Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52
Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52
Uploaded by
Rohan KondeThe document describes the steps to assign file/folder permissions using Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in Windows. It involves creating a new GPO, navigating to the file system settings, adding the file/folder, configuring permissions, auditing and ownership settings, applying the settings, linking the GPO to a domain, and enforcing the GPO. The 24 step process allows assigning detailed access permissions to files and folders using GPOs for centralized management.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ProductDefInterface FixDocument3 pagesProductDefInterface FixPARAS BAJAJNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 AutomobileManagement Using LINQ and WinFormsDocument19 pagesLab 01 AutomobileManagement Using LINQ and WinFormsnobiNo ratings yet
- O Jogo - Neil StraussDocument450 pagesO Jogo - Neil StraussEdson Costa83% (6)
- Lab 5 - Creating and Configuring Group Policy ObjectsDocument7 pagesLab 5 - Creating and Configuring Group Policy ObjectsNM ThânNo ratings yet
- Select Group Policy Management From The Tools Dropdown ListDocument7 pagesSelect Group Policy Management From The Tools Dropdown ListshairaNo ratings yet
- Window Vista Hacking (Taking Ownership)Document4 pagesWindow Vista Hacking (Taking Ownership)Abhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Create A Folder Redirection Security GroupDocument7 pagesStep 1: Create A Folder Redirection Security Grouprobertson_izeNo ratings yet
- The Office Professional 2007Document3 pagesThe Office Professional 2007Jegatheesh JakeNo ratings yet
- Prno 15Document5 pagesPrno 15Vishal Suresh KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Whatfix Deployment Document - GroupPolicyDocument12 pagesWhatfix Deployment Document - GroupPolicythiagoomNo ratings yet
- Few ExamplesDocument3 pagesFew Examplessambradshaw945No ratings yet
- Enable File Access Auditing in WindowsDocument7 pagesEnable File Access Auditing in WindowsAdrianApostolNo ratings yet
- Expt 4Document12 pagesExpt 4aniketNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Amazon Simple Storage (S3)Document11 pagesLab 1 - Amazon Simple Storage (S3)Hector AndradeNo ratings yet
- Configuring NetWeaver Development Infrastructure (NWDI) in Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence (MII) - Development ComponentDocument30 pagesConfiguring NetWeaver Development Infrastructure (NWDI) in Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence (MII) - Development Componenteeha0120No ratings yet
- Greyhound: A) Code B) Database C)Document2 pagesGreyhound: A) Code B) Database C)Rahul TonapeNo ratings yet
- Creating IBM Cloud Object StorageDocument11 pagesCreating IBM Cloud Object StorageMalabana Pantoja Maria LeahNo ratings yet
- Gina Gpo Installation GuideDocument19 pagesGina Gpo Installation GuideSojan MathewNo ratings yet
- JanusWindows 8Document1 pageJanusWindows 8cobalt_cannonNo ratings yet
- Establishing File SharingDocument9 pagesEstablishing File SharingSenthil NathanNo ratings yet
- 11.6.2.4 Lab - System Restore and Hard Drive BackupDocument7 pages11.6.2.4 Lab - System Restore and Hard Drive BackupRidwan FahmiNo ratings yet
- Folder Redirection: STEP 1: Create Organization Unit (OU)Document9 pagesFolder Redirection: STEP 1: Create Organization Unit (OU)Joel CuyuganNo ratings yet
- Auto CadDocument16 pagesAuto CadKumanLowNo ratings yet
- Questões de LaboratórioDocument15 pagesQuestões de LaboratórioQue Bacana Presentes PersonalizadosNo ratings yet
- ITP4406 - Lab07 (Depoly Software by GP and GP Central Store) v5Document7 pagesITP4406 - Lab07 (Depoly Software by GP and GP Central Store) v5rickyNo ratings yet
- Controlling Access To Local Hardware and Applications: This Lab Contains The Following Exercises and ActivitiesDocument9 pagesControlling Access To Local Hardware and Applications: This Lab Contains The Following Exercises and ActivitiesMD4733566No ratings yet
