Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Report: Wouter Meersseman, Patrick Verschueren, Thomas Tousseyn, Rita de Vos, David Cassiman
Uploaded by
mafe alvarezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Report: Wouter Meersseman, Patrick Verschueren, Thomas Tousseyn, Rita de Vos, David Cassiman
Uploaded by
mafe alvarezCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Report
PAS-positive macrophages—not always infection
Wouter Meersseman, Patrick Verschueren, Thomas Tousseyn, Rita De Vos, David Cassiman
Lancet 2011; 377: 1890 In April, 2009, a 30-year old man of Turkish origin was infection (eg, Whipple’s disease, leishmaniasis, endemic
Department of General Internal referred to our hospital with a 5-year history of asthenia mycoses).2 However, the patient never had abnormal
Medicine (W Meersseman MD), and arthralgias. 2 years earlier he had been diagnosed inflammatory indices. He had not travelled to a region
Department of Rheumatology
with rheumatoid arthritis, which did not respond to endemic for histoplasmosis. Moreover, on Giemsa
(P Verschueren MD),
Department of Morphology non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. On examination, staining, the foamy macrophages had a sea-blue
and Molecular Pathology he had unexplained splenomegaly (span 22 cm). appearance, characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease.
(T Tousseyn MD, R De Vos PhD), Laboratory tests showed thrombocytopenia (92 × 10⁹/L), When last seen in February, 2011, our patient was well,
and Department of Hepatology
and a normal ESR. Immunological tests including without pulmonary symptoms.
(D Cassiman MD), University
Hospital Gasthuisberg, antibodies to cyclic citrullinated protein were inconclu- Niemann-Pick type B disease is a rare autosomal-
Leuven, Belgium sive. Ultrasonography of the knee joints showed bilateral recessive lysosomal storage disorder (incidence
Correspondence to: synovial proliferation. His knees were not red, hot, or 1 in 250 000), which results from the deficiency of acid
Dr Wouter Meersseman, painful, and there was no tumour. sphingomyelinase and the accumulation of lysosomal
University Hospital Gasthuisberg,
Our differential diagnosis included chronic infection sphingomyelin in the lysosomes of cells of the monocyte–
Department of General Internal
Medicine, 3000 Leuven, Belgium and lymphoma. PET with labelled 18-fluorodeoxyglucose macrophage system. The histological hallmark of the
wouter.meersseman@ did not reveal inflammatory spots in joints or muscles. disease is the foam cell, also known as the Niemann-Pick
uzleuven.be There was also no increased uptake in the spleen, making cell, in affected tissues. Biochemical abnormalities
the diagnosis of lymphoma less likely. A bone-marrow include dyslipidaemia (low HDL-cholesterol) and
biopsy sample showed infiltration of foamy, vacuolated thrombocytopenia. The diagnosis of type B disease is
macrophages with granules positive for periodic-acid- usually made in childhood after splenomegaly is found.
