Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cis 2018
Cis 2018
Uploaded by
Peter InocandoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cis 2018
Cis 2018
Uploaded by
Peter InocandoCopyright:
Available Formats
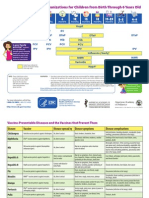
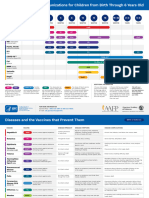
Childhood Immunization Schedule 2018
AGE IN BIRTH WEEKS MONTHS YEARS
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
BCG BCG
Hep B Hep B
Hep B* Hep B*
(DTwP - Hib Hep B* Hep B
- Hep B*) and DTwP*/
DTaP DTwP*/DTap*
DTwP*/DTap* Tdap/Td
other DTaP DTaP
Hib* Hib*
combinations Hib*
DTaP-IPV-HiB -IPV
OPV*/ IPV
OPV*/IPV
IPV/OPV* OPV*/IPV
PCV* PCV*
PCV* PCV* PCV PCV
RV* RV Series*
Influenza Influenza Yearly
Measles Measles
JE Vaccine JEV
MMR* MMR MMR MMR
Varicella Varicella Varicella Varicella
Hep A Hep A Series Hep A
HPV HPV Series
Range of Recommended Age Catch Up Immunization *Primary doses are given at least 4 weeks apart
DISCLAIMER:
The Childhood Immunization Schedule presents recommendations for immunization for children and adolescents based on updated literature review, experience
and premises current at the time of publication. The PPS, PIDSP and PFV acknowledge that individual circumstances may warrant a decision differing from the
recommendations given here. Physicians must regularly update their knowledge about specific vaccines and their use because information about safety and
efficacy of vaccines and recommendations relative to their administration continue to develop after a vaccine is licensed.
Vaccines in the Philippine National Immunization Program (NIP)
The following vaccines are in the 2018 NIP:
• BCG, monovalent Hep B, Pentavalent vaccine (DTwP-Hib-HepB), bivalent OPV, IPV, PCV, MMR, MR, Td and HPV.
Recommended Vaccines
These are vaccines not included in the NIP which are recommended by the Philippines Pediatric Society (PPS), Pediatric Infectious Disease Society of the Philippines
(PIDSP) and the Philippine Foundation for Vaccination (PFV).
ANNOTATIONS
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) • Children 6 months to 8 years receiving influenza vaccine for the 1st time
• Given intradermally (ID) should receive 2 doses separated by at least 4 weeks
• The dose of BCG is 0.05 ml for children < 12 months of age and 0.1 ml for • If only one dose was given during the previous influenza season, give 2 doses
children > 12 months of age of the vaccine then one dose yearly thereafter
• Given at the earliest possible age after birth preferably within the first 2 • Children aged 9 to 18 years should receive one dose of the vaccine yearly
months of life • Annual vaccination should begin in February but may be given throughout the
• For healthy infants and children > 2 months who were not given BCG at birth, year
PPD prior to BCG vaccination is not necessary. However, PPD is
recommended prior to BCG vaccination if any of the following is present: Measles Vaccine
− Congenital TB • Given subcutaneously (SC)
− History of close contact to known or suspected infectious TB cases • Given at the age of 9 months, but may be given as early as 6 months of age in
− Clinical findings suggestive of TB and/or chest x-ray suggestive of TB cases of outbreaks as declared by public health authorities
In the presence of any of these conditions, an induration of ≥ 5mm is considered • If monovalent measles is not available, MMR may be given
positive and BCG is no longer recommended.
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine (JE)
Hepatitis B Vaccine (HBV) • Given subcutaneously (SC)
• Given intramuscularly (IM) • Given at a minimum age of 9 months
• Administer the first dose of monovalent HBV to all newborns >2kgs within 24 • Children 9 months to 17 years of age should receive one primary dose
hours of life. followed by a booster dose 12-24 months after the primary dose
• A 2nd dose is given 1-2 months after the birth dose • Individuals 18 years and older should receive a single dose only
• The final dose is administered not earlier than 24 weeks of age. Another dose
is needed if the last dose was given at age <24 weeks. Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
For infants born to HBsAg (+) mothers: • Given subcutaneously (SC)
• Administer HBV and HBIG (0.5ml) within 12 hours of life. HBIG should be • Given at a minimum age of 12 months
administered not later than 7 days of age if not immediately available. • 2 doses of MMR vaccine are recommended
For infants born to mothers with unknown HBsAg status: • The 2nd dose is usually given from 4-6 years of age but may be given at an
• with birth weight >2kgs, administer HBV within 12 hours of birth and earlier age with a minimum of 4 weeks interval between doses.
