Professional Documents
Culture Documents
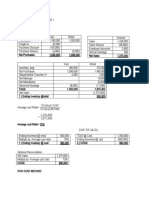
Economic Order Quantity ( (2 D S) /H) ( (2 75 29) /35) 3524.42
Uploaded by
VaibhavOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economic Order Quantity ( (2 D S) /H) ( (2 75 29) /35) 3524.42
Uploaded by
VaibhavCopyright:
Available Formats
Q. Outlook Gateways has a demand of 75 Lakhs per year.
Setup cost and holding cost are 29 and 35
per unit. Number of pieces in a order includes 2.3 Lakhs per order. Printing is done 300 days and
2 days to deliver this magazine.
Q. What can be the EOQ of this? With above data find the Setup Cost and Holding cost for a year.
What is the Reorder Point?
ANS:
Economic order quantity (EOQ), refers to the optimum amount of an item that should be ordered at any
given point in time, such that the total annual cost of carrying and ordering that item is minimized. EOQ is
also sometimes known as the optimum lot size. Simply put – how much product should you purchase to
maintain a cost-efficient supply chain?
The EOQ helps companies minimize the cost of ordering and holding inventory. As explained by the
economic concept known as economies of scale, the cost per unit of ordering a product falls, the larger the
total quantity of the order. However, the larger the total quantity of an order, the higher the cost to hold and
carry your inventory.
Fig 01: Economic Order Quantity
For this particular EOQ we can calculate it as below:
Demand(D) = 75 lakhs
Setup cost (Ordering cost) (S) = 29/unit
Holding cost (H) = 35/unit
Order Quantity = 2.3 lakhs
Working days = 300 days
Delivery/ Lead time = 2 days
Economic Order Quantity = √[(2*D*S)/H]
= √ [(2*75*29)/35]
=3524.42
Annual Holding cost = Avg. inventory level * Holding
cost (Yearly)
= (Order Quantity/2) * H
= (2300000/2) * 35
= 40250000
Annual Setup cost = No. of orders * cost per
order (Yearly)
= (Annual demand/Order quantity) * cost per order
= (75000000/230000) * 29
= 945.65
Time between orders = 300/32.61
= 9.2 days
Daily Demand =D/300
= 75,00,000/300
= 25000
Re-order point = (D/300) * 2
= (7500000/300) * 2
= 50000
Q. What is the annual demand to production ratio in this case? What does it indicate for the
company?
ANS:
In order to get the demand to production ratio we need to understand the overall demand and production of
the products, this can be either done by using production order quantity or Economic Production Quantity. In
either of the cases, we need data for daily production so as to get the overall annual production rate, but as
the data is not available for this particular instance, we will go by the ratio that was provided. Outlook India
suggested that for every order they print an extra magazine which that the ratio of demand to production is
9:10
For Economic Production Quantity or Production Order Quantity we use,
Fig 02: Economic Production Quantity
Economic Production Quantity- Square root of {2xDx O/ H(1-x)}
Since we don’t have the required data, we use the ratio that was provided
If we go by that,
Ratio= 9:10
Demand =
75000000
Production = X
= 9:10
=Demand: Production
=7500000: X
=75000000:8333333.33
=9:10
The Annual Demand to Production Ratio is 9:10 i.e., for 75000000 Magazines we have 8333333.33
Magazines in production.
