Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction Part2 150126075038 Conversion Gate02
Uploaded by
Sudesh KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction Part2 150126075038 Conversion Gate02
Uploaded by
Sudesh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
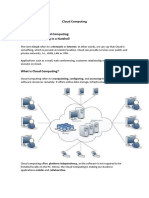
Cloud Computing
Amir H. Payberah
amir@sics.se
Amirkabir University of Technology
(Tehran Polytechnic)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 1 / 80
What is Cloud Computing?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 2 / 80
Cloud Disclaimers
We’ve redefined Cloud Computing to include everything that we
already do. I don’t understand what we would do differently other
than change the wording of some of our ads.
- Larry Ellison (Oracle CEO)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 3 / 80
Cloud Disclaimers
It’s stupidity. It’s worse than stupidity: it’s a marketing hype cam-
paign. Somebody is saying this is inevitable - and whenever you hear
somebody saying that, it’s very likely to be a set of businesses cam-
paigning to make it true.
- Richard Stallman
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 4 / 80
Cloud Definition (1/3)
I Cloud Computing refers to both
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 5 / 80
Cloud Definition (1/3)
I Cloud Computing refers to both
1 the applications delivered as services over the Internet, and
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 5 / 80
Cloud Definition (1/3)
I Cloud Computing refers to both
1 the applications delivered as services over the Internet, and
2 the hardware and systems software in the datacenters that provide
those services.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 5 / 80
Cloud Definition (1/3)
I Cloud Computing refers to both
1 the applications delivered as services over the Internet, and
2 the hardware and systems software in the datacenters that provide
those services.
I The services themselves have long been referred to as Software as
a Service (SaaS).
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 5 / 80
Cloud Definition (1/3)
I Cloud Computing refers to both
1 the applications delivered as services over the Internet, and
2 the hardware and systems software in the datacenters that provide
those services.
I The services themselves have long been referred to as Software as
a Service (SaaS).
I The datacenter hardware and software is what we will call a Cloud.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 5 / 80
Cloud Definition (2/3)
I When a Cloud is made available in a pay-as-you-go manner to the
public, we call it a Public Cloud.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 6 / 80
Cloud Definition (2/3)
I When a Cloud is made available in a pay-as-you-go manner to the
public, we call it a Public Cloud.
I The service being sold is Utility Computing.
• Amazon Web Services, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 6 / 80
Cloud Definition (2/3)
I When a Cloud is made available in a pay-as-you-go manner to the
public, we call it a Public Cloud.
I The service being sold is Utility Computing.
• Amazon Web Services, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure
I Private Cloud refers to internal datacenters of a business or other
organization that are not made available to the public.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 6 / 80
Cloud Definition (3/3)
Cloud Computing is the sum of SaaS and Utility Computing, but
does not normally include Private Clouds.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 7 / 80
I Based on the NIST definition, the cloud model is composed of:
• Five characteristics
• Three service models
• Four deployment models
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 8 / 80
Cloud Characteristics
[http://cdn.katescomment.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/CloudCube1.png]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 9 / 80
Cloud Characteristics
I On-demand self-service
I Broad network access
I Resource pooling
I Measured service
I Rapid elasticity
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 10 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - On-demand Self-Service
I A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities without
human interaction with the service provider.
I Computing capabilities
• Server time, network storage, number of servers, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 11 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Broad Network Access
I Capabilities are
• Available over the network.
• Accessed through standard mechanisms.
I Promote use by
• Heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms, e.g., mobile phones,
laptops, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 12 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Resource Pooling
I Provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple con-
sumers.
I Computing resources
• Storage, processing, memory, network bandwidth and virtual
machines
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 13 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Resource Pooling
I Provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple con-
sumers.
I Computing resources
• Storage, processing, memory, network bandwidth and virtual
machines
I Location independence
• No control over the exact location of the resources
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 13 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Measured Service
I Control and optimize resource use automatically.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 14 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Measured Service
I Control and optimize resource use automatically.
I Metering capability of service/resource abstractions.
• Storage, processing, bandwidth, active user accounts, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 14 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Measured Service
I Control and optimize resource use automatically.