- BCSL 063 Solved Assignment 2022 23 UlptmtDocument15 pagesBCSL 063 Solved Assignment 2022 23 UlptmtShubham SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Windows Group Policy InterviewWindows Group Policy Interview Questions QuestionsDocument4 pagesWindows Group Policy InterviewWindows Group Policy Interview Questions QuestionsRaja Mozumder0% (1)
- Data DomainDocument11 pagesData DomainAsma RizwanNo ratings yet
- Submitting Written and Video AssignmentsDocument2 pagesSubmitting Written and Video AssignmentsKalpattyNo ratings yet
- Fix: Cannot Access Network Shares After Update 1709: Try GCP FreeDocument7 pagesFix: Cannot Access Network Shares After Update 1709: Try GCP FreeFrusinoiu CristinaNo ratings yet
- NW Admin Lab Exercise 3-2Document3 pagesNW Admin Lab Exercise 3-2xyzalimohamed76No ratings yet
- (2165338) Azure Assignment 2Document12 pages(2165338) Azure Assignment 2Kiran KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Backtomyvillage: A) Code B) Data Base C)Document2 pagesBacktomyvillage: A) Code B) Data Base C)Supreeti KoneruNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15-16 File Service FinalDocument5 pagesExercise 15-16 File Service FinalAlexis LarosaNo ratings yet
- Defect Tracking System: A) Code B) Data Base C)Document2 pagesDefect Tracking System: A) Code B) Data Base C)Eric HernandezNo ratings yet
- Fleet Management System: A) Code B) Data Base C)Document3 pagesFleet Management System: A) Code B) Data Base C)ethanlevin213No ratings yet
- Process of Create The New CIGAS Executable FileDocument12 pagesProcess of Create The New CIGAS Executable Filekalana heshanNo ratings yet
- Things To FollowDocument3 pagesThings To FollowsanjaykumarguptaaNo ratings yet
- -Document8 pages-Dewi Puspita sariningsihNo ratings yet
- How To Delete Files Protected by TrustedInstallerDocument7 pagesHow To Delete Files Protected by TrustedInstallerhighmountainbearNo ratings yet
- EncryptionDocument1 pageEncryptionAurang Zeb SheikhNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Create and Configure A Package: 118 Packages Create Package Next Model Presentation View Sales Target Sales NextDocument6 pages4.5 Create and Configure A Package: 118 Packages Create Package Next Model Presentation View Sales Target Sales NextHarry KonnectNo ratings yet
- Manage Media in DriveDocument4 pagesManage Media in DriveCyril Danica LimareNo ratings yet
- Expt 4Document3 pagesExpt 4nagbalidhumal.2005No ratings yet
- How To Integrate Firefox With Windows Group PolicyDocument14 pagesHow To Integrate Firefox With Windows Group PolicyDragan LakovskiNo ratings yet
- Deploy Folder Redirection With Offline Files - Microsoft DocsDocument9 pagesDeploy Folder Redirection With Offline Files - Microsoft DocsAggrey-Anthony DuncanNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Shared Database: An Example Using Postgresql and Pgadmin4Document19 pagesHow To Create A Shared Database: An Example Using Postgresql and Pgadmin4Freddy IANo ratings yet
- Win7 FixDocument7 pagesWin7 FixThomas KuzinasNo ratings yet
- 2274b Mod09 LADocument10 pages2274b Mod09 LALuis RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Changes To Group Policy: Windows Server 2008 Directory ServicesDocument26 pagesChanges To Group Policy: Windows Server 2008 Directory ServicesMoldoveanu Horia MihailNo ratings yet
- Carrier Path: A) Code B) Database C)Document2 pagesCarrier Path: A) Code B) Database C)Shashi CampherNo ratings yet
- Google Drive InstructionsDocument17 pagesGoogle Drive InstructionsDAYTABASE TheProducerNo ratings yet
- Simple File ServerDocument9 pagesSimple File ServerAbigail PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Assigning Software: Create A Distribution PointDocument4 pagesAssigning Software: Create A Distribution PointthebukiNo ratings yet
- Tasksheet 9 Configure Folder RedirectionDocument4 pagesTasksheet 9 Configure Folder RedirectionClark DomingoNo ratings yet
- SIL Solver Pre-Installation Procedure v6 CombinedDocument7 pagesSIL Solver Pre-Installation Procedure v6 CombinedMarcio GranatoNo ratings yet
