Professional Documents
Culture Documents
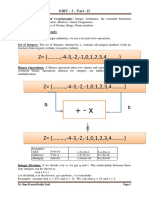
Introduction To Oracle Statement: CREATE ROLE Role - Name
Uploaded by
Ram Prasad Reddy SadiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Oracle Statement: CREATE ROLE Role - Name
Uploaded by
Ram Prasad Reddy SadiCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Oracle
CREATE ROLE statement
A role is a group of privileges. Instead of granting individual privileges to
users, you can group related privileges into a role and grant this role to
users. Roles help manage privileges more efficiently.
To create a new role, you use the CREATE ROLE statement. The basic syntax of
the CREATE ROLE statement is as follows:
CREATE ROLE role_name
[IDENTIFIED BY password]
[NOT IDENTIFIED]
In this syntax:
First, specify the name of the role that you want to create.
Second, use IDENTIFIED BY password option to create a local role
and indicate that the user, who was granted the role, must
provide the password to the database when enabling the role.
Third, use NOT IDENTIFIED to indicate that the role is authorized by
the database and the user, who was granted this role, don’t need
a password to enable the role.
After a role is created, it is empty. To grant privileges to a role, you use
the GRANT statement:
GRANT {system_privileges | object_privileges} TO role_name;
In addition, you can use the GRANT statement to grant privileges of a role to
another role:
GRANT role_name TO another_role_name;
Oracle CREATE ROLE statement examples
Let’s take some examples of using the CREATE ROLE statement.
1) Using Oracle CREATE ROLE without a password example
First, create a new role named mdm (master data management) in the sample
database:
CREATE ROLES mdm;
Second, grant object privileges
on customers, contacts, products, product_categories, warehouses, locations, emp
loyees tables to the mdm role:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON customers
TO mdm;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON contacts
TO mdm;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON products
TO mdm;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON product_categories
TO mdm;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON warehouses
TO mdm;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON locations
TO mdm;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON employees
TO mdm;
Third, create a new user named alice and grant the CREATE SESSION privilege
to alice:
CREATE USER alice IDENTIFIED BY abcd1234;
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO alice;
Fourth, log in to the database as alice:
Enter user-name: alice@pdborcl
Enter password:
and attempt to query data from the ot.employees table:
SELECT * FROM ot.employees;
Oracle issued the following error:
ORA-00942: table or view does not exist
Go back to the first session and grant alice the mdm role:
GRANT mdm TO alice;
Go to the alice’s session and enable role using the SET ROLE statement:
SET ROLE mdm;
To query all roles of the current user, you use the following query:
SELECT * FROM session_roles;
Here is the role of alice:
ROLE
------
MDM
Now, alice can manipulate data in the master data tables such
as customers and employees.
2) Using Oracle CREATE ROLE to create a role with IDENTIFIED BY
password example
First, create a new role named order_entry with the password xyz123:
CREATE ROLE order_entry IDENTIFIED BY xyz123;
Next, grant object privileges on the orders and order_items tables to
the order_entry role:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON orders
TO order_entry;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
ON order_items
TO order_entry;
Then, grant the order_entry role to the user alice:
GRANT order_entry TO alice;
After that, log in as alice and enable the order_entry role by using the SET
ROLE statement:
SET ROLE
order_entry IDENTIFIED BY xyz123,
mdm;
Finally, use the following statement to get the current roles of alice:
SELECT * FROM session_roles;
Here are the current roles of alice:
ROLE
-------------
MDM
ORDER_ENTRY
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Resolución de Problema en FísicaDocument4 pagesResolución de Problema en FísicaCindy ChiribogaNo ratings yet
