Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Dynamic Routing Protocols
Uploaded by
Sahil KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Dynamic Routing Protocols
Uploaded by
Sahil KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
TEST TIME- (2.35 pm – 3.20 pm)
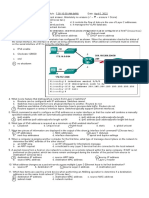
1. If a PC on an Ethernet network attempts to communicate with a host on a different
subnet, what destination IP address and destination MAC address will be placed in the
packet/frame header sent by the PC?
a. Dest. IP: IP address of default gateway. Dest. MAC: MAC address of default gateway.
b. Dest. IP: IP address of remote host. Dest. MAC: MAC address of default gateway.
c. Dest. IP: IP address of remote host. Dest. MAC: MAC address of remote host.
d. Dest. IP: IP address of remote host. Dest. MAC: MAC address of local PC.
2. What protocol is used to request a MAC address that corresponds to a known IPv4
address on the local network?
a. IGMP
b. TTL
c. ICMP
d. ARP
3. What is the network address and subnet mask of a default route?
a. 255.255.255.255/32
b. 0.0.0.0/32
c. 255.255.255.255/0
d. 0.0.0.0/0
4. What routing protocol characteristic indicates the believability of the routing
protocol (as opposed to other routing protocols)?
a. Weight
b. Metric
c. Administrative distance
d. SPF algorithm
5. Which of the following are distance-vector routing protocol features that can
prevent routing loops? (Choose two.)
a. Reverse path forwarding (RPF) check
b. Split horizon
c. Poison reverse
d. Rendezvous point
6. Which of the following is a distance-vector routing protocol with a maximum usable hop
count of 15?
a. BGP
b. IS-IS
c. RIP
d. OSPF
7. Which of the following routing protocols is an EGP?
a. BGP
b. IS-IS
c. RIP
d. OSPF
8. What NAT IP address is a public IP address that maps to an inside device?
a. Inside local
b. Inside global
c. Outside local
d. Outside global
9. What NAT variation automatically assigns an inside global address from a pool of available
addresses?
a. SNAT
b. DNAT
c. PAT
d. GNAT
10. What multicast protocol is used between clients and routers to let routers know which
of their interfaces are connected to a multicast receiver?
a. IGMP
b. PIM-DM
c. PIM-SM
d. SPT switchover
11. Consider the following three statements about link state and distance vector routing
protocols, for a large network with 500 network nodes and 4000 links.
[S1] The computational overhead in link state protocols is higher than in distance vector
protocols.
[S2] A distance vector protocol (with split horizon) avoids persistent routing loops, but not a
link state protocol.
[S3] After a topology change, a link state protocol will converge faster than a distance vector
protocol.
Which one of the following is correct about S1, S2, and S3?
a. S1, S2, and S3 are all true.
b. S1, S2, and S3 are all false.
c. S1 and S2 are true, but S3 is false
d. S1 and S3 are true, but S2 is false
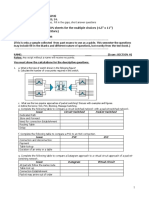
12. Consider a network with five nodes, N1 to N5, as shown below.
The network uses a Distance Vector Routing protocol. Once the routes have stabilized, the
distance vectors at different nodes are as following.
N1: (0, 1, 7, 8, 4)
N2: (1, 0, 6, 7, 3)
N3: (7, 6, 0, 2, 6)
N4: (8, 7, 2, 0, 4)
N5: (4, 3, 6, 4, 0)
Each distance vector is the distance of the best-known path at the instance to nodes, N1 to
N5, where the distance to itself is 0. Also, all links are symmetric and the cost is identical in
both directions. In each round, all nodes exchange their distance vectors with their
respective neighbors. Then all nodes update their distance vectors. In between two rounds,
any change in cost of a link will cause the two incident nodes to change only that entry in
their distance vectors. 52. The cost of link N2-N3 reduces to 2(in both directions). After the
next round of updates, what will be the new distance vector at node, N3.
