Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 13 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model - 1)
Lecture 13 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model - 1)
Uploaded by
yasar khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views25 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture 13 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model_1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views25 pagesLecture 13 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model - 1)
Lecture 13 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model - 1)
Uploaded by
yasar khanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
SNMP V1 Network Management:
Organization and Information
Models
Video Lecture Links
› https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=spbZmJaoitY&list=PL
4j_fCKQ7Bso1wGplcaF2pcDGeLVCuKHU
› https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-
55DYxgzuEQ&list=PL4j_fCKQ7Bso1wGplcaF2pcDGeLVCu
KHU&index=2
› https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E44m7BSKGc4&list=
PL4j_fCKQ7Bso1wGplcaF2pcDGeLVCuKHU&index=3
(Courtesy: FLAMINGO Project)
› Introduction
› Case Study and Real-Time Example of
OUTLINES SNMP
› SNMP History and Standards
› SNMP Architecture
› Organization Model
› Information Model
– SMI v1 & v2
– MIB I & II
INTRODUCTION
Introduction (1)
› SNMP management refers as Internet management but it
manage more than internet such as
– Intranet and telecommunication networks
– Any network using TCP/IP suite
– Non-TCP/IP network elements using proxy agents
› SNMP is widely used NMS
– Network element has built-in agent, which respond to NMS
– It can easily start managing the newly added hardware as most of
device have built-in SNMP agent.
– The ease of adding and configuring components, added to its
acceptance and popularity
Introduction (2)
› Initially, SNMP is started as interim set of specifications
– Enhanced by development of v2 & v3
› Power of technology could result in positive and negative
results. HOW?
› NMS could also bring network down. HOW?
› To identify the error using Artificial Intelligence. HOW?
› To identify the network failure reason, which is due to newly
added Interface card, done from NOC. How?
Case Study and Real-
Time Example of SNMP
Case Study – Managed LAN using NMS (1)
› NMS auto-discover the network component as long as it has
management agent
› Management agent could be as simple as it respond to ping
› Modern agents are more sophisticated
› The network shown is configured as
– 1 router with 2 hubs, connecting to a backbone network
› Once a network component is discovered & mapped by NMS
› The system manager can query and acquire on system
parameter and statistic on network element.
CASE STUDY –
MANAGED LAN USING
NMS (1)
Network IP configuration
Router IP: 172.16.46.1
Hub 1 IP: 172.16.46.2
Hub 2 IP: 172.16.46.3
NMS physical and logically
located remotely
configured on LAN
192.168.252.1
NMS IP: 192.168.252.110
CASE STUDY –
MANAGED LAN USING
NMS (2)
No specific names
System Information acquired by
the NMS from the network
elements
Enterprise # 43
Private MIB of 3Com # 1.8.5
Description and Object Id are
factory set
Up timing
CASE STUDY –
MANAGED LAN USING
NMS (3)
Addresses Information
Acquired by an SNMP NMS
History of SNMP
History of SNMP (1)
› SNMP begins in 1970s, ICMP develop to manage ARPANET
› Use to transfer control messages between nodes e-g: PING
› Adopted the name “Internet ”from “ARPANET” in 1984
› With the growth of Internet
– SGMP was developed for remote monitoring
– SNMP is enhancement of SGMP
– SNMP is interim solution, OSI standard CMIP/CMIS was long term
solution
– SNMP become de-facto standard, due to simplicity and extensive
implementation
– SNMPv2 with new features, overcome few limitations of v1.
– SNMPv3 address security features
History of SNMP (2)
› IAB was designed to managed two task forces
– IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
› Protocol engineering, development and standardization
– IRTF (Internet Research Task Force)
› Long and short term research projects related to protocols, application,
architecture and technology
› IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority)
– Responsible for assignment of unique parameters such as
› Internet Address, domain name, autonomous system number, protocol
number, port number, MIB object identifier (private enterprise number) and
many others
History of SNMP (3)
› InterNIC (Internet Network Information Center) maintains
documents such as
– RFC (STD): Specify the Internet standard
– RFC (FYI): For document overview and introductory topics
› Both RFCs are indexed and retrieved by RFC number, with
the addition of unique STD and FYI number
Organization Model
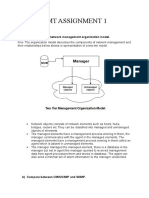
TWO-TIER MODEL
Agent process resides in
managed object
Network manager process
resides in NMS
Agent respond to any
management system using
SNMP
Multiple managers can interact
with agent
Two-Tier Model
› Why the need of multiple managers?