- HelpFile FiltercraveDocument3 pagesHelpFile FiltercraveHandoko MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Windows 10 Version 1709 - CFA IssueDocument6 pagesWindows 10 Version 1709 - CFA Issuejan2No ratings yet
- Special Permission On SPDocument6 pagesSpecial Permission On SPjose moguelNo ratings yet
- Using Group Policy To Deploy Software PackagesDocument9 pagesUsing Group Policy To Deploy Software PackagesManojNo ratings yet
- Group Policy: Fundamentals, Security, and the Managed DesktopFrom EverandGroup Policy: Fundamentals, Security, and the Managed DesktopNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Document4 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Rohan KondeNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Document3 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Rohan KondeNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Experiment No. 2 Title: Perform Backup and Restore of The System. Performing Backup StepsDocument2 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Experiment No. 2 Title: Perform Backup and Restore of The System. Performing Backup StepsRohan KondeNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Title: A) - Install and Configure Antivirus Software On SystemDocument4 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Title: A) - Install and Configure Antivirus Software On SystemRohan KondeNo ratings yet
- MNFSTDocument8 pagesMNFSTakimoriNo ratings yet
- ECW Workstation and Windows SettingsDocument4 pagesECW Workstation and Windows SettingsÂn Lê ThiênNo ratings yet
- Compu-Zone Hardware - 20-05-2020Document2 pagesCompu-Zone Hardware - 20-05-2020JP Ast100% (1)
- Chapter 17 - Transient Stability AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 17 - Transient Stability AnalysisAbhijeet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Online Manual: DrivewizardDocument129 pagesOnline Manual: DrivewizardLP MaxNo ratings yet
- First Steps - With - ShotcutDocument17 pagesFirst Steps - With - ShotcutEmannuel FernandesNo ratings yet
- How To Reset Autocad To Defaults: SupportDocument4 pagesHow To Reset Autocad To Defaults: SupportYudhiHermantoSimbolonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Advanced User Interface Enhancement in WinFormsDocument50 pagesChapter 2-Advanced User Interface Enhancement in WinFormsTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- How To Use The KeyboardDocument5 pagesHow To Use The KeyboardHanz Andre ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- HI Hello WorldDocument11 pagesHI Hello WorldYousuf ShahNo ratings yet
- Kosp User ManualDocument6 pagesKosp User ManualNguyen Duc BinhNo ratings yet
- Advanced Excel HandbookDocument71 pagesAdvanced Excel HandbookChiduNo ratings yet
- Hud SightDocument7 pagesHud Sightshivang sharmaNo ratings yet
- Practical Workbook CS-101/CS-113 (PHY/TC/EL/BM) : Introduction To ComputingDocument82 pagesPractical Workbook CS-101/CS-113 (PHY/TC/EL/BM) : Introduction To ComputingAbdullah HassanNo ratings yet
- Centum VP Graphics Lesson 9: Objectives of This LessonDocument28 pagesCentum VP Graphics Lesson 9: Objectives of This LessonadamsNo ratings yet
- Windows 10 RedStone 3 AIO Full Version Terbaru - BAGAS31Document6 pagesWindows 10 RedStone 3 AIO Full Version Terbaru - BAGAS31Juniatus Cornelis Talibura TubulauNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Mimaki Engineering Co., LTDDocument176 pagesOperation Manual: Mimaki Engineering Co., LTDPablo SoberanisNo ratings yet
- Sabrina Sjahputra CVDocument2 pagesSabrina Sjahputra CVapi-298367672No ratings yet
- Vikas ResumeDocument2 pagesVikas ResumeVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document22 pagesModule 4Sanjana PrakashNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Base 8156 - Mass Deployment of The ClickShare Desktop App (Version 4.28 and Higher) Across Your CompanyDocument2 pagesKnowledge Base 8156 - Mass Deployment of The ClickShare Desktop App (Version 4.28 and Higher) Across Your Companycat dogNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 3 Computer Practice Worksheet (11) - With AnswersDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 3 Computer Practice Worksheet (11) - With AnswersRajesh Singh67% (9)
