0% found this document useful (0 votes)
865 views2 pagesProbability and Statistics: Foundation
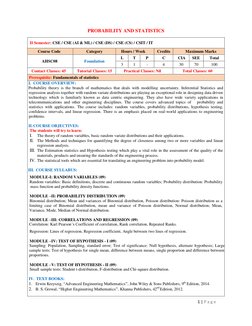
This document provides an overview of a course on probability and statistics. The course covers random variables, probability distributions like binomial and Poisson, hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and linear regression. The course objectives are to learn about random variables and distributions, correlation and regression analysis, estimation statistics and hypothesis testing. The course is divided into five modules covering random variables, common probability distributions, correlations and regression, hypothesis testing techniques, and small sample tests. The course aims to provide statistical tools for engineering problems.
Uploaded by
s sCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
865 views2 pagesProbability and Statistics: Foundation
This document provides an overview of a course on probability and statistics. The course covers random variables, probability distributions like binomial and Poisson, hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and linear regression. The course objectives are to learn about random variables and distributions, correlation and regression analysis, estimation statistics and hypothesis testing. The course is divided into five modules covering random variables, common probability distributions, correlations and regression, hypothesis testing techniques, and small sample tests. The course aims to provide statistical tools for engineering problems.
Uploaded by
s sCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Course Outline
- References