– However, its easy to monitor all objects in the network with the
standard messages
– To configure a system in detail a more intimate knowledge of object
is needed, hence NMS provided by the same vendor could have
more capabilities than another vendor
– It’s common practice to use multiple vendor products and multiple’
NMSs
› Sometimes, temporal data is require rather than continuous
data or we want to look at traffic statistics
THREE-TIER
ORGANIZATION
MODEL
RMON is used, it constantly
monitors the object and send
temporal data to manager
RMON is implemented between
managed object and network
manager
Manager received data from
both RMON and agent directly
Implemented in distributed
fashion on the network, which
greatly increases the central
management of the network
PROXY SERVER
ORGANIZATION
A pure SNMP management
system, to manage a network
element without the SNMP
agent
In cases like outside plant or
equipment in customer
premises
Proxy server is used that
converts data to SNMP
compatible format
NMS BEHAVING AS
AN AGENT AND A
MANAGER
Two NMSs exchange
information when both
networks are connected
through gateway
For example: two customer
service provider wants to
communicate
SNMP Network
Management Architecture
SNMP Network Management Architecture
› It represents the data path between manager and agent
application process via four transport function protocols
UDP, IP, DLC & PHY
› RFC 1157 define SNMP as
– “by which a management information for a network element can be
inspected or altered by logically remote users”
› Communication management information among
management entities is done through five exchange protocol
messages
– Three of those are initiated by the manager process and two by
agent process
SNMP
ARCHITECTURE
Communication is done
thorough 5 (3+2) protocol
messages
Get-Request to the value of the
object
Get-Next-Request to get
multiple instance of the object
Set-Request to initialize or reset
the value of the object
Get-Response a reply to any of
the above two messages
Trap is a unsolicited messages
generated against the event
such as threshold value, link
up/down
SNMP Architecture – MIB & MDB
› MIB (Management Information Base)
– Contains information about the objects
– Virtual and static database
– It is compiled in manager during implementation
– During discovery process MIB need to be their else discovered
object is marked as unidentified
– PING is used to discover the network components
– MIB must be implemented in both manager and agent to acquire the
information such as System Information
› MDB (Managed Database)
– is dynamic and contains measured values associated with objects
(can be implemented using any database architecture)
– Only manager have MDB
You might also like
- Hacker's Manual 2021, 11th EditionDocument164 pagesHacker's Manual 2021, 11th EditionMihai PistruiNo ratings yet
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)Document16 pagesSimple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)elly-naike nkya100% (1)
- Introduction To Quality of Service (QoS)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Quality of Service (QoS)yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 (Chap#5-SNMPv1-Communication and Functional Model)Document22 pagesLecture 15 (Chap#5-SNMPv1-Communication and Functional Model)yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Simple Network Management Protocol: BackgroundDocument8 pagesSimple Network Management Protocol: BackgroundswamisettyramyaNo ratings yet
- Simple Network Management ProtocolDocument41 pagesSimple Network Management Protocolsimon_acc2387No ratings yet
- Network Management Protocol 223 oAm65gUDocument13 pagesNetwork Management Protocol 223 oAm65gUmahendrarm2112No ratings yet
- Simple Network Management ProtocolDocument37 pagesSimple Network Management Protocolgames mediaNo ratings yet
- 6-Network Management SNMPDocument31 pages6-Network Management SNMPabdirahmanNo ratings yet
- NMT Assignment 1: Q1) A) Explain Two-Tier Network Management Organization ModelDocument12 pagesNMT Assignment 1: Q1) A) Explain Two-Tier Network Management Organization ModelTarun HarjaniNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 SNMPDocument20 pagesLec 6 SNMPbgodfreyaNo ratings yet
- RFC 2570Document23 pagesRFC 2570chetan666123No ratings yet
- Network Management: Network Management Involves Detecting and Correcting Problems That Make Communication InefficientDocument19 pagesNetwork Management: Network Management Involves Detecting and Correcting Problems That Make Communication Inefficientprakashreddy4007No ratings yet
