Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Induction Case - Summary
Uploaded by
NM KPTOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Induction Case - Summary
Uploaded by
NM KPTCopyright:
Available Formats
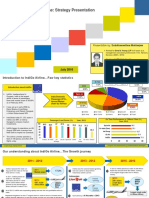
Jayesh Sharaf | PGP’37 (E) | 9 July 2021
SIA India entry - JV Tata – 2013
Written in brief to make it quick read, facts may not be precise. (Have avoided numbers, what’s the point in memorizing?)
Time frame: Feb 2013
Question: Wise for Singapore Airline (SIA) to enter India in partnership with Tata (for full service carrier) considering Tata was partnering with AirAsia
for low-cost carrier? (Conflict of interest for Tata?)
Why problem? :
Full service and low cost are different markets elsewhere but becoming not so distinct in India (because prices not so different in India)
Tata good local partner: Clout, Financial Support, Professionalism
SIA:
Strategy not aligned with low cost:
o Leader in customer service, enhances standards on ground, comfort, cuisines, entertainment
Never posted negative annual return since operations started
o Excl. Indigo, all Indian airlines posted loss in FY 12
SIA India growth restricted by Gov. refusal for bilateral flying agreement on India-Singapore route
INDIAN AVIATION
Opportunities Problems
9th largest market by passenger traffic Loss making (check figures in exhibit)
Expected to be 3rd largest by 2020 (Case is from 2013) Low cost airlines market share reached 59% (had entered in
Increasing affordability, growing connectivity driven by gov. 2004/5)
initiatives, strengthening of viable airlines (especially low Slowing economy
cost), increased FDI High oil prices
Rising Middle class, increasing disposable income, tourism Hostile cost environment (weak rupee)
growth, local business integrating in global market Liquidity constraints
Decline in domestic passenger traffic in 12/13 (Excl. Indigo,
all Indian airlines posted loss in FY 12)
High Cost due to over taxation
High combined debt of Indian Airlines (Air India ~60%)
Indian Airports raising charges, major airports still
experienced sever congestion
GLOBAL AVIATION
2002 to 2012: Growing trend in revenue and passenger volume (excl. 2009)
2012: Week net profit (Global economic slowdown + high jet fuel prices)
Regional situation:
o North America: 31% global revenue (Better efficiency driven by industry consolidation in US – Large carriers reduced from 10 to 5)
(Consolidation: Less players, higher market share for each)
o Europe: 2nd Largest but barely profitable (Eurozone recession: Several European nations unable to repay gov. debt since 2009)
o Asia Pacific:
#3 by revenue but largest profit and largest passenger volume
2012-2032 (20yrs): Faster growth rate than global rate
expected APAC CAGR: 5.5% (vs 4.7% global)
North America and Europe: Decline expected
Significant Overcapacity in 2012
o Cargo load factor: 66%
o Passenger load factor: 79.3% (# of passengers carried / # of available seats)
2nd page: Kaafi history ( Regulation, De regulation, Fragmented market etc)
o CodeSharing: Airlines formed alliances to sell destinations not on their routes – Increased Network
Allows an airline to place its two-letter identification code on the flight schedules of another airline. Flights can be
marketed by one airline and operated by another
o Deregulation in 2nd half of 20th century
o Fare per km per passenger reduced - increased competition – customer more price sensitive
o Struggling to profit as good margin over cost became difficult
o Consolidation in US after many years of losses; not so much in Europe
o 10 largest airlines by revenue: Only 40.8% market share
You might also like
- EIB Group Survey on Investment and Investment Finance 2020: EU overviewFrom EverandEIB Group Survey on Investment and Investment Finance 2020: EU overviewNo ratings yet
- Air AsiaDocument20 pagesAir AsiaAngela TianNo ratings yet
