Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integración Metabólica - Bioquímica
Uploaded by
Sergio D. Sánchez VillamarínOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integración Metabólica - Bioquímica
Uploaded by
Sergio D. Sánchez VillamarínCopyright:
Available Formats
Metabolic integration
Universidad Nacional de Colombia
Bioquímica
Metabolic integration
Presented to: Dr. Jorge Eduardo Caminos Pinzón
Sergio David Sanchez Villamarín
Medicine
C.C 1000974719
11 de Septiembre de 2020
Universidad Nacional de Colombia 1
Metabolic integration
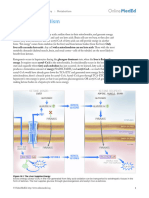
M etabolic integration refers to the pro-
cess of using nutrients for subsequent
use. In this case, here in the concept map, it
In the period immediately following the con-
sumption of glucose, it enters accompanied
by sodium to the enterocytes. This molecule
is shown in part the explanation of the pro- travels through the Portal System to the liver
cess in periods of fasting and feeding, where where it passes into the systemic circulation,
different types of tissue fuels are used for the since the liver does not fix glucose if it does
formation of either ATP or Glycogen (latent not have insulin. The beta cells in the pan-
fuel that will later be used to form ATP). creas stop the increase in blood glucose and
these generate the increase in insulin so that
The pre-prandial, or fasting process, is a sys- the process returns to normal.
tem where the consumption of carbohydra-
tes does not occur. By this fact the synthesis Glucose is a molecule capable of entering
of insulin is stopped. This process opens the any tissue if there is a sufficient amount of
way for other types of tissue fuels to act and insulin. This molecule can generate two pro-
generate glucose, mainly glycogen. cesses in different organs:
The glucose generated in the body can only An oxidative process in any tissue where it
enter the cells thanks to glucose transporters produces ATP and NADPH. The ATP, an es-
(GLUT). Organs such as the brain and eryth- sential molecule in the process of energy
rocyte can enter glucose since these trans- generation and other metabolic processes, is
porters do not need insulin as an activator to generated by glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle.
enter it and then, thanks to Hexokinase, they NADPH as an electron donor for the reduc-
fix the glucose for its use. Others, such as the tion process is very important for catabolic
muscles and adipocytes, cannot enter gluco- and anabolic processes.
se since they need insulin as a ligand. A very
important case to mention is that of the liver:
although it is an independent insulin, the A non-oxidative process that occurs in the
coupling of glucose does not occur very well muscles and in the liver to a greater extent.
since the kinase that generates this, Glucoki- This process instead of generating ATP from
nase, is in very low quantity due to lack of glucose, stores it in small capsules called
insulin, so glucose enters and leaves the liver glycogen for future use where food is not
without generating any change. available.
On the other hand, in the postprandial state, All these processes are very important for the
in the state generated after ingesting food, proper functioning of the human body and
the insulin is triggered at the same time that other living beings.
the exit of lipids, proteins and glucose by the
glycogen is closed.
Link to open the diagram :
https://www.goconqr.com/es-ES/flowchart/
25550427/Integraci-n-Metab-lica
Universidad Nacional de Colombia 2
Metabolic integration
Universidad Nacional de Colombia 3
You might also like
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument16 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismKiran NiaziNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - SOR - BaptismDocument8 pagesStudy Notes - SOR - BaptismYousef Yohanna100% (1)
- Haal E Safar Az Farsh Ta Arsh or Read OnlineDocument174 pagesHaal E Safar Az Farsh Ta Arsh or Read OnlineHaal e Safar100% (4)
- Additional Character OptionsDocument30 pagesAdditional Character Optionsdreaming geckoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Roles of Major Biochemical MoleculesDocument13 pagesMetabolic Roles of Major Biochemical MoleculesJames SoeNo ratings yet
- Incidence of Alveoloplasty PDFDocument4 pagesIncidence of Alveoloplasty PDFaleeza sanaNo ratings yet
- Contract of LeaseDocument4 pagesContract of LeaseIelBarnachea100% (5)
- A Flowering Tree NotesDocument4 pagesA Flowering Tree Notesparidhi50% (4)
- Glucose John SantangeloDocument45 pagesGlucose John Santangelosaint5470No ratings yet
- 100 Dance SongsDocument3 pages100 Dance Songssndakshin@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Pierre Jeanneret Private ResidencesDocument21 pagesPierre Jeanneret Private ResidencesKritika DhuparNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis & Glycogen 2011Document35 pagesGluconeogenesis & Glycogen 2011glenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Importance of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Human Body: Fig.1 - Glucose StructureDocument4 pagesImportance of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Human Body: Fig.1 - Glucose StructureRimsha EramNo ratings yet