I Metering capability of service/resource abstractions.
• Storage, processing, bandwidth, active user accounts, ...
I Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported providing
transparency for both the provider and consumer.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 14 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Rapid Elasticity
I Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases
automatically.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 15 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Rapid Elasticity
I Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases
automatically.
I To quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 15 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Rapid Elasticity
I Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases
automatically.
I To quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in.
I To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often
appear to be unlimited.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 15 / 80
Cloud Characteristics - Rapid Elasticity
I Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases
automatically.
I To quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in.
I To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often
appear to be unlimited.
I Capabilities can be purchased in any quantity at any time.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 15 / 80
More About Elasticity
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 16 / 80
Elasticity
I Cloud Computing’s ability to add or remove resources at a fine grain
and with a lead time of minutes rather than weeks allows matching
resources to workload much more closely.
[Armbrust et al., Above the Clouds: A Berkeley View of Cloud Computing, Tech. Doc, 2009]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 17 / 80
Over Provisioning
[Armbrust et al., Above the Clouds: A Berkeley View of Cloud Computing, Tech. Doc, 2009]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 18 / 80
Under Provisioning
[Armbrust et al., Above the Clouds: A Berkeley View of Cloud Computing, Tech. Doc, 2009]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 19 / 80
Dynamic Provisioning
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 20 / 80
Cloud Service Models
[http://cdn.katescomment.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/CloudCube1.png]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 21 / 80
Service Models
I Software as a Service (SaaS)
I Platform as a Service (PaaS)
I Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 22 / 80
I Assume, you just moved to a city and
you are looking for a place to live.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 23 / 80
I What is your choice?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 24 / 80
I What is your choice?
• Built a new house?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 24 / 80
I What is your choice?
• Built a new house?
• Buy an empty house?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 24 / 80
I What is your choice?
• Built a new house?
• Buy an empty house?
• Live in a hotel?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 24 / 80
I Let’s built a new house!
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 25 / 80
I Let’s built a new house!
I You can fully control
everything your like your
new house to have.
I But that is a hard work.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 25 / 80
I What if you buy an empty
house?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 26 / 80
I What if you buy an empty
house?
I You can customize some part
of your house.
I But never change the original
architecture.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 26 / 80
I How about live in a hotel?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 27 / 80
I How about live in a hotel?
I Live in a hotel will be a
good idea if the only thing
you care is enjoy your life.
I There is nothing you can
do with the house except
living in it.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 27 / 80
Let’s translate it to
Cloud Computing
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 28 / 80
Service Models
I Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): similar to build a new house.
I Platform as a Service (PaaS): similar to buy an empty house.
I Software as a Service (SaaS): similar to live in a hotel.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 29 / 80
IaaS - (1/3)
I Vendor provides computing resources.
• Processing, storage, network, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 30 / 80
IaaS - (1/3)
I Vendor provides computing resources.
• Processing, storage, network, ...
I Consumer is provided customized virtual machines.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 30 / 80
IaaS - (1/3)
I Vendor provides computing resources.
• Processing, storage, network, ...
I Consumer is provided customized virtual machines.
I Consumer has control over:
• OS, memory
• Storage
• Servers and deployment configurations
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 30 / 80
IaaS - (1/3)
I Vendor provides computing resources.
• Processing, storage, network, ...
I Consumer is provided customized virtual machines.
I Consumer has control over:
• OS, memory
• Storage
• Servers and deployment configurations
I Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Rackspace, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 30 / 80
IaaS - (2/3)
I System architecture
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 31 / 80
IaaS - (3/3)
I Advantages:
• Infrastructure scalability
• Native integrated management: performance, resource
consumption/utilization, load
• Economical cost: hardware, IT support
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 32 / 80
PaaS - (1/3)
I Vendor provides development environment.
• Tools and technology selected by vendor.
• Control over data life-cycle.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 33 / 80
PaaS - (1/3)
I Vendor provides development environment.
• Tools and technology selected by vendor.
• Control over data life-cycle.