(A) (3, 2, 0, 2, 5)
(B) (3, 2, 0, 2, 6)
(C) (7, 2, 0, 2, 5)
(D) (7, 2, 0, 2, 6)
You might also like
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Hcda AllDocument69 pagesHcda Allsamu1991tan100% (1)
- HCDA ALL Correct AnswerDocument79 pagesHCDA ALL Correct AnswerHafizul Hazmi WahabNo ratings yet
- Ccna Question PaperDocument22 pagesCcna Question Paperpavithra aishuNo ratings yet
- Materi MateriDocument69 pagesMateri MateriAditya Widya Manggala100% (1)
- HCNA ReviewerDocument69 pagesHCNA ReviewerFranz Mejorada Ccie100% (5)
- CCNP ENCOR 350-401 Practice Exam - V1Document41 pagesCCNP ENCOR 350-401 Practice Exam - V1waleniy710No ratings yet
- Dc792tutorial AssinmentDocument5 pagesDc792tutorial AssinmentKanu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Answer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?Document37 pagesAnswer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?dijeshkelothNo ratings yet
- SRM NRA - CT3 - Set BDocument8 pagesSRM NRA - CT3 - Set BSANDESH RAJNATH RAJBHAR (RA2111003010261)No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3Ekansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- (MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT5Document22 pages(MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT5raghad mejeedNo ratings yet
- W2019-2140709-APY MAterialDocument2 pagesW2019-2140709-APY MAterialMeet PatelNo ratings yet
- Class Test 1: LevelDocument15 pagesClass Test 1: LevelKiki Net0% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDocument199 pagesPractice QuestionsCarl CarpenterNo ratings yet
- SRM NRA - CT3 - Set ADocument9 pagesSRM NRA - CT3 - Set ASANDESH RAJNATH RAJBHAR (RA2111003010261)No ratings yet
- 08.703 Computer Networks Question Bank: Ans: PPP Data FrameDocument7 pages08.703 Computer Networks Question Bank: Ans: PPP Data Framesendtomerlin4uNo ratings yet
- Hcia RSDocument131 pagesHcia RSZveZ100% (1)
- Multiple Choice: 100 Points Possible (Graded)Document9 pagesMultiple Choice: 100 Points Possible (Graded)Shuvo IT OfficerNo ratings yet
- Trắc nghiệm CCNA - Chương 1 Tổng quanDocument8 pagesTrắc nghiệm CCNA - Chương 1 Tổng quanvanchieu.at3.stNo ratings yet
- 04H12 211 Mock RevisionDocument16 pages04H12 211 Mock RevisionjlhfcNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 AnswersDocument3 pagesQuiz 4 AnswersChloe CarreonNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 6 MC TF QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter5 6 MC TF QuestionsbottbottNo ratings yet
- Quiz PreparatorioDocument30 pagesQuiz PreparatorioGalacticoRM100% (1)
- Network Layer Unit IVDocument213 pagesNetwork Layer Unit IVGunjanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 AnswerDocument3 pagesQuiz 5 AnswerChloe CarreonNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksDocument64 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworkssamiNo ratings yet
- Soal Mtcre Des 2020 - 1 Hanya Soalnya Saja: Mikrotik Routers and WirelessDocument4 pagesSoal Mtcre Des 2020 - 1 Hanya Soalnya Saja: Mikrotik Routers and Wirelessrmtpcr33% (3)
- CCNA 2 Gold Bible PDFDocument0 pagesCCNA 2 Gold Bible PDFrichbartonNo ratings yet
- Cisco Networking Academy Program - CCNA1 3.1.1 FINAL EXAM #2Document16 pagesCisco Networking Academy Program - CCNA1 3.1.1 FINAL EXAM #2Issa kandji100% (2)
