Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CAC Notes #1
CAC Notes #1
Uploaded by
Peach MontefalcoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CAC Notes #1
CAC Notes #1
Uploaded by
Peach MontefalcoCopyright:
Available Formats
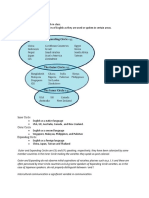
Cost Accounting
systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of
manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail.
also a method of managerial accounting
o aims to capture the total production cost of a business by measuring
variable costs of each production phase as well as fixed cost.
Merchandising vs. Manufacturing
Merchandising
buys a product that is ready for resale when it is purchased.
product will not be changed to make it salable
only merchandise inventory in the financial statements
Manufacturing
buys raw materials and processes it in to finished goods to be sold.
direct labor and overhead are incurred
three kinds of inventories namely – raw materials, work in process and finished goods.
Product Costs/Manufacturing Costs
1. Direct Materials
o basic ingredients that are transformed into finished products
o can be traced to the finished product
o made from basic direct materials
2. Direct Labor
o amount paid as wages to those working directly on the product
o direct labor for table and chair is the wages paid to carpenter, for bread
the bakers’ wages, and chef’s wages for cooked meals/product.
3. Factory Overhead
o manufacturing costs that cannot be classified as direct material or direct
labor
o indirect materials, indirect labor, depreciation of plant building and
machineries, repairs and maintenance.
Indirect Materials
Cannot be conveniently or economically traced to specific product.
Indirect Labor
People who aren't actually present on the process of converting raw materials to finished
goods.
Non Manufacturing Costs/Period Costs
1. Marketing or selling expenses
o all costs necessary to secure customer orders and get the finished product
or service into the hands of the customer.
o advertising, shipping, sales travel, sales commissions, sales salaries and
expenses associated with finished goods.
2. Administrative or general expenses
o all executive, organizational and clerical expenses that cannot logically be
included under either production or marketing.
o executive compensation, general accounting, secretarial and similar
expenses having to do with the overall administration.
Costs classified as to Variability
1. Fixed costs
o constant in total, irrespective of the volume of production.
o not related to activity within the relevant range
o assignable to department based on different allocation methods.
o Cost per unit decreases as volume increases, and increases as volume
decreases.
o salaries of production executives, depreciation of equipment computed on
a straight line method, periodic rent payments and insurance.
2. Variable costs
o items of cost which vary directly, in total, in relation to volume of
production.
o Cost per unit remains constant as volume changes within a relevant range.
o direct materials, direct labor, royalties and commission of salesmen.
3. Mixed costs
o items with fixed and variable components.
o vary with the level of production, though not in direct relation to it,
probably because part of the cost is fixed while the rest is variable.
You might also like
- (Case) Chow Tai Fook Driving Towards A Century of Jewellery MakingDocument20 pages(Case) Chow Tai Fook Driving Towards A Century of Jewellery Makingphuongpham.6969No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and Control by Sir ChuaDocument92 pagesCost Accounting and Control by Sir ChuaAnalyn Lafradez100% (3)
- Financial Supply Chain ManagementDocument32 pagesFinancial Supply Chain ManagementRambabu VelanatiNo ratings yet
- TOYOTA Indus Motor Co FinalDocument8 pagesTOYOTA Indus Motor Co FinalImran Memon0% (1)
- Ben & Jerry's Homemade I. Point of View: A.1 Income Statement H-AnalysisDocument3 pagesBen & Jerry's Homemade I. Point of View: A.1 Income Statement H-AnalysisJeanDianeJovelo100% (1)
- Mountain Man Brewing CompanyDocument2 pagesMountain Man Brewing CompanySharon Goh67% (3)
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Cap. 1.: (Introducción y Tipos de Costos)Document15 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Cap. 1.: (Introducción y Tipos de Costos)Eugenio CamposNo ratings yet
- LP3-Product Costing MethodsDocument12 pagesLP3-Product Costing MethodsCarla GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2B - Unit 2 - Cost Classification Behaviour & Estimation - Workbook SOLUTIONS - 2022Document47 pages2B - Unit 2 - Cost Classification Behaviour & Estimation - Workbook SOLUTIONS - 2022Bono magadaniNo ratings yet
- Part III-Managerial AccountingDocument91 pagesPart III-Managerial AccountingGebreNo ratings yet
- MAF Notes Mid ExamDocument8 pagesMAF Notes Mid ExamPenguin Da Business GooseNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and ClassificationsDocument3 pagesCost Concepts and ClassificationsCONCORDIA RAFAEL IVANNo ratings yet
- 2017 Course 28 Module 5 Basic Cost ConceptsDocument10 pages2017 Course 28 Module 5 Basic Cost ConceptsPushpendra Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet NewDocument25 pagesCost Sheet Newnagesh dashNo ratings yet