Indication/Assumption for the Company:
In spite of producing more than demand, there are stock outs mentioned by the company. The probable
reasons can be:
1. Inaccurate forecasting
2. Failure to re-order in a timely manner
3. Poor management of people, processes, and technology
4. Poor communication or relationships with your
suppliers
5. Not enough working capital
You might also like
- Task 4 Report - Uday Arun Sakat - SIOMDocument14 pagesTask 4 Report - Uday Arun Sakat - SIOMBalagovind S100% (1)
- Log (S20) - Inventory Models-2Document40 pagesLog (S20) - Inventory Models-2Aqib LatifNo ratings yet
- Outlook Operatons Task (J Narendhar)Document9 pagesOutlook Operatons Task (J Narendhar)J NarenNo ratings yet
- Rishibha ASM Task 2 CRMDocument16 pagesRishibha ASM Task 2 CRMGauravNo ratings yet
- Task 3: Analytics and Decision Planning: Uttranshu V Chauhan Symbiosis Institute of Management StudiesDocument8 pagesTask 3: Analytics and Decision Planning: Uttranshu V Chauhan Symbiosis Institute of Management StudiesYuvi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Managemen ProjectDocument10 pagesCustomer Relationship Managemen ProjectDishank BaidNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - PG - June 2024 Assignment AnsDocument6 pagesCorporate Finance - PG - June 2024 Assignment AnsBalamuralikrishna YadavNo ratings yet
- ACC Limited MISDocument14 pagesACC Limited MISVIVEK JAISWAL100% (1)
- Aggregate Planning: OMII, Term III, Sessions 8-10 Harpreet KaurDocument44 pagesAggregate Planning: OMII, Term III, Sessions 8-10 Harpreet Kaurayushmehar22No ratings yet
- Inventory Management - Shubhum KR SinghDocument26 pagesInventory Management - Shubhum KR SinghPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Sarthak Patil SIP TASKSDocument9 pagesSarthak Patil SIP TASKSSarthak PatilNo ratings yet
- Or Problems For LINGO ExerciseDocument10 pagesOr Problems For LINGO ExerciseVisakh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- EDW at HDFCDocument26 pagesEDW at HDFCYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Dabur SCMDocument36 pagesDabur SCMEkta Roy0% (1)
- Project Guide Lines-Bcom-Final YearDocument14 pagesProject Guide Lines-Bcom-Final Yearrushi kolliNo ratings yet
- Outlook Report-MbaDocument33 pagesOutlook Report-MbaRAJDEEP BORUAHNo ratings yet
- SMch07 RADocument8 pagesSMch07 RACoriolisTimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management NotesDocument127 pagesSupply Chain Management NotesPedina SibakrishnaNo ratings yet
- CIMA E1 - OM - Chapter - 6Document50 pagesCIMA E1 - OM - Chapter - 6MichelaRosignoliNo ratings yet
- Globus BrandDocument7 pagesGlobus BrandAayushi PathakNo ratings yet
- Big Bazaar PresentaionDocument47 pagesBig Bazaar PresentaionShalini Singh25% (8)
- PFR Report FINALDocument30 pagesPFR Report FINALSohini Mitra100% (1)
- Pom Inventory ProblemsDocument8 pagesPom Inventory ProblemsSharath Kannan0% (2)
- Consimer Base and Future Aspects of MagazineDocument65 pagesConsimer Base and Future Aspects of MagazinePankaj Maurya100% (2)
- Study of Brand Awareness and Expectation From Hettich Brand Among The Contractors of Ahmedabad CityDocument6 pagesStudy of Brand Awareness and Expectation From Hettich Brand Among The Contractors of Ahmedabad CityChintan Leo PatelNo ratings yet
- Inventory Norms AnalysisDocument4 pagesInventory Norms AnalysisanurgNo ratings yet
- Session 12 CVP AnalysisDocument52 pagesSession 12 CVP Analysismuskan mittalNo ratings yet
- Bgel - Poem ProjDocument13 pagesBgel - Poem ProjABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- Outlook TaskDocument89 pagesOutlook Taskurvashi soniNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Case Study - Ops Analyst Candidate - LOGISTIC EXECUTIVEDocument6 pagesAssignment - Case Study - Ops Analyst Candidate - LOGISTIC EXECUTIVEWendi OfficialNo ratings yet
