Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fonemas 2021
Fonemas 2021
Uploaded by
Roxana Aguirre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThe document classifies consonants based on two criteria: manner of articulation, which is how air escapes, and place of articulation, which is where in the mouth the air escapes. There are seven main types of consonants: plosives like /p/ and /b/ which block air flow then release it; fricatives like /f/ and /v/ which cause turbulence; affricates like /ʧ/ and /dʒ/ which are a combination of plosives and fricatives; nasals like /m/ and /n/ which allow air to escape through the nose; laterals like /l/ which allow air to escape around the sides of the tongue;
Original Description:
fonemas en italiano
Original Title
fonemas 2021
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document classifies consonants based on two criteria: manner of articulation, which is how air escapes, and place of articulation, which is where in the mouth the air escapes. There are seven main types of consonants: plosives like /p/ and /b/ which block air flow then release it; fricatives like /f/ and /v/ which cause turbulence; affricates like /ʧ/ and /dʒ/ which are a combination of plosives and fricatives; nasals like /m/ and /n/ which allow air to escape through the nose; laterals like /l/ which allow air to escape around the sides of the tongue;
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesFonemas 2021
Fonemas 2021
Uploaded by
Roxana AguirreThe document classifies consonants based on two criteria: manner of articulation, which is how air escapes, and place of articulation, which is where in the mouth the air escapes. There are seven main types of consonants: plosives like /p/ and /b/ which block air flow then release it; fricatives like /f/ and /v/ which cause turbulence; affricates like /ʧ/ and /dʒ/ which are a combination of plosives and fricatives; nasals like /m/ and /n/ which allow air to escape through the nose; laterals like /l/ which allow air to escape around the sides of the tongue;
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
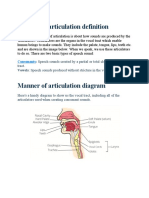
CONSONANTS (two classifications: manner of articulation (the way in
which the air escapes HOW? and place of articulation WHERE?)
1) PLOSIVES (the way air escapes)
a-bilabial (lips)
/p/ voiceless /b/ voiced
b-alveolar (palate, tongue)
/t/ voiceless /d/ voiced
c-velar (soft palate and tongue)
/k/ voiceless /g/ voiced
2) FRICATIVES
/f/ labio-dental voiceless (few, flower)
/v/ labio-dental voiced (vase, voice)
ᶿ dental fricative – voiceless (think, thanks, breath(n.) )
ᶞ dental fricative- voiced (there, they, weather, breath (v.) )
/s/ alveolar – fricative voiceless (snake, sand, sing)
/z/ alveolar fricative voiced (zoo, easy, Brazil, example)
ᶴ palatal –alveolar fricative voicelss (shower, shoes, shopping)
ʒ palatal – alveolar fricative voiced (pleasure, measure, confusion,
television, vision)
/h/ glottal fricative voiceless (hello, house, hat, hand)
3) AFFRICATES
/ʧ/ palato-alveolar voiceles (chair, chesse, child, church)
/dʒ/ palato-alveolar voiced (George, July, jealous, jungle)
4) NASALS (voiced)
/m/ nasal, bilabial voiced
/n/ nasal, alveolar voiced
/ɳ/ nasal velar voiced (sing, along )
5) LATERAL
/l/ alveolar lateral voiced (lamp, field)
6) FRINCTIONLESS CONTINUANT
/r/ post alveolar voiced (the air escapes continuously) (right, write,
rite)
7) SEMIVOWELS (sound like a vowel but they behave as consonant)
/j/ palatal voiced (yellow, yes, you)
/w/ labio-velar voiced (which, what, away)
You might also like
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument49 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyPatricio SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument100 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyFheil Karl Failma100% (6)
- Phonetics & PhonologyDocument10 pagesPhonetics & Phonologysmxlpxngx98No ratings yet
- 10 Tips For Teaching Word StressDocument10 pages10 Tips For Teaching Word StressRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- English PhoneticsDocument49 pagesEnglish PhoneticsEMRAN BIN EZRALNo ratings yet
- Foudations of PhonologyDocument66 pagesFoudations of PhonologyLevente JambrikNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument22 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyYulia DeaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Vs PhonologyDocument53 pagesPhonetics Vs PhonologyValquiria CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Practicas Discursivas de La Comunicación Oral 1Document6 pagesPracticas Discursivas de La Comunicación Oral 1Brenda GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument11 pagesPhoneticsNguyễn Anh VyNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Analysis: English Vs Bahasa Indonesia (Phonological Systems)Document43 pagesContrastive Analysis: English Vs Bahasa Indonesia (Phonological Systems)13.Naelis Tri BintariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Consonants & Their Classification: English PhoneticsDocument16 pagesUnit 3: Consonants & Their Classification: English PhoneticsNguyễn Hữu NguyênNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument6 pagesPhoneticsErica CacalNo ratings yet