Schiff (PAS) (figure). The material was also highlighted Survival well into adulthood is common; the oldest
by a Grocott silver stain, which raised the suspicion of patient alive is 65 years old. In contrast to types A and C
histoplasmosis, and he was treated with itraconazole. of the disease, neurological features are rare. Frequent
However, after 4 months of treatment, there was no symptoms include bleeding (49%), pulmonary infections
resolution of symptoms, and thrombocytopenia and and shortness of breath due to interstitial lung disease
splenomegaly persisted. A new biopsy sample of bone (42%), and joint or limb pain (39%)3, which was the main
marrow was taken. Ultrastructural examination of the complaint in our patient. Growth can be delayed during
macrophages revealed cytoplasmatic lamellar lysosomal adolescence, and studies with standard questionnaires
inclusions as described in lysosomal storage disorders report only mild impairment of quality of life.3 Premature
with splenomegaly such as Gaucher disease, cholesterol coronary artery disease can occur because of the abnormal
ester storage disease, and Niemann-Pick disease lipid profiles.3 There is currently no available treatment
See Online for webappendix (webappendix).1 Peripheral leucocyte enzyme assay for this disease. Clinical trials with enzyme replacement
showed pronounced sphingomyelinase deficiency therapy are planned for the near future.4 Close follow-up
(1·7 nmol/mg, normal 5·1–18·7), which accords with a is needed because of the risk of interstitial lung disease
diagnosis of Niemann-Pick type B disease. Sequence and premature coronary artery disease.5 Our patient’s
analysis of the SMPD1 coding region revealed a case illustrates that some cases of apparent infections,
homozygous mutation (p.Leu163Pro), which has not presenting with PAS-positive macrophages, spleno-
been described previously. When PAS is found in megaly, and arthralgia actually represent a type of
macrophages, the most common underlying diagnosis is lysosomal storage disease. Correct diagnosis allows
genetic counselling and avoids unnecessary treatment
References
1 vom Dahl S, Mengel E. Lysosomal storage diseases as differential
diagnosis of hepatosplenomegaly. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenter
2010; 24: 619–28.
2 Venmans BJ, Claessen FA. Presentation of Whipple’s disease.
Lancet 1997; 349: 433–34.
3 McGovern MM, Wasserstein MP, Giugliani R, et al. A prospective,
cross-sectional survey study of the natural history of Niemann-Pick
disease type B. Paediatrics 2008; 122: e341–49.
4 Beck M. Emerging drugs for lysosomal storage diseases.
Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2010; 15: 495–507.
5 Simpson WL, Mendelson D, Wasserstein MP, et al. Imaging
manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease type B. Am J Roentgenol
2010; 194: 12–19.
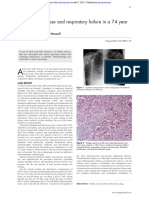
Figure: PAS stain of bone marrow showing macrophages with PAS-positive granules
An increased number of lipid-laden macrophages (arrow) can be seen as intracytoplasmatic granules with PAS
staining with and without diastase pretreatment.
1890 www.thelancet.com Vol 377 May 28, 2011
You might also like
- Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument26 pagesMetabolism of CarbohydratesMM Qizill67% (3)
- Pharmacology of Uterotonics & TocolyticsDocument60 pagesPharmacology of Uterotonics & TocolyticsSiddiq Blackhell Cakep100% (2)
- Eosinophilic Meningitis Due To Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in GermanyDocument3 pagesEosinophilic Meningitis Due To Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in GermanyjohndeereNo ratings yet
- Primary Psoas Abscess: Alexandru Crisan, Emilia Nicoara, Karina Bota, Doru BordosDocument3 pagesPrimary Psoas Abscess: Alexandru Crisan, Emilia Nicoara, Karina Bota, Doru BordosNataliaMaedyNo ratings yet
- Medical Progress: Review ArticlesDocument12 pagesMedical Progress: Review ArticlesgibsonrajanNo ratings yet
