Professional Documents
Culture Documents
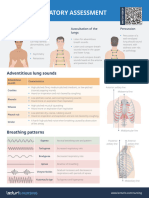
Lungs and Thorax
Lungs and Thorax
Uploaded by
Ja LoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lungs and Thorax
Lungs and Thorax
Uploaded by
Ja LoCopyright:
Available Formats
Body Part Actual Finding Normal Finding Clinical
Examined Significance
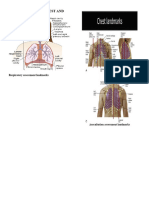
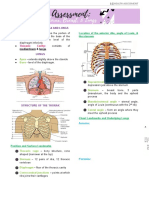
THORAX &
LUNGS
Posterior Normal chest Anteroposterior to
Thorax shape with no the transverse Assessment of
I: shape & deformities and diameter in ratio the symmetry
spine vertically 1:2. and shape of the
symmetry from
aligned. Chest symmetric. spine is to
posterior-lateral
Sipinal column is determine any
views; spinal abnormalities
straight, right and
alignment for left shoulders, and that will indicate
deformities hips are at the deformities such
same heights. as barrel chest,
kyphosis, or
scoliosis.
Assessment is
Equal temp from performed to
both sides of the
Skin is intact with determine any
body. No use of abnormalities
Pa: temperature, uniform
accessory associated with
temperature.
bulges, muscle, neck, the breathing
Chest wall intact,
tenderness, shoulder, and and to
no tenderness, no
abnormal abdominal muscle investigate the
masses.
movements, during respiration lung size and to
respiratory No tenderness is palpate for good
excursion, appreciated upon ventilation of the
vocal fremitus palpation of the lungs.
chest wall.
Full and symmetric
To assess for
The patient does chest expansion.
any trouble
Pe: for symmetry not exhibit signs Bilateral symmetry
of resonance; of tactile fremitus. associated
of respiratory distr breathing and
diaphragmatic ess. Excurison is 3:5
excursion breathing
cm bilaterally in
pattern. To
women, and 5:6
determine the
cm in men.
size of the
diaphragm and
Regular Quit rythmic, and
its normal
A: breath sounds respiratory movement.
effortless
John Lloyd B. Agasang
BSN 2-3
rhythm. Quit and respirations. Auscultation of
unlabored the breath sound
respiration. to rule out any
respiratory
disorder.
Coastal angle is
Normal breathing less than 90
Anterior Thorax pattern with no degrees and the
I: breathing tenderness upon ribs insert into the
pattern, coastal palpation of spine at
and costovertebral approximately a 45
costovertebral with its position in angle.
angle the right area and
angle. Full symmetric
excursion, thumbs
normally seperate
3:5 cm.
Equal and Should sound with
moderate resonant and full
Pa: respiratory vibration during sound.
excursion, speech
tactile fremitus Bronchial and
tubular breath
sounds.
Tracheal is very
load and high Broncho vesicular
Pe: symmetry of pitched sounds. breath sounds.
resonance duration of
A: breath sounds inspiration and
expiration is
equal. Bronchial
is loud and
medium pitched
sound and the
vesicular is low
pitched as
examined.
John Lloyd B. Agasang
BSN 2-3
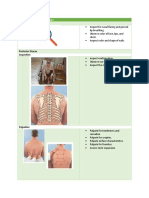
Heart Normal heart The precordium is A thrill is a
I: precordium for sound with S1 symmetrical. palpable murmur
pulsations & sounding with low S1 should be whereas a heave
lifts or heaves louder at the apex, is a sign of left
pitched sound and
lower pitch, and ventricular
A: heart sounds clearly heard from
longer than S2. hypertrophy. A
(S1, S2, etc.) the apex, and the thrill feels like a
S2 should be
S2 heard loudly at vibration and a
louder at the base,
the base with no higher pitch and heave feels like
murmurs. shorter than S1. an abnormally
large beating of
the heart. Feel
for these all over
the precordium
Central Vessels: No bruit sound A pulse is normally
Carotid Arteries heard during heard, but without
P: volume, quality auscultation and sounds during
A: bruit with clear and systole.