- Policies to Support the Development of Indonesia’s Manufacturing Sector during 2020–2024: A Joint ADB–BAPPENAS ReportFrom EverandPolicies to Support the Development of Indonesia’s Manufacturing Sector during 2020–2024: A Joint ADB–BAPPENAS ReportNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Singapore Airlines - The India DecisionDocument27 pagesCase Study:: Singapore Airlines - The India DecisionCon FluenceNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Cooperation and Integration Between Indonesia and Timor-Leste: Scoping StudyFrom EverandEnhanced Cooperation and Integration Between Indonesia and Timor-Leste: Scoping StudyNo ratings yet
- Sustainability of Airlines in India With Covid19 Challenges Ahead and Possible Wayouts2020journal of Revenue and Pricing ManagementDocument16 pagesSustainability of Airlines in India With Covid19 Challenges Ahead and Possible Wayouts2020journal of Revenue and Pricing ManagementashishNo ratings yet
- Indigo Airlines: Monopolizing Indian Skies: Overview of The Indian Civil Aviation MarketDocument11 pagesIndigo Airlines: Monopolizing Indian Skies: Overview of The Indian Civil Aviation MarketDaivik TandelNo ratings yet
- Swot and Pestle Analysis of Various Regional and International AirlinesDocument26 pagesSwot and Pestle Analysis of Various Regional and International AirlinesrohitmahaliNo ratings yet
- Airlines Industry - IndiaDocument28 pagesAirlines Industry - Indiasumankumarpatra100% (1)
- Capacity Planning DemoDocument21 pagesCapacity Planning DemoSantosh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Soaring Into The High Skies: SSRN Electronic Journal November 2016Document10 pagesCase Study - Soaring Into The High Skies: SSRN Electronic Journal November 2016akanksha kumariNo ratings yet
- Indigo AirlinesDocument23 pagesIndigo AirlinesniravhariaNo ratings yet
- Growth of Indian Aviation IndustryDocument5 pagesGrowth of Indian Aviation IndustryNikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aviation Industry: Integrated Industry Analysis by Ltc03Document15 pagesAviation Industry: Integrated Industry Analysis by Ltc03shruti guptaNo ratings yet
- Macro Environmental Study of Indian Aviation Industry:PEST AnalysisDocument13 pagesMacro Environmental Study of Indian Aviation Industry:PEST AnalysisTahsin Akhtar100% (1)
- Marketingprojectlatest 140916041816 Phpapp02Document60 pagesMarketingprojectlatest 140916041816 Phpapp02kappilNo ratings yet
- Pestel Analysis: Indigo AirlinesDocument10 pagesPestel Analysis: Indigo AirlinesVIRESH NANo ratings yet
- IndiGo Airlines Monopolizing Indian SkiesDocument11 pagesIndiGo Airlines Monopolizing Indian SkiesShubham JhaNo ratings yet
- Jet AirwaysDocument11 pagesJet AirwaysAnonymous tgYyno0w6No ratings yet
- The Clipped Wings 'Jet Airways'Document17 pagesThe Clipped Wings 'Jet Airways'RohanNo ratings yet
- Airline Insolvency DraftDocument4 pagesAirline Insolvency DraftDeepshikhaNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis of Low Cost Carriers in Aviation SectorDocument4 pagesSwot Analysis of Low Cost Carriers in Aviation SectorDivya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Bankruptcy of Jet Airways in India: Jashim Uddin AhmedDocument15 pagesThe Bankruptcy of Jet Airways in India: Jashim Uddin AhmedKelly maria RodriguesNo ratings yet
- W19161 PDF EngDocument11 pagesW19161 PDF EngJithu JoseNo ratings yet
- IndiGo Airlines - Monopolizing Indian SkiesW19161-PDF-ENGDocument11 pagesIndiGo Airlines - Monopolizing Indian SkiesW19161-PDF-ENGSuchira NethaNo ratings yet
- Cooperative & Competitive Strategies Midterm ProjectDocument14 pagesCooperative & Competitive Strategies Midterm ProjectVivek ChhariNo ratings yet
- Automotive Supply ChainDocument13 pagesAutomotive Supply Chaincoolprashant220% (1)
- Indigo: Strategic Management ProjectDocument17 pagesIndigo: Strategic Management ProjectSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- IndiGo Airlines Case StudyDocument11 pagesIndiGo Airlines Case StudyYousuf HossainNo ratings yet
- Team12 MKTG 361 Project Phase 1Document6 pagesTeam12 MKTG 361 Project Phase 1api-638485134No ratings yet
- Spicejet: Credit Rating AnalysisDocument9 pagesSpicejet: Credit Rating Analysissatyakidutta007No ratings yet