- Boss Zonke Network ManagementDocument5 pagesBoss Zonke Network ManagementSimbarashe HlanyaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Technique For SNMP Bandwidth Reduction: Simulation and EvaluationDocument7 pagesA Novel Technique For SNMP Bandwidth Reduction: Simulation and EvaluationRoyal JenishNo ratings yet
- DCN - SNMPDocument31 pagesDCN - SNMPSandip Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring: Simple Network Management Protocol)Document29 pagesMonitoring: Simple Network Management Protocol)maminnurdinNo ratings yet
- Network Management ProtocolsDocument35 pagesNetwork Management ProtocolsGemma TsotetsiNo ratings yet
- SNMPDocument31 pagesSNMPjeevasakthiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On SNMP: Name - Deeksha ROLL NO - 20605Document12 pagesPresentation On SNMP: Name - Deeksha ROLL NO - 20605Deeksha 3003No ratings yet
- SNMP: Simplified: F5 White PaperDocument10 pagesSNMP: Simplified: F5 White PaperJuan OsorioNo ratings yet
- Simple Network Management ProtocolDocument4 pagesSimple Network Management ProtocolsangeetadineshNo ratings yet
- YnDocument48 pagesYnkaz7878No ratings yet
- SNMPDocument31 pagesSNMPGeancarlo Guarniz MartosNo ratings yet
- SNMPDocument31 pagesSNMPsaikat_bandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- SNMPDocument31 pagesSNMPAstri MayasariNo ratings yet
- A 02Document55 pagesA 02Laxman YadavNo ratings yet
- IT19115962 Lab-6 SNMPDocument9 pagesIT19115962 Lab-6 SNMPKashmika GamageNo ratings yet
- Networking Monitoring and Analysis 4Document12 pagesNetworking Monitoring and Analysis 4earl bagainNo ratings yet
- 18 Network Management and OMDocument34 pages18 Network Management and OMAsma ElmangoushNo ratings yet
- AN870 - SNMP V2c Agent For Microchip TCPIP StackDocument40 pagesAN870 - SNMP V2c Agent For Microchip TCPIP StacknanosunbkNo ratings yet
- System Administration Toolkit:: Using SNMP DataDocument10 pagesSystem Administration Toolkit:: Using SNMP DataFrance CalNo ratings yet
- V UnitDocument25 pagesV Unitsuganya004No ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Test IP Network Intelligent Monitoring System Based On SNMPDocument4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Test IP Network Intelligent Monitoring System Based On SNMPAldrey PhadmaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Training New CCNA - SNMP QuestionsDocument2 pagesCCNA Training New CCNA - SNMP Questionsokotete evidenceNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University School of Engineering & Technology: Computer Network ProtocolsDocument31 pagesPondicherry University School of Engineering & Technology: Computer Network Protocolsnivi_09No ratings yet
- SNMP EvolutionDocument13 pagesSNMP EvolutionAndi AndalasNo ratings yet
- SNMPDocument31 pagesSNMPVinay VermaNo ratings yet
- SNMPDocument74 pagesSNMPfsdgNo ratings yet
- NETWORKINGDocument13 pagesNETWORKINGraghuvarunbtech777No ratings yet
- Networking Basics 1Document32 pagesNetworking Basics 1raghuvarunbtech777No ratings yet
- Introduction To Internet Network ManagementDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Internet Network Managementbooksofpavan2224No ratings yet
- Tema 14. SNMPNetflowDocument48 pagesTema 14. SNMPNetflowPaola GagñayNo ratings yet
- SNMP Agent: This Software Runs On The Hardware or Service BeingDocument3 pagesSNMP Agent: This Software Runs On The Hardware or Service BeingAhmedAbdelZaherNo ratings yet
- SNMP Tutorial:: The Fast Track Introduction To SNMP Alarm Monitoring by Marshall DenhartogDocument20 pagesSNMP Tutorial:: The Fast Track Introduction To SNMP Alarm Monitoring by Marshall DenhartogtavadedipakNo ratings yet
- Syslog SNMP Netflow ExplainingDocument8 pagesSyslog SNMP Netflow ExplainingOmarB.El-DeenNo ratings yet
- Virtual MemoryDocument8 pagesVirtual MemorySandip PaulNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - 5: Aim-To Configure SNM Protocol On Cisco Packet Tracer Software-Cisco Packet Tracer TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment No - 5: Aim-To Configure SNM Protocol On Cisco Packet Tracer Software-Cisco Packet Tracer TheoryNabeel KarvinkarNo ratings yet
- NMA Solved PP 14-17Document17 pagesNMA Solved PP 14-17ReeDa SaeedNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To SNMP & Versions of SNMPDocument54 pagesAn Introduction To SNMP & Versions of SNMPanimatoroNo ratings yet
- Slide TuDNDocument34 pagesSlide TuDNtudnNo ratings yet
