Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I. Supply and Demand Curve For Bicycles
Uploaded by
KhairulBasherSujonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I. Supply and Demand Curve For Bicycles
Uploaded by
KhairulBasherSujonCopyright:
Available Formats
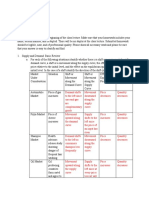
i. Supply and demand curve for bicycles.
a.
ii. As per the graph the equilibrium quantity is 50 and the price that shows a point of
equilibrium is $300. At this point, the powers of demand and supply are equal.
iii. If there is an increase occurs in both demand and supply, the equilibrium price will rise
higher than 300. An increase in equilibrium price and quantity shows that the demand for
a product increased with an increase in their prices. The equilibrium price will also
increase and become more significant than 50, which is the current. Both the equilibrium
price and quantity would increase in the same proportions.
iv. If the demand for bicycles increases more than the supply, it will create an economic
condition called excess demand. The equilibrium price would thus increase to more
proportion than the supply of the bikes. Suppose an equal increase in both EQ and EP
were $400 and 60 respectively, the new rates would thus be $500 and 62. This shows a
small increase in the equilibrium quantity than the equilibrium price.
Reference.
Leoni, B., & Epstein, R. A. (2017). The Problem of Economic Calculation in a Planned
Economy. In Law, Liberty, and the Competitive Market (pp. 39-82). Routledge.
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Price DeterminationDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Price DeterminationNeelabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Economics BasicsDocument9 pagesEconomics BasicsGermaine CasiñoNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand and Market EquilibriumDocument10 pagesSupply and Demand and Market EquilibriumMerliza JusayanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Demand SupplyDocument4 pagesTutorial Demand SupplyLena LeezNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply With Surplus and ShortageDocument4 pagesDemand and Supply With Surplus and Shortagemanish KumarNo ratings yet
- Price DeterminationDocument8 pagesPrice DeterminationIruoluwaniosi OwolabiNo ratings yet
- Economics CSEETDocument30 pagesEconomics CSEETx6rrvvdg46No ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium (Students)Document23 pagesMarket Equilibrium (Students)Melroy PereiraNo ratings yet
- Economics Question & AnswerDocument5 pagesEconomics Question & AnswerumeshNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Is Perhaps One of The Most Fundamental Concepts of Economics and It Is The Backbone of A Market EconomyDocument6 pagesSupply and Demand Is Perhaps One of The Most Fundamental Concepts of Economics and It Is The Backbone of A Market EconomySheikh MohsinNo ratings yet
- Real World Connections: Supply, Demand and Equilibrium PriceDocument7 pagesReal World Connections: Supply, Demand and Equilibrium PriceHaseeb KhâñNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument35 pagesDemand and SupplysiribandlaNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics-Demand & SupplyDocument8 pagesEconomics Basics-Demand & SupplyNahiyan Islam ApuNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Law of DiminishingDocument6 pagesDemand and Supply Law of DiminishinggralenekovaNo ratings yet
- Economics ReviewerDocument15 pagesEconomics ReviewerPatriciaNo ratings yet
- 3 Demand ForecastingDocument8 pages3 Demand ForecastingShanmukh GollapudiNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics - Supply and Demand - InvestopediaDocument5 pagesEconomics Basics - Supply and Demand - Investopediaddeww100% (1)
- 09-20-2009 12 54 35PMDocument1 page09-20-2009 12 54 35PManyashataledmundNo ratings yet
- Suply Demand CurvesDocument7 pagesSuply Demand CurvesonkaliyaNo ratings yet
- Demand & SupplyDocument6 pagesDemand & SupplySoham GuhaNo ratings yet
- Health Economics SupplyDocument7 pagesHealth Economics SupplyPao C EspiNo ratings yet
- Answerstohomework 2 Summer 2010Document10 pagesAnswerstohomework 2 Summer 2010Abul KashemNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics: Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesEconomics Basics: Supply and Demandrizqi febriyantiNo ratings yet
- Economics BasicsDocument17 pagesEconomics BasicsmdsalmanarNo ratings yet
- Economics Basic3 Supply DemandDocument6 pagesEconomics Basic3 Supply Demandwaluyo2010No ratings yet
- Law of SupplyDocument15 pagesLaw of SupplyZahid RaihanNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply: A. The Law of DemandDocument4 pagesDemand Supply: A. The Law of DemandJoshua KeanuNo ratings yet