- STP Strategy Analysis: SegmentationDocument8 pagesSTP Strategy Analysis: SegmentationAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Issues in Indigo AirlinesDocument5 pagesIssues in Indigo Airlinesanji_2303No ratings yet
- AirIndia Report Group4Document4 pagesAirIndia Report Group4Ajit YadavNo ratings yet
- Aviation Industry AnalysisDocument28 pagesAviation Industry AnalysisKaranNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Jet AirwaysDocument6 pagesGroup 2 - Jet AirwaysAdhip PanditaNo ratings yet
- AirAsia CaseDocument22 pagesAirAsia CaseAdarsh Chhajed100% (1)
- LITERATURE REVIEW (Future Low Cost Carrier) SatishDocument18 pagesLITERATURE REVIEW (Future Low Cost Carrier) SatishSatishNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan of Indigo AirlinesDocument14 pagesMarketing Plan of Indigo AirlinesShrey Chaurasia100% (4)
- Anchal Sir Case Study SPICEJETDocument6 pagesAnchal Sir Case Study SPICEJETOM PRAKASH MALLIKNo ratings yet
- Indigo AirlinesDocument34 pagesIndigo AirlinesRavi Jaisinghani100% (1)
- Ejbe2020vol13no25p091 Shome VermaDocument19 pagesEjbe2020vol13no25p091 Shome VermaManan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MKTG 6650 - Individual AssignmentDocument14 pagesMKTG 6650 - Individual AssignmentShehriyar AhmedNo ratings yet
- IndiGo Airline - Strategy Presentation by Suddhwasattwa MukherjeeDocument19 pagesIndiGo Airline - Strategy Presentation by Suddhwasattwa Mukherjeemukherjee_suddhwa89% (9)
- Micro AnalysisDocument289 pagesMicro AnalysisAPOORV ASTHANANo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument4 pagesSwot Analysisnur syazrinaNo ratings yet
- FSA Assignment On Aviation IndustryDocument4 pagesFSA Assignment On Aviation IndustryPoojaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Strategies Selection Process: A) Build Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities Threats (SWOT) Matrix Swot Analysis Matrix - Air Asia AirlinesDocument7 pagesAlternative Strategies Selection Process: A) Build Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities Threats (SWOT) Matrix Swot Analysis Matrix - Air Asia Airlinesmalikldu50% (2)
- Indian Aviation IndustryDocument7 pagesIndian Aviation IndustryAMAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- IIMA - Industry ReportsDocument52 pagesIIMA - Industry ReportsParth SOODANNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by The Aviation IndustryDocument5 pagesChallenges Faced by The Aviation Industryshiv000291No ratings yet
- Equity Research Case StudyDocument14 pagesEquity Research Case StudyDr. Kamini RaiNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument4 pagesSwot AnalysisShubhamSoodNo ratings yet
- Emirates Airline Case Study: Khalil Ullah TO: ADNAN KHER CMS: 121-17-0017Document17 pagesEmirates Airline Case Study: Khalil Ullah TO: ADNAN KHER CMS: 121-17-0017AliNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation: Project ReportDocument10 pagesStrategy Implementation: Project ReportAayushi ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- Business Turnaround and Organizational Transformation (Btot) Group Assignment: The Fall and Rise of SpicejetDocument16 pagesBusiness Turnaround and Organizational Transformation (Btot) Group Assignment: The Fall and Rise of SpicejetAayushi ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- Iata Financial Committee White PaperDocument46 pagesIata Financial Committee White PaperShotin Patanasorn100% (1)
- Group Group - IV IVDocument24 pagesGroup Group - IV IVAshish MishraNo ratings yet
- Indian Aviation: A Review of 2009 and Outlook For 2010: Prepared by CAPA India's Research & Intelligence UnitDocument24 pagesIndian Aviation: A Review of 2009 and Outlook For 2010: Prepared by CAPA India's Research & Intelligence UnitRussell MendoncaNo ratings yet
- Priyanshi Pathak Harshita Mathur Swagata Dass Aishwarya BarthwalDocument21 pagesPriyanshi Pathak Harshita Mathur Swagata Dass Aishwarya BarthwalHARSHITA MATHURNo ratings yet
- You TubeDocument1 pageYou TubeNM KPTNo ratings yet
- (TGX) Downloaded From Torrentgalaxy - ToDocument1 page(TGX) Downloaded From Torrentgalaxy - Topavan kurapatiNo ratings yet