determine the mother’s HBsAg as soon as possible. If HBsAg (+), administer
also HBIG not later than 7 days of age. Varicella Vaccine
• with birth weight <2kgs, administer HBIG in addition to HBV within 12 hours • Given subcutaneously (SC)
of life. • Given at a minimum age of 12 months
For preterm infants: • 2 doses of varicella vaccine are recommended
• If born to HBsAg (-) mothers and medically stable, the 1st dose of HBV maybe • The 2nd dose is usually given at 4-6 years of age, but may be given earlier at
given at 30 days of chronological age regardless of weight, and this can be an interval of 3 months from the first dose.
counted as part of the 3-dose primary series. • If the 2nd dose was given 4 weeks from the first dose, it is considered valid.
• For those <2 kgs, the 1st dose received at birth is not counted as part of the • For children 13 years and above, the recommended minimum interval between
vaccine series. Additional 3 HBV doses are needed. doses is 4 weeks.
Haemophilus influenzae Type b Conjugate Vaccine (Hib) Hepatitis A Vaccine (HAV)
• Given intramuscularly (IM) • Given intramuscularly (IM)
• Given as a 3-dose primary series with a minimum age of 6 weeks and a • Given at a minimum age of 12 months
minimum interval of 4 weeks • 2 doses of the vaccine are recommended
• A booster dose is given between 12-15 months of age with an interval of 6 • The 2nd dose is given at least 6 months from the 1st dose
months from the 3rd dose
Refer to Vaccines for Special Groups for Hib recommendation in high risk Measles-Mumps-Rubella-Varicella Vaccine (MMRV)
children • Given subcutaneously (SC)
• Given at a minimum age of 12 months
Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoid and Pertussis Vaccine (DTP) • MMRV may be given as an alternative to separately administered MMR and
• Given intramuscularly (IM) Varicella vaccines
• Given at a minimum age of 6 weeks with a minimum interval of 4 weeks • The maximum age is 12 years
• Complete a 5-dose series at ages 2, 4, 6, 15 through 18 months, and 4 • The recommended minimum interval between doses is 3 months
through 6 years. The recommended interval between the 3rd and 4th dose is 6
months, but a minimum interval of 4 months is valid Human Papillomavirus Vaccine (HPV)
• The 5th dose of DTaP vaccine may not be given if the 4th dose was • Given intramuscularly (IM)
administered at age 4 years or older. • For ages 9-14 years, a 2-dose series is recommended
− Bivalent HPV (2vHPV), quadrivalent (4vHPV) or nonavalent (9vHPV) given
Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine (IPV) at 0 and 6 months
• Given intramuscularly (IM) − If the interval between the 1st and 2nd dose is less than 6 months a 3rd
• Usually given in combination with DTaP and Hib, with or without Hep B dose is needed. The minimum interval between the 2nd and 3rd dose is 3
• Given at a minimum age of 6 weeks with a minimum interval of 4 weeks months.
• The primary series consists of 3 doses • For ages 15 years and older, a 3-dose series is recommended,.
• A booster dose should be given on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6 – Bivalent HPV (2vHPV), quadrivalent (4vHPV) or nonavalent (9vHPV) at 0, 2
months from the previous dose and 6 months.
– The minimum interval between the 1st and the 2nd dose is 1 month and
Rotavirus Vaccine (RV) the minimum interval between the 2nd and 3rd dose is 3 months. The 3rd
• Given per orem (PO) dose should be given at least 6months from the 1st dose.
• Given at a minimum age of 6 weeks with a minimum interval of 4 weeks For males 9-18 years of age, a 4vHPV and 9vHPV can be given for the prevention
between doses. The last dose should be administered not later than 32 weeks of anogenital warts and anal cancer
of age.