- Report - MBA 103 - Supply, Demand, Equilibrium PriceDocument28 pagesReport - MBA 103 - Supply, Demand, Equilibrium PriceJamil DiligNo ratings yet
- How Is Equilibrium EstablishedDocument5 pagesHow Is Equilibrium EstablishedJudy Mar Valdez, CPANo ratings yet
- SG ch03Document15 pagesSG ch03Fathiah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Demand Curve: The Chart Below Shows That The Curve Is A Downward SlopeDocument7 pagesDemand Curve: The Chart Below Shows That The Curve Is A Downward SlopePrince Waqas AliNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply and Market Equilibrium PDFDocument7 pagesDemand Supply and Market Equilibrium PDFAishwarya VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- DEmand and SupplyDocument3 pagesDEmand and SupplyAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Intro On EquilibriumDocument3 pagesIntro On EquilibriumNikunj JainNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Notes 2020: FREE and DownloadableDocument20 pagesIGCSE Economics Notes 2020: FREE and DownloadableMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- ManEcon Module 3Document8 pagesManEcon Module 3Lili PadNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesSupply and Demandabhi1910100% (1)
- Problem Set 3Document5 pagesProblem Set 3Nguyễn Vũ ThanhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document35 pagesLecture 04Hoda AmrNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument6 pagesDemand and SupplyAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Group A: Reading: What Is Demand?Document7 pagesGroup A: Reading: What Is Demand?Agyekum FrancisNo ratings yet
- Basic Analysis of Demand and Supply 1Document6 pagesBasic Analysis of Demand and Supply 1Jasmine GarciaNo ratings yet
- Course Material - Demand and Supply Analysis 2Document14 pagesCourse Material - Demand and Supply Analysis 2JAMES CRISTOFER TARROZANo ratings yet
- SupplyDocument3 pagesSupplyHaridha NurFadillaNo ratings yet
- Microecons P3 NotesDocument19 pagesMicroecons P3 NotesLee Wei ChuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - DemandDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - DemandVaruna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument8 pagesMarket EquilibriumSourav SinghNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Week 3 (Market Demand - Supply Equilibrium)Document59 pagesApplied Economics Week 3 (Market Demand - Supply Equilibrium)ALCondezEdquibanEbuenNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument7 pagesDemandLakshayNo ratings yet
- I 3 EC Introduction-Demand SupplyDocument28 pagesI 3 EC Introduction-Demand SupplyDaliah Abu JamousNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply, and EquilibriumDocument21 pagesDemand, Supply, and Equilibriump4d2w8s5pbNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Economics For Managers-4Document9 pagesUnit 4 Economics For Managers-4umangrathod613No ratings yet
- Answer:: EC1301 Tutorial 2Document3 pagesAnswer:: EC1301 Tutorial 2Seyoum LeulNo ratings yet
- ECON 519 DATE: 10/27/09 Jose Cintron, MbaDocument26 pagesECON 519 DATE: 10/27/09 Jose Cintron, MbaJeff RamosNo ratings yet
- Google Market Equilibrium ExamplesDocument11 pagesGoogle Market Equilibrium ExamplesAllicamet SumayaNo ratings yet
- Unec 1705578602Document27 pagesUnec 1705578602shshshithffNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Part 4Document13 pagesAnswer Key Part 4Alfina TabitaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Demand and SupplyDocument3 pagesRelationship Between Demand and SupplyViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- As A Low Cost Airline How Ryanair Ensures Quality Throughout Its Operation Final With ReferenceDocument2 pagesAs A Low Cost Airline How Ryanair Ensures Quality Throughout Its Operation Final With ReferenceKhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- Case Study Dhaka Structure Plan 2016 2035Document395 pagesCase Study Dhaka Structure Plan 2016 2035KhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- 460 Report SampleDocument54 pages460 Report SampleKhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- Project Guidelines MGT 314 Summer2021 1Document3 pagesProject Guidelines MGT 314 Summer2021 1KhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- Easton 6E Module 2 (7 Files Merged)Document445 pagesEaston 6E Module 2 (7 Files Merged)KhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 HRM 20Document1 pageCase Study 1 HRM 20KhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 FADocument1 pageQuiz 2 FAKhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- Bus172 MidDocument73 pagesBus172 MidKhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet
- AusruDocument1 pageAusruKhairulBasherSujonNo ratings yet