- A Summary of Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis TechniquesDocument9 pagesA Summary of Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis TechniquesErick CruzNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Server Monitoring System Based On SNMPDocument3 pagesDesign and Implementation of Server Monitoring System Based On SNMPMuhammad RaflyNo ratings yet
- Loverview of Lnetwork Management L& The Role of SNMPDocument44 pagesLoverview of Lnetwork Management L& The Role of SNMPNeeraj AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Network Management SecurityDocument33 pagesUnit 4: Network Management SecurityAbhishek yadavNo ratings yet
- Network Management ApplicationDocument14 pagesNetwork Management ApplicationBiniyamGtsadikNo ratings yet
- HC110110031 Simple Network Management ProtocolDocument14 pagesHC110110031 Simple Network Management ProtocolDimitris FergadiotisNo ratings yet
- C++ Networking 101: Unlocking Sockets, Protocols, VPNs, and Asynchronous I/O with 75+ sample programsFrom EverandC++ Networking 101: Unlocking Sockets, Protocols, VPNs, and Asynchronous I/O with 75+ sample programsNo ratings yet
- Python Networking 101: Navigating essentials of networking, socket programming, AsyncIO, network testing, simulations and AnsibleFrom EverandPython Networking 101: Navigating essentials of networking, socket programming, AsyncIO, network testing, simulations and AnsibleNo ratings yet
- Sohair SE As3Document7 pagesSohair SE As3yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model - 2)Document23 pagesLecture 14 (Chap#4-SNMPv1-Organization and Information Model - 2)yasar khanNo ratings yet
- SNMP Management: Snmpv2Document24 pagesSNMP Management: Snmpv2yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Class DiagramDocument1 pageClass Diagramyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Multi Beam PedrottiDocument4 pagesMulti Beam Pedrottiyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 (Chap#3-Standard, Models and Languages 1)Document17 pagesLecture 10 (Chap#3-Standard, Models and Languages 1)yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Characterizing Network Traffic by Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument13 pagesLecture 7 Characterizing Network Traffic by Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Logical Network Design by Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument12 pagesLecture 11 Logical Network Design by Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Network Management: SNMP: Computer Communication & NetworksDocument39 pagesNetwork Management: SNMP: Computer Communication & Networksyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Abstract Syntax Notation OneDocument26 pagesAbstract Syntax Notation Oneyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Qos Requirements: Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument7 pagesCharacterizing Qos Requirements: Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khan100% (1)
- Telecom Network Design: Assignment # 001Document4 pagesTelecom Network Design: Assignment # 001yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Analyzing The Exisiting Internetwork by Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument25 pagesLecture 6 Analyzing The Exisiting Internetwork by Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Traffic Behavior: Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument10 pagesCharacterizing Traffic Behavior: Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Characterizing Network Traffic Part II by Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument29 pagesLecture 8 Characterizing Network Traffic Part II by Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Technical Goals and Tradeoffs: Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument24 pagesAnalyzing Technical Goals and Tradeoffs: Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Existing Internetwork: Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument21 pagesAnalyzing The Existing Internetwork: Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Network Design Process: DR - Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument30 pagesNetwork Design Process: DR - Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Rab Nawaz Jadoon: Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument62 pagesRab Nawaz Jadoon: Data Communication and Computer Networksyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Telecom Network Design Assignment 003Document8 pagesTelecom Network Design Assignment 003yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Name - Date - Roll Number - Science Grade 3Document5 pagesName - Date - Roll Number - Science Grade 3yasar khanNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: Women Protection Android AppDocument13 pagesProject Proposal: Women Protection Android Appyasar khanNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Threats in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDocument6 pagesA Survey On Threats in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksIJeeteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 07 - TutorialDocument5 pagesTutorial 07 - TutorialFarah CakeyNo ratings yet