- Kikuchi's Disease: Malathi Sathiyasekaran R. Varadharajan So. ShivbalanDocument3 pagesKikuchi's Disease: Malathi Sathiyasekaran R. Varadharajan So. Shivbalanzulfikar adiNo ratings yet
- 74 Year Old Woman With Fatigue, Anorexia, and AbdoDocument6 pages74 Year Old Woman With Fatigue, Anorexia, and AbdoRamiro Arraya MierNo ratings yet
- Poster LESDocument6 pagesPoster LESAlejandra LuqueNo ratings yet
- Patogenesis IMNDocument23 pagesPatogenesis IMNshiloinNo ratings yet
- Tsoi 1997Document7 pagesTsoi 1997Araceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Myositis Overlap Syndrome: Report of 6 CasesDocument4 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus-Myositis Overlap Syndrome: Report of 6 Casesirsyah dwi rNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Polyarteritis Nodosa in A Child FollowinDocument2 pagesCutaneous Polyarteritis Nodosa in A Child FollowinandresrogersNo ratings yet
- Estenosis Esofagica en LlaDocument3 pagesEstenosis Esofagica en LlaResidencia PediatriaNo ratings yet
- Letters To The Editors: Primary Sjögren's Syndrome As Paraneoplastic Disorder: A Case ReportDocument1 pageLetters To The Editors: Primary Sjögren's Syndrome As Paraneoplastic Disorder: A Case ReportDarian AngNo ratings yet
- M: Elaine Crystine Vieira de Paiva Rua Pedro I, 1.033 Centro 60035-101 - Fortaleza - CE - BrazilDocument2 pagesM: Elaine Crystine Vieira de Paiva Rua Pedro I, 1.033 Centro 60035-101 - Fortaleza - CE - Brazilpruebaprueba321765No ratings yet
- 72 - Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in An Immunocompetent PatientDocument7 pages72 - Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in An Immunocompetent PatientFaras ArinalNo ratings yet
- Sun 2012Document6 pagesSun 2012ntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Recent Update in The Management of Childhood Nephr PDFDocument8 pagesRecent Update in The Management of Childhood Nephr PDFREHNUMA URMINo ratings yet
- EMPD Review (Shabihkhani) 2020 Appl Immunohistochem Mol MorphDocument14 pagesEMPD Review (Shabihkhani) 2020 Appl Immunohistochem Mol MorphCarloNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0272638698001097Document6 pagesPi Is 0272638698001097Mita AdrianiNo ratings yet
- HIV Hemicorea CNS Histoplasmosis 2016Document3 pagesHIV Hemicorea CNS Histoplasmosis 2016Juan Salazar PajaresNo ratings yet
- Hemoptysis in A Healthy 13-Year-Old Boy: PresentationDocument5 pagesHemoptysis in A Healthy 13-Year-Old Boy: PresentationluishelNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Presenting As Traumatic Haemoperitoneum and Duodenal InjuryDocument2 pagesChronic Myeloid Leukaemia Presenting As Traumatic Haemoperitoneum and Duodenal InjuryhlNo ratings yet
- Membrane NephropathyDocument14 pagesMembrane NephropathyCasey GondoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis: Science in MedicineDocument7 pagesMultiple Sclerosis: Science in MedicineIhsanAkbarNo ratings yet
- Thrasivoulos: Cardiomyopathy in Children: Importance of Aetiology in PrognosisDocument2 pagesThrasivoulos: Cardiomyopathy in Children: Importance of Aetiology in PrognosisDede MarizalNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 18 05895Document13 pagesIjerph 18 05895JHon Hendrik TambunanNo ratings yet
- Group A Streptococcal Meningitis: Report of A Case and Review of Literature Since 1976Document5 pagesGroup A Streptococcal Meningitis: Report of A Case and Review of Literature Since 1976soledad88No ratings yet
- Malignant Mesothelioma Presenting With Unexplained Recurrent Pleurisy EpisodesDocument4 pagesMalignant Mesothelioma Presenting With Unexplained Recurrent Pleurisy EpisodesNurul NingrumNo ratings yet
- Eritema Nodoso: Causas Más Prevalentes en Pacientes Que Se Hospitalizan para Estudio, y Recomendaciones para El DiagnósticoDocument7 pagesEritema Nodoso: Causas Más Prevalentes en Pacientes Que Se Hospitalizan para Estudio, y Recomendaciones para El DiagnósticoCamilo PerillaNo ratings yet
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLangerhans Cell Histiocytosis Literature Reviewc5rw1ymp100% (1)
