Professional Documents
Culture Documents
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
Uploaded by
PARAM JOSHIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
Uploaded by
PARAM JOSHICopyright:
Available Formats
K. J.
Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
Batch: B4 Roll No.: 1821015
Experiment No. 02
Grade: AA / AB / BB / BC / CC / CD /DD
Signature of the Staff In-charge with date
Batch: B4 Roll No.: 1821015 Experiment / Assignment / Tutorial No.: 2
Title: Introduction to Virtualization & its application using VMware player, KVM.
(i) Virtualization on Windows using VMWare player/Oracle Virtual Box.
(ii) Virtualization on Ubuntu using KVM.
Objective:Use of VirtualBox / VMware / KVM for understanding the concept of virtualization.
CO1: Understand the fundamentals of Open Source environment
______________________________________________________________________
Expected Outcome of Experiment:
1. Understand the fundamentals of virtualization in Open source environment.
_____________________________________________________________________
Books/ Journals/ Websites referred:
1. https://www.vmware.com/in/products/workstation-player.html
2. https://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page
_____________________________________________________________________
Pre Lab/ Prior Concepts:
Basic concepts of operating system and its setup.
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 1 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
Introduction
Before discussing the different categories of virtualization in detail, it is useful to define the
term in the abstract sense. In computing, virtualization is a broad term that refers to the
abstraction of computer resources. Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of
computing resources from their users, be they applications, or end users. This includes making
a single physical resource (such as a server, an operating system, an application, or storage
device) appear to function as multiple virtual resources; it can also include making multiple
physical resources (such as storage devices or servers) appear as a single virtual resource...
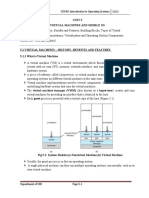
In layman’s terms virtualization is often:
1. The creation of many virtual resources from one physical resource.
2. The creation of one virtual resource from one or more physical resource.
Types of Virtualization
Today the term virtualization is widely applied to a number of concepts including:
Server Virtualization
Client / Desktop / Application Virtualization
Network Virtualization
Storage Virtualization
Service / Application Infrastructure Virtualization
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 2 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
In most of these cases, either virtualizing one physical resource into many virtual resources or
turning many physical resources into one virtual resource is occurring.
VMware Player:
VMware Player is a free desktop application from a company called VMware that runs
on Windows and Linux. This application enables you to create, configure, and run virtual
machines. A virtual machine allows you to run one operating system emulated within another
operating system. For example, you can run a Linux operating system within your Windows OS.
You can create a virtual machine using VMware Player or you can run preconfigured virtual
machines created with VMware Workstation, GSX Server, and ESX Server. On Windows hosts,
you can even run Microsoft Virtual PC virtual machines and Symantec LiveState Recovery
system images.
VMware Player features
VMware Player offers the following features:
1. Virtual machine isolation – you can isolate a virtual machine from the host PC. This way, you
can safely run programs from untrusted sources, without worrying that a virus will hurt your
host computer.
2. Copy and paste features – you can copy and paste text and files between the virtual
machine and the host PC.
3. DHCP server – VMware Player offers a built-in DHCP server.
4. Adjustable memory – virtual machine memory can be optimized for better performance.
5. Support for USB 3.0.
6. Different types of network connection for the virtual machine: bridged, host-only, or NAT.
7. Drag & drop support – you can drag files between a Windows host and a Windows virtual
machine,
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 3 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
KVM
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is a virtualization module in the Linux kernel that
allows the kernel to function as a hypervisor. KVM provides hardware-assisted
virtualization for a wide variety of guest operating systems including Linux, BSD, Additionally,
KVM provides paravirtualization support for Linux, OpenBSD,[12] FreeBSD,[13] NetBSD,[14] Plan
9[15] and Windows guests using the VirtIO[16] API. This includes a paravirtual Ethernet card,
disk I/O controller,[17] balloon device, and a VGA graphics interface
using SPICE or VMware drivers.