- NetBrain System Setup Guide Two-Server DeploymentDocument49 pagesNetBrain System Setup Guide Two-Server Deploymentajrob69_187428023No ratings yet
- Larry Mora Resume - December 2022Document2 pagesLarry Mora Resume - December 2022api-628000621No ratings yet
- (Win2k8) Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Certificate Services Step-By-Step GuideDocument22 pages(Win2k8) Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Certificate Services Step-By-Step GuideAjit WNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Architecture: Hesham El-Rewini Mostafa Abd-El-Barr Computers 5 ReviewsDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Computer Organization and Architecture: Hesham El-Rewini Mostafa Abd-El-Barr Computers 5 ReviewsMuhammad SalisNo ratings yet
- Student-Dec - 1803214924 - MANISH BHARDWAJDocument5 pagesStudent-Dec - 1803214924 - MANISH BHARDWAJswati sharmaNo ratings yet
- ICT AssessmentDocument99 pagesICT Assessmentnuraliahalias0% (1)
- Virtualize 3d Professional Graphics Design GuideDocument21 pagesVirtualize 3d Professional Graphics Design GuideOktavian AugustusNo ratings yet
- CC106 - SG2Document6 pagesCC106 - SG2Dosto kunNo ratings yet
- Networking and Phrasal Verbs 2Document5 pagesNetworking and Phrasal Verbs 2Angel Fernandez AvilesNo ratings yet
- CV Builder & Stamps: Project Advisor: Mr. Ismat UllahDocument12 pagesCV Builder & Stamps: Project Advisor: Mr. Ismat UllahRiZwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Eset KeysDocument2 pagesEset KeysLaurentiu CostacheNo ratings yet
- CN MCQ Unit 1 Set 1Document5 pagesCN MCQ Unit 1 Set 1Makbool Shah W.No ratings yet
- Kovida - The Ease: Keywords:-Smart Phone Application, Tourism, Android OSDocument4 pagesKovida - The Ease: Keywords:-Smart Phone Application, Tourism, Android OSInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nse5 Faz-6.2Document24 pagesNse5 Faz-6.2MAzfar RazaNo ratings yet
- Online Exam With Zoom Invigilation: Guide For MQ Students: Shorter Two Page Overview of This DocumentDocument19 pagesOnline Exam With Zoom Invigilation: Guide For MQ Students: Shorter Two Page Overview of This DocumentegemNo ratings yet
- Link Additional Printing ServerDocument6 pagesLink Additional Printing ServerMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- FortiAnalyzer Big Data 4500FDocument23 pagesFortiAnalyzer Big Data 4500FMaison SNo ratings yet
- Dth2E3 - Sistem Komunikasi: Modulasi PSK (Phase Shift Keying)Document26 pagesDth2E3 - Sistem Komunikasi: Modulasi PSK (Phase Shift Keying)atikNo ratings yet
- Find Any Exploit With One CommandDocument33 pagesFind Any Exploit With One CommandCole LeavittNo ratings yet
- Serveraid M5210 and M5210E Sas/Sata Controllers: Product GuideDocument22 pagesServeraid M5210 and M5210E Sas/Sata Controllers: Product Guidejuan.pasion3696No ratings yet
- Build A Full-Stack App - Ultimate Guide To AWS Amplify With ReactDocument19 pagesBuild A Full-Stack App - Ultimate Guide To AWS Amplify With ReactSayyid ShalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Chilren Orphanage Management SystemDocument31 pagesChilren Orphanage Management SystemNarasha Mepukori100% (1)
- Research Article Research Article Research Article: Article Info Article Info Article InfoDocument5 pagesResearch Article Research Article Research Article: Article Info Article Info Article InfoShubhamNo ratings yet
- Docker Inc Docker Fundamentals Course PDFDocument193 pagesDocker Inc Docker Fundamentals Course PDFJavier MoralesNo ratings yet
- HP Fortify Static Code Analyzer Performance GuideDocument35 pagesHP Fortify Static Code Analyzer Performance GuideMarapalaShruthiNo ratings yet
- FINALPROYECT2Document6 pagesFINALPROYECT2Alex PérezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To E-Business and E-CommerceDocument27 pagesIntroduction To E-Business and E-CommerceThư AnhNo ratings yet