Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOL125 Basic Biology
Uploaded by
adeeb ahmedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOL125 Basic Biology
Uploaded by
adeeb ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
LEBANESE INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
BIOL 125: Basic Biology (3 credits)
Course Syllabus
Fall Term 2011-2012
INSTRUCTOR: Sara Saad
LECTURE HOURS: T,Th: 11:00-12:15
OFFICE HOURS:
GRADE DISTRIBUTION
Exam I 30%
Exam II 30%
Final Exam 40%
COURSE DESCRIPTION
This course is designed to introduce freshman students to key biological concepts that are fundamental
to plant and animal biology. Students will be acquainted with the classification of other organisms and
familiarized with the interrelationships among living things and their non-living environment.
REQUIRED TEXTBOOK
Biology, Life on earth by Teresa Audesirk, Gerald Audesirk and Bruce Byers. 7th edition
Prentice hall Inc. 2006. (www.prenhall.com)
COURSE OUTLINE BY TOPIC
Topics Title / Chapter Assignment # Hours
(50 minutes)
An introduction to life on earth (Chapter 1; pp2-19)
1 3
What are the characteristics of living things?
How do scientists categorize the diversity of life?
What is the science of biology?
Evolution: The unifying theory of biology
Systematics: Seeking order amidst diversity (Chapter 18; pp344-357)
2 3
How are organisms named and classified?
What are the kingdoms of life?
Why do taxonomies change?
Exploring biodiversity: How many species exist?
3 The Diversity of viruses, Prokaryotes, and Protists (Chapter 19; pp. 358-385) 4
What are viruses, viroids, and prions?
Which organisms make up the prokaryotic domains- bacteria and archaea?
What are protists
- Chromists(water molds, diatoms, brown algae)
- Plasmodium (Alveolates)
- Paramecium (Ciliates)
- Red algae
- Trypanosoma (Zooflagellates)
- Green algae
4 The Diversity of fungi (Chapter 20; pp. 386- 403) 4
What are the main adaptations of fungi?
How are fungi classified?
How do fungi affect human?
Exam I
5 The Diversity of plants (Chapter 21, pp 404-421) 4
What are the key features of plant?
Evolutionary origins of plants
Invasion and flourishing of plants on land
6 Plant Anatomy and Nutrient transport (Chapter 24; pp. 464-493) 4
Organization of plant body
Tissues and cell types of plant
Roots, stem, leave
How plants acquire nutrients?
Water and sugar transport in plants
7 Animal Diversity I and II (Chapters 22 & 23 pp. 422-463) 4
Characteristics of animals
Anatomical features of animals
Animal phyla
- Sponges
- Cnidarians
- Flat worms
- Segmented worms
- Mollusqs (snail)
- Arthropods (insects)
- Round worms
Key features of Chordates
Major groups of invertebrates
Exam II
8 Population growth and regulation (Chapter 39 pp. 796-817) 4
Population growth and regulation
Spatial distribution of populations
Changing of human population
9 Community interactions (Chapter 40 pp. 818-839) 5
Importance of community interactions
Competition among species
Interactions between predators and prey
Symbiosis
Succession
10 How do ecosystems work? (Chapter 41 pp. 840-861) 5
Pathways of energy and nutrients
Energy flow through communities
Nutrient cycles
Acid rain and global warming
Final Exam
You might also like
- Lebanese International University - Beirut Campus Faculty of Arts & Sciences BIOL 365: Genetics (3 Credits) Course Syllabus Spring Term 2009-2010Document4 pagesLebanese International University - Beirut Campus Faculty of Arts & Sciences BIOL 365: Genetics (3 Credits) Course Syllabus Spring Term 2009-2010adeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- BIOL360L Human Physiology - Anatomy LabDocument2 pagesBIOL360L Human Physiology - Anatomy Labadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- BIOL360 Human Physiology - AnatomyDocument3 pagesBIOL360 Human Physiology - Anatomyadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- BIOC310 Medical BiochemistryDocument5 pagesBIOC310 Medical Biochemistryadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- BIOL275 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesBIOL275 Cell and Molecular Biologyadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Topics Title / Chapter Assignment Hours (50 Minutes) A View of Life (Chapter 1 Pp. 1-24)Document4 pagesTopics Title / Chapter Assignment Hours (50 Minutes) A View of Life (Chapter 1 Pp. 1-24)adeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- BIOC445 BiotechnologyDocument3 pagesBIOC445 Biotechnologyadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