- When You Are Logged Into A Switch, Which Prompt Indicates That You Are in Privileged Mode? A. % B. at C. D. $Document29 pagesWhen You Are Logged Into A Switch, Which Prompt Indicates That You Are in Privileged Mode? A. % B. at C. D. $ĐinhĐạiĐồngNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 (Introduction of Computer Networks)Document5 pagesUnit - 1 (Introduction of Computer Networks)Abhinavv GandhiNo ratings yet
- HCIE Latest PDFDocument69 pagesHCIE Latest PDFhoussem100% (1)
- CCNA 1 Final ExamDocument54 pagesCCNA 1 Final ExamAdha Estu RizqiNo ratings yet
- Intrebari ReteleDocument54 pagesIntrebari ReteleAnastasia SusciucNo ratings yet
- Examen 8-10Document27 pagesExamen 8-10Jhon RojasNo ratings yet
- QT CuoiKy MMT1 2009 Draft EditDocument11 pagesQT CuoiKy MMT1 2009 Draft EditPhạm Cao CườngNo ratings yet
- Datalink AnswersDocument3 pagesDatalink AnswersNguyễn Văn HiếnNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Chap 1419212324 No SolDocument10 pagesExam 3 Chap 1419212324 No SolhaniNo ratings yet
- Cmu 15 441 Final Spring2009Document19 pagesCmu 15 441 Final Spring2009NickHenryNo ratings yet
- Destination Network Address: Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals - Chapter 5 Exam 100% CommonDocument8 pagesDestination Network Address: Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals - Chapter 5 Exam 100% CommonPeejay OllabracNo ratings yet
- Unit-3Network Layer-2 Computer NetworksDocument20 pagesUnit-3Network Layer-2 Computer NetworksKhushNo ratings yet
- 18it502 - DCCN - Question Bank-1Document6 pages18it502 - DCCN - Question Bank-1SHANMUGAM SNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Exam Final en AnglaisDocument54 pagesCCNA 1 Exam Final en AnglaisRoland FoyemtchaNo ratings yet
- Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad: Assignment On Network LayerDocument4 pagesMotilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad: Assignment On Network LayerSwati AgarwalNo ratings yet
- IT Questions Bank Final ExamDocument77 pagesIT Questions Bank Final ExamfeyisaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Questions For: Nokia IP Networks and Services Fundamentals (Exam Number: 4A0-100)Document7 pagesPractice Exam Questions For: Nokia IP Networks and Services Fundamentals (Exam Number: 4A0-100)DanielVillavicencio100% (1)
- SRM NRA - CT3 - Set DDocument11 pagesSRM NRA - CT3 - Set DSANDESH RAJNATH RAJBHAR (RA2111003010261)No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 2 2022-2023 AnswerDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 2 2022-2023 AnswerZam SkemaNo ratings yet
- HCIA Datacom Mock Exam 1.0 PDFDocument18 pagesHCIA Datacom Mock Exam 1.0 PDFyomif tamiru100% (1)
- CCNA 1 Full Introduction To Networks PDFDocument46 pagesCCNA 1 Full Introduction To Networks PDFRazvan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksDocument49 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksChristian StyriaNo ratings yet
- CN Chapterwise Question Bank SH-2022Document3 pagesCN Chapterwise Question Bank SH-2022Pushpa RazNo ratings yet
- ComNet MiniExam2 SolutionDocument5 pagesComNet MiniExam2 SolutionMohammed HoushanNo ratings yet
- Unit III and IVDocument21 pagesUnit III and IVharishNo ratings yet
- Ccna MCQDocument5 pagesCcna MCQMohamed Mounir FekriNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 2015Document7 pagesAssignment - 2 2015Shulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- CCNA QuestionsDocument5 pagesCCNA Questionsdineshkumar20107156100% (2)
