OSHA STANDARDS
OSHA
OSHA stands for Occupational Safety and Health administration. It implements and
regulates Safety & Health Standards for the Construction Industry in design, detailing,
fabrication & erection of Steel members. The main work of OSHA is to enhance erection safety
and reduce erection hazards.
SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
The detailer and erector should communicate best to solve the issue of temporary
bracing and aids. The goal obviously is to stabilize the structure during and after erection. As
temporary framing is often not within the detailer’s or fabricator’s scope of work, the erector is
cautioned to make.
The most common issue is that of fall protection. Multistory structures require guardrail
cable at the floor perimeter and at large interior floor and roof openings. This setup has been
incorporated in the shop details.
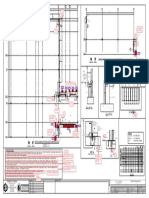
COLUMN BASE PLATES
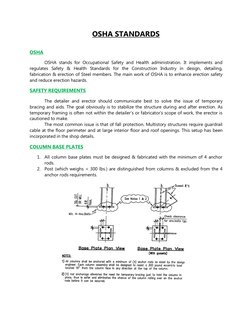
1. All column base plates must be designed & fabricated with the minimum of 4 anchor
rods.
2. Post (which weighs < 300 lbs.) are distinguished from columns & excluded from the 4
anchor rods requirements.
�COLUMN SPLICE LOCATION
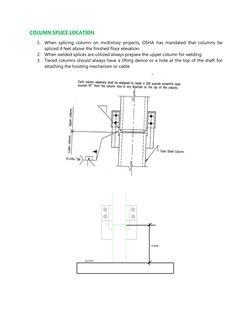
1. When splicing column on multistory projects, OSHA has mandated that columns be
spliced 4 feet above the finished floor elevation.
2. When welded splices are utilized always prepare the upper column for welding.
3. Tiered columns should always have a lifting device or a hole at the top of the shaft for
attaching the hoisting mechanism or cable.
�BEAM TO COLUMN/BEAM WEB DOUBLE CONNECTION
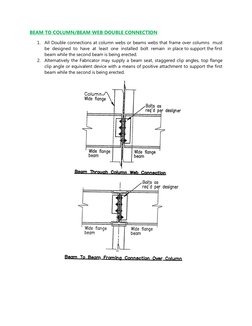
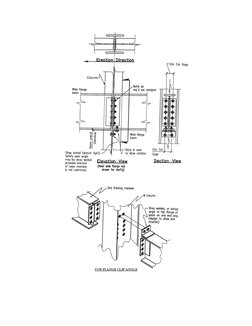
1. All Double connections at column webs or beams webs that frame over columns must
be designed to have at least one installed bolt remain in place to support the first
beam while the second beam is being erected.
2. Alternatively the Fabricator may supply a beam seat, staggered clip angles, top flange
clip angle or equivalent device with a means of positive attachment to support the first
beam while the second is being erected.
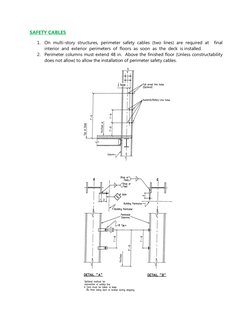
��SAFETY CABLES
1. On multi-story structures, perimeter safety cables (two lines) are required at final
interior and exterior perimeters of floors as soon as the deck is installed.
2. Perimeter columns must extend 48 in. Above the finished floor (Unless constructability
does not allow) to allow the installation of perimeter safety cables.
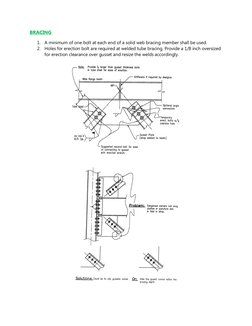
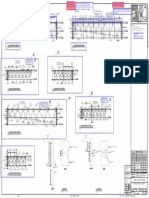
�BRACING
1. A minimum of one bolt at each end of a solid web bracing member shall be used.
2. Holes for erection bolt are required at welded tube bracing. Provide a 1/8 inch oversized
for erection clearance over gusset and resize the welds accordingly.
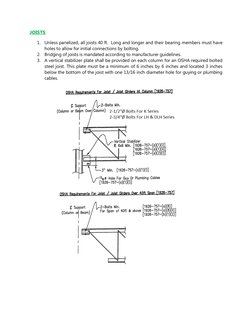
�JOISTS
1. Unless panelized, all joists 40 ft. Long and longer and their bearing members must have
holes to allow for initial connections by bolting.
2. Bridging of joists is mandated according to manufacturer guidelines.
3. A vertical stabilizer plate shall be provided on each column for an OSHA required bolted
steel joist. This plate must be a minimum of 6 inches by 6 inches and located 3 inches
below the bottom of the joist with one 13/16 inch diameter hole for guying or plumbing
cables.
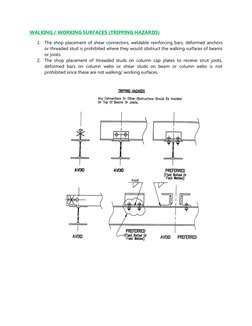
�WALKING / WORKING SURFACES (TRIPPING HAZARDS)
1. The shop placement of shear connectors, weldable reinforcing bars, deformed anchors
or threaded stud is prohibited where they would obstruct the walking surfaces of beams
or joists.
2. The shop placement of threaded studs on column cap plates to receive strut joists,
deformed bars on column webs or shear studs on beam or column webs is not
prohibited since these are not walking/ working surfaces.
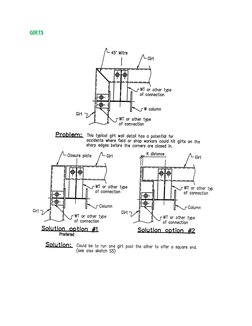
�GIRTS
�BOLTING
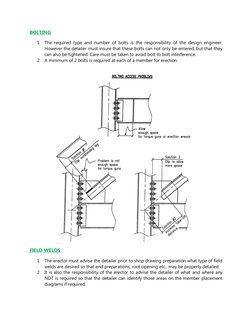
1. The required type and number of bolts is the responsibility of the design engineer.
However the detailer must insure that these bolts can not only be entered, but that they
can also be tightened. Care must be taken to avoid bolt to bolt interference.
2. A minimum of 2 bolts is required at each of a member for erection.
FIELD WELDS
1. The erector must advise the detailer prior to shop drawing preparation what type of field
welds are desired so that end preparations, root opening etc., may be properly detailed.
2. It is also the responsibility of the erector to advise the detailer of what and where any
NDT is required so that the detailer can identify those areas on the member placement
diagrams if required.
�ERECTABILITY
1. Important step is to check the erectability of a member, interference of other members
in the structure like bolting, shop assembling, erection with special notes etc.,.