0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6K views7 pagesVariance Analysis (Practice Problems)
(1) The document contains 4 practice problems involving variances. Problem I involves direct materials variances. Problem II involves direct labor variances. Problem III involves multiple variances including materials, labor, and factory overhead. Problem IV is the most complex involving many types of overhead variances.
(2) Each problem provides standard and actual data and requires the calculation of specific variances. The responses provide the calculations and numerical answers for the required variances in each problem.
(3) The document contains practice problems and solutions for calculating different types of cost variances commonly used in standard costing systems.
Uploaded by
Godwin De GuzmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6K views7 pagesVariance Analysis (Practice Problems)
(1) The document contains 4 practice problems involving variances. Problem I involves direct materials variances. Problem II involves direct labor variances. Problem III involves multiple variances including materials, labor, and factory overhead. Problem IV is the most complex involving many types of overhead variances.
(2) Each problem provides standard and actual data and requires the calculation of specific variances. The responses provide the calculations and numerical answers for the required variances in each problem.
(3) The document contains practice problems and solutions for calculating different types of cost variances commonly used in standard costing systems.
Uploaded by
Godwin De GuzmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Problem I: Presents a problem related to material price variance and usage.
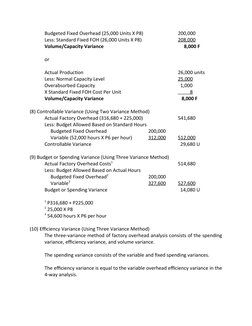
- Problem III: Deals with factory overhead cost variances and various analysis methods.
- Problem II: Describes labor rate variance and efficiency variance in soap production.
- Volume Variance Analysis: Concludes the volume variance analysis within various analytical approaches.