• The monovalent human rotavirus vaccine (RV1) is given as a 2-dose series Tetanus and Diphtheria Toxoid (Td)/ Tetanus and Diphtheria Toxoid and
and the pentavalent human bovine rotavirus vaccine (RV5) is given as a Acellular Pertussis Vaccine (TdaP)
3-dose series. • Given intramuscularly (IM)
• For children who are fully immunized, Td booster doses should be given every
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines (PCV) 10 years.
• Given intramuscularly (IM) • For children aged > 7 years old, a single dose of Tdap can be given and can
• Given at a minimum age of 6 weeks for PCV10 and PCV 13 replace due Td. It can be administered regardless of the interval since the last
• Primary vaccination consists of 3 doses with an interval of at least 4 weeks tetanus and diphtheria toxoid containing vaccine. Subsequent doses are given
between doses plus a booster dose given 6 months after the 3rd dose. as Td
• Healthy children 2 to 5 years old who do not have previous PCV vaccination *Fully immunized is defined as 5 doses of DTP or 4 doses of DTP if the 4th dose
may be given 1 dose of PCV 13, or 2 doses of PCV 10 at least 8 weeks apart was given on or after the 4th birthday
Refer to Vaccines for Special Groups for Pneumococcal Vaccine recommendation For pregnant adolescents
in high-risk children. • Fully immunized:
– administer 1 dose of Tdap vaccine during 27 to 36 wks AOG regardless of
Influenza Vaccine (Trivalent/Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine) previous Td or Tdap vaccination
• Trivalent influenza vaccine (TIV) given intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously • Unimmunized:
(SC) – administer a 3 dose tetanus-diphtheria containing vaccine (Td) following a
• Quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV) given intramuscularly (IM) 0-1-6 month schedule. Tdap should replace one dose of Td given during
• Given at a minimum age of 6 months 27 to 36 wks AOG
• The dose of influenza vaccine is 0.25 ml for children 6 months to 35 months
and 0.5 ml for children 36 months to 18 years
ANNOTATIONS: VACCINES FOR HIGH RISKS / SPECIAL GROUPS 2018
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV)/ Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Meningococcal Vaccines
Vaccine (PPSV23) • Tetravalent meningococcal (ACYW-135) conjugate vaccine MCV4-D, MCV4-
• Given intramuscularly (IM) TT, MCV4-CRM given intramuscularly (IM)
– All recommended PCV doses should be given prior to PPSV23 if possible. • Indicated for those at high risk for invasive disease:
The two vaccines should not be co-administered. If a dose of PPSV23 is Persistent complement component deficiencies (including those with inherited
inadvertently given earlier than the recommended interval, the dose need or chronic deficiencies in C3, C5-9, properdin, factor D, factor H), anatomic/
not be repeated. functional asplenia (including sickle cell disease), HIV, travelers to or
– The following tables summarizes the indication and schedule of PCV/PPSV resident of areas where meningococcal disease is hyperendemic or epidemic,
administration to children with high risk conditions according to age group: including countries in the African meningitis belt or the Hajj, or belonging to
a defined risk group during a community or institutional meningococcal
SCHEDULE OF PCV 13-PPSV23 outbreak
INDICATION
VACCINATION SEQUENCE
Dosing schedule:
Age: 24 mos to 5 years •Chronic heart disease, particularly • MCV4-D: minimum age is 9 months. For children 9-23 months give 2 doses 3
•Administer 1 dose of PCV13 if any cyanotic congenital heart disease and months apart. For children 2 years and above give one dose, except in cases
incomplete schedule of 3 doses of cardiac failure
PCV13 was received previously. •Chronic lung disease, including asthma if of asplenia, HIV and persistent complement component deficiency where 2
•Administer 2 doses of PCV13 at least treated with high-dose oral corticosteroid doses, 8 weeks apart are recommended.