KVM provides device abstraction but no processor emulation. It exposes
the /dev/kvm interface, which a user mode host can then use to:
Set up the guest VM's address space. The host must also supply a firmware image (usually a
custom BIOS when emulating PCs) that the guest can use to bootstrap into its main OS.
Feed the guest simulated I/O.
Map the guest's video display back onto the system host.
On Linux, QEMU versions 0.10.1 and later is one such userspace host. QEMU uses KVM when
available to virtualize guests at near-native speeds, but otherwise falls back to software-only
emulation.
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 4 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
Implementation details:
1. Check whether CPU has hardware virtualization support.
2. Install KVM and supporting packages.
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 5 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
3. Create User.
4. Check whether everything is working correctly.
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 6 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
5. Open Virtual Machine Manager application and Create Virtual Machine
6. Create and run Virtual Machines
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 7 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
7. Locate your install media
8. Choose memory and CPU Setting
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 8 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
9. Enable Storage for the virtual machine
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 9 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
10. Ready to begin the installation
11. Windows Screen appears
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 10 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
12. Click on the install now option
13. Installing Windows
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 11 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
14. Choose a username for your account
15. Set a password for your account
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 12 OSL/JAN 20
K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77
(Autonomous College Affiliated to University of Mumbai)
16. Windows desktop appears
Conclusion: Thus we learned about Virtualization & its application using VMware player, KVM.
Department of Computer Engineering
Page No. 13 OSL/JAN 20
You might also like
- Sephora Brand AuditDocument30 pagesSephora Brand Auditapi-294767507100% (2)
- Fonterra and Talent ManagementDocument36 pagesFonterra and Talent ManagementEmma Allison100% (1)
- Metrics For Responsible Property Investing: Developing and Maintaining A High Performance PortfolioDocument43 pagesMetrics For Responsible Property Investing: Developing and Maintaining A High Performance PortfolioLisa Michelle GalleyNo ratings yet
- Amilan® CM3001G30Document3 pagesAmilan® CM3001G30agungNo ratings yet
- Globelics Athens 2017 Program BookletDocument60 pagesGlobelics Athens 2017 Program BookletIsrael Sanches Marcellino100% (1)
- ITIL®4 Reference Guide: General Management Practices (14) Service Management PracticesDocument1 pageITIL®4 Reference Guide: General Management Practices (14) Service Management PracticesStanley Ke BadaNo ratings yet
- Raj Agrawal - Expt-5 - VAPTDocument9 pagesRaj Agrawal - Expt-5 - VAPTraj.maNo ratings yet
- Cloud Lab Record 1Document81 pagesCloud Lab Record 1Velan GNo ratings yet
- Surveyof Server VirtualizationDocument11 pagesSurveyof Server VirtualizationVIVENCIONo ratings yet
- Operating System Support For Virtual MachinesDocument14 pagesOperating System Support For Virtual MachinesLuciNo ratings yet
- Surveyof Server VirtualizationDocument11 pagesSurveyof Server VirtualizationVIVENCIONo ratings yet
- Cloud Lab RecordDocument54 pagesCloud Lab RecordVelan GNo ratings yet