Jugular Veins visible and normal The normal mean
The internal
I: distention alignment of jugular venous
carotid arteries
pressure,
jugular vein are of vital
determined as the
without skin importance for
vertical distance
discoloration oxygenated
above the midpoint
around the skin on blood supply to
of the right atrium,
veins. the brain, and so
is 6 to 8 cm H2O
they are of major
importance in
clinical
Peripheral Upon inspection, evaluation. They
Vessels skin is pink and Absence of are susceptible
I: presence or normal, no signs swelling of the to
appearance of of swelling veins that atherosclerosis,
superficial indication indicate which can cause
veins, signs of phlebitis. stenosis and
phlebitis. Skin
In a limb with a embolization of
phlebitis color able to normal
*Buerger’s Test return back to plaque distally
circulation the towards the
*Capillary Refill normal skin color toes and sole of brain.
within 2 seconds the foot, stay
indicating normal pink, even The peripheral
capillary refill. when the limb is vascular
And still is normal raised by 90 examination
upon doing the degrees. provides
buerger’s test with The normal valuable
skin being able to CRT is <2 information on
seconds; a general health
retain its normal
CRT of >2 status and can
pinkish color even seconds help to determine
when raised to 90 suggests poor the status of the
John Lloyd B. Agasang
BSN 2-3
degrees high. peripheral arteries and
perfusion and veins.
may be an early
sign of shock.
Assessment of
Upon inspection,
Bilateral breasts the breast and
breast is equal in axilla is to gather
are
Breast & Axillae size and is symmetrical, objective
I: breast for size, symmetrical. No nontender, no information about
symmetry, skin discoloration suspicious the condition of
contour or appeared during masses, skin or the body part.
shape, inspection and ni nipple changes This is to
discoloration, swelling or or determine any
retraction, tenderness during lymphadenopat palpable mass,
hypervascularit palpation. Nothing hy. skin discoloration
y, swelling, mass felt in the indicating
edema underlying
breast and no
serious health
: areola for size, lesion seen and risks.
shape, texture normal
symmetry, during inspection
color, surface of the areola.
characteristics, Nipple is in the
masses, lesions center position,
: nipples for color is good no
size, shape, lesion and dry and
position, color, good upon
discharge, inspection and
lesion palpation.
Upon palpation of
the lymph nodes,
P: lymph nodes, breast, areola, and
breast, areola nipples there is no
& nipples for tenderness felt and
tenderness, no pain felt by the
masses, patient during
nodules, assessment. No
discharge masses and
nodules and
without any
discharge and all
normal upon
examination.
John Lloyd B. Agasang
BSN 2-3
You might also like
- Cardiology NotesDocument13 pagesCardiology NotesFreeNursingNotes78% (9)
- Assessment of Chest and LungsDocument23 pagesAssessment of Chest and LungsBaniwas Marie Agnes100% (1)
- Respiratory System AssessmentDocument7 pagesRespiratory System AssessmentCristine Sy100% (1)
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THDocument6 pagesManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Thorax and LungsDocument4 pagesAssessing The Thorax and LungsLorenz Jude Cańete100% (2)
- Chest Tubes: From Indication To RemovalDocument49 pagesChest Tubes: From Indication To Removaldara octavianiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presentation On Stroke by Wubet & Worku: University of Gondar College of Medicine and Health ScienceDocument40 pagesSeminar Presentation On Stroke by Wubet & Worku: University of Gondar College of Medicine and Health Sciencealemante tafeseNo ratings yet
- Chest To Abdomen AssessmentDocument16 pagesChest To Abdomen AssessmentLuzel Lapuz100% (1)
- Head To Toe Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesHead To Toe Physical AssessmentGarrett BatangNo ratings yet
- Visceral OMT: AAO Convocation March 2018 Kenneth Lossing DODocument59 pagesVisceral OMT: AAO Convocation March 2018 Kenneth Lossing DODiana SchlittlerNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesPhysical Examination of The Respiratory SystemMark CatabijanNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft SurgeryDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graft SurgeryRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- A New Concept of ShockDocument52 pagesA New Concept of ShockKADEK ARTAWANNo ratings yet
- Thorax and LungsDocument13 pagesThorax and LungsSherwyn Uy Hatab100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Circulatory SystemOliver Fullente86% (7)
- Journal Win 2018 - Postural AsymmetriesDocument4 pagesJournal Win 2018 - Postural AsymmetriesDanielle GraceNo ratings yet
- The Thorax and Lungs Assessment (Autosaved)Document49 pagesThe Thorax and Lungs Assessment (Autosaved)Arlyn Mendenilla100% (4)
- Anatomy Ospe PDFDocument25 pagesAnatomy Ospe PDFrizki ardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Lung Assessment: Physical Examination of The Thorax and The LungsDocument16 pagesThoracic and Lung Assessment: Physical Examination of The Thorax and The Lungsshannon c. lewis100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN: Risk For Fetal Injury Related To Shoulder DystociaDocument5 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN: Risk For Fetal Injury Related To Shoulder DystociaJa Lo67% (3)
