Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 1 Revision (System Analysis)
Uploaded by
Yousef ALmahmoudOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 1 Revision (System Analysis)
Uploaded by
Yousef ALmahmoudCopyright:
Available Formats
---------Ch 1 Revision--------
Q1 / What is IT?
Combination of hardware and software products and services
that companies use to manage, access, communicate, and
share information.
Q2/ What IT did change the world?
Changes in the world
Changes in technology
Changes in client demand
Q3/what Systems Analysis can do? .
-Plan, develop, and maintain information systems.
-Also manages IT projects, including tasks, resources, schedules, and
costs.
-manage meetings, delivers presentations, and writes memos, reports, and
documentation.
Q4/ What is information system components?
5 key components:
1-hardware.
2-software:
Application software: Horizontal system. Vertical system. Legacy systems
3-data. 4-processes.
5-people.
Q5/ What is E-commerce sectors?
1- B2C.
2- B2B: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
Supply chain management (SCM).
Supplier relationship management (SRM).
Q6/ What is Business Profile?
A business profile is an overview of a company’s mission, functions, organization,
products, services, customers, suppliers, competitors, constraints, and future
direction.
Q7/ What is Business process
and Business process model?
a. Business Processes is a
Specific set of transactions,
events, and results that can be
described and documented.
b. A business process model
(BPM) is a graphically
displays one or more business
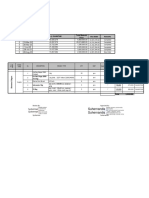
processes. See figure1.
Figure 1
Q8/ What is the new system?
1-Enterprise Computing system. 2- Transaction Processing system.
3- Business Support system. 4- Knowledge Management system. 5- User Productivity
system.
Q9/ What are the techniques of system development tools?
1-modeling. 2-prototyping. 3-computer-aided systems.
Q10/ What are the system development methods?
a. Structured Analysis :
Uses (SDLC) system development life cycle.
The SDLC model includes:
1- System planning.
2- System Analysis
3- System Design.
4- System Implementation.
5- System Security & Support.
b. object-orientated Analysis:
1- Combines data and the processes that act on the data into things called
objects.
2- Objects are members of a class, which is a collection of similar objects.
c. Agile Method:
1- A series of prototypes are built and adjusted to meet user requirements.
2- As the process continues, developers revise, extend, and merge earlier
versions into the final product.
3- Agile method emphasizes continuous feedback
Iterative development.
d. JAD & RAD Method.
**Analysts should understand the pros and cons of any approach before
selecting a development method.
The IT Department:
You might also like
- Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 SolutionsPashaJO100% (1)
- SDLC StagesDocument15 pagesSDLC Stagestulasinad123No ratings yet
- Attendance Challenge ToolkitDocument19 pagesAttendance Challenge Toolkitapi-197489652No ratings yet
- S7SDocument336 pagesS7S217469492100% (1)
- Types of Air Conditioning UnitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning Unitssnowgalvez44No ratings yet
- VsamDocument24 pagesVsamRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Questions Answers: Legarda vs. Saleeby: The Real Purpose of The Torrens System Is To Quiet Title To Land To Put A StopDocument19 pagesQuestions Answers: Legarda vs. Saleeby: The Real Purpose of The Torrens System Is To Quiet Title To Land To Put A StopNico RoaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 The Rise of Instrumental Music - 141-152Document8 pagesCHAPTER 8 The Rise of Instrumental Music - 141-152Aleksandre Roderick-LorenzNo ratings yet
- Belt Weigh FeederDocument808 pagesBelt Weigh FeedersatfasNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDocument31 pagesDynamic Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- cobas8000-DataManager - Host Interface Manual10205 PDFDocument286 pagescobas8000-DataManager - Host Interface Manual10205 PDF박수희No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SADDocument62 pagesChapter 1 SADXavier DominguezNo ratings yet
- BearingsDocument26 pagesBearingstmscorreiaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Intro To Systems Analysis and Design 2Document50 pagesChap 1 Intro To Systems Analysis and Design 2Hai MenNo ratings yet
- Systems Development: Phases, Tools, and TechniquesDocument59 pagesSystems Development: Phases, Tools, and TechniquesSharifah RubyNo ratings yet