- Exp 9Document9 pagesExp 9Peeyush ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document7 pagesExperiment 2Shruti TyagiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machine SeminarDocument37 pagesVirtual Machine SeminarVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- 113 CC Exp1Document29 pages113 CC Exp1Arpan SoniNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 - Virtualization Using VMWare WorkstationDocument4 pagesLab 8 - Virtualization Using VMWare WorkstationraytamsNo ratings yet
- Empirical Study of Virtual Disks Performance With KVM On DasDocument8 pagesEmpirical Study of Virtual Disks Performance With KVM On Dasshaahin13631363No ratings yet
- An Architectural Perspective For Cloud Virtualization: Yiming Zhang Qiao Zhou Dongsheng Li Kai Yu Chengfei ZhangDocument8 pagesAn Architectural Perspective For Cloud Virtualization: Yiming Zhang Qiao Zhou Dongsheng Li Kai Yu Chengfei ZhangChris DwarfNo ratings yet
- Bromium Micro-VirtualizationDocument8 pagesBromium Micro-VirtualizationDadeNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is A Virtual Machine?Document2 pages1) What Is A Virtual Machine?Beatriz GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 8709Document4 pagesNI Tutorial 8709newscop1No ratings yet
- Weekly Seminar Presentation by Anirban Basumallik, M.Tech 2, ERTS Lab, IIT Bombay. 2 September, 2010Document12 pagesWeekly Seminar Presentation by Anirban Basumallik, M.Tech 2, ERTS Lab, IIT Bombay. 2 September, 2010shrekbkNo ratings yet
- Uptane: Securing Software Updates For AutomobilesDocument11 pagesUptane: Securing Software Updates For AutomobilesLaroyNo ratings yet
- OS Assignment 1Document5 pagesOS Assignment 1Usama Nasir GillNo ratings yet
- Darjeeling, A Feature-Rich VM For The Resource Poor: Niels Brouwers Koen Langendoen Peter CorkeDocument14 pagesDarjeeling, A Feature-Rich VM For The Resource Poor: Niels Brouwers Koen Langendoen Peter Corkejoseph.stewart9331No ratings yet
- An Exhaustive Survey On Security Concerns and Solutions at Different Components of VirtualizationDocument38 pagesAn Exhaustive Survey On Security Concerns and Solutions at Different Components of Virtualizationjaime_parada3097No ratings yet
- Department of Software Engineering Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, JamshoroDocument8 pagesDepartment of Software Engineering Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, JamshoroUnzilla AliNo ratings yet
- Bringing Virtualization To The X86 Architecture With The Original Vmware WorkstationDocument51 pagesBringing Virtualization To The X86 Architecture With The Original Vmware WorkstationYogirajNo ratings yet
- Using Cooja For WSN Simulations: Some New Uses and Limits: Kévin Roussel Ye-Qiong Song Olivier ZendraDocument6 pagesUsing Cooja For WSN Simulations: Some New Uses and Limits: Kévin Roussel Ye-Qiong Song Olivier Zendramuhammad naufalNo ratings yet
- 19 Virtualizationppt 2550Document45 pages19 Virtualizationppt 2550RohnikiNo ratings yet
- Patch Auditing in Infrastructure As A Service Clouds: Lionel Litty David LieDocument11 pagesPatch Auditing in Infrastructure As A Service Clouds: Lionel Litty David LiepulaksayNo ratings yet
- I2v Pov AvDocument9 pagesI2v Pov AvNIRMALYA_NJRCSNo ratings yet
- CG PecDocument66 pagesCG PecAFTAB AHMED QURESHINo ratings yet
- Virtualization SurveyDocument5 pagesVirtualization SurveypalashahujaNo ratings yet
- Uses of Virtualization: Innovating in ITDocument20 pagesUses of Virtualization: Innovating in ITsrikanthm44No ratings yet
- Identifying and Analyzing Security Threats To Virtualized Cloud Computing InfrastructuresDocument5 pagesIdentifying and Analyzing Security Threats To Virtualized Cloud Computing InfrastructuresIBM222No ratings yet
- Automated Dynamic Firmware Analysis at Scale - A Case Study On Embedded Web InterfacesDocument12 pagesAutomated Dynamic Firmware Analysis at Scale - A Case Study On Embedded Web InterfacesdeinemamaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machine Security Challenges: Case StudiesDocument14 pagesVirtual Machine Security Challenges: Case StudiesShaurya KapoorNo ratings yet