8 weeks apart if unvaccinated or any therapy • MCV4-TT given to children 12 months and above as a single dose
incomplete schedule of fewer than 3 •Diabetes mellitus • MCV4-CRM given to children 2 years and above as a single dose
doses of PCV13 was received •Cerebrospinal fluid leaks • Revaccinate with a MCV4 vaccine every 5 years as long as the person remains
previously. •Cochlear implant(s) at increased risk of infection
•The minimum interval between doses •Sickle cell disease and other • Co-administration of MCV4 and other vaccines
of PCV13 is 8 weeks. hemaglobinopathies MCV4-D and PCV13
•For children with no history of •Congenital or acquired asplenia, or – If MCV4-D is administered to a child with asplenia (including sickle cell
PPSV23 vaccination, administer splenic dysfunction
PPSV23 at least 8 weeks after the •HIV infection disease) or HIV infection, do not administer MCV4-D until age 2 years and
most recent dose of PCV13. •Chronic renal failure and nephrotic at least 4 weeks after the completion of all PCV13 doses
syndrome MCV4-D and Tdap
•Diseases associated with treatment with – If MCV4-D is to be administered to a child at high risk for meningococcal
Age: 6 yrs to 18 years immunosuppresive drugs or radiation disease, it is recommended that MCV4-D be given either before or at the
•Administer 1 dose of PCV13 if they have therapy, including malignant neoplasms, same time as DTaP.
not previously received this vaccine, leukemias, lymphomas, and Hodgkin
regardless of whether the previous vac- MCV4-TT with Tetanus toxoid (TT) containing vaccines
disease; or solid organ transplantation – Whenever feasible, MCV4-TT should be co-administered with TT-
cine received was PCV7 or PPSV 23 •Congenital immunodeficiency (includes
Children aged 2 years to 64 years old, with B- (humoral) or T-lymphocyte deficiency, containing vaccines, or administer MCV4-TT 1 month before the other
any 1 of the listed chronic medical complement deficiencies (particu TT- containing vaccines
conditions should get 1 dose of PPSV23 larly C1, C2, C3, and C4 deficiencies),
and phagocytic disorders (excluding Rabies Vaccine
chronic granulomatous disease) • Given intramuscularly (IM) or intradermally (ID)
• Recommended regimens for pre-exposure prophylaxis:
– Intramuscular regimen (IM):
NO. OF DOSES OF PPSV 23 ACCORDING TO INDICATION Purified Vero Cell Rabies (PVRV) 0.5 ml OR
Purified Chick Embryo Cell Vaccine (PCECV) 1 ml given on days 0, 7, 21
Children aged 2 years to 64 years old, with •Chronic heart disease, including heart or 28
any 1 of the listed chronic medical condi- failure and cardiomyopathies – Intradermal regimen (ID): PVRV or PCECV 0.1 ml given on days 0, 7, 21
tions should get 1 dose of PPSV23 •Chronic lung disease, including chronic or 28
obstructive pulmonary disease, • A repeat dose should be given if the vaccine is inadvertently given
emphysema, and asthma subcutaneously.
•Diabetes mellitus
•Cerebrospinal fluid leaks • Rabies vaccine should never be given in the gluteal area since absorption is
•Cochlear implant(s) unpredictable.
•Alcoholism • In the event of subsequent exposures, those who have completed 3 doses of
•Chronic liver disease pre-exposure prophylaxis regardless of the interval between exposure and last
dose of the vaccine will require only booster doses given on day 0 and 3.
Booster doses may be given IM (0.5 ml PVRV or 1 ml PCECV) or ID (0.1 ml of
Children 2 years to 64 years old, with Congenital or acquired immunodeficien-
any 1 of the listed immunocompromising cies includes B- (humoral) or T-lympho-
PVRV or PCECV). There is no need to give rabies immune globulin.
conditions should get 2 doses of PPSV23, cyte deficiency, complement deficiencies
5 years apart (particularly C1, C2, C3, and C4 deficien- Typhoid Vaccine
cies), and phagocytic disorders (excluding • Given intramuscularly (IM)
chronic granulomatous disease) • Given at a minimum age of 2 years old with revaccination every 2—3 years
• HIV infection • Recommended for travelers to areas where there is a risk for exposure and
• Chronic renal failure or nephrotic for outbreak situations as declared by public health authorities
syndrome
• Leukemia or lymphoma Cholera Vaccine
• Hodgkin's disease
• Generalized malignancy • Given per orem (PO)
• Iatrogenic immunosuppression (diseases • Given at a minimum age of 12 months as a 2-dose series two weeks apart.
