Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Results Background and Aims Results: - Kaplan-Meier
Results Background and Aims Results: - Kaplan-Meier
Uploaded by
Jo Ma Sa DuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Results Background and Aims Results: - Kaplan-Meier
Results Background and Aims Results: - Kaplan-Meier
Uploaded by
Jo Ma Sa DuCopyright:
Available Formats
Outcomes from brain death donors with cardiac arrest (caDBD)
accepted for pancreas transplantation
Pedro Ventura-Aguiar1,2, Joana Ferrer3, David Paredes4, Camino Rodriguez-Villar4, Angel Ruiz4, Josep Fuster3, Constantino Fontdevilla3, Enric Esmatjes5, Ramon Adália4, Federico
NOTHING TO DISCLOSE
Oppenheimer1,2,6, Josep M Campistol1,6, Fritz Diekmann1,2,6, Maria J Ricart1.
1. Renal Transplant Unit, Nephrology and Kidney Transplant Department, Hospital Clinic Barcelona, Spain; 2. Laboratori Experimental de Nefrologia I Trasplantament (LENIT), CRB CELLEX, Fundació Clínic, IDIBAPS, Barcelona, Spain;
3. Hepatobiliopancreatic and Liver & Pancreas Transplant Departmen; 4. Donation and Transplantation Coordination Unit,; 5. Diabetes Unit, Department of Endocrinology and Nutrition,. REDinREN
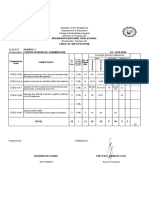
Table 2 – Pancreas surgical complications
BACKGROUND AND AIMS RESULTS caDBD
(n= 49)
RESULTS
Other DBD
(n= 296)
p
Admission length
13 [10-19] 15 [11-24] .56
(days; median [IQR])
Donors after cardiocirculatory death (DCD) have been used for Pancreas transplants Graft failure <90 days (n/%) 4 (8.2%) 29 (9.8%) .79
pancreas transplantation, with good outcomes. Warm ischemia (n=345) Technical Failure 4 (8.2%) 27 (9.2%) .62
Clavien-Dindo (%)* .53
times documented in these reports vary from an average of 5.3 No complication 69.6% 58.3%
to 30minutes 7–10, and up to a maximum of 57 minutes. Grade I 2.2% 7.3%
Grade II 4.3% 5.8%
Literature reports on the effect of cardiac arrest prior to Grade IIIa 6.5% 4.2%
Grade IIIb 15.2% 22.8%
pancreas donation from donors after brain death (DBD) are Grade IVa 2.2% 1.5%
scarce. In pre-procurement P-PASS score emphasis is given caDBD Grade VIb 0% 0%
Other DBD Grade V 0% 0%
to donor cardiac arrest, with a cufoff value of 5min determined (n=49) (n=296) Re-laparotomy (n/%) 14 (29%) 83 (28%) .88
by expert opinion. Days to re-laparotomy
8 [2-19] 14 [4-44] .62
Figure 2 - ROC curve analysis performed
• median Cardiac arrest time (CAT): 5.0 min [IQR 2.5-15.0]; (median [IQR]) to discriminate cardiac arrest time (CAT)
We aimed at evaluating the effect of a cardiac arrest in DBD minimum 1min, maximum 45min), Graft Thrombosis
(partial or total; %)
22.4% 20.8% .85
and the incidence of technical failure (TF).
donors on pancreas graft outcomes. • age of 29.0 years (SD 10.2)
Thrombosis treatment (%)
• BMI of 23.6 Kg/m2 (SD 3.4).
• COD: Anoxic encephalopathy most frequent (32.7% vs Conservative 36.4% 50.0% .80
1.8% in other DBD; p=0.000). Interventional radiology 27.2% 26.8%
METHODS • P-PASS score higher (16.9 vs 15.6 in other DBD; p=0.005).
• P-PASS sub-categories - only cardiac arrest scores
Surgical 36.4% 23.2%
*Clavien-Dindo was calculated to pancreas complications only;
significantly higher (2.5 vs 1.0 in other DBD; p=0.000).
We conducted a single center retrospective analysis • PDRI similar between both groups
• All remaining demographic and clinical characteristics were
including all DBD donors accepted for pancreas similar between both groups (p>0.05). Figure 3 – Kaplan-Meier
transplantation (PTx) from January 1st, 2000 until December pancreas graft survival
31st, 2016, including simultaneous pancreas-kidney (SPK), estimates in caDBD with
pancreas after kidney (PAK), and pancreas transplant alone a CAT over 15minutes
(caDBD>15) is
(PTA) recipients.
significant inferior (log-
Definitions: rank p=0.001) compared
to caDBD with CAT <
a) Patient survival: last day of follow-up, date of death with a 15min (caDBD<15) and
functioning pancreas graft, or at 90 days following failure of other DBD.