- Spiraling Out of Control: Clinical Problem-SolvingDocument6 pagesSpiraling Out of Control: Clinical Problem-SolvingjjjkkNo ratings yet
- Tsai (2007) - NSDocument2 pagesTsai (2007) - NSIlma ArifaniNo ratings yet
- Transverse Myelitis: Clinical PracticeDocument9 pagesTransverse Myelitis: Clinical PracticearnabNo ratings yet
- Pyogenic Spinal InfectionsDocument16 pagesPyogenic Spinal InfectionsFrancisco Escobar MoralesNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Seven Cases and Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesHypopituitarism in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Seven Cases and Literature ReviewafdtfngqbNo ratings yet
- Lipophagic Panniculitis of Childhood: Chronic Actinic DermatitisDocument8 pagesLipophagic Panniculitis of Childhood: Chronic Actinic DermatitisHellgenius SantomauroNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Symposium: NephrologyDocument4 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: Symposium: Nephrologypramuliansyah haqNo ratings yet
- Cancer de Testiculo e Down 2Document4 pagesCancer de Testiculo e Down 2paulinhamericoNo ratings yet
- 1009 Case 2Document4 pages1009 Case 2willygopeNo ratings yet
- Modpathol 201783Document14 pagesModpathol 201783Tian Nopita SariNo ratings yet
- LewisuweDocument2 pagesLewisuweDian NovitasariNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal Gammopathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: PaperDocument4 pagesMonoclonal Gammopathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: PaperNguyễn Nhựt MinhNo ratings yet
- 13 CR Lethal MidlineDocument3 pages13 CR Lethal MidlineSudhir BayyaNo ratings yet
- Colitis Por CMVDocument5 pagesColitis Por CMVLeny CastilloNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Fever, Hepatosplenomegaly, and Pancytopenia in A 46-Year-Old WomanDocument6 pagesProlonged Fever, Hepatosplenomegaly, and Pancytopenia in A 46-Year-Old WomanFerdy AlviandoNo ratings yet
- Crescentic Glomerulonephritis and Membranous NephropathyDocument8 pagesCrescentic Glomerulonephritis and Membranous NephropathyVíctor Cruz CeliNo ratings yet
- Adult Still's Disease and Respiratory Failure in A 74 Year Old WomanDocument3 pagesAdult Still's Disease and Respiratory Failure in A 74 Year Old WomanEduardo Romero StéfaniNo ratings yet
- Transient Myeloproliferative Disorder: What's Eosinophilia Got To Do With It?Document1 pageTransient Myeloproliferative Disorder: What's Eosinophilia Got To Do With It?wadeschulzNo ratings yet
- CE Update: Wegener's Granulomatosis: A Review of The Clinical Implications, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument3 pagesCE Update: Wegener's Granulomatosis: A Review of The Clinical Implications, Diagnosis, and TreatmentAfif FaiziNo ratings yet
- 12 OA Evaluation of Febrile Thrombocytopenia CasesDocument5 pages12 OA Evaluation of Febrile Thrombocytopenia CasesVimal NishadNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Jaad 2019 05 096Document8 pages10 1016@j Jaad 2019 05 096JohnNo ratings yet
- Ijpd 24 221Document2 pagesIjpd 24 221intan yunni aztiNo ratings yet
- Jcad 6 8 23Document6 pagesJcad 6 8 23Hadi FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Prognostic Factors of Death in Leptospirosis: A Prospective Cohort Study in Khon Kaen, ThailandDocument8 pagesPrognostic Factors of Death in Leptospirosis: A Prospective Cohort Study in Khon Kaen, ThailandSilvia RNo ratings yet
- Seizures in Adults With Bacterial MeningitisDocument9 pagesSeizures in Adults With Bacterial MeningitiselaNo ratings yet
- Eritema Nodoso y HodgkinsDocument4 pagesEritema Nodoso y HodgkinsGuada SosaNo ratings yet
- Miyoshi 1998Document7 pagesMiyoshi 1998dad dzd adaNo ratings yet