- Spatix ManualDocument50 pagesSpatix ManualGutiérrez SalasNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument27 pagesDX DiagHudson Cristiano OliveiraNo ratings yet
- HoverSelect Quickcard - English - v1.2 - 27 Nov 13Document5 pagesHoverSelect Quickcard - English - v1.2 - 27 Nov 13arquibotimagineNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Practice ActivitiesDocument3 pagesEXCEL Practice Activitiescatalina doogaruNo ratings yet
- 01 Eh5500 1 3kvaDocument1 page01 Eh5500 1 3kvasales sumberrejekiNo ratings yet
Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52
Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52
Uploaded by
Rohan Konde0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesThe document describes the steps to assign file/folder permissions using Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in Windows. It involves creating a new GPO, navigating to the file system settings, adding the file/folder, configuring permissions, auditing and ownership settings, applying the settings, linking the GPO to a domain, and enforcing the GPO. The 24 step process allows assigning detailed access permissions to files and folders using GPOs for centralized management.
Original Description:
Original Title
acn 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the steps to assign file/folder permissions using Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in Windows. It involves creating a new GPO, navigating to the file system settings, adding the file/folder, configuring permissions, auditing and ownership settings, applying the settings, linking the GPO to a domain, and enforcing the GPO. The 24 step process allows assigning detailed access permissions to files and folders using GPOs for centralized management.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52
Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52
Uploaded by
Rohan KondeThe document describes the steps to assign file/folder permissions using Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in Windows. It involves creating a new GPO, navigating to the file system settings, adding the file/folder, configuring permissions, auditing and ownership settings, applying the settings, linking the GPO to a domain, and enforcing the GPO. The 24 step process allows assigning detailed access permissions to files and folders using GPOs for centralized management.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Name: Rohan Konde
Roll No:52
Experiment No. 4
Topic: Apply security to file folder or application using access permissions
and verify
Steps to Assign File/Folder Permissions
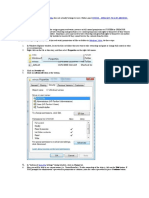
1. Go to “Start Menu” ➔ “Administrative Tools”, and click “Group Policy Management”
to access its console.
2. In left panel of “Group Policy Management Console”, you have to create a new
Group Policy Object or edit an existing Group Policy Object.
3. To create a new GPO, right click “Group Policy Objects”, and select “New” from the
context menu. It shows “New GPO” window.
Figure 1: Creating a new GPO
4. Enter a name for the Group Policy Object (GPO) (in this case it is Assigning
Folder Permissions), leave “Source Starter GPO” as “(none)”.
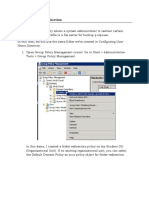
5. Right-click on the newly created “User Folder Permissions” GPO, and select “Edit
GPO”. Group Policy Management Editor window appears on the screen
6. Navigate to “Computer Configuration” ➔ “Policies” ➔ “Windows Settings” ➔
“Security Settings” ➔ “File System”
Figure 2: Navigate to File System
7. Right-click on “File System” in the left pane and select “Add File…” It shows the
following dialog box. Figure 3: Select
file or folder
which you want to assign permissions on
8. Browse the folder or file that you wish to assign permissions on, and left click to select it.
Click “OK”.