- Cost Classification or Cost Flow in An OrgaizationDocument8 pagesCost Classification or Cost Flow in An OrgaizationvaloruroNo ratings yet
- Cost NOTES - MIDTERMDocument33 pagesCost NOTES - MIDTERMChenary Magne FetalsanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Manufacturing BusinessDocument4 pagesLesson 10 - Manufacturing BusinessVISITACION JAIRUS GWENNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting - Guerrerro Notes: Chapter 1-Cost Accounting - Basic Concepts and Job Order Cost CycleDocument6 pagesCost Accounting - Guerrerro Notes: Chapter 1-Cost Accounting - Basic Concepts and Job Order Cost CycleAyraaahNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Cost AccountingDocument5 pagesDefinitions of Cost AccountingMarina BennNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and ControlDocument14 pagesCost Accounting and Controlkaye SagabaenNo ratings yet
- ModuleNo1 BasicConceptsDocument4 pagesModuleNo1 BasicConceptsLyerey Jed MartinNo ratings yet
- ACTG 22A-Cost Accounting and Control-ReviewerDocument8 pagesACTG 22A-Cost Accounting and Control-ReviewerLolli PopNo ratings yet
- Accounting PDFDocument38 pagesAccounting PDFSanwal ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument15 pagesCost SheetDikshit Kothari100% (2)
- Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationDocument2 pagesCost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationMitos Cielo NavajaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Terms and Concepts: 2.1. DefinitionDocument10 pagesBasic Cost Terms and Concepts: 2.1. DefinitionalemayehuNo ratings yet
- Final Cost SheetDocument21 pagesFinal Cost Sheetneerajmgoyal100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Product CostingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Product Costingchelsea kayle licomes fuentesNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 The-Manager-and-Management-AccountingDocument11 pagesChap 2 The-Manager-and-Management-Accountingqgminh7114No ratings yet
- CT 206 Notes-1Document56 pagesCT 206 Notes-1Flex GodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Hilton 10th Instructor NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Hilton 10th Instructor NotesKD MV100% (1)
- NOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlDocument11 pagesNOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlHanna CasasNo ratings yet
- Costing in BriefDocument47 pagesCosting in BriefRezaul Karim TutulNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Introduction To Cost and Managerial AccountingDocument38 pagesChapter Four: Introduction To Cost and Managerial AccountingSelam TsigieNo ratings yet
- Notes On Classification of Costs and Cost ConceptsDocument5 pagesNotes On Classification of Costs and Cost ConceptsAngela Mae Balanon RafananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Saeym SegoviaNo ratings yet
- c1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesc1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingAndrea Camille AquinoNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptsDocument32 pagesCost Conceptsamira samirNo ratings yet
- COGM Type of CostDocument3 pagesCOGM Type of Costanika chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument1 pageCost AccountingJajajaNo ratings yet
- Hum 2217 (Acc) CostingDocument6 pagesHum 2217 (Acc) CostingNourin TasnimNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesCost AccountingClarivelle NonesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Classification of CostDocument4 pagesUnit 2 - Classification of Costavinal malikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Answer KeyDocument18 pagesChapter-2 Answer KeyKylie sheena MendezNo ratings yet
- I. Answers To Questions: Cost Accounting and Control - Solutions Manual Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsDocument18 pagesI. Answers To Questions: Cost Accounting and Control - Solutions Manual Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsYannah HidalgoNo ratings yet
- FIN600 Module 3 Notes - Financial Management Accounting ConceptsDocument20 pagesFIN600 Module 3 Notes - Financial Management Accounting ConceptsInés Tetuá TralleroNo ratings yet
- Product Costing Methods: Table 1 Shows The Differences Between Product Cost and Period CostDocument5 pagesProduct Costing Methods: Table 1 Shows The Differences Between Product Cost and Period CostMa Trixia Alexandra CuevasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2Hk100% (1)
- CA Notes4Document21 pagesCA Notes4jeyoon13No ratings yet
- 25885110Document21 pages25885110Llyana paula SuyuNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and TerminologiesDocument13 pagesCost Concepts and TerminologiesAprile AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Costs - TutorialDocument1 pageClassification of Costs - TutorialAnimesh MayankNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Process CostingDocument5 pagesTopic 2 - Process CostingAfrina SyazwinaNo ratings yet
- Tute 3 Homework - Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsDocument3 pagesTute 3 Homework - Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsKyleNo ratings yet