- English+Phonetics+and+Phonology +unit+1 +consonants +lecture+1Document11 pagesEnglish+Phonetics+and+Phonology +unit+1 +consonants +lecture+1tinoNo ratings yet
- Word Advance Linguistic Group 1Document12 pagesWord Advance Linguistic Group 1Muhammad Yasin NugrohoNo ratings yet
- 1) PhonologyDocument14 pages1) PhonologyAnna-Marie DroščínováNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: The Sounds of Languag EDocument35 pagesPhonetics: The Sounds of Languag Edini khanafiNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: The Sounds of LanguageDocument42 pagesPhonetics: The Sounds of LanguageZahwa Khotrunnada JannahNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument4 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyGD_girlNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics Lesson 3Document14 pagesEnglish Phonetics Lesson 3Doaa Fat-hyNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument5 pagesPhoneticsmatyokavikiNo ratings yet
- English+Phonetics+and+Phonology +unit+1 +consonants +lecture+1Document2 pagesEnglish+Phonetics+and+Phonology +unit+1 +consonants +lecture+1tinoNo ratings yet
- CONSONANTAL SOUNDS Lez 7Document7 pagesCONSONANTAL SOUNDS Lez 7silviasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ConsonantsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Consonantslongvutrinh1105No ratings yet
- Meeting 4-5 (ENGLISH CONSONANT (1) )Document31 pagesMeeting 4-5 (ENGLISH CONSONANT (1) )luna loudNo ratings yet
- Pucminas: IEC Fonética E FonologiaDocument54 pagesPucminas: IEC Fonética E FonologiaValcarolNo ratings yet
- Self-Access Systems Teaching Pronunciation V1.0 01Document10 pagesSelf-Access Systems Teaching Pronunciation V1.0 01airbank700No ratings yet
- Đề cương giữa kì ngôn ngữ họcDocument19 pagesĐề cương giữa kì ngôn ngữ họcTran ThaoNo ratings yet
- 44 SoundsDocument17 pages44 SoundsEhsanur Rahman JoyNo ratings yet
- PhonologyDocument45 pagesPhonologyVegaNo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument26 pagesConsonantsNguyệt MaiNo ratings yet
- PhoneticDocument7 pagesPhoneticNuriNo ratings yet
- Tema 48,49,50,51Document50 pagesTema 48,49,50,51Mario LacatusNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology 2021Document21 pagesPhonetics and Phonology 2021Anaíde dos Santos RodriguesNo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument8 pagesConsonantskieu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Phonetic (Part 2)Document17 pagesChapter 2-Phonetic (Part 2)Park YumiNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology Chapter 3Document31 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Chapter 3Keven MirandaNo ratings yet
- Some Help With Phonetic Transcription and Sounds of EnglishDocument8 pagesSome Help With Phonetic Transcription and Sounds of EnglishInna SerbaewaNo ratings yet
- (Basics Of) Phonetics and Phonology (With Images)Document27 pages(Basics Of) Phonetics and Phonology (With Images)Adela C.No ratings yet
- Âm vị học (Phọnọlọgy) - 203 - DNN0390 - 01, 02, 03, 04Document30 pagesÂm vị học (Phọnọlọgy) - 203 - DNN0390 - 01, 02, 03, 04Thanh Thảo Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation DefinitionDocument9 pagesManner of Articulation DefinitionAdmin LinguizNo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument8 pagesConsonantsM S100% (1)
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesPhonetics and Phonologynikol.elias2305No ratings yet
- Âm VịDocument8 pagesÂm VịHuyHoàng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionتقوى ميسونNo ratings yet
- Chapter III The Classification of The English Speech SoundsDocument7 pagesChapter III The Classification of The English Speech SoundsMinh LiểuNo ratings yet
- LAB PhoneticsDocument18 pagesLAB PhoneticsMenaka PriyaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 - The Physiology Aspect of Language Phonetics and PhonologyDocument28 pagesGROUP 4 - The Physiology Aspect of Language Phonetics and PhonologyDavina AzhaarNo ratings yet
- Phonetics-The Basics: Chapter 4: The Sounds of Language (Document18 pagesPhonetics-The Basics: Chapter 4: The Sounds of Language (AlbaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinguisticDocument12 pagesIntroduction To LinguisticJulia RheintanataNo ratings yet
- English Language DefinitivoDocument18 pagesEnglish Language Definitivog.levatino8No ratings yet
- Linguistics Kelompok 3Document17 pagesLinguistics Kelompok 3Salman Farizi100% (1)
- Romanian Phonology and PhoneticsDocument9 pagesRomanian Phonology and PhoneticsDragoş-Stelian OlteanuNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 & 4 - Phonetics (The Sounds of Language)Document31 pagesMeeting 3 & 4 - Phonetics (The Sounds of Language)Nadifah ZahraNo ratings yet