- What Is Virtual Machine EscapeDocument2 pagesWhat Is Virtual Machine EscapesjmpakNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machines and Networks - Installation, Performance, Study, Advantages and Virtualization OptionsDocument16 pagesVirtual Machines and Networks - Installation, Performance, Study, Advantages and Virtualization OptionsMichael SavannaNo ratings yet
- Exp3 - 71, 76, 81 - Kaustubh, Mihir, ZenilDocument10 pagesExp3 - 71, 76, 81 - Kaustubh, Mihir, ZenilCHINTAN MODINo ratings yet
- Dobrilović, Odadžić - Virtualization Technology As A Tool For Teaching Computer Networks (2008)Document5 pagesDobrilović, Odadžić - Virtualization Technology As A Tool For Teaching Computer Networks (2008)Kresimir RakicNo ratings yet
- 1 Virtualization Technology Literature ReviewDocument9 pages1 Virtualization Technology Literature Reviewyo yoNo ratings yet
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Document10 pagesIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report: University Institute of Engineering and Technology Kurukshetra UniversityDocument28 pagesSummer Training Report: University Institute of Engineering and Technology Kurukshetra UniversityAnonymous 3RUfcbAhqdNo ratings yet
- Bishal Paudyal 159202209: ICO155 Lab 2 - Virtualization Part 1Document7 pagesBishal Paudyal 159202209: ICO155 Lab 2 - Virtualization Part 1Be InnovativeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1letitolesa472No ratings yet
- CCA 1st SchemeDocument7 pagesCCA 1st SchemegangambikaNo ratings yet
- InProc ComponentsDocument57 pagesInProc Componentssangeethaag19No ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Keamanan Siber - Tugas 1 - Kelas C - Kelompok 3Document20 pagesLaporan Praktikum Keamanan Siber - Tugas 1 - Kelas C - Kelompok 3I Gede Arie Yogantara SubrataNo ratings yet
- Tech Note 656 - Building Wonderware Solutions On VMwareDocument13 pagesTech Note 656 - Building Wonderware Solutions On VMwareMichael MavenekaNo ratings yet
- Shivani 232 PDFDocument17 pagesShivani 232 PDFdigNo ratings yet
- Virtual MachineDocument8 pagesVirtual MachineSrinivas Rapelli0% (1)
- Application Delivery With Mesosphere DCOSDocument110 pagesApplication Delivery With Mesosphere DCOSaaaaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Virtual Machines and Virtualization of Clusters and Data CentersDocument28 pagesUnit - 2 Virtual Machines and Virtualization of Clusters and Data CentersAkkireddi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document36 pagesUnit 5AmudariaNo ratings yet
- COA Lab Journal 2022-23Document50 pagesCOA Lab Journal 2022-23VIRAL FARIANo ratings yet
- Core JavaDocument108 pagesCore JavaRohnak AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Caracas 2009Document9 pagesCaracas 2009Minh LongNo ratings yet
- CS-223Quiz 1Document3 pagesCS-223Quiz 1Ayesha RahimNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science DepartmentDocument12 pagesElectrical Engineering and Computer Science Departmenteecs.northwestern.eduNo ratings yet
- Design A Mini Operating System Using Open Source SystemDocument13 pagesDesign A Mini Operating System Using Open Source SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Windows Virtual Machines On A Linux HostDocument12 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Windows Virtual Machines On A Linux HostEdson LivongueNo ratings yet
- Storage Optimization with Unity All-Flash Array: Learn to Protect, Replicate or Migrate your data across Dell EMC Unity Storage and UnityVSAFrom EverandStorage Optimization with Unity All-Flash Array: Learn to Protect, Replicate or Migrate your data across Dell EMC Unity Storage and UnityVSARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Application of Cloud Computing Technology in Metal ExplorationDocument4 pagesApplication of Cloud Computing Technology in Metal ExplorationPARAM JOSHINo ratings yet
