Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Charles Law
Uploaded by
Ma. Celeste LipOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Charles Law
Uploaded by
Ma. Celeste LipCopyright:
Available Formats
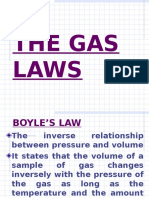
12 The Gas Laws
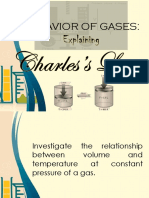
CHARLES’S LAW
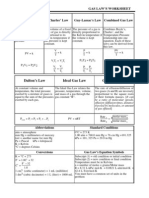
Charles’ Law states the volume of a gas varies directly with the Kelvin temperature, assuming the pressure is
constant. We use the following formulas:
V1 V2
or V1 T2 = V2 T1
T1 T2
K = C + 273
Solve the following problems assuming a constant pressure. Assume all numbers are 3 significant figures.
1. A sample of nitrogen occupies a volume of 250 mL at 25 C. What volume will it occupy at 95 C?
2. Oxygen gas is at a temperature of 40 C when it occupies a volume of 2.30 Liters. To what temperature
should it be raised to occupy a volume of 6.50 Liters?
3. Hydrogen gas was cooled from 150 C to 50 C. Its new volume is 75.0 mL. What was its original
volume?
4. Chlorine gas occupies a volume of 25.0 mL at 300 K. What volume will it occupy at 600 K?
5. A sample of neon gas at 50 C and a volume of 2.50 Liters is cooled to 25 C. What is the new volume?
6. Fluorine gas at 300 K occupies a volume of 500 mL. To what temperature should it be lowered to bring
the volume to 300 mL?
7. Helium occupies a volume of 3.80 Liters at –45 C. What volume will it occupy at 45 C?
8. A sample of argon gas is cooled and its volume went from 380 mL to 250 mL. If its final temperature was
–55 C, what was its original temperature?
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- CHARLES-LAWDocument25 pagesCHARLES-LAWstaanajessamae3No ratings yet
- Gas Law PracticeDocument5 pagesGas Law PracticeKaly CantongNo ratings yet
- Gas-Law-Worksheets-AutosavedDocument8 pagesGas-Law-Worksheets-AutosavedTrinity Marie HablanNo ratings yet
- Solve The Following Gas Law Problems. Show All Pertinent SolutionsDocument1 pageSolve The Following Gas Law Problems. Show All Pertinent SolutionsElliah Joy AcioNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Temperature and Gas VolumeDocument18 pagesRelationship Between Temperature and Gas VolumeCasandra PeñaverdeNo ratings yet
- CHARLES' LAW ACTIVITY SHEETDocument2 pagesCHARLES' LAW ACTIVITY SHEETVanessa QuinolNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument23 pagesCharles LawJanetMagnayeLapitan100% (2)
- Gaseous StatesDocument55 pagesGaseous StatesGail DomingoNo ratings yet
- Boyles and Charles Law NotesDocument2 pagesBoyles and Charles Law Notesomsaiboggala811No ratings yet
- The Gas LawsDocument110 pagesThe Gas Lawsapi-266061131No ratings yet
- Module 5.2a: Gas Laws Part 1Document26 pagesModule 5.2a: Gas Laws Part 1Ryan PazonNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument33 pagesGas LawsTheresa Margaretta SiraitNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet #1 - Boyle's, Charles', Gay-Lussac's, and Combined Gas LawDocument8 pagesGas Laws Worksheet #1 - Boyle's, Charles', Gay-Lussac's, and Combined Gas Lawnina lykka calaraNo ratings yet
- Thegaslawscomplete 120227061412 Phpapp01Document51 pagesThegaslawscomplete 120227061412 Phpapp01Bustami Muhammad Sidik100% (1)
- Ideal Gas LawsDocument43 pagesIdeal Gas LawsRenz FerrerNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Heat and TemperatureDocument31 pagesGas Laws Heat and TemperatureAfiqahAliasNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4W3 v2Document14 pagesScience10 Q4W3 v2Cesar RofuliNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument55 pagesGASESja_QuinineNo ratings yet
- Charles_Law_PowerPointDocument15 pagesCharles_Law_PowerPointStephanie PorioNo ratings yet
- Intro To Gases and Gas LawsDocument44 pagesIntro To Gases and Gas Lawsivy omongosNo ratings yet
- Charles' Law: Gr11 Chem Unit 2: Gases and The Atmosphere, Lesson 6: Volume, TemperatureDocument3 pagesCharles' Law: Gr11 Chem Unit 2: Gases and The Atmosphere, Lesson 6: Volume, TemperatureKristian GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument69 pagesGas LawsXandra CallantaNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Gases: Charles' LAWDocument33 pagesBehavior of Gases: Charles' LAWJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 - Charles LAWDocument1 pageWEEK 2 - Charles LAWRufa NarioNo ratings yet
- Intro To Gases and Gas LawsDocument61 pagesIntro To Gases and Gas LawsLuigie100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Handout 2Document4 pagesThermodynamics Handout 2Demetrio C. Villanueva IIINo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Lesson - 1 - The+Gas+LawsDocument23 pagesModule 12 - Lesson - 1 - The+Gas+LawsMihadNo ratings yet
- Gases-and-Gas-LawsDocument49 pagesGases-and-Gas-LawsArianne LaruscainNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Document47 pagesTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Joshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Gas Law Problems Answers (4)Document2 pagesGas Law Problems Answers (4)kavleshgalhotra711No ratings yet