I Example: Google app engine, Microsoft Azure
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 33 / 80
PaaS - (2/3)
I System architecture
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 34 / 80
PaaS - (3/3)
I Advantages:
• Rapid development and deployment
• Small startup cost
I Disadvantages:
• Choice of development technology is limited to vendor
provided/supported tools and services
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 35 / 80
SaaS - (1/4)
I Vendor provides applications accessed over the network.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 36 / 80
SaaS - (1/4)
I Vendor provides applications accessed over the network.
I Example: Google Docs, Salesforce.com
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 36 / 80
SaaS - (2/4)
I System architecture
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 37 / 80
SaaS - (3/4)
I Web Service
I Web 2.0 is the trend of using the full potential of the web.
I Viewing the Internet as a computing platform.
I Running interactive applications through a web browser.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 38 / 80
SaaS - (4/4)
I Advantages:
• Easy to use
• Scalability startup
• Lower cost
• Upgrades
I Disadvantages:
• Dependency on network, cloud service provider
• Performance: limited client bandwidth
• User privacy
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 39 / 80
IaaS - PaaS - SaaS
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 40 / 80
IaaS - PaaS - SaaS
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 41 / 80
Cloud Deployment Models
[http://cdn.katescomment.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/CloudCube1.png]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 42 / 80
Deployment Models
I Public cloud
I Private cloud
I Community cloud
I Hybrid cloud
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 43 / 80
Public Cloud
I Infrastructure is made available to the general public.
I Owned by an organization selling cloud services.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 44 / 80
Private Cloud
I Infrastructure is operated solely for an organization.
I Managed by the organization or by a third party.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 45 / 80
Community Cloud
I Supports a specific community.
I Infrastructure is shared by several organizations.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 46 / 80
Hybrid Cloud
I Infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds deployment
models.
I Enables data and application portability.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 47 / 80
Cloud Providers
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 48 / 80
Main Players
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 49 / 80
Cloud Platform Services
I Computing
I Storage
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 50 / 80
Cloud Platform Services
I Computing
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
I Storage
• Relational storage: with support SQL
• NoSQL databases: massively scalable, but not support SQL
• Blobs: storage for Binary Large OBjects in the cloud, e.g., videos,
backups, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 50 / 80
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Computing Storage
Provider IaaS PaaS Relational NoSQL Blobs
Elastic Relational Simple
Elastic SimpleDB
AWS Compute Database Storage
Beanstalk DynamoDB
Cloud (EC2) Service (RDS) Service (S3)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 51 / 80
Computing Storage
Provider IaaS PaaS Relational NoSQL Blobs
Elastic Relational Simple
Elastic SimpleDB
AWS Compute Database Storage
Beanstalk DynamoDB
Cloud (EC2) Service (RDS) Service (S3)
Google App Engine Datastore Blobstore
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 52 / 80
Microsoft
Computing Storage
Provider IaaS PaaS Relational NoSQL Blobs
Elastic Relational Simple
Elastic SimpleDB
AWS Compute Database Storage
Beanstalk DynamoDB
Cloud (EC2) Service (RDS) Service (S3)
Google App Engine Datastore Blobstore
Windows Windows SQL Windows
Microsoft
Azure Azure Tables Azure Azure Blobs
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 53 / 80
Cloud Platforms
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 54 / 80
Cloud Platforms
I Tools to deploy a cloud infrastructure plan.
I These tools provide different services, i.e., IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 55 / 80
OpenStack
I Open source cloud computing platform.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 56 / 80
OpenStack
I Open source cloud computing platform.
I It controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources
throughout a datacenter.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 56 / 80
OpenStack
I Open source cloud computing platform.
I It controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources
throughout a datacenter.
I All managed through a dashboard through a web interface.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 56 / 80
OpenStack
I Open source cloud computing platform.
I It controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources
throughout a datacenter.
I All managed through a dashboard through a web interface.
I Launched by NASA and Rackspace in 2010.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 56 / 80
OpenStack Architecture
[http://www.openstack.org/software/]
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 57 / 80
OpenStack Compute - Nova
I OpenStack Compute: cloud computing controller, called Nova.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 58 / 80
OpenStack Compute - Nova
I OpenStack Compute: cloud computing controller, called Nova.