- $Ssolfdwlrqriforxgfrpsxwlqjwhfkqrorj/Lqphwdo H (SorudwlrqDocument4 pages$Ssolfdwlrqriforxgfrpsxwlqjwhfkqrorj/Lqphwdo H (SorudwlrqPARAM JOSHINo ratings yet
- K. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77Document26 pagesK. J. Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai-77PARAM JOSHINo ratings yet
- DCC Exp 7Document25 pagesDCC Exp 7PARAM JOSHINo ratings yet
- Database Intrusion Detection SystemDocument4 pagesDatabase Intrusion Detection SystemPARAM JOSHI0% (1)
- Ece 255 Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design Fall 2017: Division 2: Chew TR 1:30PM - 2:45PM ECE 170Document3 pagesEce 255 Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design Fall 2017: Division 2: Chew TR 1:30PM - 2:45PM ECE 170Dildar Khan BhatiNo ratings yet
- Inspection Design and Inspector BehaviorDocument32 pagesInspection Design and Inspector BehavioryachamidNo ratings yet
- Ryzen Price 22 08 15Document3 pagesRyzen Price 22 08 15Jhover BernalNo ratings yet
- Wills and Succession Reviewer 1Document3 pagesWills and Succession Reviewer 1Richard Allan Lim100% (1)
- Motstart Three-Phase Start-Up Supervision For Motors: 1Mrs752307-MumDocument16 pagesMotstart Three-Phase Start-Up Supervision For Motors: 1Mrs752307-MumrajeshNo ratings yet
- HP CNB Price List User - 20 Agustus 2014Document2 pagesHP CNB Price List User - 20 Agustus 2014begudulNo ratings yet
- PL SQLDocument12 pagesPL SQLIsha ThakreNo ratings yet
- Pension Gratuity Management Center vs. AAA (Full Text, Word Version)Document9 pagesPension Gratuity Management Center vs. AAA (Full Text, Word Version)Emir MendozaNo ratings yet
- Keyman Insurance Lic India PolicyDocument2 pagesKeyman Insurance Lic India PolicyPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDaniella A. LazaroNo ratings yet
- Cleaning of Water BodiesDocument14 pagesCleaning of Water BodiesSaiTimmaraoNo ratings yet
- Pradeep Chandelia: Sub: Appropriate Career Opening in Your Esteemed OrganizationDocument4 pagesPradeep Chandelia: Sub: Appropriate Career Opening in Your Esteemed OrganizationSajidZiaNo ratings yet
- IsmailDocument25 pagesIsmailMubarak BegumNo ratings yet
- Max Diff TechDOcDocument21 pagesMax Diff TechDOcNeri David MartinezNo ratings yet
- Markes Nicole Resume Online PortfolioDocument2 pagesMarkes Nicole Resume Online Portfolioapi-283615713No ratings yet
- ValvesDocument87 pagesValvesbaishakhi_b90100% (3)
- MEIC 56905 Andre Viegas DissertacaoDocument58 pagesMEIC 56905 Andre Viegas DissertacaoCabdirisaq Xusen CaliNo ratings yet
- Calculated Uncertainty of Temperature Due To The Size-of-Source EffectDocument8 pagesCalculated Uncertainty of Temperature Due To The Size-of-Source EffectRONALD ALFONSO PACHECO TORRESNo ratings yet
- 6.5.2.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Static Routes Instructions PDFDocument2 pages6.5.2.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Static Routes Instructions PDFaakash muthurama lingamNo ratings yet
- C++: A General Purpose Language and LibraryDocument24 pagesC++: A General Purpose Language and LibrarySobar KhanNo ratings yet
- EE-211 Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument28 pagesEE-211 Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherHadeedAhmedSherNo ratings yet
- 2-Behavioral Biases Influencing The Decision Making of Portfolio Managers of Capital Securities and Traders in MoroccoDocument14 pages2-Behavioral Biases Influencing The Decision Making of Portfolio Managers of Capital Securities and Traders in MoroccoBebe Recah SacedaNo ratings yet
- D4N Mini Safety Limit Switch C130 E1 01 DsDocument24 pagesD4N Mini Safety Limit Switch C130 E1 01 DsciprianNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For A Chemical Spill Into A RiverDocument11 pagesRisk Assessment For A Chemical Spill Into A RiverWayne GajadharNo ratings yet