9. “Database Security” window appears on the screen
Figure 4: Database security window
10. Click “Advanced” button to access “Advanced Security Settings” window. Stay on
the “Permissions” tab that appears by default.
Figure 5: Advanced security settings window
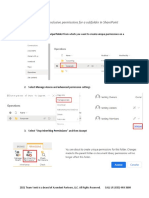
11. On this tab, either select an existing user and click “Edit…” or click “Add…” to add a
new user to the permissions.
12. “Permissions Entry for…” dialog box opens up. Here, you will see that there is a list of
permissions available for your users, and you can also choose where you want to apply those
permissions.
Figure 6: Permissions entry folders
13. Use the drop-down menu in the “Apply to” field to assign selected permissions to desired
folders.
14. Check the permissions as needed. These are self-explanatory.
15. Click “OK” to apply the permissions. It takes you back to “Advanced Security” window.
16. Now, move to the “Auditing” tab. Under this tab, you can do audit settings for the folder, so
that any change done to this folder or its permission will be audited. Configure the auditing
settings as per requirement.
17. Similarly, you can do ownership settings for the folder under “Owner” tab.
18. Once you have done “Permission”, “Auditing” and “Ownership” settings, click “OK”
to close “Advanced Security…” window.
19. Click “OK” to close “Database Security…” window. Next, you will see “Add Object”
window.
20. Figure 7: Add object window
21. There are three options on the “Add Object” window:
a. Configure this file or folder then: Select this option to apply the settings. It contains
the following two options.
i. Propagate inheritable permissions to all subfolders and files: Selecting this
option means, all the subfolders and files will inherit permissions from the parent
folder. In case of a mismatch or conflict, explicit permissions that were assigned
to the subfolders or files will override the inherited permissions.
ii. Replace existing permissions on all subfolders and files with inheritable
permissions: This option will overwrite all the settings on all subfolders and files
with the ones on the parent, so ultimately they will have identical permissions to the
parent folder.
b. Do not allow permissions on this file or folder to be replaced: Use this setting for
subfolders and files that you do not want to inherit permissions. For this, make an
additional entry for those subfolders and files that will not inherit permissions e.g. let’s
say you want the “A” folder to inherit permission but don’t want “B” folder to inherit
permissions, in that case create an entry for the “B” folder.
NOTE: In this case, option “a” has been selected. Click “OK” to close the “Add Object”
window.
22. Close “Group Policy Management Editor” window.
23. Right-click the domain you want to apply this GPO to, and then select “Link
an Existing GPO…” option from the context menu. “Select GPO” window
opens up.
Figure 8: Select the new GPO
24. Select the new “Assigning Folder Permissions” GPO, then click OK.
25. In the right pane, stay on the “Linked Group Policy Objects” tab that appears by
default.
26. Right-click on the “Assigning Folder Permissions”, and select “Enforced” from
the context menu. A confirmation message appears on the screen.
