Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Describing Trends - Graph
Uploaded by
adna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views4 pagesOriginal Title
DESCRIBING TRENDS- GRAPH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views4 pagesDescribing Trends - Graph
Uploaded by
adnaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
DESCRIBING TRENDS, GRAPHS, AND CHANGES
In business and everyday English, you sometimes have to describe changes in trends
(movement or tendency), graphs, and diagrams.
In the business context, you may have to describe trends in reports, meetings, and
presentations. In everyday life, you could describe changes in any subject because
things change all the time!
Describing changes and trends generally consists of three parts:
Use a verb (or an adjective and a noun) to describe movement
Describe the speed or size of the movement
Explain the reason or consequence of the change
You can also view it this way: Verb + Speed or Size + Result/Reason/Consequence
Example
In 2011, Samsung's profits increased considerably thanks to its successful Galaxy S
series.
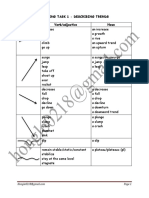
Here are some verbs you can use to describe change and movement.
Upward Movement Horizontal Movement
To climb
To rise To even out
To go up To remain stable
To improve To stabilize
To pick up
To recover Speed of Change
To increase Rapid - Rapidly
To reach a peak Slow - Slowly
Sudden - Suddenly
Downward Movement Sharp - Sharply
To fall Steady - Steadily
To decline Gradual - Gradually
To bottom out Fast - Quickly
To decrease
To drop Size of Change
To plummet Noticeable - Noticeably
To deteriorate Substantial - Substantially
To hit a low Considerable - Considerably
To slip back Slight - Slightly
To do down Significant - Significantly
Dramatic - Dramatically
Example:
• Sales rose slightly in the final quarter.
• Profits fell a little last year.
• Demand increased gently
• Turnover decreased steadily
• Turnover dropped suddenly
• Turnover decreased quickly.
• Demand increased rapidly.
• Profits fell dramatically.
• At the beginning of this year sales stagnated.
• At the end of last year demand peaked.
• In the first quarter of 2008 sales plummeted.
• In the second quarter of 2007 sales flattened out.
• In the third quarter of 2007 sales leveled off.
• In the last quarter of 2007 sales remained steady.
DESCRIBING TRENDS
Introducing Visuals
• I'd like you to look at this graph...
• Let me show you this pie chart...
• Let's have a look at this model...
• Let's turn to this map...
• To illustrate my point let’s look at some diagrams...
• As you can see from these figures...
• If you look at these photographs you'll see...
• If you look at this bar chart you'll notice...
• If you look at this histogram you'll appreciate...
• If you look at this flow chart you'll understand ...
• If you look at this matrix...
Naming the parts of diagrams
The vertical axis represents total annual sales. The horizontal axis shows our market
share. The curve, The solid line, The dotted line, The broken line, The shaded area,
The unshaded section, The dotted column, The coloured segment, The red bar…
Explaining diagrams
• Sales rose slightly in the final quarter.
• Profits fell a little last year.
• Demand increased gently
• Turnover decreased steadily
• Turnover dropped suddenly
• Turnover decreased quickly.
• Demand increased rapidly.
• Profits fell dramatically.
• At the beginning of this year sales stagnated.
• In the middle of August profits slumped.
• At the end of last year demand peaked.
• In the first quarter of 2008 sales plummeted.
• In the second quarter of 2007 sales flattened out.
• In the third quarter of 2007 sales leveled off.
• In the last quarter of 2007 sales remained steady.