requiring treatment with immunosuppres • Recommended for outbreak situations and natural disasters as declared by
sive drugs, including long-term systemic public health authorities
corticosteroids and radiation therapy)
• Solid organ transplant Hepatitis A Vaccine
• Multiple myeloma • Given intramuscularly (IM)
• Administer 2 doses of Hepatitis A vaccine at least 6 months apart to
Hemophlus influenzae Type b Conjugate Vaccine (Hib) unvaccinated individuals who are at increased risk for infection:
• Given intramuscularly (IM) – Travelers to or are working in countries with intermediate or high
• Indications for children with the following high risk conditions: endemicity of infection,
– Chemotherapy recipients, anatomic/functional asplenia including sickle – Men having sex with men (MSM)
cell disease, HIV infection, immunoglobulin or early component – Users of injection and non-injection illicit drugs,
complement deficiency – Working with HAV infected primates or with HAV in research laboratories,
• Children aged 12-59 months: – With clotting factor disorders and chronic liver disease
– Unimmunized* or with one Hib vaccine dose received before age 12
months, give 2 additional doses 8 weeks apart Human Papillomavirus Vaccine (HPV)
– With ≥ 2 Hib vaccine doses received before age 12 months, give 1 • Given intramuscularly (IM)
additional dose • Give 3 doses of HPV vaccine following the 0, 1-2, and 6 month schedule,
• For children ≤ 5 years old who received a Hib vaccine dose(s) during or within regardless of age at vaccine initiation to the following:
14 days of starting chemotherapy or radiation treatment, repeat the dose(s) of – Children with history of sexual abuse or assault starting at age 9 years
Hib vaccine at least 3 months after completion of therapy – Immunocompromised children including those with HIV infection
• For children who are hematopoetic stem cell transplant recipients, • HPV vaccination is not recommended during pregnancy. If HPV vaccine
revaccination with 3 doses of Hib vaccine given 4 weeks apart, starting 6-12 is inadvertently given during pregnancy, delay the remaining doses until after
months after transplant, is recommended regardless of vaccination history. pregnancy. Pregnancy testing is not necessary before initiating HPV
• Unimmunized* children ≥ 15 months of age and undergoing elective vaccination.
splenectomy should be given 1 dose of Hib-containing vaccine at least 14 days
before the procedure Dengue Vaccine
• Unimmunized* children 5-18 years old and with either anatomic or functional Recommendation under review, pending re-labelling of the product
asplenia (including sickle cell disease) or HIV infection, should be given 1
dose of Hib vaccine
* Unimmunized children are those without a primary series and booster dose or
those without at least one dose of the vaccine after 14 months of age
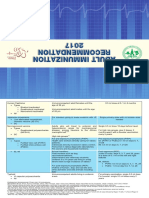
SUMMARY TABLE 2018: Immunization of
Pre-Adolescents and Adolescents (7 to 18 yrs.old)
Range of Dose(s) Schedule of Route of Precautions &
Vaccine
Recommended Age Needed Immunization Administration Contradiction
Unvaccinated • Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
Hep B Vaccine 7-18 yrs. old
3 0,1,6 months IM • Moderate to severe illness
2nd dose given at least 6 months • Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
Hep A Vaccine Unvaccinated 7-18 yrs. old 2 from the 1st dose
IM • Moderate to severe illness
• Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
Unvaccinated 7-18 yrs. old 2 4 weeks interval between doses • Pregnancy
MMR SC • Immunosuppression
Incompletely vaccinated 2nd dose given anytime but at least 4 weeks • Recent receipt of blood products
1
7-18 yrs. old from 1st dose • Moderate to severe illness
Minimum interval between doses is 3
Unvaccinated 7-12 yrs. old 2
months
• Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
Minimum interval between doses is • Pregnancy
Unvaccinated ≥ 13 yrs. old 2
Varicella one month SC • Immunosuppression
• Recent receipt of blood products
Given anytime 7-12 yrs. old at least 3 mos. from • Moderate to severe illness
Incompletely vaccinated
1 the 1st dose,13 yrs.old at least 1 month from the
7-18 yrs. old 1st dose
• Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
Influenza • Moderate to severe illness
9-18 yrs. old 1 Give annually beginning February IM/SC • History of Guillain-Barre syndrome following a
Vaccine previous dose
0,1 and 6 months Tdap preferably as the 1st dose
Unvaccinated 7-18 yrs. old 3 then Td for the remaining doses
Incompletely vaccinated • Severe allergic reaction to vaccine
1-2 One dose Tdap then Td for remaining dose
Td/Tdap 7-18 yrs. old IM component,
• Moderate to severe illness
Fully vaccinated
7-18 yrs. old
(Fully vaccinated defined as 5 doses of 1 1 dose Tdap then Td every 10 years
DTaP or 4 doses of DTap if the 4th dose was
administered on or after the 4th birthday)
HPV:
Females: 15-18 yrs. old 3 0,1,6 months
Bivalent HPV (2vHPV) • Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
• Moderate to severe illness
IM • If found to be pregnant after starting immunization,
Females: delay remaining doses until completion of
Qaudrivalent HPV pregnancy
15-18 yrs. old 3 0,2 and 6 months
(4vHPV)/Nonavalent HPV (9vHPV) Males: 15-18 yrs.old
For Females: (2vHPV)/
• Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
Quadrivalent HPV (4vHPV/)/ • Moderate to severe illness
Nonavalent HPV (9vHPV) 9-14 yrs. old 2 0,6-12 months IM • If found to be pregnant after starting immunization,
delay remaining doses until completion of
For Males: 4vHPV/9vHPV pregnancy
You might also like
- Oxford Handbook of Epidemiology For Clinicians PDFDocument417 pagesOxford Handbook of Epidemiology For Clinicians PDFDanTe D' Winchester100% (3)
- Case Analysis RLE MODULE TEMPLATE Nursery 1 (One)Document7 pagesCase Analysis RLE MODULE TEMPLATE Nursery 1 (One)PanJan BalNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument21 pagesNeonatal SepsisDyah Ayu Puspita AnggarsariNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Reference Chart 1.2 - 1 PDFDocument1 pageVital Signs Reference Chart 1.2 - 1 PDFSerious Leo100% (1)
- 2018 DPRI Booklet (April 2019) PDFDocument34 pages2018 DPRI Booklet (April 2019) PDFShaenie Lou Gatillo67% (3)
- Gestational Diabetes Research PaperDocument16 pagesGestational Diabetes Research Paperapi-251486092No ratings yet
- Concept Map LungDocument1 pageConcept Map LungThea Eya FayeNo ratings yet
- Ncma219 Ob Lec: BSN 2Nd Year 2Nd Semester Prelim 2022: Bachelor of Science in Nursing 2YBDocument59 pagesNcma219 Ob Lec: BSN 2Nd Year 2Nd Semester Prelim 2022: Bachelor of Science in Nursing 2YBEARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- CHN TopicsDocument19 pagesCHN TopicsKristine AnaenNo ratings yet
- Week 1 RUBRICS Wound Care and DressingDocument2 pagesWeek 1 RUBRICS Wound Care and DressingPaola CruzNo ratings yet
- Philippines TB CP Guidelines 2006Document151 pagesPhilippines TB CP Guidelines 2006wiltechworksNo ratings yet
- Programs and Projects in The National SettingDocument58 pagesPrograms and Projects in The National SettingAnn Grethel Tan100% (1)
- Part 1 RenalDocument8 pagesPart 1 RenalKatherine ApostolNo ratings yet
- HAB ManualDocument102 pagesHAB ManualSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- MCN 4th QuizDocument27 pagesMCN 4th Quizastraeax pandaNo ratings yet
- PHC2. The Philippine Health Care Delivery SystemDocument55 pagesPHC2. The Philippine Health Care Delivery SystemHumilyn NgayawonNo ratings yet
- DARDocument4 pagesDARfritzroseNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Document28 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)The Living SonneteerNo ratings yet
- Newborn ScreeningDocument23 pagesNewborn Screeningloglesb1No ratings yet
- Physician Order SheetDocument2 pagesPhysician Order SheetEunick VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- 8. Care of Child With GI Dysfunction (1) ءءءءDocument44 pages8. Care of Child With GI Dysfunction (1) ءءءءNuhaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care Services: by DR - Chinedu Ibeh Thursday, 16 APRIL 2015Document81 pagesAntenatal Care Services: by DR - Chinedu Ibeh Thursday, 16 APRIL 2015SehaRizaNo ratings yet
- Demonstrating Theory in Practice Examples of The McGill Model of NursingDocument10 pagesDemonstrating Theory in Practice Examples of The McGill Model of NursingFerdy LainsamputtyNo ratings yet