I Provision and manage large networks of virtual machines.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 58 / 80
OpenStack Compute - Nova
I OpenStack Compute: cloud computing controller, called Nova.
I Provision and manage large networks of virtual machines.
I Compute resources are accessible via APIs for developers, web in-
terfaces for administrators and users.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 58 / 80
OpenStack Storage - Swift/Cinder
I OpenStack Storage: object and block storage for use with servers
and applications, called Swift and Cinder.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 59 / 80
OpenStack Storage - Swift/Cinder
I OpenStack Storage: object and block storage for use with servers
and applications, called Swift and Cinder.
I Swift: distributed storage system for static data, e.g., VM images,
photo storage, email storage.
• Redundancy, backup, archive and failover management
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 59 / 80
OpenStack Storage - Swift/Cinder
I OpenStack Storage: object and block storage for use with servers
and applications, called Swift and Cinder.
I Swift: distributed storage system for static data, e.g., VM images,
photo storage, email storage.
• Redundancy, backup, archive and failover management
I Cinder: block storage, e.g., databases, and file systems
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 59 / 80
OpenStack Networking - Neutron
I OpenStack Networking: network and IP management, called Neu-
tron.
• Provides flexible networking models.
• Manages IP addresses, allowing for dedicated static IPs or DHCP.
• Software Define Network (SDN)
• Different network services, e.g., intrusion detection systems, load
balancing, firewalls and virtual private networks.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 60 / 80
OpenStack Administration - Horizon (1/3)
I OpenStack Administration: administration interface (dashboard),
called Horizon.
• Automate complex deployments
• Control provisioning
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 61 / 80
OpenStack Administration - Horizon (2/3)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 62 / 80
OpenStack Administration - Horizon (3/3)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 63 / 80
Virtualization
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 64 / 80
Virtualization
I Technique for hiding the physical characterizes of computing re-
sources from the way other systems, applications or end users inter-
act with them.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 65 / 80
Virtualization
I Technique for hiding the physical characterizes of computing re-
sources from the way other systems, applications or end users inter-
act with them.
I Offer a different interface.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 65 / 80
Virtualization
I Technique for hiding the physical characterizes of computing re-
sources from the way other systems, applications or end users inter-
act with them.
I Offer a different interface.
I Virtualized interface is not necessarily simpler.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 65 / 80
Different Types of Virtualization
I Process-level virtualization
I OS-level virtualization
I System-level virtualization
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 66 / 80
Process-Level Virtualization (1/2)
I Usually implemented on top of an OS.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 67 / 80
Process-Level Virtualization (1/2)
I Usually implemented on top of an OS.
I Application has to be written specifically for the VM.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 67 / 80
Process-Level Virtualization (1/2)
I Usually implemented on top of an OS.
I Application has to be written specifically for the VM.
I The virtual machine runs one application (one process).
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 67 / 80
Process-Level Virtualization (2/2)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 68 / 80
OS-Level Virtualization (1/2)
I The virtual machine runs a set of userland processes.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 69 / 80
OS-Level Virtualization (1/2)
I The virtual machine runs a set of userland processes.
I Userland domains are separated.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 69 / 80
OS-Level Virtualization (1/2)
I The virtual machine runs a set of userland processes.
I Userland domains are separated.
I Kernel is the same for all userland domains.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 69 / 80
OS-Level Virtualization (2/2)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 70 / 80
System-Level Virtualization (1/3)
I Emulates a computer similar to a real physical one.
• With CPU(s), memory, disk(s), network interface(s), etc.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 71 / 80
System-Level Virtualization (1/3)
I Emulates a computer similar to a real physical one.
• With CPU(s), memory, disk(s), network interface(s), etc.
I The virtual machine runs a full OS.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 71 / 80
System-Level Virtualization (2/3)
I Full virtualization vs. Paravirtualization.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 72 / 80
System-Level Virtualization (2/3)
I Full virtualization vs. Paravirtualization.
I Full virtualization: the guest OS is not aware it is being virtualized
and requires no modification.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 72 / 80
System-Level Virtualization (2/3)
I Full virtualization vs. Paravirtualization.