pancreas graft (or both grafts in SPK).
b) Pancreas graft failure: graft removal, C-peptide <1ng/mL,
total daily insulin need >0,5U/Kg, or patient death;
c) Kidney graft failure: return to dialysis, re-transplantation, or
patient death. CONCLUSIONS
d) Technical failure (TF) was defined as any non- •caDBDs are suitable for routine use in pancreas transplantation;
immunological graft failure during the first 90 days following •Technical failure incidence was similar between caDBD and other DBD
pancreas transplantation. donors.
e) Anticoagulation: enoxaparin 20mg bid starting 8h post- Figure 1 – Kaplan-Meier pancreas graft survival estimates •Cardiac arrest time over 15 minutes was associated with an increased
for DBDs with previous cardiac arrest (caDBD) and all risk for technical failure (HR 5.80 [95% CI 1.82-18.56]; p=0.003), with a
surgery and maintained until patient discharge and aspirin sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 75% for this outcome.
other DBDs accepted for pancreas transplantation.
50mg/day until discharge, then increased up to 100mg/day
FOLLOW ME
@PVentura_Aguiar Contact: pventura@clinic.cat
Pedro_Aguiar7 POSTER DOWNLOAD
You might also like
- 2004 - Road Design StandardsDocument44 pages2004 - Road Design Standardsanik_kurpNo ratings yet
- Alex Ferguson - Alex Ferguson - My Autobiography PDFDocument543 pagesAlex Ferguson - Alex Ferguson - My Autobiography PDFAldia Palma Yudhasta100% (5)
- Catalogo de Pecas Carregadeira Pneus Volvo L120e PDFDocument1,172 pagesCatalogo de Pecas Carregadeira Pneus Volvo L120e PDFPedro Matheus90% (10)
- Case Study DBM Maths - 3Document11 pagesCase Study DBM Maths - 3Gnabry100% (2)
- Stem-and-Leaf Plots & Histograms QuizDocument8 pagesStem-and-Leaf Plots & Histograms QuizRaghuveer ChandraNo ratings yet
- BS EN 50310-2010 BondingDocument40 pagesBS EN 50310-2010 Bondingruhuna01380% (5)
- FS 10 AttachmentDocument3 pagesFS 10 AttachmentWizeri Zegarra GálvezNo ratings yet
- Newborns EEG Seizure Detection Using A Time-Frequency ApproachDocument5 pagesNewborns EEG Seizure Detection Using A Time-Frequency Approachmobile 1360No ratings yet
- Case Study DBM Maths - 3Document11 pagesCase Study DBM Maths - 3GnabryNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Schedulability Analysis of Multiple Distiller Crude Oil Operations in Refinery With Oil Residency Time ConstraintDocument16 pagesShort-Term Schedulability Analysis of Multiple Distiller Crude Oil Operations in Refinery With Oil Residency Time Constraintkhaled_behery9934No ratings yet
- Fault Diagnosis of Power Transformers With Membership DegreeDocument8 pagesFault Diagnosis of Power Transformers With Membership DegreeShoaibMeraj SamiNo ratings yet
- GRP 07 Exp 06 Ieclab 2Document9 pagesGRP 07 Exp 06 Ieclab 2esumshunNo ratings yet
- SegmentNT Annotating The Genome at Single Nucleotide Resolution With DNA Foundation ModelsDocument28 pagesSegmentNT Annotating The Genome at Single Nucleotide Resolution With DNA Foundation ModelsRachid JelloulNo ratings yet
- Form Deskripsi Coring FIXDocument1 pageForm Deskripsi Coring FIXMochamad AprilliantoNo ratings yet
- Nilai Semester 6 - (Sistem Operasi) - 2018-2019 - (Triyono)Document210 pagesNilai Semester 6 - (Sistem Operasi) - 2018-2019 - (Triyono)Ariyanto Kurniawan PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- June 2010 (v3) QP - Paper 5 CIE Physics A-LevelDocument8 pagesJune 2010 (v3) QP - Paper 5 CIE Physics A-LevelDamien SibandaNo ratings yet
- Stat 110 Syllabus: A Customized Edition of Statistics Department, King Abdulaziz UniversityDocument12 pagesStat 110 Syllabus: A Customized Edition of Statistics Department, King Abdulaziz UniversityT RNo ratings yet
- Achiever Course: Classroom Contact ProgrammeDocument5 pagesAchiever Course: Classroom Contact ProgrammeManu PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Buenavista National High School Table of Specification Science 7 S.Y. 2019-2020Document4 pagesBuenavista National High School Table of Specification Science 7 S.Y. 2019-2020Gerald Vinz GenyosoNo ratings yet
- 9702 s11 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pages9702 s11 QP 22 PDFShantoshCumarasurierNo ratings yet
- Damping Scaling Models For Elascc Response SpectraDocument35 pagesDamping Scaling Models For Elascc Response SpectraGermar PorquerinoNo ratings yet