- P2 Manufacturing Learning MaterialDocument5 pagesP2 Manufacturing Learning Materialchen.abellar.swuNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 PRT 2 Cost AccountingDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 1 PRT 2 Cost AccountingJohn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Accounting For Manufacturing OperationsDocument16 pagesReviewer: Accounting For Manufacturing Operationsgab mNo ratings yet
- Cost Terms, Concepts, and Classifications: Solutions To QuestionsDocument14 pagesCost Terms, Concepts, and Classifications: Solutions To QuestionsTrishia OliverosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Answer Cost AccountingDocument18 pagesChapter-2-Answer Cost AccountingJuline Ashley A Carballo100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Aklil TeganewNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cost Accounting Final With PDFDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Cost Accounting Final With PDFLemon EnvoyNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesLESSON 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingChriselda CabangonNo ratings yet
- Inventory: COST OF PRODUCTIONDocument104 pagesInventory: COST OF PRODUCTIONHAFIZ MUHAMMAD UMAR FAROOQ RANANo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sample/practice Exam 2020, Questions and Answers Sample/practice Exam 2020, Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesSample/practice Exam 2020, Questions and Answers Sample/practice Exam 2020, Questions and AnswersPeach MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Math in The Modern World Notes #8Document2 pagesMath in The Modern World Notes #8Peach MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Rhythmic Activity Notes #7Document9 pagesRhythmic Activity Notes #7Peach MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Rhythmic Activities Notes #5Document3 pagesRhythmic Activities Notes #5Peach MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Notes#6Document5 pagesPurposive Communication Notes#6Peach MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Notes #5Document3 pagesPurposive Communication Notes #5Peach Montefalco0% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Mod3 Recognize and Understand A MarketDocument14 pagesEntrepreneurship Mod3 Recognize and Understand A MarketEver BrandinoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Corporate FinanceDocument22 pagesTutorial Corporate FinanceAlya NadhirahNo ratings yet
- MKTG446 Case 11-2Document2 pagesMKTG446 Case 11-2kanyaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016: Pearson Edexcel GCE AS Level in Business (8BS0) Paper 01 Marketing and PeopleDocument20 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016: Pearson Edexcel GCE AS Level in Business (8BS0) Paper 01 Marketing and PeopleHady JawadNo ratings yet
- 9706 m17 Ms 32Document16 pages9706 m17 Ms 32FarrukhsgNo ratings yet
- (Effective October 2006 Examination) : The Cpa Licensure Examination Syllabus - Auditing TheoryDocument7 pages(Effective October 2006 Examination) : The Cpa Licensure Examination Syllabus - Auditing TheoryJanine Bernadette C. Bautista3180270No ratings yet
- BRM Research AssignmentDocument4 pagesBRM Research AssignmentNeha KadamNo ratings yet
- 5 Cash Book 08-2022 Regular 2023Document8 pages5 Cash Book 08-2022 Regular 2023jahnaviNo ratings yet
- Indenpendent Demand EOQDocument18 pagesIndenpendent Demand EOQAlec Matthew TisaraNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Business Environemtn (PESTLE and Porters Forces Analysis)Document25 pagesWeek 1 - Business Environemtn (PESTLE and Porters Forces Analysis)Micu AnamariaNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument2 pagesTime TableMustapha Opeyemi BojuwonNo ratings yet
- A201 - 1 - Intro To Cost Accounting (Jamero 2022)Document23 pagesA201 - 1 - Intro To Cost Accounting (Jamero 2022)MARIAN DORIANo ratings yet
- Air BN BDocument31 pagesAir BN BHanno PoeschlNo ratings yet
- Mg2451 Eeca Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesMg2451 Eeca Questions and Answerskarthiksubramanian94No ratings yet
- Demand and Supply-It's What Economics Is About! Lesson Plan: Inside The VaultDocument15 pagesDemand and Supply-It's What Economics Is About! Lesson Plan: Inside The VaultVikas RathiNo ratings yet
- Rumble - 2022-04-01 - FDD - Xponential FitnessDocument248 pagesRumble - 2022-04-01 - FDD - Xponential FitnessFuzzy PandaNo ratings yet
- Inditex Group Annual ReportDocument520 pagesInditex Group Annual Reportdavid juNo ratings yet
- 2024 ResumeDocument4 pages2024 ResumeKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Cost Allocation: Joint Products and ByproductsDocument54 pagesCost Allocation: Joint Products and ByproductsMicka EllahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting Lecture 3Document21 pagesPrinciples of Accounting Lecture 3Masum HossainNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Sample Questions (With Answers/hints)Document24 pagesManagerial Economics Sample Questions (With Answers/hints)Vikas BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Private Equity Buy Side Financial Model and ValuationDocument19 pagesPrivate Equity Buy Side Financial Model and ValuationBhaskar Shanmugam100% (3)
- 1Document6 pages1Namita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kode QDocument11 pagesKode QatikaNo ratings yet
- Sevilla - Unit 1 - IA3Document14 pagesSevilla - Unit 1 - IA3Hensel SevillaNo ratings yet