You might also like
- Roads Curtis MicrosoundDocument423 pagesRoads Curtis MicrosoundAlexander Formosa100% (19)
- Trip GenerationDocument6 pagesTrip GenerationHanamant Hunashikatti100% (1)
- Bear Market Day Trading Strategies: Day Trading Strategies, #1From EverandBear Market Day Trading Strategies: Day Trading Strategies, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vectors and Scalars: John O'Connor St. Farnan's PPS ProsperousDocument15 pagesVectors and Scalars: John O'Connor St. Farnan's PPS ProsperousTemesgen BihonegnNo ratings yet
- Outline Line GraphsDocument8 pagesOutline Line GraphsHương Nguyễn Hồng SôngNo ratings yet
- COBOL Quick RefresherDocument39 pagesCOBOL Quick Refresherpeeyush_pce2010No ratings yet
- Forex Range Trading with Price ActionFrom EverandForex Range Trading with Price ActionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- 2ND Chart Patterns For Price Action TradingDocument23 pages2ND Chart Patterns For Price Action TradingSandeep Reddy100% (2)
- Report Writing (Part I) Trends, Patterns and General DirectionsDocument9 pagesReport Writing (Part I) Trends, Patterns and General DirectionsZabri ZakariaNo ratings yet
- How to effectively present visual aidsDocument5 pagesHow to effectively present visual aidsNuriaNo ratings yet
- Statical Calculation of 50m TowerDocument25 pagesStatical Calculation of 50m TowerAntenasmNo ratings yet
- Geomechanics NotesDocument72 pagesGeomechanics NotesCarlos Plúa GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Describing Graphs WorksheetDocument1 pageDescribing Graphs Worksheetducvilla100% (1)
- Example of Describing Trends PDFDocument1 pageExample of Describing Trends PDFWardiati Yusuf100% (2)
- Describing Graphs and ChartsDocument6 pagesDescribing Graphs and ChartsDevi AndistaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Stone ColumnsDocument12 pagesCase Study For Stone ColumnsChinchu CherianNo ratings yet
- Example of Describing Trends-1 PDFDocument1 pageExample of Describing Trends-1 PDFWardiati Yusuf100% (1)
- Useful Language For Chart DescriptionsDocument2 pagesUseful Language For Chart DescriptionsMaripinkyNo ratings yet
- Multi Digit Numbers Concepts and OperationsDocument12 pagesMulti Digit Numbers Concepts and OperationsRafikh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Academic Writing VocabularyDocument8 pagesTask 1 Academic Writing VocabularyAmal Xavier RozarioNo ratings yet
- Air Travel Describing Trends and MovementsDocument27 pagesAir Travel Describing Trends and MovementsMarilynSultanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Trends and MovementsDocument45 pagesUnit 1 - Trends and MovementsMarkoNo ratings yet
- Describing TrendsDocument5 pagesDescribing TrendsChristopher Anthony Kanikula FernandezNo ratings yet
- Describing Trends, Graphs and Changes: ExampleDocument4 pagesDescribing Trends, Graphs and Changes: ExampleJuly RojasNo ratings yet
- Paper Group 5 - English CDocument10 pagesPaper Group 5 - English Claelatul FajriyahNo ratings yet
- ENSM - Reading and Describing Graphs STUDENTSDocument20 pagesENSM - Reading and Describing Graphs STUDENTSmed27919No ratings yet
- Expressing The Movement of A LineDocument2 pagesExpressing The Movement of A LineasdfasdNo ratings yet
- Herramientas (Ingles) para Presentar Cifras y Gráficos.Document3 pagesHerramientas (Ingles) para Presentar Cifras y Gráficos.Anonymous WwLdG6fh4No ratings yet
- Describing Graphs and Trends Classroom Posters 46996Document2 pagesDescribing Graphs and Trends Classroom Posters 46996MarijaNo ratings yet
- Describing Changes (Handout)Document4 pagesDescribing Changes (Handout)Salma ChboukiNo ratings yet