- Address: Mobile: Email Id: Linkedin:: Organizational ExperienceDocument5 pagesAddress: Mobile: Email Id: Linkedin:: Organizational ExperienceNM KPTNo ratings yet
- Rajat GoswamiDocument2 pagesRajat GoswamiNM KPTNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov-2 (Covid 19) Detection (Qualitative) by Real Time RT PCRDocument3 pagesSars-Cov-2 (Covid 19) Detection (Qualitative) by Real Time RT PCRNM KPTNo ratings yet
- Faizan Khan Ayub KhanDocument22 pagesFaizan Khan Ayub KhanGani GaneyanNo ratings yet
- Ease of Doing Business - Dir Maria Luisa Salonga-AgamataDocument55 pagesEase of Doing Business - Dir Maria Luisa Salonga-AgamataVoltaire M. BernalNo ratings yet
- Instagram and Facebook MarketingDocument6 pagesInstagram and Facebook Marketingaadarsh mahajanNo ratings yet
- Customer Segmentation MatrixDocument4 pagesCustomer Segmentation MatrixRA ArafatNo ratings yet
- Branding British English TeacherDocument5 pagesBranding British English TeacherІрина МиколаївнаNo ratings yet
- Types of Enterprenures - MICRODocument1 pageTypes of Enterprenures - MICRONeelmaniNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis TimberlandDocument21 pagesSWOT Analysis TimberlandGloria NüsseNo ratings yet
- To Marketing: Marketing - Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsDocument24 pagesTo Marketing: Marketing - Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsWaliid Khan MamodeNo ratings yet
- MXN MLMDocument11 pagesMXN MLMKC CarreonNo ratings yet
- Exide Life Insurance - PO 1200011572Document16 pagesExide Life Insurance - PO 1200011572Joan AliNo ratings yet
- 1 StandardReportDocument12 pages1 StandardReportPolo Delehandro YogAjunoNo ratings yet
- CS Form No. 212 Attachment - Work Experience SheetDocument1 pageCS Form No. 212 Attachment - Work Experience SheetNoel Ephraim AntiguaNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory ServicesDocument14 pagesManagement Advisory ServicesChrizzele Quiohilag Sonsing100% (1)
- DM21A24 - Hitakshi ThakkarDocument8 pagesDM21A24 - Hitakshi ThakkarRAHUL DUTTANo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide To Crypto Airdrops in 2024 - 20240113 - 085833 - 0000Document24 pagesUltimate Guide To Crypto Airdrops in 2024 - 20240113 - 085833 - 0000jonathanjasper842No ratings yet
- Management of ULD in AirtransportDocument20 pagesManagement of ULD in AirtransportM AsadNo ratings yet
- Statistics Passing PackageDocument12 pagesStatistics Passing PackageResh RamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Allocation of Joint Costs and Accounting For by ProductDocument18 pagesChapter 11 Allocation of Joint Costs and Accounting For by ProductCelestaire LeeNo ratings yet
- Terms of Reference On AfaDocument15 pagesTerms of Reference On AfaAnonymous 5k7iGy100% (1)
- Model Green BankDocument51 pagesModel Green BankAzraNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Chapter 8-Profitability QuizDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chapter 8-Profitability Quizfatima mohamedNo ratings yet
- Module 03 Supply Chain ManagementDocument21 pagesModule 03 Supply Chain ManagementClinton SamsonNo ratings yet
- Environmental Analysis 3 (8-10M)Document72 pagesEnvironmental Analysis 3 (8-10M)Sania KhanNo ratings yet
- Tiona Langley Resume 2Document1 pageTiona Langley Resume 2tionalangleyNo ratings yet
- (TOEIC650) Exam Practice 1 (16 Bản)Document10 pages(TOEIC650) Exam Practice 1 (16 Bản)Hải YếnNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Hotel (Periwal Eco Tourism Hotels and Resort)Document29 pagesA Project Report On Hotel (Periwal Eco Tourism Hotels and Resort)sauravperiwal50% (2)
- 20220720-MODIG-Supply Chain Manager (ENG)Document2 pages20220720-MODIG-Supply Chain Manager (ENG)abhilNo ratings yet
- Module 2 NotesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Notescriselyn agtingNo ratings yet
- CSE - Dividends Updated 21-12-2020Document4 pagesCSE - Dividends Updated 21-12-2020nandikaNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: RevisionDocument77 pagesBusiness Communication: RevisionTrang TrươngNo ratings yet