I Full virtualization: the guest OS is not aware it is being virtualized
and requires no modification.
I Paravirtualization: the guest OS should be modified in order to be
operated in the virtual environment.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 72 / 80
System-Level Virtualization (3/3)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 73 / 80
Hypervisor
I In the system-level virtualization, virtual machines are managed by
another software layer.
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 74 / 80
Hypervisor
I In the system-level virtualization, virtual machines are managed by
another software layer.
I It is called hypervisor or Virtual Machine Manager (VMM).
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 74 / 80
Hypervisor
I In the system-level virtualization, virtual machines are managed by
another software layer.
I It is called hypervisor or Virtual Machine Manager (VMM).
I Two types of hypervisors:
• Type 1: runs directly on hardware (Native/Bare-Metal)
• Type 2: hosted on top of another operating system (Hosted)
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 74 / 80
Bare Metal Hypervisor
I Xen, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 75 / 80
Hosted Hypervisor
I VMWare, KVM, Virtualbox, ...
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 76 / 80
Summary
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 77 / 80
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 78 / 80
References:
I Michael Armbrust, Above the Clouds: A Berkeley View of Cloud
Computing, Technical Document, 2009
I Peter Mell et al., The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing, National
Institute of Standards and Technology, 2011
I VMWare, Understanding Full Virtualization, Paravirtualization, and
Hardware Assist, 2007
I Daniel Firestone, A Comparison of Public Clouds: Amazon Web
Services, Windows Azure and Google App Engine, 2011
I http://docs.openstack.org
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 79 / 80
Questions?
Amir H. Payberah (Tehran Polytechnic) Cloud Computing 1393/6/24 80 / 80
You might also like
- Salesforce Admin Interview QuestionsDocument77 pagesSalesforce Admin Interview QuestionsFaizNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing 101 TutorialDocument203 pagesCloud Computing 101 TutorialYunis Iklil100% (1)
- ORACLEDocument60 pagesORACLEWissen InfotechNo ratings yet
- Azure Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesAzure Interview QuestionsTarunNo ratings yet
- ISF Using Cloud Services Securely Harnessing Core ControlsDocument92 pagesISF Using Cloud Services Securely Harnessing Core ControlsAnthonyNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- It Q&aDocument91 pagesIt Q&aKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing All Units PDFDocument110 pagesCloud Computing All Units PDFRahul Gudla100% (1)
- Understanding The Risks of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Risks of Cloud ComputingJournal of Computing100% (3)
- AWS Academy Cloud Foundations Module 01 Student Guide: 100-ACCLFO-20-EN-SGDocument49 pagesAWS Academy Cloud Foundations Module 01 Student Guide: 100-ACCLFO-20-EN-SGperbankan100% (3)
- T-GCPBDML-B - M1 - Big Data and Machine Learning On Google Cloud - ILT SlidesDocument70 pagesT-GCPBDML-B - M1 - Big Data and Machine Learning On Google Cloud - ILT SlidesAdha JamilNo ratings yet
- Gartner - Magic Quadrant For Enterprise Backup and Recovery Software SolutionsDocument29 pagesGartner - Magic Quadrant For Enterprise Backup and Recovery Software Solutionsmugahed5606No ratings yet
- 3.1 All Slides AZ900Document254 pages3.1 All Slides AZ900DrewNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Cloud Computing Notes-1Document40 pagesUnit 4-Cloud Computing Notes-1HOD IT100% (3)
- Risshie Certified SRE DevOps EngineerDocument8 pagesRisshie Certified SRE DevOps EngineerGopikrishna VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Cloud ComputingDocument59 pagesFundamental of Cloud ComputingTôThànhCôngNo ratings yet
- Survey Paper On Cloud Computing: International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology April 2014Document7 pagesSurvey Paper On Cloud Computing: International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology April 2014Princess JeanNo ratings yet
- CISv2 Student Guide - Final PDFDocument545 pagesCISv2 Student Guide - Final PDFShyam VermaNo ratings yet
- Scalable and Trustworthy Load Balancing Technique For Cloud EnvironmentDocument7 pagesScalable and Trustworthy Load Balancing Technique For Cloud EnvironmentanuragNo ratings yet