- Biometrics in Credit Cards: AnewwaytopayDocument31 pagesBiometrics in Credit Cards: AnewwaytopayRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Short Learning Article CompleteDocument169 pagesBiomedical Short Learning Article Completenebiyu mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part-IIIDocument7 pagesUnit-1 - Part-IIIRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part-IIDocument24 pagesUnit-1 - Part-IIRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part-IDocument8 pagesUnit-1 - Part-IRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - Part-IDocument24 pagesUnit-2 - Part-IRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Ear RecognitionDocument42 pagesEar RecognitionRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- The Evaluation of Face Recognition Systems: Face Recognition Technology Program & F Ace Recognition Vendor TestDocument40 pagesThe Evaluation of Face Recognition Systems: Face Recognition Technology Program & F Ace Recognition Vendor TestRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Biometrics in Computerized Patient Record: Presented by Qi Ling Temo BardzimashviliDocument33 pagesBiometrics in Computerized Patient Record: Presented by Qi Ling Temo BardzimashviliRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Subqueries With The SELECT Statement: ExampleDocument4 pagesSubqueries With The SELECT Statement: ExampleRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Domain Relational Calculus - Google FormsDocument4 pagesDomain Relational Calculus - Google FormsRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- AI Updated Format Without AdvDocument110 pagesAI Updated Format Without AdvRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2aDocument5 pagesAssignment 2aRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- TechNucleus - SQL QueriesDocument39 pagesTechNucleus - SQL QueriesRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Education Sciences: Artutor-An Augmented Reality Platform For Interactive Distance LearningDocument12 pagesEducation Sciences: Artutor-An Augmented Reality Platform For Interactive Distance LearningRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Capability-Linked Options For Undergraduate StudentsDocument8 pagesCapability-Linked Options For Undergraduate StudentsRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Ram Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Ram Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Joint IPR WorkshopDocument1 pageJoint IPR WorkshopRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document4 pagesAssignment 5Ram Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document11 pagesExperiment 6CarlosLorenzoSaninNo ratings yet
- When Bad Things Happen To Good MissilesDocument9 pagesWhen Bad Things Happen To Good Missilesmykingboody2156No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - SkullDocument10 pagesChapter 11 - Skullwamaithamargaret257No ratings yet
- Kalman FilterDocument14 pagesKalman FilterNeetaa MunjalNo ratings yet
- 1 Seam 2 LM FinalDocument84 pages1 Seam 2 LM FinalTrestan TenegraNo ratings yet
- sbd0105 33 71 1BBE0 000011Document1 pagesbd0105 33 71 1BBE0 000011NetflixNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Example 797Document15 pagesCommissioning Example 797linkangjun0621No ratings yet
- How To Build An Offshore CraneDocument5 pagesHow To Build An Offshore CraneWestMarineNo ratings yet
- 10K Ductile Cast Iron Gate Valve (Flange Type) TOYO VALVE Gate ValvesDocument4 pages10K Ductile Cast Iron Gate Valve (Flange Type) TOYO VALVE Gate ValvesFredie LabradorNo ratings yet
- Warn 2013-2014 Application GuideDocument75 pagesWarn 2013-2014 Application Guideapi-238139220No ratings yet
- COE Test 06 Code A JEE Main 2024 XII 09 10 2023answer KeyDocument1 pageCOE Test 06 Code A JEE Main 2024 XII 09 10 2023answer KeyaebagnedhNo ratings yet
- 3D ShapesDocument5 pages3D Shapesdeez000No ratings yet
- Structure HarvesterDocument3 pagesStructure HarvesterOliva R. SeguraNo ratings yet
- Certification of eVTOL AircraftDocument19 pagesCertification of eVTOL AircraftrlwersalNo ratings yet
- B.S. in Electronics Engineering - BSECE 2008 - 2009Document2 pagesB.S. in Electronics Engineering - BSECE 2008 - 2009Vallar RussNo ratings yet
- 2009 06 02 Library-Cache-LockDocument9 pages2009 06 02 Library-Cache-LockAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Nice Neotech - Opera Plus Warmer 5000 - 6Document1 pageNice Neotech - Opera Plus Warmer 5000 - 6David Gnana DuraiNo ratings yet
- ACUCOBOL-GT Users Guide v8 Tcm21-18390Document587 pagesACUCOBOL-GT Users Guide v8 Tcm21-18390Miquel CerezuelaNo ratings yet
- Smart Four Channel Highside Power Switch: BTS711L1Document17 pagesSmart Four Channel Highside Power Switch: BTS711L1Giapy Phuc TranNo ratings yet
- MPLS22LGDocument81 pagesMPLS22LGTerri DuranNo ratings yet
- BBBBBDocument11 pagesBBBBBAlfredo ErguetaNo ratings yet
- AsdDocument10 pagesAsdsalman khanNo ratings yet
- Velocity Analysis-Instantaneous Center MDocument7 pagesVelocity Analysis-Instantaneous Center MSuman_SamadderNo ratings yet
- Dke672 ch2Document44 pagesDke672 ch2Siraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Fuse Link KDocument6 pagesFuse Link KABam BambumNo ratings yet
- Application SMS MD720-3 DOKU V2 1 enDocument52 pagesApplication SMS MD720-3 DOKU V2 1 enerendira77No ratings yet
- FSX Cessna 172SP OldDocument4 pagesFSX Cessna 172SP Oldaccgh5No ratings yet
- Embedded Linux Course SlidesDocument571 pagesEmbedded Linux Course SlidesKuan Xing Li100% (2)