- USETDocument8 pagesUSETguerrerokarina276No ratings yet
- En s3000 Dats Quidway s3000 Ei Intelligent Ethernet Switches v1.03 (20060303)Document2 pagesEn s3000 Dats Quidway s3000 Ei Intelligent Ethernet Switches v1.03 (20060303)Geet MadhaviNo ratings yet
- WindowsServer2012R2-Tutorial v2Document56 pagesWindowsServer2012R2-Tutorial v2Harfic Hanifah Hj SuhailiNo ratings yet
- Auh192 Auh2353Document33 pagesAuh192 Auh2353Mohammad Noor AlamNo ratings yet
- Marvell 88Q5072 Secure Multi-Gig Automotive Switch With Integrated 100BASE-T1 PHYDocument2 pagesMarvell 88Q5072 Secure Multi-Gig Automotive Switch With Integrated 100BASE-T1 PHYBeyond TechnologyNo ratings yet
- NSE 4 Sample Exam 6.0Document19 pagesNSE 4 Sample Exam 6.0Kali LinuxNo ratings yet
- Fix Unidentified Network and No Network Access Errors in Windows 7Document5 pagesFix Unidentified Network and No Network Access Errors in Windows 7zceljakNo ratings yet
- United States Trustee Program's Wireless LAN Security ChecklistDocument5 pagesUnited States Trustee Program's Wireless LAN Security ChecklistChidi OkerekeNo ratings yet
- QoS Analysis For IPTV1Document8 pagesQoS Analysis For IPTV1quangfetNo ratings yet
- AirLive WH-5400CPE SpecsDocument2 pagesAirLive WH-5400CPE SpecsRieky WijayaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet IPBrickI16.32.64.EnDocument1 pageDatasheet IPBrickI16.32.64.EnRicardo TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Netcat Hacker Manual: A Handy Pocket Guide For Your CatDocument28 pagesNetcat Hacker Manual: A Handy Pocket Guide For Your CatodoggzNo ratings yet
- Junos OverviewDocument438 pagesJunos Overviewhoward zhangNo ratings yet
- Foundation: Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. DavieDocument60 pagesFoundation: Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. DavieHaftamu HailuNo ratings yet
- The OSI Model's Seven Layers Defined and Functions ExplainedDocument3 pagesThe OSI Model's Seven Layers Defined and Functions ExplainedAnuja KhamitkarNo ratings yet
- 3500 91 Egd Communication Gateway Module Datasheet 0Document6 pages3500 91 Egd Communication Gateway Module Datasheet 0dikastaloneNo ratings yet
- FortiOS 6.4.6 Administration GuideDocument1,880 pagesFortiOS 6.4.6 Administration GuideSandro Henrique de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- PCN001 - PoeDocument2 pagesPCN001 - Poelight visualizerNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.2Document7 pagesLab 2.2Riia PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Documento AtpDocument7 pagesDocumento AtpmanuelNo ratings yet
- Can ProtocolDocument4 pagesCan ProtocolratheeshbrNo ratings yet
- How Fast-Flux Service Networks Work - The Honeynet ProjectDocument1 pageHow Fast-Flux Service Networks Work - The Honeynet ProjectddroNo ratings yet
- 07-Module 5 - Implementing IPv4Document50 pages07-Module 5 - Implementing IPv4Anderson Lobo de SousaNo ratings yet
- AcronymDocument5 pagesAcronymRaviNo ratings yet
- Automotive Ethernet Black BookDocument44 pagesAutomotive Ethernet Black BookGrulletto Grullone100% (1)
- Wa0002.Document3 pagesWa0002.Project WorkNo ratings yet
- TechNoteRX SNTP SetupDocument14 pagesTechNoteRX SNTP SetupChristine VelascoNo ratings yet
- X11Document3 pagesX11sandraNo ratings yet
- Fortinet NSE4Document34 pagesFortinet NSE4Hamed Ghabi100% (1)
- Fortinet Wireless Product MatrixDocument9 pagesFortinet Wireless Product MatrixLigalNo ratings yet