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- Lecture - System Analysis and DesignDocument5 pagesLecture - System Analysis and DesignEdzhell MacamNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Learning Active ProcessDocument3 pagesHands-On Learning Active Processjackielyn75% (8)
- Chapter 1 SummaryDocument10 pagesChapter 1 SummaryGeorge Adly Kamel FahmyNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument40 pagesSystem Analysis and Designpaul sarinoNo ratings yet
- Sad 2Document7 pagesSad 2cnp147No ratings yet
- CA FINAL MICS NOTES REVISION GUIDEDocument39 pagesCA FINAL MICS NOTES REVISION GUIDEPrabha GovindasamyNo ratings yet
- MIS Chapter 1 NotesDocument17 pagesMIS Chapter 1 Notesprabahar126No ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and DesignDocument48 pagesSystems Analysis and DesignmaryamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 System Analysis and Design (SAD) NoteDocument6 pagesChapter 4 System Analysis and Design (SAD) NoteAden Kheire MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01cDocument26 pagesChapter 01csubiramwansasu7No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Systems Analysis and DesignDocument44 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Systems Analysis and DesignMario_Bros_GameNo ratings yet
- Information Technologyss March 2023Document3 pagesInformation Technologyss March 2023patience muchemwaNo ratings yet
- SAD Chapter OneDocument8 pagesSAD Chapter OneabdallaNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument35 pagesManagement Information Systemسجن سجيدNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document25 pagesUnit 1work accountNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Sesi II 2021 2022 - Road Trip Dfc40243Document58 pagesChapter 1 - Sesi II 2021 2022 - Road Trip Dfc40243ShaluNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentJaira Mier GalloNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design FundamentalsDocument158 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and Design FundamentalsRakesh PanghalNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Avi ZionDocument6 pagesClass 1 Avi ZionzionfriedlandNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems PDFDocument277 pagesManagement Information Systems PDFKaleli RockyNo ratings yet
- What Is Information Technology, and Why Is It Important To A Business?Document5 pagesWhat Is Information Technology, and Why Is It Important To A Business?Maxbuub AxmedNo ratings yet
- CbisDocument35 pagesCbisRavinathMudavathNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Models and System AnalysisDocument102 pagesUnderstanding Business Models and System Analysisbhuvana67% (3)
- SADI Notes S10 11 - StephDocument38 pagesSADI Notes S10 11 - StephKhagesh JoshNo ratings yet
- System ConceptsDocument4 pagesSystem Conceptsjai232100% (6)
- Chapter 1. The Systems Analyst and Information Systems DevelopmentDocument42 pagesChapter 1. The Systems Analyst and Information Systems DevelopmentBob LongNo ratings yet
- System Development Life CycleDocument12 pagesSystem Development Life CycleReiny Rose AutrizNo ratings yet
- Se Practical FileDocument58 pagesSe Practical FileDivya Gupta100% (1)
- Clinical Information System Answer KeysDocument8 pagesClinical Information System Answer KeysJhasseryne Orias SanchezNo ratings yet
- SDLC Phases and FunctionsDocument54 pagesSDLC Phases and FunctionsHenicel Diones San JuanNo ratings yet
- GIT Notes 2Document8 pagesGIT Notes 2Aya Xiara HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- 04 06 Systems Acquisition - Development ProcessDocument30 pages04 06 Systems Acquisition - Development ProcessSweeto SaniNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design SDLC OverviewDocument45 pagesSystems Analysis and Design SDLC OverviewJames GitongaNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design Chapter 1Document45 pagesSystem Analysis and Design Chapter 1Randy Lamarca Alabab100% (1)
- HW Introduction To Information SystemsDocument6 pagesHW Introduction To Information SystemsNhi HànNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 3 PDFAnonymous HUovc6ROH100% (2)
- Modern Systems Analysis and Design Lecture 1 SDLC Agile MethodologiesDocument39 pagesModern Systems Analysis and Design Lecture 1 SDLC Agile Methodologiesuzma siddiqaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 System DevelopmentDocument18 pagesChapter1 System DevelopmentJohn Wanyoike MakauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Systems Analysis and DesignDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Systems Analysis and Designphongdi2003No ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument80 pagesSystem Analysis and DesignComfort AlfredNo ratings yet