- Lecture PCAPDocument3 pagesLecture PCAPRoy Anthony CenizaNo ratings yet
- CHN Lec Finals ReviewerDocument23 pagesCHN Lec Finals ReviewerMarron Jane GanoticeNo ratings yet
- 107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineDocument6 pages107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineGiel Margareth LindoNo ratings yet
- Preventive Pediatrics Part 1Document6 pagesPreventive Pediatrics Part 1mkct111No ratings yet
- Concept Map of DMDocument1 pageConcept Map of DMRobert Timothy YapNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Integrated Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in and Out Patient Treatment 12.2011Document182 pagesGuidelines For The Integrated Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in and Out Patient Treatment 12.2011Jonathan Renier VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Assessment ToolDocument3 pagesPediatric Assessment ToolKrystel BatinoNo ratings yet
- Cga - 1Document19 pagesCga - 1Kenji Tolero100% (1)
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineCj LowryNo ratings yet
- Demo Teaching Physical Health AssessmentDocument5 pagesDemo Teaching Physical Health AssessmentJulie May SuganobNo ratings yet
- Immunization ChartDocument1 pageImmunization ChartDesilva ThampiNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument7 pagesVital SignsEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudySORENI SORENINo ratings yet
- Growth Monitoring - GIDocument19 pagesGrowth Monitoring - GIokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- IMCI NewDocument81 pagesIMCI NewBianca de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Reaction Algorithm V 2 FINAL 2016 11 02 PDFDocument1 pageTransfusion Reaction Algorithm V 2 FINAL 2016 11 02 PDFnohe992127No ratings yet
- Course Task 8 Drug Study On Respiratory AgentsDocument23 pagesCourse Task 8 Drug Study On Respiratory AgentsAdrienne Nicole PaneloNo ratings yet
- CDC Immunization 0-6 YrsDocument2 pagesCDC Immunization 0-6 Yrsxoxo318100% (1)
- Newborn Screening Policy Catarman Doctors Hospital, Inc.: University of Eastern PhilippinesDocument7 pagesNewborn Screening Policy Catarman Doctors Hospital, Inc.: University of Eastern PhilippinesGenn Medrano GirayNo ratings yet
- Handouts CD Prof. RojasDocument6 pagesHandouts CD Prof. RojasChallen CulturaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Adult Immunization Recommendation 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesPhilippine Adult Immunization Recommendation 2017 PDFLinius CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Nutritional Needs of A NewbornDocument13 pagesChapter 19: Nutritional Needs of A NewbornAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Nelec2 Week 17Document13 pagesNelec2 Week 17Michelle MallareNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal 1Document30 pagesCompetency Appraisal 1mirai desuNo ratings yet
- CPG Acute Infectious DiarrheaDocument10 pagesCPG Acute Infectious DiarrheaKristine Jade OdtujanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Document3 pagesPediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Jonah MaasinNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing 1 Skills Lab Modele s1Document3 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing 1 Skills Lab Modele s1Crystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- DOH Maternal Health ProgramDocument5 pagesDOH Maternal Health ProgramErwin Jake TagubaNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument24 pagesCase PresentationDarlen RabanoNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Part 1 & 2Document35 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Part 1 & 2Kei Amphi BarlintangcoNo ratings yet
- SLMC GC Ipch Osoe (Age) Oct 2019Document4 pagesSLMC GC Ipch Osoe (Age) Oct 2019Alvin FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Labor Monitoring RecordDocument2 pagesLabor Monitoring RecordZyrilleNo ratings yet
- Immunization ScheduleDocument3 pagesImmunization ScheduleNiranjan HegdeNo ratings yet
- Immunisation Schedule: Recommended Age Mandatory VaccinesDocument1 pageImmunisation Schedule: Recommended Age Mandatory VaccinessharanamayyappaNo ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsunmundoextranopodcastNo ratings yet
- Recommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0 Through 6 YearsDocument1 pageRecommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0 Through 6 YearshendergmNo ratings yet
- For Those Who Fall Behind or Start Late, See The Catch-Up ScheduleDocument4 pagesFor Those Who Fall Behind or Start Late, See The Catch-Up ScheduleTony MichelNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pakai 3 (Etiologi) Efusi PerikardiumDocument10 pagesJurnal Pakai 3 (Etiologi) Efusi PerikardiumSatrya DitaNo ratings yet
- Wounds in GeneralDocument19 pagesWounds in GeneralMuhammad ReyhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Cardio Intensive CasesDocument32 pagesLecture 12 Cardio Intensive Casesraul0% (1)
- Gordon's Functional Assessment HistoryDocument5 pagesGordon's Functional Assessment HistoryJachel Kathleen Laguio100% (1)
- 베트남 여름은 5월부터 시작한다Document5 pages베트남 여름은 5월부터 시작한다Tieu LinhNo ratings yet
- Shane P. Prejean, MD, Munaib Din, BSC, Eliana Reyes, MD, PHD, and Fadi G. Hage, MD, FasncDocument8 pagesShane P. Prejean, MD, Munaib Din, BSC, Eliana Reyes, MD, PHD, and Fadi G. Hage, MD, FasncwidyadariNo ratings yet
- Bio Infertility Before Final PDFDocument31 pagesBio Infertility Before Final PDFmanojkumar200624No ratings yet
- Acidemia and HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageAcidemia and HyperkalemiaDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Arnold-Chiari Malformations Clinicl Features PDFDocument3 pagesArnold-Chiari Malformations Clinicl Features PDFsridharNo ratings yet
- Last Aid Dermatology SARPDocument7 pagesLast Aid Dermatology SARPskNo ratings yet
- Family Care Plan-Health DeficitDocument3 pagesFamily Care Plan-Health DeficitGia Espinosa Ocbeña100% (1)
- Progress in Retinal and Eye ResearchDocument35 pagesProgress in Retinal and Eye ResearchYegor KharkovNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument11 pagesDisaster ManagementLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)No ratings yet
- Classification of Infectious DiseaseDocument64 pagesClassification of Infectious DiseaseSaadTamNo ratings yet
- Copper Ridge Health and Rehabilitation Center 07-31-2018Document3 pagesCopper Ridge Health and Rehabilitation Center 07-31-2018NBC MontanaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care Plan - Dr. DominguezDocument2 pagesNutrition Care Plan - Dr. DominguezMonique Angela Turingan GanganNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Research PaperDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia Research Paperapi-534301945No ratings yet
- GRIFTDocument15 pagesGRIFTjellyjohnNo ratings yet
- Transkrip Nilai 2 PDFDocument1 pageTranskrip Nilai 2 PDFkrisna129No ratings yet
- Postoperative Care: Nursing ManagementDocument25 pagesPostoperative Care: Nursing ManagementHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- Garlic Kills Brain Cancer Cells Without Side EffectsDocument3 pagesGarlic Kills Brain Cancer Cells Without Side EffectsactoolNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Copd (Bronchitis & Emphysema)Document7 pagesRespiratory System: Copd (Bronchitis & Emphysema)Rhea Lyn LamosteNo ratings yet
- Reflux Hypersensitivity: A New Functional Esophageal DisorderDocument9 pagesReflux Hypersensitivity: A New Functional Esophageal DisorderniemandNo ratings yet
- Perceptions of Behavior Consuming Betel Nut in Poverty Communities Kupang West Timor IndonesiaDocument7 pagesPerceptions of Behavior Consuming Betel Nut in Poverty Communities Kupang West Timor IndonesiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Addiction Therapy For Drugs, Alcohol, Caffeine, and Sugar - Reagan HoustonDocument4 pagesAddiction Therapy For Drugs, Alcohol, Caffeine, and Sugar - Reagan HoustonThalesNo ratings yet
- Hiv HistoryDocument4 pagesHiv HistoryJohnson BrownNo ratings yet
- Alopecia Areata enDocument6 pagesAlopecia Areata enLester FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bell' S Palsy - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment - Southern Cross NZDocument3 pagesBell' S Palsy - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment - Southern Cross NZRoxan PacsayNo ratings yet