedical Imaging - Seminar Topics Project Ideas On Computer ...Andabi JoshuaNo ratings yet
- PricelistDocument2,276 pagesPricelistadilcmsNo ratings yet
- Work Systems The Methods Measurement and Management of Work 1St Edition Groover Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesWork Systems The Methods Measurement and Management of Work 1St Edition Groover Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdieulienheipgo100% (8)
- John Constantine Rouge Loner Primordial Orphan Paranormal DetectiveDocument4 pagesJohn Constantine Rouge Loner Primordial Orphan Paranormal DetectiveMirko PrćićNo ratings yet
- Abstract PracticeDocument4 pagesAbstract PracticerifqiNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Blended Learning with Synchronous and Asynchronous TechnologiesDocument24 pagesOptimizing Blended Learning with Synchronous and Asynchronous TechnologiesAnonymous GOUaH7FNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam SchedDocument16 pagesComprehensive Exam SchedMark ErvinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans For Class ObservationDocument7 pagesLesson Plans For Class ObservationArnel NavalesNo ratings yet
- ABB Softstarters, Type PSR, PSS, PST/PSTBDocument50 pagesABB Softstarters, Type PSR, PSS, PST/PSTBElias100% (1)
- Rizal's Works Inspire Filipino PrideDocument2 pagesRizal's Works Inspire Filipino PrideItzLian SanchezNo ratings yet
- Gathering Statistical DataDocument8 pagesGathering Statistical DataianNo ratings yet
- SARTIKA LESTARI PCR COVID-19 POSITIVEDocument1 pageSARTIKA LESTARI PCR COVID-19 POSITIVEsartika lestariNo ratings yet
- Official Statement On Public RelationsDocument1 pageOfficial Statement On Public RelationsAlexandra ZachiNo ratings yet
- The Tower Undergraduate Research Journal Volume VI, Issue IDocument92 pagesThe Tower Undergraduate Research Journal Volume VI, Issue IThe Tower Undergraduate Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Sims4 App InfoDocument5 pagesSims4 App InfooltisorNo ratings yet
- USP-NF 1251 Weighing On An Analytical BalanceDocument7 pagesUSP-NF 1251 Weighing On An Analytical BalanceZerish InaayaNo ratings yet
- Manual Reductora IVECO TM 265 - TM 265ADocument31 pagesManual Reductora IVECO TM 265 - TM 265ARomà ComaNo ratings yet
- Shimano 105 Gear Change ManualDocument1 pageShimano 105 Gear Change Manual1heUndertakerNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Predict The Failure of Water Mains Under Climatic VariationsDocument16 pagesAn Approach To Predict The Failure of Water Mains Under Climatic VariationsGeorge, Yonghe YuNo ratings yet
- University of Delhi Third Admission List - Bachelor of Education (B.Ed.)-2021Document8 pagesUniversity of Delhi Third Admission List - Bachelor of Education (B.Ed.)-2021FERA Future electronics and research administrationNo ratings yet
- Catalan NumbersDocument17 pagesCatalan NumbersVishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Professor Barry T Hart - BiographyDocument1 pageProfessor Barry T Hart - BiographyadelNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkFrom EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityFrom EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindFrom EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!From EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsFrom EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesFrom EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryFrom EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Design and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsFrom EverandDesign and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsMarco CecarelliNo ratings yet
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationFrom EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Learning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsFrom EverandLearning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsNo ratings yet
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Modeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesFrom EverandModeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Data Analytics and Innovation for BeginnersFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: Data Analytics and Innovation for BeginnersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- RoboNexus: Bridging Realms: The Confluence of Mechanics, Electronics, and ProgrammingFrom EverandRoboNexus: Bridging Realms: The Confluence of Mechanics, Electronics, and ProgrammingNo ratings yet