- Architectures in Cloud ComputingDocument35 pagesArchitectures in Cloud Computingsuga1990No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit 4 NotesDocument41 pagesCloud Computing Unit 4 Notesgambler yeagerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document31 pagesUnit 2Nirbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- Security Challenges in Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive StudyDocument4 pagesSecurity Challenges in Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Studydesx redjNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewMonica NaviriNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Resource Allocation Scheme in Cloud Computing: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesDynamic Resource Allocation Scheme in Cloud Computing: SciencedirectKrishna Kumar VelappanNo ratings yet
- Potey 2016Document7 pagesPotey 2016tieula.9030No ratings yet
- A Study On Tools For Cloud Disaster ManagementDocument5 pagesA Study On Tools For Cloud Disaster ManagementVirtualian BrainNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingSrijita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Data Security in Cloud Computing Using Cramer - Shoup CryptosystemDocument5 pagesData Security in Cloud Computing Using Cramer - Shoup CryptosystemEminetou Didi Abd Errezagh Eminetou Didi Abd ErrezaghNo ratings yet
- DR - Subbiah RR 07.09.2020Document3 pagesDR - Subbiah RR 07.09.2020Subbiah SNo ratings yet
- CC Security in Cloud Computing - 1Document67 pagesCC Security in Cloud Computing - 1PANDYA CHITRANGDANo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 FinalDocument40 pagesUNIT 4 FinalSivakumar SathasivamNo ratings yet
- Security Issues in Cloud Computing and Risk Assessment: Darshan R, Smitha G RDocument6 pagesSecurity Issues in Cloud Computing and Risk Assessment: Darshan R, Smitha G RInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Loheswaran 2016Document16 pagesLoheswaran 2016Omosekeji TimilehinNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Analysis of Cloud Environment: Prof. S.M. Ranbhise, Prof. K.K.JoshiDocument4 pagesSimulation and Analysis of Cloud Environment: Prof. S.M. Ranbhise, Prof. K.K.JoshiMukund KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 532-Article Text-1186-1-10-20180802Document8 pages532-Article Text-1186-1-10-20180802Ezekiel ChoosenNo ratings yet
- Study On Fault Tolerance MethodsDocument6 pagesStudy On Fault Tolerance Methods121823605028 BORRA KALKINo ratings yet
- Swarm Intelligence For Cloud Computing 0367030551 9780367030551 CompressDocument219 pagesSwarm Intelligence For Cloud Computing 0367030551 9780367030551 CompressFernandoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: From Hype To Reality. Fast Tracking Cloud AdoptionDocument6 pagesCloud Computing: From Hype To Reality. Fast Tracking Cloud Adoptionright nowNo ratings yet
- Why I Am Taking Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesWhy I Am Taking Cloud ComputingSANDHYA RANI N 218002114No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit 5Document7 pagesCloud Computing Unit 5kejagoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Simulation Using CloudSim PDFDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Simulation Using CloudSim PDFGhofrane FerchichiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Applications & SecurityDocument7 pagesCloud Computing Applications & SecuritynishankmahoreNo ratings yet
- Massive Data Crunching: Cloud and Its Impact: Prof. K. Thammi ReddyDocument27 pagesMassive Data Crunching: Cloud and Its Impact: Prof. K. Thammi ReddyThammi Reddy KonalaNo ratings yet
- Cloud, Edg, FogDocument10 pagesCloud, Edg, FogTrần Văn DũngNo ratings yet
- Ijaerv10n20spl 493Document5 pagesIjaerv10n20spl 493amit khapardeNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Issues and Future Direction: Global Sci-Tech January 2017Document9 pagesCloud Computing: Issues and Future Direction: Global Sci-Tech January 2017saadNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument20 pagesUnit Ivrachananandhan3007No ratings yet
- Chapter #3 Understanding Cloud ComputingDocument15 pagesChapter #3 Understanding Cloud ComputingMuhammad Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Survey Paper On Cloud Computing-38295886Document6 pagesSurvey Paper On Cloud Computing-38295886FisehaNo ratings yet
- Unit IvDocument20 pagesUnit Ivrachananandhan3007No ratings yet