- 1.overview of MetabolismDocument6 pages1.overview of Metabolismقتيبه خالد دحام خلفNo ratings yet
- The Human Pancreas Has 1 To 2 Million Islets of LangerhansDocument5 pagesThe Human Pancreas Has 1 To 2 Million Islets of LangerhansCHAYNEX 1No ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and The Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument24 pagesGluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and The Pentose Phosphate PathwayMelisa Halilovic100% (1)
- Metabolism - Glycolysis-2Document8 pagesMetabolism - Glycolysis-2Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- The Role of Liver in Metabolism An Updated ReviewDocument6 pagesThe Role of Liver in Metabolism An Updated Reviewرشاد خالد عماد Rashad Khaled EmadNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Location of GluconeogenesisDocument31 pagesGlycolysis: Location of GluconeogenesisTahera AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesChemistry of CarbohydratesYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- Sugar MetabolismDocument113 pagesSugar MetabolismmismaelNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Biokimia Blok 2.4.1Document44 pagesKuliah Biokimia Blok 2.4.1Prajna PNo ratings yet
- Briefly Summarize The Involving Steps in The ATP SynthesisDocument7 pagesBriefly Summarize The Involving Steps in The ATP SynthesisXuân ViNo ratings yet
- B314 AssignmentDocument23 pagesB314 AssignmentPalesa NtsekalleNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Brain The Most Important Consumer of Glucose?Document11 pagesWhy Is The Brain The Most Important Consumer of Glucose?PojangNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDocument124 pagesمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- Final BiochemistryDocument17 pagesFinal BiochemistryXuân ViNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Insulin Dan GlukagonDocument7 pagesMetabolisme Insulin Dan GlukagonDinda saylaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Metabolism Fasted State: Year 1 Semester 1Document7 pagesRegulation of Metabolism Fasted State: Year 1 Semester 1NikhilBalajiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy and PathophyDocument6 pagesAnaphy and PathophyMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Material Estudio Practico 2 BIO135cDocument10 pagesMaterial Estudio Practico 2 BIO135cFelipe Nicolas UrraNo ratings yet
- InMet I Well-Fed State Spring 23Document32 pagesInMet I Well-Fed State Spring 23Erin HillNo ratings yet
- 8glycogen Metabolism2013 PDFDocument90 pages8glycogen Metabolism2013 PDFNazeer Baig MogalmearjaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism - Ketone MetabolismDocument5 pagesMetabolism - Ketone Metabolismdagehi6880No ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Part II (Glycolysis)Document9 pagesCARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Part II (Glycolysis)InshaNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - HW No.4Document4 pagesGroup 7 - HW No.4MoreartiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: (1st Slide)Document4 pagesCarbohydrates: (1st Slide)ronneldeleyvaNo ratings yet
- Location of GluconeogenesisDocument4 pagesLocation of GluconeogenesisAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Glucose Transport ProteinsDocument4 pagesGlucose Transport ProteinsMade Oka HeryanaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis Group 3Document10 pagesGluconeogenesis Group 3PatPat GalaxyNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: Unit 2Document7 pagesGluconeogenesis: Unit 2Vaishali PathakNo ratings yet
- Signaling Pathways of Glucose in Our Body - PART ONEDocument9 pagesSignaling Pathways of Glucose in Our Body - PART ONEMaria Jose MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chemistru Final ProjectDocument26 pagesChemistru Final ProjectSanskar MohanNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument9 pagesGluconeogenesisPankaj Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Bioquímica: Blgo. Carlos Enrique Cubas Zúñiga M. Sc. Ccubasz@unp - Edu.peDocument18 pagesBioquímica: Blgo. Carlos Enrique Cubas Zúñiga M. Sc. Ccubasz@unp - Edu.peALISSA STEFANY REQUENA JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrateskathleenmaisiedevilla.021105No ratings yet
- Terms For A Medical Student:: 1. GlycolysisDocument24 pagesTerms For A Medical Student:: 1. Glycolysischarmin_limNo ratings yet
- 13 Cau Hoa SinhDocument37 pages13 Cau Hoa SinhTran Danh NhanNo ratings yet
- Bch242-Bch252 2021 CarbohydrateDocument31 pagesBch242-Bch252 2021 CarbohydrateEmmanuella OffiongNo ratings yet
- Overview of GlycolysisDocument6 pagesOverview of GlycolysisAniKvirkviaNo ratings yet
- This Is A SampleDocument10 pagesThis Is A SampleNashi TagazaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Report v2Document14 pagesMid Term Report v2Sana NazNo ratings yet