- The Continuous Acceptance Sampling of Truncated Frechet Distribution Based On CUSUM SchemesDocument9 pagesThe Continuous Acceptance Sampling of Truncated Frechet Distribution Based On CUSUM SchemesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Influence of Minor Components On Haze Formation in Palm Oil BiodieselDocument1 pageInfluence of Minor Components On Haze Formation in Palm Oil BiodieselvladimirplataNo ratings yet
- SAIKRISHNAVDocument5 pagesSAIKRISHNAVShaik vaseemNo ratings yet
- Update On Fevar: SciencedirectDocument4 pagesUpdate On Fevar: SciencedirectTameTheNo ratings yet
- Modified SMBDDocument6 pagesModified SMBDbachirNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification SampleDocument2 pagesTable of Specification SampleRyan OriasNo ratings yet
- Msas PosterDocument1 pageMsas Posterapi-753059042No ratings yet
- 9702 s10 QP 41Document24 pages9702 s10 QP 41Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- UNIQUAC Matlab CodeDocument27 pagesUNIQUAC Matlab CodeMaythee SaisriyootNo ratings yet
- ECE D NT FINAL II ECE I Sem (2021-Batch) - IM's AY 22-23 I Sem - R20Document113 pagesECE D NT FINAL II ECE I Sem (2021-Batch) - IM's AY 22-23 I Sem - R20shaikNo ratings yet
- Format Nilai Gasal 2023-2024 - XiiDocument8 pagesFormat Nilai Gasal 2023-2024 - Xiikhoirulanam05No ratings yet
- November 2011 (v2) QPDocument12 pagesNovember 2011 (v2) QPbidush dahalNo ratings yet
- Proceeding 2018Document2 pagesProceeding 2018Dang Son TungNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Second-Order Ordinary Differential Equations by Improved Runge-Kutta Nystrom MethodDocument4 pagesNumerical Solution of Second-Order Ordinary Differential Equations by Improved Runge-Kutta Nystrom MethodprabeshjhaNo ratings yet
- 48 - 60CR Project Guide - MarineDocument510 pages48 - 60CR Project Guide - MarineIgorNo ratings yet
- Thesis 1Document39 pagesThesis 1Konki CharishmaNo ratings yet
- Cunha 1996Document4 pagesCunha 1996LUIS. F RuizNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/53Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/53Susan GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Travers Poster Presentation 4 21 17Document1 pageTravers Poster Presentation 4 21 17api-323100338No ratings yet
- Polylactic Acid As A Material For Three-Dimensional Printing of Provisional RestorationsDocument2 pagesPolylactic Acid As A Material For Three-Dimensional Printing of Provisional RestorationsBalavigneshwaran bt18ipf04No ratings yet
- Quantitavtive TechnicsDocument10 pagesQuantitavtive TechnicsChandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- ESOC 2023 - Póster DefinitivoDocument1 pageESOC 2023 - Póster Definitivolaurafernadezperez18No ratings yet
- NDT and E International: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesNDT and E International: SciencedirectAle RojasNo ratings yet
- Killing It With Zero-Shot Adversarially Robust Novelty DetectionDocument5 pagesKilling It With Zero-Shot Adversarially Robust Novelty DetectionJorge CasajusNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Math P2 (English and Afrikaans) November 2017 Possible AnswersDocument10 pagesGr10 Math P2 (English and Afrikaans) November 2017 Possible Answerslwazilushaba2461No ratings yet
- The Double-Generalized Gamma Distribution and Its Application To V2V CommunicationsDocument7 pagesThe Double-Generalized Gamma Distribution and Its Application To V2V CommunicationsjayNo ratings yet
- Parallel Simulation of 3-D Turbul Ent Flow Through Hydraulic Machinery"Document6 pagesParallel Simulation of 3-D Turbul Ent Flow Through Hydraulic Machinery"mani manisNo ratings yet
- Solved 0580 - m16 - QP - 22..''..typedDocument13 pagesSolved 0580 - m16 - QP - 22..''..typedJohn Raza100% (1)
- Boundary Conditions For The Solution of Compressible Navier-Stokes Equations by An Implicit Factored MethodDocument26 pagesBoundary Conditions For The Solution of Compressible Navier-Stokes Equations by An Implicit Factored MethodIan RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Tony Ma Eng 1ST Year ResultDocument1 pageTony Ma Eng 1ST Year ResultTony DinakaranNo ratings yet
- 2018 Review Course Equations You Should Know 1Document22 pages2018 Review Course Equations You Should Know 1BăraBucurNo ratings yet
- Open-Loop Process Identification: Reformulation of Response Rate CalculationDocument5 pagesOpen-Loop Process Identification: Reformulation of Response Rate CalculationAhmad Ca'inNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelNoor MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Meth p4 RaDocument20 pagesMeth p4 RaIrllyshouldslepepNo ratings yet