- Example: Speed and Travel TimeDocument17 pagesExample: Speed and Travel TimeRowena NimNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws - F3Document17 pagesGas Laws - F3Kiama GitahiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 GasesDocument20 pagesLesson 7 GasesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument23 pagesCharles LawDRIFT KMG0% (1)
- Practice problems on gas lawsDocument4 pagesPractice problems on gas lawstaptech004No ratings yet
- Charles' Law and Gas LawsDocument8 pagesCharles' Law and Gas LawsAce Vincent LunaNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument47 pagesBoyles Lawcloudyblues69No ratings yet
- 12 Gases PhychemDocument116 pages12 Gases PhychemCharmaine Padua BrizuelaNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument8 pagesCharles LawJenny Maglasang SabioNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law Equations and ApplicationsDocument1 pageIdeal Gas Law Equations and ApplicationsLarry BugaringNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Gas Laws PPT 2017 GoodDocument34 pagesChapter 14 Gas Laws PPT 2017 GoodBlist ers100% (2)
- Charles LawDocument9 pagesCharles LawShabina KhalidNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws ProblemsDocument46 pagesGas Laws ProblemsIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 and 6Document63 pagesChapter 5 and 6Athaliah Del MonteNo ratings yet
- Gas_Law_Pt_1Document31 pagesGas_Law_Pt_1darkrealms98No ratings yet
- The Gas LawsDocument40 pagesThe Gas LawsLailanie PinedaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet GasesDocument6 pagesWorksheet GasesakladffjaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Gas LawsDocument1 pageClass 9 Gas Lawssuranjana26No ratings yet
- Science10 - Q4 - Week 2 Charles Law Volume and TemperatureDocument14 pagesScience10 - Q4 - Week 2 Charles Law Volume and TemperatureJomelyn Arzaga100% (1)
- Boyle's Law ExplainedDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law ExplainedannmarieNo ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 2-Charles's LawDocument21 pagesQ4-WEEK 2-Charles's LawAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- 5 16 53 600Document14 pages5 16 53 600sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Gas-Laws-worksheetDocument4 pagesGas-Laws-worksheetelgincolinvictor9No ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Temperature andDocument8 pagesThe Relationship Between Temperature andthenderingNo ratings yet
- 4-3 Physics WK 3 Combined Gas LawDocument3 pages4-3 Physics WK 3 Combined Gas Lawlaisha chanNo ratings yet
- GLWS9Document6 pagesGLWS9Vince HernándezNo ratings yet
- Charles' Law Problems & SolutionsDocument1 pageCharles' Law Problems & Solutionsadimegha100% (2)
- Meal Planner 3 From SundayDocument1 pageMeal Planner 3 From SundayMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Closure (SAMPLE)Document1 pageAffidavit of Closure (SAMPLE)Ma. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Nens SIM in ScienceDocument38 pagesNens SIM in SciencezahnodjiNo ratings yet
- SF Triangle Clipper HUMSS 11Document4 pagesSF Triangle Clipper HUMSS 11Ma. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- SF Triangle Clipper HUMSS 11Document4 pagesSF Triangle Clipper HUMSS 11Ma. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Project On Isotopes Nuclear ChemistryDocument11 pagesProject On Isotopes Nuclear ChemistryNick wavesNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Output Assessment GuideDocument1 pageSession 3 Output Assessment GuideMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Molecular Models ActivityDocument28 pagesMolecular Models ActivityMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Request for free Covid-19 testing and school disinfectionDocument3 pagesRequest for free Covid-19 testing and school disinfectionMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Molecular & Empirical Formula DeterminationDocument8 pagesMolecular & Empirical Formula DeterminationMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Cover Page Design For Business Expense ReportDocument1 pageCover Page Design For Business Expense ReportMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Form C Statement of Commitment 1 (Noah Nibbles)Document1 pageForm C Statement of Commitment 1 (Noah Nibbles)Ma. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Foodlane Accreditation FormDocument1 pageFoodlane Accreditation FormGreg TayonaNo ratings yet
- Form C: Statement of CommitmentDocument1 pageForm C: Statement of CommitmentArthur NierraNo ratings yet
- Form B Foodlane Reference Form 1Document1 pageForm B Foodlane Reference Form 1Ma. Celeste LipNo ratings yet
- Form B Foodlane Reference Form Noah Daniel NibblesDocument1 pageForm B Foodlane Reference Form Noah Daniel NibblesMa. Celeste LipNo ratings yet