- Marathur Butar Butar 0906557171 Production Planning and Inventory Control Chapter 2 (Even Numbers + No.17)Document4 pagesMarathur Butar Butar 0906557171 Production Planning and Inventory Control Chapter 2 (Even Numbers + No.17)Aileen AllenNo ratings yet
- Sbi Free Mock Test - QuestionsDocument16 pagesSbi Free Mock Test - QuestionsJyoshna Reddy0% (1)
- ForecastingDocument87 pagesForecastingaman prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Om0012 - Supply Chain ManagementDocument6 pagesOm0012 - Supply Chain ManagementSolved AssignMents100% (1)
- Project: A Study ON Evaluation of Customer Centricity AT Value Format Reliance Fresh Stores DelhiDocument62 pagesProject: A Study ON Evaluation of Customer Centricity AT Value Format Reliance Fresh Stores DelhiVIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- LG Case StudyDocument5 pagesLG Case StudyShipra SinghNo ratings yet
- (N D Vohra Unsolved Q-4 Page-594) (Solution: 6 Years)Document15 pages(N D Vohra Unsolved Q-4 Page-594) (Solution: 6 Years)Lokesh GagnaniNo ratings yet
- Faculty Mentor-Dr. Nisha Pandey BY Amar S. Sawant Roll No - 91Document14 pagesFaculty Mentor-Dr. Nisha Pandey BY Amar S. Sawant Roll No - 91ramya patra100% (1)
- Notes HRM DasslerDocument10 pagesNotes HRM DasslerMd Shadab Alam0% (1)
- Anudeep Gill: Big TeamDocument29 pagesAnudeep Gill: Big TeamKaran VohraNo ratings yet
- Sales and Operations Planning - Tutorial QuestionsDocument1 pageSales and Operations Planning - Tutorial QuestionshfjffjNo ratings yet
- MRP CaseStudies2008Document24 pagesMRP CaseStudies2008Sachin ElfNo ratings yet
- Trading MechanismDocument18 pagesTrading MechanismUttam GauravNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of ProductionDocument4 pagesElasticity of ProductionNoman Azhar0% (1)
- Lecture 10&11 SDM Unit III (Sales Budget) ER AMDocument10 pagesLecture 10&11 SDM Unit III (Sales Budget) ER AMArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Hand Made Silver Filigree / Jewellery Cluster at Cuttak - OrrisaDocument5 pagesCase Study of Hand Made Silver Filigree / Jewellery Cluster at Cuttak - OrrisasupriyadhageNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management - OutlookDocument12 pagesCustomer Relationship Management - Outlook202112070 imtnagNo ratings yet
- Inventory Numericals SolvedDocument3 pagesInventory Numericals Solvedwahab_pakistan100% (1)
- Ch19 Aggregate PlanningDocument3 pagesCh19 Aggregate Planningnurul_azizah01No ratings yet
- Godrej Builds 'Sampark' With Distributors - E-Business - Express Computer IndiaDocument2 pagesGodrej Builds 'Sampark' With Distributors - E-Business - Express Computer IndiaPradeep DubeyNo ratings yet
- Safety Stock CalculationDocument4 pagesSafety Stock Calculationsksk1911No ratings yet
- White Papers Forecast Measurement Evaluation White PaperDocument7 pagesWhite Papers Forecast Measurement Evaluation White PaperAditya GolhaniNo ratings yet
- Transportation and Inventory Aggregation in Supply Chain ManagemenDocument28 pagesTransportation and Inventory Aggregation in Supply Chain ManagemenMoshmi MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Bharti Airtel Limited Performance AppraisalDocument13 pagesBharti Airtel Limited Performance AppraisalmullolidivyaNo ratings yet
- Eureka ForbesDocument4 pagesEureka ForbesAniket PandeNo ratings yet
- Tybms Sem 5Document10 pagesTybms Sem 5Gaurav Bhanusghare100% (1)
- Examples of Inventory ManagementDocument17 pagesExamples of Inventory ManagementtasbihnihadNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management ProblemsDocument6 pagesInventory Management ProblemsJagadeesh RajNo ratings yet
- LeVy s3741026 Supply Chain Analytics Asm1Document15 pagesLeVy s3741026 Supply Chain Analytics Asm1Vy LêNo ratings yet
- TusmingmobDocument5 pagesTusmingmobRadinne Fakhri Al Wafa100% (1)
- Medical Devices Supply Chain - Strategy Presentation: Presented By: Syed Ali Saboor ZaidiDocument8 pagesMedical Devices Supply Chain - Strategy Presentation: Presented By: Syed Ali Saboor ZaidiMuhammad RehmanNo ratings yet