- Energy Consumption Forecasting Model For Puerto Princesa Distribution System Using Multiple Linear RegressionDocument4 pagesEnergy Consumption Forecasting Model For Puerto Princesa Distribution System Using Multiple Linear RegressionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Bowtie Filtration On Cone-Beam CT Image QualityDocument12 pagesThe Influence of Bowtie Filtration On Cone-Beam CT Image QualityÖzgür Kara (OncoHealth)No ratings yet
- Form Fit To WorkDocument1 pageForm Fit To WorkIin NasutionNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Reliability Method Formulations IDocument17 pagesInvestigation of Reliability Method Formulations IMsegade2No ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Spinal Cord Using FDM ProcessDocument38 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Spinal Cord Using FDM ProcessKonduru NaniNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 4Document20 pagesDatasheet 4hidro citarumNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Nov 2002 PhysicsDocument12 pagesPaper 2 Nov 2002 PhysicssolarixeNo ratings yet
- Planning and Design Considerations of Obstruction Elimination of A Shield TunnellingDocument7 pagesPlanning and Design Considerations of Obstruction Elimination of A Shield Tunnellingdj_taipeiNo ratings yet
- 2VanAmburgh - NDF and uNDFDocument17 pages2VanAmburgh - NDF and uNDFRoger BarrosNo ratings yet
- List of NBFCDocument188 pagesList of NBFCDevansh Sanghvi (QubeHealth)No ratings yet
- Elements JointsDocument52 pagesElements JointssdsdsdnNo ratings yet
- The Correspondence Theory of Truth PDFDocument14 pagesThe Correspondence Theory of Truth PDFhammoudeh13No ratings yet
- Iofi Code of Practice 5th RevisionDocument60 pagesIofi Code of Practice 5th RevisionVALERIA HERRERA CHALARCANo ratings yet
- HyderabadDocument8 pagesHyderabadNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument46 pagesBusiness PlanJhon Fernan MadolidNo ratings yet
- Winsor Pilates - Tips, and Some Exercises To DoDocument8 pagesWinsor Pilates - Tips, and Some Exercises To DoudelmarkNo ratings yet
- Organic DPPDocument11 pagesOrganic DPPRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Iwonder 1-4 Answer KeyDocument3 pages2 Iwonder 1-4 Answer KeyAlina CheNo ratings yet
- Theory of Magnetic Adjustment PDFDocument8 pagesTheory of Magnetic Adjustment PDFNoli VirgoNo ratings yet
- Central Sterile RoomDocument12 pagesCentral Sterile Roomripss09100% (1)
- Seminar Presentation 7Document60 pagesSeminar Presentation 7emma_ade92007No ratings yet
- Analysis of The Essential Oils From Calendula Officinalis Growing in BrazilDocument5 pagesAnalysis of The Essential Oils From Calendula Officinalis Growing in BrazilAslı Gök-GamsızkanNo ratings yet
- 1 Cylinder Diesel EngineDocument3 pages1 Cylinder Diesel Engineramniwas123No ratings yet
- Wcfs2019 FlyerDocument10 pagesWcfs2019 FlyerZhi Yung TayNo ratings yet
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument39 pagesShigley's Mechanical Engineering Design賴信宏No ratings yet
- Mozambique Recipes: Traditional Diet in Mozambique: Rice, Cornmeal, Grits, Tropical Fruits, VegetablesDocument4 pagesMozambique Recipes: Traditional Diet in Mozambique: Rice, Cornmeal, Grits, Tropical Fruits, VegetablesAyerango HarrietNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D.: Câu 1: Which of The Following Is NOT A Minimal Pair?Document9 pagesA. B. C. D. A. B. C. D.: Câu 1: Which of The Following Is NOT A Minimal Pair?Lan PhongNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Working of MetalsDocument53 pagesMechanical Working of Metalsmurari100% (3)
- Grade 7 Algebra Expressions and Equations inDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Algebra Expressions and Equations inYesan SellanNo ratings yet
- Catalogue and Indexes of San Charts and Other Hydrographic PublicationsDocument27 pagesCatalogue and Indexes of San Charts and Other Hydrographic PublicationsCodruţ ErașcuNo ratings yet
- MDP408a Lecture08Document42 pagesMDP408a Lecture08Hisham Ahmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Método de Generación EngranajesDocument1 pageMétodo de Generación EngranajesJaime Orlando Sanchez OlarteNo ratings yet
- Anti DiabeticDocument34 pagesAnti DiabeticEJ GabaoNo ratings yet
- Seam 4 Semi Final ExamDocument2 pagesSeam 4 Semi Final ExamKe Ken EstenzoNo ratings yet