- DiphthongsDocument18 pagesDiphthongsAshley Bohol AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Articulation 140925161829 Phpapp02Document10 pagesArticulation 140925161829 Phpapp02zenie nacionNo ratings yet
- English Phonology 05Document24 pagesEnglish Phonology 05luna loudNo ratings yet
- English Grammar and WritingDocument35 pagesEnglish Grammar and WritingDhivyaNo ratings yet
- Phonetic and PhonologyDocument57 pagesPhonetic and PhonologyjimmyNo ratings yet
- Summary of English PhoneticsDocument6 pagesSummary of English PhoneticsDarkPrincessNo ratings yet
- Texto de Comprension 1 Presente SimpleDocument18 pagesTexto de Comprension 1 Presente SimpleRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology REVISION 2021Document10 pagesPhonetics and Phonology REVISION 2021Roxana Aguirre100% (1)
- Language and Culture 1: Superpower GeographyDocument5 pagesLanguage and Culture 1: Superpower GeographyRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Assignment N° 1: Connected Speech: Assimilation-Coalescence - Elision - LiaisonDocument5 pagesAssignment N° 1: Connected Speech: Assimilation-Coalescence - Elision - LiaisonRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Magic Lyrics Kylie MinogueDocument3 pagesMagic Lyrics Kylie MinogueRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Essay About The Environment Week: Conservation of Bats in Covid-19 TimesDocument1 pageEssay About The Environment Week: Conservation of Bats in Covid-19 TimesRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Study Guide To Discuss in ClassDocument1 pageStudy Guide To Discuss in ClassRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Economy and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesEconomy and DevelopmentRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Globalization and The Transformation of Political CommunityDocument6 pagesGlobalization and The Transformation of Political CommunityRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Economy and Development-2Document8 pagesEconomy and Development-2Roxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Emerging PowersDocument12 pagesEmerging PowersRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Storytelling: Isfd 19 Profesorado de Inglés. Lengua y Expresión Oral 3. Profesora Scándali Andrea. Guide OnDocument1 pageStorytelling: Isfd 19 Profesorado de Inglés. Lengua y Expresión Oral 3. Profesora Scándali Andrea. Guide OnRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Storytelling IdeasDocument6 pagesStorytelling IdeasRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- ISFD 19student Practice1Document3 pagesISFD 19student Practice1Roxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Grigori PerelmanDocument1 pageGrigori PerelmanRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Doc1 Summary Oral 3Document1 pageDoc1 Summary Oral 3Roxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Suffixes Examples Exceptions Neutral S./ Accent Neutral S.: Ɛndlɪs HəʊmlɪsDocument4 pagesSuffixes Examples Exceptions Neutral S./ Accent Neutral S.: Ɛndlɪs HəʊmlɪsRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Separate Into Thought Groups, Mark The Stresses, Underline The Most Prominent Syllable, and Circle All Possible Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument1 pageSeparate Into Thought Groups, Mark The Stresses, Underline The Most Prominent Syllable, and Circle All Possible Aspects of Connected SpeechRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Scandali 2018Document6 pagesScandali 2018Roxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Cronograma Anual Por EjesDocument3 pagesCronograma Anual Por EjesRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Rubric For Storytelling Student's Name: - Level: - Speaker Number: - Time: - MinDocument1 pageEvaluation Rubric For Storytelling Student's Name: - Level: - Speaker Number: - Time: - MinRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Isfd 19 Profesorado de Inglés. Lengua y Expresión Oral 3. Profesora Scándali Andrea. ProsodyDocument1 pageIsfd 19 Profesorado de Inglés. Lengua y Expresión Oral 3. Profesora Scándali Andrea. ProsodyRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Theory: Leo 3 3º2º Prof - Scándali Midterm RevisionDocument2 pagesTheory: Leo 3 3º2º Prof - Scándali Midterm RevisionRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- 2 Stress GuideDocument5 pages2 Stress GuideRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation Exercise Sounds and Spelling: Pronunciation © BBC Learning EnglishDocument2 pagesPronunciation Exercise Sounds and Spelling: Pronunciation © BBC Learning EnglishRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet
- 1 Guide Based On Get Rid of Your Accent Advanced LevelDocument13 pages1 Guide Based On Get Rid of Your Accent Advanced LevelRoxana AguirreNo ratings yet