- CS 507 Current SubjectiveDocument12 pagesCS 507 Current Subjectivezahidwahla1No ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design - NidhiDocument11 pagesSystem Analysis and Design - Nidhinidhi_ojha23No ratings yet
- AIS Ch-5Document10 pagesAIS Ch-5Rabbumaa KabbadaaNo ratings yet
- 05 MIS Development ProcessDocument29 pages05 MIS Development ProcessFLOREANN A. BASCO100% (1)
- Systems Analysis and Design Chapter 1: SDLC and MethodologiesDocument33 pagesSystems Analysis and Design Chapter 1: SDLC and MethodologiesshalvenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08: Systems Analysis: Overview 1Document14 pagesChapter 08: Systems Analysis: Overview 1Aubsz26No ratings yet
- MIS Types and Importance in BusinessDocument10 pagesMIS Types and Importance in BusinessUmema FatimaNo ratings yet
- Intro to IS Systems & ComponentsDocument19 pagesIntro to IS Systems & ComponentsNarender KumarNo ratings yet
- It For Managers and Mis OBJECTIVE: To Provide A Clear, Complete Understanding of How Business Professionals Can UseDocument1 pageIt For Managers and Mis OBJECTIVE: To Provide A Clear, Complete Understanding of How Business Professionals Can UseChirack Singh Tony AntonyNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design: CS 231 Akim State University College Safianu OmarDocument47 pagesSystems Analysis and Design: CS 231 Akim State University College Safianu OmarJ A Y T R O NNo ratings yet
- The Systems Development EnvironmentDocument47 pagesThe Systems Development EnvironmentAditya BhusalNo ratings yet
- 11Document10 pages11tazebachew birkuNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Design and Analysis of Information SystemDocument8 pagesAssignment of Design and Analysis of Information Systembir5311No ratings yet
- Book Series: Increasing Productivity of Software Development, Part 1: Productivity and Performance Measurement - Measurability and MethodsFrom EverandBook Series: Increasing Productivity of Software Development, Part 1: Productivity and Performance Measurement - Measurability and MethodsNo ratings yet
- Bindura University of Science Education March - August 2015 Admissions PDFDocument12 pagesBindura University of Science Education March - August 2015 Admissions PDFLuke MadzikotoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledKaren CobachaNo ratings yet
- Blogger TemplateDocument15 pagesBlogger TemplateSteffi Jasmyn BelderolNo ratings yet
- VKS INFRA DPR Submission for NHAI Bihar ProjectDocument1 pageVKS INFRA DPR Submission for NHAI Bihar ProjectamirNo ratings yet
- Panjab University, Chandigarh: (Theory Examinations) TIME OF EXAMINATION: 9.30 A.M. To 12.30 P.MDocument3 pagesPanjab University, Chandigarh: (Theory Examinations) TIME OF EXAMINATION: 9.30 A.M. To 12.30 P.MManav ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Har Rabia Bins Fax Tunisia 2018Document8 pagesHar Rabia Bins Fax Tunisia 2018vacomanoNo ratings yet
- Letter of RecommendationDocument2 pagesLetter of RecommendationnaveenNo ratings yet
- Pizza Hut Training Manual FinishedDocument34 pagesPizza Hut Training Manual FinishedEdilson MaziveNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guide: Multifunctional Digital SystemsDocument132 pagesTroubleshooting Guide: Multifunctional Digital SystemsnguyenhieuproNo ratings yet
- Effecta WoodyDocument21 pagesEffecta WoodyMR XNo ratings yet
- Independent ConsultantDocument8 pagesIndependent ConsultantNaveen GowdaNo ratings yet
- Cilegon-Order Material Pt. Quantum Radja Perkasa-280823Document1 pageCilegon-Order Material Pt. Quantum Radja Perkasa-280823Ria Maretta DewiNo ratings yet
- Daniel Fast Recipes A Couple CooksDocument12 pagesDaniel Fast Recipes A Couple CooksmariamNo ratings yet
- VampireRev4-Page Editable PDFDocument4 pagesVampireRev4-Page Editable PDFNicholas DoranNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming Algorithm Explained in ECE 551 LectureDocument11 pagesDynamic Programming Algorithm Explained in ECE 551 Lectureadambose1990No ratings yet
- Presented by - Aniket Ghosh Dastidar Construction Engg. 4 Year Jadavpur UniversityDocument20 pagesPresented by - Aniket Ghosh Dastidar Construction Engg. 4 Year Jadavpur UniversitySaurabh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- W 2HotlineContacts2019 - 0 2 PDFDocument3 pagesW 2HotlineContacts2019 - 0 2 PDFNathan Townsend Levy100% (1)
- CPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 7, Chapter 24Document47 pagesCPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 7, Chapter 24dheerajbhagwatNo ratings yet
- Mana Paribhsha RSBKDocument31 pagesMana Paribhsha RSBKlohiyakankshaNo ratings yet