27. Click “OK” to close the dialog box.
You might also like
- ProductDefInterface FixDocument3 pagesProductDefInterface FixPARAS BAJAJNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 AutomobileManagement Using LINQ and WinFormsDocument19 pagesLab 01 AutomobileManagement Using LINQ and WinFormsnobiNo ratings yet
- O Jogo - Neil StraussDocument450 pagesO Jogo - Neil StraussEdson Costa83% (6)
- Lab 5 - Creating and Configuring Group Policy ObjectsDocument7 pagesLab 5 - Creating and Configuring Group Policy ObjectsNM ThânNo ratings yet
- Select Group Policy Management From The Tools Dropdown ListDocument7 pagesSelect Group Policy Management From The Tools Dropdown ListshairaNo ratings yet
- Window Vista Hacking (Taking Ownership)Document4 pagesWindow Vista Hacking (Taking Ownership)Abhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Create A Folder Redirection Security GroupDocument7 pagesStep 1: Create A Folder Redirection Security Grouprobertson_izeNo ratings yet
- The Office Professional 2007Document3 pagesThe Office Professional 2007Jegatheesh JakeNo ratings yet
- Prno 15Document5 pagesPrno 15Vishal Suresh KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Whatfix Deployment Document - GroupPolicyDocument12 pagesWhatfix Deployment Document - GroupPolicythiagoomNo ratings yet
- Few ExamplesDocument3 pagesFew Examplessambradshaw945No ratings yet
- Enable File Access Auditing in WindowsDocument7 pagesEnable File Access Auditing in WindowsAdrianApostolNo ratings yet
- Expt 4Document12 pagesExpt 4aniketNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Amazon Simple Storage (S3)Document11 pagesLab 1 - Amazon Simple Storage (S3)Hector AndradeNo ratings yet
- Configuring NetWeaver Development Infrastructure (NWDI) in Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence (MII) - Development ComponentDocument30 pagesConfiguring NetWeaver Development Infrastructure (NWDI) in Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence (MII) - Development Componenteeha0120No ratings yet
- Greyhound: A) Code B) Database C)Document2 pagesGreyhound: A) Code B) Database C)Rahul TonapeNo ratings yet
- Creating IBM Cloud Object StorageDocument11 pagesCreating IBM Cloud Object StorageMalabana Pantoja Maria LeahNo ratings yet
- Gina Gpo Installation GuideDocument19 pagesGina Gpo Installation GuideSojan MathewNo ratings yet
- JanusWindows 8Document1 pageJanusWindows 8cobalt_cannonNo ratings yet
- Establishing File SharingDocument9 pagesEstablishing File SharingSenthil NathanNo ratings yet
- 11.6.2.4 Lab - System Restore and Hard Drive BackupDocument7 pages11.6.2.4 Lab - System Restore and Hard Drive BackupRidwan FahmiNo ratings yet
- Folder Redirection: STEP 1: Create Organization Unit (OU)Document9 pagesFolder Redirection: STEP 1: Create Organization Unit (OU)Joel CuyuganNo ratings yet
- Auto CadDocument16 pagesAuto CadKumanLowNo ratings yet
- Questões de LaboratórioDocument15 pagesQuestões de LaboratórioQue Bacana Presentes PersonalizadosNo ratings yet
- ITP4406 - Lab07 (Depoly Software by GP and GP Central Store) v5Document7 pagesITP4406 - Lab07 (Depoly Software by GP and GP Central Store) v5rickyNo ratings yet
- Controlling Access To Local Hardware and Applications: This Lab Contains The Following Exercises and ActivitiesDocument9 pagesControlling Access To Local Hardware and Applications: This Lab Contains The Following Exercises and ActivitiesMD4733566No ratings yet
- BCSL 063 Solved Assignment 2022 23 UlptmtDocument15 pagesBCSL 063 Solved Assignment 2022 23 UlptmtShubham SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Windows Group Policy InterviewWindows Group Policy Interview Questions QuestionsDocument4 pagesWindows Group Policy InterviewWindows Group Policy Interview Questions QuestionsRaja Mozumder0% (1)
- Data DomainDocument11 pagesData DomainAsma RizwanNo ratings yet
- Submitting Written and Video AssignmentsDocument2 pagesSubmitting Written and Video AssignmentsKalpattyNo ratings yet
- Fix: Cannot Access Network Shares After Update 1709: Try GCP FreeDocument7 pagesFix: Cannot Access Network Shares After Update 1709: Try GCP FreeFrusinoiu CristinaNo ratings yet