- Materi - Kenal Profesi - Warehouse Supervisor - Latih - Co (Francisca Risti Aprilia)Document17 pagesMateri - Kenal Profesi - Warehouse Supervisor - Latih - Co (Francisca Risti Aprilia)syafiularif34No ratings yet
- INTL729 Mod 02 ActivityDocument6 pagesINTL729 Mod 02 ActivityIshtiak AmadNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Cost Accounting 14e by Carter Ch09Document26 pagesTest Bank Cost Accounting 14e by Carter Ch09Jamaica DavidNo ratings yet
- Lean System Thinking - Overview-Awareness SessionDocument97 pagesLean System Thinking - Overview-Awareness SessionBayoumy ElyanNo ratings yet
- Abdul Moiz Shakeel 22348 3rd Class ActivityDocument4 pagesAbdul Moiz Shakeel 22348 3rd Class ActivityMoizShakeelNo ratings yet
- BRP-1 Final Report Borjan Private LimitedDocument38 pagesBRP-1 Final Report Borjan Private LimitedArsalan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Rdm2020Document18 pagesQuestion Bank Rdm2020Afad Khan100% (1)
- App 5Document18 pagesApp 5sustarm technicalNo ratings yet
- Pergudangan 2Document34 pagesPergudangan 2endangNo ratings yet
- LMGT 211 Material Management With NOTESDocument4 pagesLMGT 211 Material Management With NOTESNeil RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Strategic Purchasing 2017-18-v3 - 3upDocument20 pagesLecture 6 Strategic Purchasing 2017-18-v3 - 3upCorina CalinelNo ratings yet
- IA ActivityDocument2 pagesIA ActivityCASTRO, JHONLY ROEL C.No ratings yet
- Ensayo: Raul Andres Castellanos GarzonDocument24 pagesEnsayo: Raul Andres Castellanos Garzonanbago123No ratings yet
- C8 - Inventory Management - SVDocument30 pagesC8 - Inventory Management - SVNguyen MyNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Sourcing, Transportation and Pricing ProductsDocument32 pagesUnit-V Sourcing, Transportation and Pricing ProductsSachin KhotNo ratings yet
- SAP EWM - Part+Entitled+to+Dispose,+Owner+and+CustodianDocument8 pagesSAP EWM - Part+Entitled+to+Dispose,+Owner+and+CustodianRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Supply ChainDocument33 pagesUnderstanding The Supply ChainZain ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT IN HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY-Module PreLimDocument11 pagesSUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT IN HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY-Module PreLimArmand Padernos100% (18)
- Material QuestionDocument20 pagesMaterial QuestionMukund SinghNo ratings yet
- Developing Key Performance Indicators For Supply Chain: An Industry PerspectiveDocument7 pagesDeveloping Key Performance Indicators For Supply Chain: An Industry PerspectivePhilia Magdalena SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Course Instructor: Manish Chauhan: 410-MCC-UMDocument41 pagesCourse Instructor: Manish Chauhan: 410-MCC-UMLlanraeyNo ratings yet
- Medical Technologies Corporation (MTC) : Case StudyDocument11 pagesMedical Technologies Corporation (MTC) : Case StudyNeetu AmarNo ratings yet
- Tema 5-2 - Inventory Management Planning PurchasingDocument65 pagesTema 5-2 - Inventory Management Planning PurchasingTinna CondracheNo ratings yet
- Report (1) Midnapore EDocument4 pagesReport (1) Midnapore EAvijitSinharoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 MMSDocument30 pagesLesson 12 MMSRitter GamingNo ratings yet
- Demand Planning & ForecastingDocument34 pagesDemand Planning & ForecastingDebashishDolonNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management: Russell and Taylor Operations Management, 8th EditionDocument54 pagesInventory Management: Russell and Taylor Operations Management, 8th EditionLie Jasen100% (1)
- Benefits of MRP 001Document4 pagesBenefits of MRP 001lynnthuNo ratings yet
- Business-to-Business Activities: Improving Efficiency and Reducing CostsDocument55 pagesBusiness-to-Business Activities: Improving Efficiency and Reducing Coststhanh nguyen100% (1)