- B4 Unit 3 TRENDS 2021 1Document20 pagesB4 Unit 3 TRENDS 2021 1AVILA PLACENCIO MARCELO ALEJANDNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 PDFDocument6 pagesWriting Task 1 PDFCamieNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 - How ComGraphStdDocument6 pagesWriting Task 1 - How ComGraphStdLuhdy SardinhaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 LanguageDocument5 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 LanguageQuỳnh Anh Nguyễn HồNo ratings yet
- List Two: Nouns: To 25,000 in 2010. by 5,000 Between 2005 and 2010Document4 pagesList Two: Nouns: To 25,000 in 2010. by 5,000 Between 2005 and 2010GPPW ASSESSMENTNo ratings yet
- Describing Trends or Movements in Graphs/ChartsDocument17 pagesDescribing Trends or Movements in Graphs/ChartsMaruthi MaddipatlaNo ratings yet
- Graphs Charts Statistics TrendsDocument2 pagesGraphs Charts Statistics TrendsMarcia OhtaNo ratings yet
- Describing Graph in PresentationDocument13 pagesDescribing Graph in PresentationMuhammad AllansahNo ratings yet
- The Vocabulary of Graphs and Charts: Line Charts and Graphs Bar Charts and Graphs Pie Charts Exploded Pie ChartsDocument3 pagesThe Vocabulary of Graphs and Charts: Line Charts and Graphs Bar Charts and Graphs Pie Charts Exploded Pie ChartsRakib mansuriNo ratings yet
- How To Talk About A Visual AidDocument5 pagesHow To Talk About A Visual AidGedeon LitengoNo ratings yet
- ELC590 Informative Speech Language Used in Describing Charts or GraphsDocument2 pagesELC590 Informative Speech Language Used in Describing Charts or GraphsSyafiqah Suhaimi100% (1)
- Writing Task 1 VocabDocument7 pagesWriting Task 1 VocabSu Thiri KhitNo ratings yet
- Graphs Charts VocabularyDocument2 pagesGraphs Charts VocabularyEmil KorbusNo ratings yet
- Describing Trends and ChangeDocument16 pagesDescribing Trends and ChangeAnakinNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document9 pagesTask 1Ngọc Quân TrươngNo ratings yet
- Advanced Online Speaking - WritingDocument74 pagesAdvanced Online Speaking - WritingDinh Quynh MaiNo ratings yet
- How Com Graph STDDocument5 pagesHow Com Graph STDnadiakhaled2005No ratings yet
- Graphs and Charts - Introduction. Answer KeyDocument6 pagesGraphs and Charts - Introduction. Answer KeyAna Pociello Samperiz100% (1)
- Describing Graphs and TendenciesDocument4 pagesDescribing Graphs and TendenciesCarmen Maria Tebar PlazaNo ratings yet
- Line GraphDocument8 pagesLine GraphMaMi 9a7No ratings yet
- Task 1 - Bar ChartDocument6 pagesTask 1 - Bar Chartbao ttrangNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary for charts and graphsDocument3 pagesVocabulary for charts and graphsarbabatif9442No ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 Precious VocabularyDocument5 pagesWriting Task 1 Precious VocabularySaeed RahimpourNo ratings yet
- Guide 3Document17 pagesGuide 3Afiqah NazriNo ratings yet
- Task 1 VocabsDocument5 pagesTask 1 VocabsPhạm Nguyễn Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Saying Numbers in English: A GuideDocument9 pagesSaying Numbers in English: A GuideAlison CamachoNo ratings yet
- MUET Writing Question 1 TipsDocument6 pagesMUET Writing Question 1 TipsgovinjementahNo ratings yet
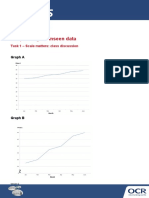
- Lesson Element Responding To Unseen Data: Task 1 - Scale Matters: Class DiscussionDocument10 pagesLesson Element Responding To Unseen Data: Task 1 - Scale Matters: Class DiscussionaaNo ratings yet
- Graphs - Charts: The Meaning of Words Relating To Statistics, Results and TrendsDocument2 pagesGraphs - Charts: The Meaning of Words Relating To Statistics, Results and TrendsAna GalacNo ratings yet
- Graphs - Charts: The Meaning of Words Relating To Statistics, Results and TrendsDocument2 pagesGraphs - Charts: The Meaning of Words Relating To Statistics, Results and TrendsAna GalacNo ratings yet
- Vocab For Ielts Task 1Document13 pagesVocab For Ielts Task 1bangami1234No ratings yet