- EN + EosinofiliaDocument3 pagesEN + EosinofiliaAna Flavia BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Wells Syndrome (Eosinophilic Cellulitis) : Proposed Diagnostic Criteria and A Literature Review of The Drug-Induced VariantDocument8 pagesWells Syndrome (Eosinophilic Cellulitis) : Proposed Diagnostic Criteria and A Literature Review of The Drug-Induced VariantAnamaria IuoraşNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Tuberculous Myositis in A Child With Acut 2009 Pediatrics NeoDocument4 pagesDisseminated Tuberculous Myositis in A Child With Acut 2009 Pediatrics NeoFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Auto-Inflammatory Syndromes: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and ManagementFrom EverandAuto-Inflammatory Syndromes: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and ManagementPetros EfthimiouNo ratings yet
- AE403BIOMEDICALINSTRUMENTATION (Careeryuga)Document2 pagesAE403BIOMEDICALINSTRUMENTATION (Careeryuga)Akhil A BNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceArabelle GONo ratings yet
- 478-Article Text-909-1-10-20210923Document10 pages478-Article Text-909-1-10-20210923Puspitadewi HensNo ratings yet
- FELINE-Hepatic Lipidosis - Pathophysiology, Clinical Signs and DiagnosisDocument8 pagesFELINE-Hepatic Lipidosis - Pathophysiology, Clinical Signs and Diagnosistaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Third Degree Block After Mi........ Observe The PatientDocument23 pagesThird Degree Block After Mi........ Observe The PatientSunn Ren TeeNo ratings yet
- Attachment 181014031633Document35 pagesAttachment 181014031633lalalalalililililiNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Its TypesDocument3 pagesImmunity and Its TypesBenazir SheikhNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Breast CancerDocument72 pagesCase Study: Breast CancerJoy Mariel Isadora BurgosNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument29 pagesAbortionMujeeb Choudhary100% (2)
- Robert Koch - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesRobert Koch - Britannica Online EncyclopediakamilapufflerovaNo ratings yet
- MCHCDocument119 pagesMCHCibrarulhaqi313No ratings yet
- HPB Case 4Document2 pagesHPB Case 4saya001No ratings yet
- Transurethral Resection of The Prostate (TURP)Document16 pagesTransurethral Resection of The Prostate (TURP)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- BDC Guidelines of The New Norm During PandemicDocument18 pagesBDC Guidelines of The New Norm During PandemicJoshua Christian TeopengcoNo ratings yet
- Keeping Older Adults Safe at Home: Fall Risks Add UpDocument6 pagesKeeping Older Adults Safe at Home: Fall Risks Add UpBj DuquesaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Browns Atlas of Regional Anesthesia 2 PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Browns Atlas of Regional Anesthesia 2 PDFgeorge.pittman905100% (16)
- Wound Class AlgorithmDocument1 pageWound Class AlgorithmManuel Opazo ToledoNo ratings yet
- OB PACU Severe PreeclampsiaDocument65 pagesOB PACU Severe Preeclampsiasurbakti_christineNo ratings yet
- Icmr Specimen Referral Form For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) : (If Yes, Attach Prescription If No, Test Cannot Be Conducted)Document2 pagesIcmr Specimen Referral Form For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) : (If Yes, Attach Prescription If No, Test Cannot Be Conducted)gopimicroNo ratings yet
- JAMA Psychiatry - : Original InvestigationDocument10 pagesJAMA Psychiatry - : Original InvestigationMesianissimoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of A Anxiety Disorder PDFDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of A Anxiety Disorder PDFpragna novaNo ratings yet
- DM CaseDocument14 pagesDM CaseNormana ZureikatNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Superbowl Summary 2021Document7 pagesCovid19 Superbowl Summary 2021Chris VaughnNo ratings yet
- MCQ's With KEY GAYNAE - BDocument7 pagesMCQ's With KEY GAYNAE - BSiraj Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Physiological Birth Vs LSCS (Ceserean)Document2 pagesPhysiological Birth Vs LSCS (Ceserean)tushardashoraNo ratings yet
- GIt HormonesDocument8 pagesGIt Hormonesriskyy1No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument19 pagesAplastic AnemiaNadia Puspita DewiNo ratings yet