- Glucose As A Cell Transport ModelDocument6 pagesGlucose As A Cell Transport ModelStudent Kalli RaderNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Ketonemia Witf Fetus DevelopmentDocument8 pagesPregnancy Ketonemia Witf Fetus DevelopmentAcca Malik MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Functions of CarbohydrateDocument11 pagesFunctions of CarbohydrateAbdulbaasit AyoolaNo ratings yet
- Lehninger 5º Edicion - Capitulo 15Document45 pagesLehninger 5º Edicion - Capitulo 15Paz VazquezNo ratings yet
- Overview of Metab and Carbo 1Document16 pagesOverview of Metab and Carbo 1Jubilee Christiene AngNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: CharacteristicsYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Regulation of Glucose HomeostasisDocument20 pagesPancreatic Regulation of Glucose Homeostasiseki_herawatiNo ratings yet
- Insulin Secretion: 1. Pancreatic Beta CellsDocument6 pagesInsulin Secretion: 1. Pancreatic Beta CellsAlicia Tormos EsteveNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument4 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasClayton VerBerkmösNo ratings yet
- Sargsyan-Herman2019 Article RegulationOfGlucoseProductionIDocument11 pagesSargsyan-Herman2019 Article RegulationOfGlucoseProductionIMajo CamargoNo ratings yet
- Type 1 DiabetesDocument5 pagesType 1 DiabetesKehoe MathsNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument11 pagesGluconeogenesisChymuul MarthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-IIDocument36 pagesChapter 4-IIefiNo ratings yet
- Bab Ii PDFDocument14 pagesBab Ii PDFyevanharrybrataNo ratings yet
- Irregularity of Glycogen Synthase Homeostasis Complications Hepatic and Neuro DefectsDocument11 pagesIrregularity of Glycogen Synthase Homeostasis Complications Hepatic and Neuro DefectsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Cases - Mcqs CH 1 Cases - McqsDocument55 pagesCH 1 Cases - Mcqs CH 1 Cases - McqsChaudhary AdeelNo ratings yet
- 2019 Admax CataDocument30 pages2019 Admax CataEVENTIA AFRICANo ratings yet
- Providing Technical Support and Essential Supplies: Asia Pacific Strategy For Emerging Diseases (APSED)Document2 pagesProviding Technical Support and Essential Supplies: Asia Pacific Strategy For Emerging Diseases (APSED)Legal Affairs OfficeNo ratings yet
- Gian Jyoti Institute of Management and Technology, Mohali Assignment No-1 Academic Session January-May 202Document4 pagesGian Jyoti Institute of Management and Technology, Mohali Assignment No-1 Academic Session January-May 202Isha aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Profit Loss Account TemplateDocument4 pagesProfit Loss Account TemplatesnehaNo ratings yet
- 2023 - Ver4.3 - Landslide Assessments in British Columbia Version 4.1Document184 pages2023 - Ver4.3 - Landslide Assessments in British Columbia Version 4.1yehnafarNo ratings yet
- Culture and CraftDocument27 pagesCulture and CraftFreya UmelNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Platform Management Interface Firmware, Upgrade: Operational InstructionDocument23 pagesIntelligent Platform Management Interface Firmware, Upgrade: Operational InstructionLayth WaellNo ratings yet
- 312 Listening List III FinalDocument2 pages312 Listening List III FinalJakeNo ratings yet
- English NotesDocument39 pagesEnglish NotesNorAini MohamadNo ratings yet
- Short VowelDocument3 pagesShort VowelNidzar ZulfriansyahNo ratings yet
- Askehave and Nielsen - Digital Genres PDFDocument22 pagesAskehave and Nielsen - Digital Genres PDFChristopher SmithNo ratings yet
- Solar Geometry FinalDocument17 pagesSolar Geometry Finalsarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- U59cbu5f97u897fu5c71u5bb4u904au8a18-U6307u5b9au6587u8a00u7d93u5178u7cbeu7de8u53c3u8003u7b54u6848.docx - 1 10 (Document1 pageU59cbu5f97u897fu5c71u5bb4u904au8a18-U6307u5b9au6587u8a00u7d93u5178u7cbeu7de8u53c3u8003u7b54u6848.docx - 1 10 (Yo YuuiNo ratings yet
- From St. Francis To Dante-Translations From The Chronicle of The Franciscan Salimbene, 1221-1288Document489 pagesFrom St. Francis To Dante-Translations From The Chronicle of The Franciscan Salimbene, 1221-1288Jake SalNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documenthakimfriends3No ratings yet
- FRC Team 2637, Phatnom Catz, Techbinder 2023 - 2024 CrescendoDocument17 pagesFRC Team 2637, Phatnom Catz, Techbinder 2023 - 2024 CrescendoShrey Agarwal (Drago Gaming)No ratings yet
- Internal Guide-BE Project Groups 2015-16Document28 pagesInternal Guide-BE Project Groups 2015-16Aravind IyerNo ratings yet
- Tugas BingDocument10 pagesTugas BingAmelasNo ratings yet
- Bank of South Sudan Act, 2011 - Bank of South SudanDocument59 pagesBank of South Sudan Act, 2011 - Bank of South SudanAnnadevaraNageswararaoNo ratings yet
- NPJH50465Document3 pagesNPJH50465Samuel PerezNo ratings yet
- FY EDC 2020 Decor-Combinations en EASTDocument14 pagesFY EDC 2020 Decor-Combinations en EASTCristian VasileNo ratings yet