- KKKKMHMVMNDocument5 pagesKKKKMHMVMNKarolina MleczakNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing 1 Tips (1)Document42 pagesIelts Writing 1 Tips (1)Cemre Irmak KayalanNo ratings yet
- Graph Shows Microsoft Share Price FluctuationsDocument6 pagesGraph Shows Microsoft Share Price FluctuationslyaviolNo ratings yet
- TASK 1 - Describing Trends BASICDocument7 pagesTASK 1 - Describing Trends BASICTuấn Việt VũNo ratings yet
- Writing Ielts Task 1Document5 pagesWriting Ielts Task 1Nguyễn Thùy TrangNo ratings yet
- Graph Vocab & StructureDocument4 pagesGraph Vocab & Structuretabasimaladnan02No ratings yet
- Homework - Dimensional - Analysis-Fm 2020-IDocument1 pageHomework - Dimensional - Analysis-Fm 2020-IFelipe CastiblancoNo ratings yet
- G.C.E. Advanced Level – 2017 Theory Exam: Basic Mathematics QuestionsDocument20 pagesG.C.E. Advanced Level – 2017 Theory Exam: Basic Mathematics Questionswissam riyasNo ratings yet
- Six Meter Heliax Duplexers: Low-Band VHF Heliax Duplexer Performance On 6 Meters, Notch StyleDocument20 pagesSix Meter Heliax Duplexers: Low-Band VHF Heliax Duplexer Performance On 6 Meters, Notch Stylelu1agpNo ratings yet
- Hertz Electric Waves 1892Document17 pagesHertz Electric Waves 1892roberto-martins100% (1)
- Os Lab Exno 1 To 5Document38 pagesOs Lab Exno 1 To 5Vairavel ChenniyappanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07Document17 pagesLecture 07RandomNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Physics 151Document23 pagesMechanics: Physics 151nghaNo ratings yet
- 403 S. H. S. C. E. Physics Objective and Essay TestsDocument11 pages403 S. H. S. C. E. Physics Objective and Essay TestsAyomide sayo-AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of P, Pi & Pid Controller From Matlab SimulinkDocument30 pagesBehaviour of P, Pi & Pid Controller From Matlab SimulinkDineshNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Systems: Laurette TUCKERMAN Laurette@Document23 pagesDynamical Systems: Laurette TUCKERMAN Laurette@sevkaxNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning in Antenna Design An Overview On Machine Learning Concept and AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesMachine Learning in Antenna Design An Overview On Machine Learning Concept and AlgorithmssagarduttaNo ratings yet
- A Das Gupta MCQ PDFDocument72 pagesA Das Gupta MCQ PDFBhavya ChawatNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics 2011-QNDocument5 pagesBasic Mathematics 2011-QNEmanuel John BangoNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Dynamics: 6.1 Response To ControlsDocument10 pagesLongitudinal Dynamics: 6.1 Response To ControlsAlbertoNo ratings yet
- 10Document14 pages10radiobrunoNo ratings yet
- Formal Methods: Finite State Machine - Regular ExpressionsDocument14 pagesFormal Methods: Finite State Machine - Regular ExpressionsStatus LifeNo ratings yet
- Boundary-Aware 3D Building Reconstruction From A Single Overhead ImageDocument11 pagesBoundary-Aware 3D Building Reconstruction From A Single Overhead ImageJan KristantoNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion MCQsDocument23 pagesRotational Motion MCQsDeepanshu LullaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3Asmidar HaniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 5 - 2021Document8 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 5 - 2021martinajoan1No ratings yet
- Time Series Forecasting - Sparkling - Buisness ReportDocument70 pagesTime Series Forecasting - Sparkling - Buisness ReportPriyanka PatilNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase To Two-Phase/One-Phase Conversion Using TWO TRANSFORMERS (Scott Connection)Document13 pagesThree-Phase To Two-Phase/One-Phase Conversion Using TWO TRANSFORMERS (Scott Connection)Bhavani Chandra UniqueNo ratings yet