- NW Admin Lab Exercise 3-2Document3 pagesNW Admin Lab Exercise 3-2xyzalimohamed76No ratings yet
- (2165338) Azure Assignment 2Document12 pages(2165338) Azure Assignment 2Kiran KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Backtomyvillage: A) Code B) Data Base C)Document2 pagesBacktomyvillage: A) Code B) Data Base C)Supreeti KoneruNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15-16 File Service FinalDocument5 pagesExercise 15-16 File Service FinalAlexis LarosaNo ratings yet
- Defect Tracking System: A) Code B) Data Base C)Document2 pagesDefect Tracking System: A) Code B) Data Base C)Eric HernandezNo ratings yet
- Fleet Management System: A) Code B) Data Base C)Document3 pagesFleet Management System: A) Code B) Data Base C)ethanlevin213No ratings yet
- Process of Create The New CIGAS Executable FileDocument12 pagesProcess of Create The New CIGAS Executable Filekalana heshanNo ratings yet
- Things To FollowDocument3 pagesThings To FollowsanjaykumarguptaaNo ratings yet
- -Document8 pages-Dewi Puspita sariningsihNo ratings yet
- How To Delete Files Protected by TrustedInstallerDocument7 pagesHow To Delete Files Protected by TrustedInstallerhighmountainbearNo ratings yet
- EncryptionDocument1 pageEncryptionAurang Zeb SheikhNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Create and Configure A Package: 118 Packages Create Package Next Model Presentation View Sales Target Sales NextDocument6 pages4.5 Create and Configure A Package: 118 Packages Create Package Next Model Presentation View Sales Target Sales NextHarry KonnectNo ratings yet
- Manage Media in DriveDocument4 pagesManage Media in DriveCyril Danica LimareNo ratings yet
- Expt 4Document3 pagesExpt 4nagbalidhumal.2005No ratings yet
- How To Integrate Firefox With Windows Group PolicyDocument14 pagesHow To Integrate Firefox With Windows Group PolicyDragan LakovskiNo ratings yet
- Deploy Folder Redirection With Offline Files - Microsoft DocsDocument9 pagesDeploy Folder Redirection With Offline Files - Microsoft DocsAggrey-Anthony DuncanNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Shared Database: An Example Using Postgresql and Pgadmin4Document19 pagesHow To Create A Shared Database: An Example Using Postgresql and Pgadmin4Freddy IANo ratings yet
- Win7 FixDocument7 pagesWin7 FixThomas KuzinasNo ratings yet
- 2274b Mod09 LADocument10 pages2274b Mod09 LALuis RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Changes To Group Policy: Windows Server 2008 Directory ServicesDocument26 pagesChanges To Group Policy: Windows Server 2008 Directory ServicesMoldoveanu Horia MihailNo ratings yet
- Carrier Path: A) Code B) Database C)Document2 pagesCarrier Path: A) Code B) Database C)Shashi CampherNo ratings yet
- Google Drive InstructionsDocument17 pagesGoogle Drive InstructionsDAYTABASE TheProducerNo ratings yet
- Simple File ServerDocument9 pagesSimple File ServerAbigail PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Assigning Software: Create A Distribution PointDocument4 pagesAssigning Software: Create A Distribution PointthebukiNo ratings yet
- Tasksheet 9 Configure Folder RedirectionDocument4 pagesTasksheet 9 Configure Folder RedirectionClark DomingoNo ratings yet
- SIL Solver Pre-Installation Procedure v6 CombinedDocument7 pagesSIL Solver Pre-Installation Procedure v6 CombinedMarcio GranatoNo ratings yet
- HelpFile FiltercraveDocument3 pagesHelpFile FiltercraveHandoko MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Windows 10 Version 1709 - CFA IssueDocument6 pagesWindows 10 Version 1709 - CFA Issuejan2No ratings yet
- Special Permission On SPDocument6 pagesSpecial Permission On SPjose moguelNo ratings yet
- Using Group Policy To Deploy Software PackagesDocument9 pagesUsing Group Policy To Deploy Software PackagesManojNo ratings yet