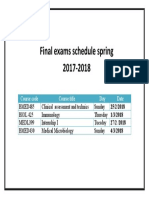
- Final Exam ScheduleDocument1 pageFinal Exam Scheduleadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- BIOL200L General Biology I LABDocument4 pagesBIOL200L General Biology I LABadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Project Management Rehabilitation of Al Nasser SchoolDocument30 pagesProject Management Rehabilitation of Al Nasser Schooladeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Chem125 Final ExamDocument5 pagesBasic Chemistry Chem125 Final Examadeeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Ratnagiri Sindhudurg Tour Report FinalDocument13 pagesRatnagiri Sindhudurg Tour Report Finalrajeevmenon2003No ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument23 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledShingo TakasugiNo ratings yet
- Train To Busan-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesTrain To Busan-WPS Officebirdsflying193No ratings yet
- Endangered Flora and Fauna of Jamuaari RiverDocument8 pagesEndangered Flora and Fauna of Jamuaari RiverGHOORANNo ratings yet
- 1 - 8 Yunita LemaDocument8 pages1 - 8 Yunita LemaFrengki SaputroNo ratings yet
- Protected Landscapes and Cultural LandscapesDocument12 pagesProtected Landscapes and Cultural Landscapesbianconero55No ratings yet
- 6.9 The Environment (Protection) ActDocument8 pages6.9 The Environment (Protection) ActSameerNo ratings yet
- Wong & Hsu - Education For Democratic-Ecological Citizens For The Next System v5 (Of)Document20 pagesWong & Hsu - Education For Democratic-Ecological Citizens For The Next System v5 (Of)Julian WongNo ratings yet
- Transition of Ecosystem Services Based On Urban Agro EcologyDocument20 pagesTransition of Ecosystem Services Based On Urban Agro EcologyAna C. PonticelliNo ratings yet
- J P SharmaDocument16 pagesJ P Sharmamahesh0% (1)
- GBS EcologySample Questions.232170421Document14 pagesGBS EcologySample Questions.232170421Kranthi VanamalaNo ratings yet
- Ap World History FRQ 2017Document13 pagesAp World History FRQ 2017kennyplayz2007No ratings yet
- Globalization As Cultural ProcessDocument4 pagesGlobalization As Cultural ProcessNixon PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Natural Farming With Organic and Biological TechnologyDocument106 pagesIntroduction To Natural Farming With Organic and Biological Technologycdwsg25492% (12)
- ICRMPDocument2 pagesICRMPGmelina Tumaliuan Manaligod100% (1)
- On Thom Hartmann and The Last Hours of Ancient SunlightDocument8 pagesOn Thom Hartmann and The Last Hours of Ancient SunlightDanut ViciuNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Loss and Biodiversity ConservationDocument8 pagesBiodiversity Loss and Biodiversity ConservationSREE HARYINI S BTYENo ratings yet
- Atlantic Forest Terrestrial Molluscs of The Taquara Municipal Nature Park, State of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilDocument55 pagesAtlantic Forest Terrestrial Molluscs of The Taquara Municipal Nature Park, State of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilpigzxcNo ratings yet
- Karianshola GrasslandsDocument3 pagesKarianshola GrasslandsMudassir AhmedNo ratings yet
- CY 1201 Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument16 pagesCY 1201 Environmental Science and EngineeringRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- Bali NTT GeoEcoanalysisDocument110 pagesBali NTT GeoEcoanalysisAsuro LearnNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Diversity of Foliar Endophytic Fungi: Progress, Challenges, and FrontiersDocument16 pagesUnderstanding The Diversity of Foliar Endophytic Fungi: Progress, Challenges, and FrontiersNancy HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Rti - 2005Document33 pagesRti - 2005Kunal Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Entomology 2nd EditionDocument2 pagesEncyclopedia of Entomology 2nd EditionexjupiterNo ratings yet
- Social Diversity UDocument11 pagesSocial Diversity UGreeshma jose.L Greeshma jose .LNo ratings yet
- CDP San Pablo Vfeb - 2022Document237 pagesCDP San Pablo Vfeb - 2022Selle Callos NaguitNo ratings yet
- Sanyam and VipashaDocument10 pagesSanyam and VipashaAnonymous zy3rAYHNo ratings yet
- SEM-II-MDC (Biological Science)Document5 pagesSEM-II-MDC (Biological Science)pm102382No ratings yet
- (Robert Phillipson (Editor) ) Rights To Language EducationDocument317 pages(Robert Phillipson (Editor) ) Rights To Language EducationJakab ZalánNo ratings yet
- 10b. PROTECTED AREADocument90 pages10b. PROTECTED AREAHarsely BayoNo ratings yet