- Unit I-CsmDocument127 pagesUnit I-Csmsubeikshap21csNo ratings yet
- Xperiment: Loud OmputingDocument7 pagesXperiment: Loud OmputingTejasNo ratings yet
- Cs8791 Cloud Computing Unit1 NotesDocument34 pagesCs8791 Cloud Computing Unit1 NotesTeju MelapattuNo ratings yet
- Key Infrastructure Elements For Cloud Computing: S.J.Mohana, M.Saroja, M.VenkatachalamDocument4 pagesKey Infrastructure Elements For Cloud Computing: S.J.Mohana, M.Saroja, M.VenkatachalamInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- CC DC HkaDocument64 pagesCC DC Hkaramakantaswain1302No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument38 pagesCloud Computing Fundamentalsmanow431bNo ratings yet
- Data Security in Cloud Computing Based On Blowfish With Md5 MethodDocument6 pagesData Security in Cloud Computing Based On Blowfish With Md5 MethodAzmi AbdulbaqiNo ratings yet
- Round Robin Load BalancingDocument6 pagesRound Robin Load BalancingRiddhi PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- A Study On Cloud Computing Applications and Security Challenges IJERTCONV5IS03077Document5 pagesA Study On Cloud Computing Applications and Security Challenges IJERTCONV5IS03077Anuj KumarNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Resource Allocation and Monitoring in Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesA Survey On Resource Allocation and Monitoring in Cloud ComputingjhoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Security Concerns and Alleviation Controls: January 2018Document7 pagesCloud Computing Security Concerns and Alleviation Controls: January 2018GjNo ratings yet
- Improving Utilization Infrastructure Management in Private and Hybrid CloudsDocument11 pagesImproving Utilization Infrastructure Management in Private and Hybrid CloudsIJERDNo ratings yet
- Bass PaperDocument10 pagesBass Paperearning.income7No ratings yet
- Authentication For Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesAuthentication For Cloud ComputingTahir HussainNo ratings yet
- A Review Data Safeguard For Cloud Computing: International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile ComputingDocument8 pagesA Review Data Safeguard For Cloud Computing: International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile ComputingDainikMitraNo ratings yet
- SCSA3Document7 pagesSCSA3naveenaNo ratings yet
- SFDC CourseMeterial V4.1Document227 pagesSFDC CourseMeterial V4.1Pournami GoudNo ratings yet
- Improving Scalability of Prism Using Distributed Cloud Based Resourse-Aware SchedulersDocument6 pagesImproving Scalability of Prism Using Distributed Cloud Based Resourse-Aware SchedulersEditor InsideJournalsNo ratings yet
- Third Party Public Auditing Scheme For Cloud Storage: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesThird Party Public Auditing Scheme For Cloud Storage: SciencedirectjyoshnaNo ratings yet
- Cloud, Fog, and Edge Computing: A Software Engineering PerspectiveDocument10 pagesCloud, Fog, and Edge Computing: A Software Engineering Perspectivejuanito bananasNo ratings yet
- Curs 11Document35 pagesCurs 11Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Loops SolutionDocument3 pagesLab 5 Loops SolutionSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Curs 1Document44 pagesCurs 1Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Curs 8Document23 pagesCurs 8Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Curs 9Document34 pagesCurs 9Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Curs 2Document38 pagesCurs 2Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 7 ECfux KH BN10 I Bqegrk EDocument18 pages7 ECfux KH BN10 I Bqegrk ESudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document1 pageLab 4Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Elementary Programming 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesLab 3 Elementary Programming 2 SolutionSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 LoopsDocument8 pagesLab 5 LoopsSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Flow of ControlDocument26 pagesFlow of ControlSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- IT ACT 2000: Dr. Kamal GulatiDocument27 pagesIT ACT 2000: Dr. Kamal GulatiSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Jan 2021 WinterDocument1 pageJan 2021 WinterSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Campus Networking Best Practices Session 2: Layer 3: Dale Smith University of Oregon & NSRC Dsmith@uoregon - EduDocument15 pagesCampus Networking Best Practices Session 2: Layer 