- Group Policy: Fundamentals, Security, and the Managed DesktopFrom EverandGroup Policy: Fundamentals, Security, and the Managed DesktopNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Document4 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Rohan KondeNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Document3 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52Rohan KondeNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Experiment No. 2 Title: Perform Backup and Restore of The System. Performing Backup StepsDocument2 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Experiment No. 2 Title: Perform Backup and Restore of The System. Performing Backup StepsRohan KondeNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Title: A) - Install and Configure Antivirus Software On SystemDocument4 pagesName: Rohan Konde Roll No:52: Title: A) - Install and Configure Antivirus Software On SystemRohan KondeNo ratings yet
- MNFSTDocument8 pagesMNFSTakimoriNo ratings yet
- ECW Workstation and Windows SettingsDocument4 pagesECW Workstation and Windows SettingsÂn Lê ThiênNo ratings yet
- Compu-Zone Hardware - 20-05-2020Document2 pagesCompu-Zone Hardware - 20-05-2020JP Ast100% (1)
- Chapter 17 - Transient Stability AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 17 - Transient Stability AnalysisAbhijeet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Online Manual: DrivewizardDocument129 pagesOnline Manual: DrivewizardLP MaxNo ratings yet
- First Steps - With - ShotcutDocument17 pagesFirst Steps - With - ShotcutEmannuel FernandesNo ratings yet
- How To Reset Autocad To Defaults: SupportDocument4 pagesHow To Reset Autocad To Defaults: SupportYudhiHermantoSimbolonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Advanced User Interface Enhancement in WinFormsDocument50 pagesChapter 2-Advanced User Interface Enhancement in WinFormsTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- How To Use The KeyboardDocument5 pagesHow To Use The KeyboardHanz Andre ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- HI Hello WorldDocument11 pagesHI Hello WorldYousuf ShahNo ratings yet
- Kosp User ManualDocument6 pagesKosp User ManualNguyen Duc BinhNo ratings yet
- Advanced Excel HandbookDocument71 pagesAdvanced Excel HandbookChiduNo ratings yet
- Hud SightDocument7 pagesHud Sightshivang sharmaNo ratings yet
- Practical Workbook CS-101/CS-113 (PHY/TC/EL/BM) : Introduction To ComputingDocument82 pagesPractical Workbook CS-101/CS-113 (PHY/TC/EL/BM) : Introduction To ComputingAbdullah HassanNo ratings yet
- Centum VP Graphics Lesson 9: Objectives of This LessonDocument28 pagesCentum VP Graphics Lesson 9: Objectives of This LessonadamsNo ratings yet
- Windows 10 RedStone 3 AIO Full Version Terbaru - BAGAS31Document6 pagesWindows 10 RedStone 3 AIO Full Version Terbaru - BAGAS31Juniatus Cornelis Talibura TubulauNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Mimaki Engineering Co., LTDDocument176 pagesOperation Manual: Mimaki Engineering Co., LTDPablo SoberanisNo ratings yet
- Sabrina Sjahputra CVDocument2 pagesSabrina Sjahputra CVapi-298367672No ratings yet
- Vikas ResumeDocument2 pagesVikas ResumeVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document22 pagesModule 4Sanjana PrakashNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Base 8156 - Mass Deployment of The ClickShare Desktop App (Version 4.28 and Higher) Across Your CompanyDocument2 pagesKnowledge Base 8156 - Mass Deployment of The ClickShare Desktop App (Version 4.28 and Higher) Across Your Companycat dogNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 3 Computer Practice Worksheet (11) - With AnswersDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 3 Computer Practice Worksheet (11) - With AnswersRajesh Singh67% (9)
- Spatix ManualDocument50 pagesSpatix ManualGutiérrez SalasNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument27 pagesDX DiagHudson Cristiano OliveiraNo ratings yet
- HoverSelect Quickcard - English - v1.2 - 27 Nov 13Document5 pagesHoverSelect Quickcard - English - v1.2 - 27 Nov 13arquibotimagineNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Practice ActivitiesDocument3 pagesEXCEL Practice Activitiescatalina doogaruNo ratings yet
- 01 Eh5500 1 3kvaDocument1 page01 Eh5500 1 3kvasales sumberrejekiNo ratings yet