- Vascular Anomalies PresentationDocument45 pagesVascular Anomalies PresentationMhinory OctNo ratings yet
- Thorax and The LungsDocument30 pagesThorax and The Lungschifunndo charles100% (1)
- Midterms (NCM 101A)Document17 pagesMidterms (NCM 101A)Shaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- HA SemisDocument25 pagesHA SemisMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- ChestDocument40 pagesChestmalyn1218100% (3)
- Thorax, Heart, Breast and Axillae ScriptDocument3 pagesThorax, Heart, Breast and Axillae ScriptAira Jean SantiagoNo ratings yet
- HA ChesttoAbdomenppt PDFDocument221 pagesHA ChesttoAbdomenppt PDFCARL ANGELA SISON100% (1)
- Assessmentr of Lungs - ThoraxDocument41 pagesAssessmentr of Lungs - ThoraxAdnan KareemNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation DutyDocument30 pagesCase Presentation DutyKathleen Daban RagudoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 A ReviewerDocument7 pagesNCM 112 A ReviewerKirsten ChavezNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Lungs AnswersDocument3 pagesThorax and Lungs AnswersHazel Anne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Age Case Presentation BSN 2hDocument40 pagesAge Case Presentation BSN 2hjomariNo ratings yet
- Posterior Thorax: and Costovertebral AngleDocument3 pagesPosterior Thorax: and Costovertebral AngleGenynne RagasaNo ratings yet
- De Veyra Assignment WK 3Document12 pagesDe Veyra Assignment WK 3adrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Plan:: Around The Circumference of The ChestDocument9 pagesPlan:: Around The Circumference of The ChestPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Thorax and LungsDocument28 pagesThorax and LungsBiBOYz 143No ratings yet
- Thorax and Lungs AssessmentDocument28 pagesThorax and Lungs AssessmentMiden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- III. Review of SystemsDocument1 pageIII. Review of SystemsPia Therese CabaticNo ratings yet
- Assessment Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesAssessment Respiratory Systemleih jsNo ratings yet
- Percussion of The ChestDocument2 pagesPercussion of The Chestagrawal02shivaniNo ratings yet
- Checklist Assessing Posterior and Anterior Thorax: Marco S. Morales BSN 3 ADocument2 pagesChecklist Assessing Posterior and Anterior Thorax: Marco S. Morales BSN 3 AMarco MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective BreathingDocument6 pagesNCP Ineffective BreathingCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - The General SurveyDocument5 pagesChapter 10 - The General SurveyNathan WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of SystemsDocument4 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of SystemsMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2Document1 pageAssessment 2younes.khalafNo ratings yet
- Chest and LungsDocument4 pagesChest and LungsDale Ros CollamatNo ratings yet
- 2.physical Exam 2Document118 pages2.physical Exam 2Althea Gabriel CastrosantoNo ratings yet
- Procedure 1 Brest Examination Self ExaminationDocument4 pagesProcedure 1 Brest Examination Self ExaminationPriyanka SheoranNo ratings yet
- 3 Assessment of The Thorax Breast and Lungs - Docx 1Document16 pages3 Assessment of The Thorax Breast and Lungs - Docx 1Cheng Bautista100% (1)
- Biomechanics Assignment - Posture-2Document11 pagesBiomechanics Assignment - Posture-2ApoorvNo ratings yet
- Inspection: Physical Assessment ProcedureDocument4 pagesInspection: Physical Assessment ProcedureAndres, Peter Pol D.No ratings yet
- Lesson Two Vocal AnatomyDocument29 pagesLesson Two Vocal Anatomyabhiaishu.kanna26No ratings yet
- Copy p1 Week 5 Nur 098 ActivityDocument5 pagesCopy p1 Week 5 Nur 098 ActivityRomelyn DellezoNo ratings yet
- Radiology Homework 1 2Document6 pagesRadiology Homework 1 2api-324380555No ratings yet
- Pale Appearing Adolescent Female.: Physical Examination and Review of SystemsDocument4 pagesPale Appearing Adolescent Female.: Physical Examination and Review of SystemsMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- PA TemplateDocument8 pagesPA TemplatePatricia Mae MirandaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Lung Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeyteDocument4 pagesThoracic and Lung Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeytePrincess Diana Jean ModesteNo ratings yet
- Assessment Tools Identifying InformationDocument10 pagesAssessment Tools Identifying InformationChinita Chin AcaboNo ratings yet
- CR InterpretationDocument2 pagesCR InterpretationDokdem AjaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument4 pagesNeurologic SystemDale Ros CollamatNo ratings yet
- YogapeDocument10 pagesYogapeDaniel ArshNo ratings yet
- PA (Revised)Document16 pagesPA (Revised)Daryl Jake FornollesNo ratings yet