3: Dale Smith University of Oregon & NSRC Dsmith@uoregon - EduSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Virtulaisation 161201021155Document57 pagesVirtulaisation 161201021155Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SANOG26 Tutorial-Intro SDN Moin 1asiaDocument64 pagesSANOG26 Tutorial-Intro SDN Moin 1asiaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Ms - Ripal RanparaDocument20 pagesCloud Computing: Ms - Ripal RanparaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sanog12 NSRC Campus Network Layer2Document33 pagesSanog12 NSRC Campus Network Layer2Sudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SDN and Mpls in Datacenters: Sam K. AldrinDocument29 pagesSDN and Mpls in Datacenters: Sam K. AldrinSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SANOG12 Merike OPsecDocument132 pagesSANOG12 Merike OPsecSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument21 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Simplicity in Network Design and Deployments: Danny PintoDocument19 pagesSimplicity in Network Design and Deployments: Danny PintoSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument49 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument30 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument44 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument24 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument43 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: By: Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of AizuDocument32 pagesInformation Theory: By: Prof. Mohamed Hamada Software Engineering Lab. The University of AizuSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Information Theory: Mohamed HamadaDocument19 pagesInformation Theory: Mohamed HamadaSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Load Balancing in Cloud Computing: Kanchani SrivastavaDocument17 pagesLoad Balancing in Cloud Computing: Kanchani SrivastavaAnkur SenNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 - Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument11 pagesChapter1 - Introduction To Cloud Computinghaithamokour11No ratings yet
- 1r gu0AwhVEZEkPrp1aCjivtb5hvPgaj9Document76 pages1r gu0AwhVEZEkPrp1aCjivtb5hvPgaj919524 AlekhyaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Testking MS-900 v2020-01-29 by Philip 70qDocument47 pagesMicrosoft Testking MS-900 v2020-01-29 by Philip 70qBogdan ZahariaNo ratings yet
- MSC in Cloud Architecture and Security RACE, REVA University Program Brochure - Jan 22Document38 pagesMSC in Cloud Architecture and Security RACE, REVA University Program Brochure - Jan 22PrashantPatilNo ratings yet
- Prelim ExaminationDocument14 pagesPrelim ExaminationShania LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Unit III VirtualizationDocument31 pagesUnit III Virtualizationsri nidhiNo ratings yet
- M2M-ControlCenter-White Paper Frost and SullivanDocument86 pagesM2M-ControlCenter-White Paper Frost and SullivanNouvric IntNo ratings yet
- Paper Review On Security Feature For Cloud ComputingDocument32 pagesPaper Review On Security Feature For Cloud ComputingendaleNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit 3Document47 pagesCloud Computing Unit 3Raj Vardhan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- IBM Cloud Computing Reference Architecture OverviewDocument42 pagesIBM Cloud Computing Reference Architecture Overviewinet777No ratings yet
- Abap in The CloudDocument27 pagesAbap in The CloudLAISE BARBOSANo ratings yet
- G Cloud v3 Windows Azure Platform Service DefinitionDocument55 pagesG Cloud v3 Windows Azure Platform Service DefinitionGermán CapdehouratNo ratings yet
- Understanding Behavioral Intention To Use A Cloud Computing Classroom A Multiple Model Comparison ApproachDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Behavioral Intention To Use A Cloud Computing Classroom A Multiple Model Comparison ApproachHamaad RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Service Models Module - 4Document29 pagesCloud Computing Service Models Module - 4moideenNo ratings yet
- AZ - 900 Part 3Document11 pagesAZ - 900 Part 3Suraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateDocument35 pagesAssignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateLam Thai Duy (FGW DN)No ratings yet
- Oracle Fact Sheet 079219Document2 pagesOracle Fact Sheet 079219Chandra S JNo ratings yet
- Windows Azure Overview TechEd v03Document23 pagesWindows Azure Overview TechEd v03mobile_hasmadi_othmanNo ratings yet