- Pelvimetría Clínica PDFDocument7 pagesPelvimetría Clínica PDFCamargo Pinto LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesAssessing The Cardiovascular SystemElaisha Mae C. CarsulaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: AbdomenDocument18 pagesHealth Assessment: AbdomenBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- Expressive Voice Culture, Including the Emerson SystemFrom EverandExpressive Voice Culture, Including the Emerson SystemNo ratings yet
- Cavite State University: College of NursingDocument6 pagesCavite State University: College of NursingJa LoNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: College of NursingDocument2 pagesReflection Paper: College of NursingJa LoNo ratings yet
- Viii IxDocument8 pagesViii IxJa LoNo ratings yet
- X. DIAGNOSTIC TEST-no Information Collected From The PT: IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesX. DIAGNOSTIC TEST-no Information Collected From The PT: IntegumentaryJa LoNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENTATION: Abdominal Assessment: Cavite State UniversityDocument2 pagesDOCUMENTATION: Abdominal Assessment: Cavite State UniversityJa LoNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENTATION: Musculoskeletal Assessment: Cavite State UniversityDocument4 pagesDOCUMENTATION: Musculoskeletal Assessment: Cavite State UniversityJa LoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Coping Related To Situational Crises: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping Related To Situational Crises: Nursing Care PlanJa LoNo ratings yet
- Skull and Face: Body Part Examined Actual Finding Normal Finding Clinical SignificanceDocument6 pagesSkull and Face: Body Part Examined Actual Finding Normal Finding Clinical SignificanceJa LoNo ratings yet
- Body Part Examined Actual Finding Normal Finding Clinical Significance Integumen TDocument2 pagesBody Part Examined Actual Finding Normal Finding Clinical Significance Integumen TJa LoNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument3 pagesActivity 4 - Critical Thinking QuestionsJa LoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 Shock SyndromesDocument46 pagesChapter 41 Shock SyndromesVasincuAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Burger Allen Exercises PDFDocument122 pagesBurger Allen Exercises PDFlucky 116No ratings yet
- NCM 118 L 3rd ExamDocument3 pagesNCM 118 L 3rd Examj UNo ratings yet
- Rat Dissection Guide: Including Pregnant FemaleDocument16 pagesRat Dissection Guide: Including Pregnant FemaleMAVIE GOMEZNo ratings yet
- End To Side Vascular AnastomosisDocument3 pagesEnd To Side Vascular AnastomosisKristabella GianinaNo ratings yet
- Importance of The Mitral Apparatus For Left Ventricular Function: An Experimental ApproachDocument8 pagesImportance of The Mitral Apparatus For Left Ventricular Function: An Experimental ApproachThanh BinhNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Heart NotesDocument2 pagesCH 11 Heart Notesummnicole0% (1)
- Arteriovenous MalformationsDocument22 pagesArteriovenous MalformationsJunus EufrataNo ratings yet
- cv3 (Repaired)Document41 pagescv3 (Repaired)JR Betonio100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Atrial Septal DefectDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Atrial Septal Defectbobtaguba50% (2)
- Bicuspid Aortic ValveDocument37 pagesBicuspid Aortic Valvesmruti prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Modified Allen Method: BSMT 1F Mlsp-Lab Group 2: Asuncion, Ian Mark Miranda, Aiko Mosca, Justine Sicat, TrishaDocument9 pagesBlood Gas Modified Allen Method: BSMT 1F Mlsp-Lab Group 2: Asuncion, Ian Mark Miranda, Aiko Mosca, Justine Sicat, TrishaTrisha Joy SicatNo ratings yet
- Science9 Reyes, J, P Q1.W2Document12 pagesScience9 Reyes, J, P Q1.W2Jeane Pineda ReyesNo ratings yet
- PE's From Mark Hammerschmidt RN: WWW Icufaqs OrgDocument22 pagesPE's From Mark Hammerschmidt RN: WWW Icufaqs OrgMark Hammerschmidt50% (2)
- 11رسالة د احمد شاهين معدلة (m)Document75 pages11رسالة د احمد شاهين معدلة (m)ahmedshahin199090No ratings yet
- A Case Report On Buergers DiseaseDocument3 pagesA Case Report On Buergers DiseaseJohn Allan PasanaNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Document10 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Gerard Selvaraj88% (26)
- Administration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyDocument8 pagesAdministration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyRonald ThakorNo ratings yet
- Sinew Surgical Technique PDFDocument8 pagesSinew Surgical Technique PDFLUNA SEQUOIANo ratings yet
- Database - of - Systematic - Reviews in Varicose VeinDocument97 pagesDatabase - of - Systematic - Reviews in Varicose VeinTomus ClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hiperakut (Dr. Dedi Sutia, SP.N (K), FINA, MARS)Document35 pagesStroke Hiperakut (Dr. Dedi Sutia, SP.N (K), FINA, MARS)Sitti Fatwan NisakNo ratings yet
- Women and Hypertension: Beyond The 2017 Guideline For Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsDocument50 pagesWomen and Hypertension: Beyond The 2017 Guideline For Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsShazi AliNo ratings yet
- Word English 2Document177 pagesWord English 2Lê LuyếnNo ratings yet