Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WWW - World Wide Web: Pay Attention To Related Hyperlinked Terms
Uploaded by
Marcos David Jimenez Castañeda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pages(1) The World Wide Web (WWW), also known as the Web, is an information system accessible over the Internet through interconnected hyperlinked web pages and resources identified by URLs.
(2) English scientist Sir Timothy Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989 while employed at CERN near Geneva, Switzerland, developing the first web browser, server, and HTML language to display web pages containing text, images, and hyperlinks.
(3) The Web began entering widespread use in the early 1990s as general interest websites became available, and it has since been central to the development of the Information Age, serving as the primary online tool for billions of people worldwide.
Original Description:
Inglés
Original Title
WWW activity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document(1) The World Wide Web (WWW), also known as the Web, is an information system accessible over the Internet through interconnected hyperlinked web pages and resources identified by URLs.
(2) English scientist Sir Timothy Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989 while employed at CERN near Geneva, Switzerland, developing the first web browser, server, and HTML language to display web pages containing text, images, and hyperlinks.
(3) The Web began entering widespread use in the early 1990s as general interest websites became available, and it has since been central to the development of the Information Age, serving as the primary online tool for billions of people worldwide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesWWW - World Wide Web: Pay Attention To Related Hyperlinked Terms
Uploaded by
Marcos David Jimenez Castañeda(1) The World Wide Web (WWW), also known as the Web, is an information system accessible over the Internet through interconnected hyperlinked web pages and resources identified by URLs.
(2) English scientist Sir Timothy Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989 while employed at CERN near Geneva, Switzerland, developing the first web browser, server, and HTML language to display web pages containing text, images, and hyperlinks.
(3) The Web began entering widespread use in the early 1990s as general interest websites became available, and it has since been central to the development of the Information Age, serving as the primary online tool for billions of people worldwide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
WWW -World Wide Web
Adapted from Wikipedia, the free enciclopedia, for academic purposes. 14-04-2021
Pay attention to related hyperlinked terms.
A web page can be displayed using a web browser. Web
browsers often highlight and underline hypertext links and web
pages can contain images.
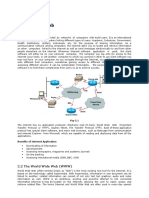
A global map of the web index for countries in 2014:
The World Wide Web
(WWW), also known as the
Web, is an information system
where documents and other
web resources are identified
by Uniform Resource Locators
(URLs, such as
https://example.com/), which may be interlinked by hyperlinks,
and are accessible over the Internet.[1][2] The resources of the
Web are transferred via the Hypertext Transfer Protocol
(HTTP), may be accessed by users by a software application
called a web browser, and are published by a software
application called a web server. The World Wide Web is not
synonymous with the Internet, which pre-dated the Web in
some form by over two decades and upon which technologies
the Web is built.
English scientist Sir Timothy Berners-Lee invented the World
Wide Web in 1989. He wrote the first web browser in 1990
while employed at CERN near Geneva, Switzerland.[3][4] The
browser was released outside CERN to other research
institutions starting in January 1991, and then to the general
public in August 1991. The Web began to enter everyday use in
1993-4, when websites for general use started to become
available.[5] The World Wide Web has been central to the
development of the Information Age, and is the primary tool
billions of people use to interact on the Internet.[6][7][8][9][10]
Web resources may be any type of downloaded media, but web
pages are hypertext documents formatted in Hypertext Markup
Language (HTML).[11] Special HTML syntax displays embedded
hyperlinks with URLs which permits users to navigate to other
web resources. In addition to text, web pages may contain
references to images, video, audio, and software components
which are either displayed or internally executed in the user's
web browser to render pages or streams of multimedia content.
Multiple web resources with a common theme and usually a
common domain name, make up a website. Websites are stored
in computers that are running a web server, which is a program
that responds to requests made over the Internet from web
browsers running on a user's computer. Website content can be
provided by a publisher, or interactively from user-generated
content. Websites are provided for a myriad of informative,
entertainment, commercial, and governmental reasons.
Task. Part A. Vocabulary building. Match each of the following
definitions on the right with the corresponding term or acronym
on the left.
Term / Definition
acronym
( ) URL 1. Information system of
linked computers all over
( ) WWW the world through the
Internet.
( ) HTTPS 2. An address or location
where a user can find
( ) Web server different media, such as
text, images, audio, video,
( ) Website among other types of
information.
( ) Browser 3. The place where the W3
was born: A French
( ) CERN research center named
“Conseil européen pour la
( ) Information recherche nucléaire”
Age 4. A historical period of time
when media became more
( ) Format accesible to people
through isolated and
( ) HTML interconnected
computers- It is also
( ) Hyperlink known as the computer
age, the digital age, or new
( ) Navigate media age, starting in
1950’s and 1960s.
( ) Domain 5. The protocol or way
name resources and media travel
through nets via
hyperlinks.
6. A URL where the users get
displayed the data they
were searching. It is also
known as landing page, or
index to a set of more
specific information.
7. A central or main
computer which keeps and
distributes hyperlinked
contents and media.
8. A graphical interface /
software used to look for
information and display it
on the screen of end-users’
computers.
9. The action of going from
one website to another,
also known as browsing,
or surfing with programs
like Firefox, Chrome, and
others.
10.A group of web sites with
commomn contents,
usually stored or running
from a web server: .org,
.com, .net, among others.
11.The way something is
displayed on a screen, for
example the text from a
web page with font type,
size, color among other
features.
12.HyperText Markup
Language, a code or
programming language
that tells the text and
images on a website how
to look like and how to
behave when the user
clicks on it.
13.Enriched text in a website
that, when clicked, takes
end-user to another URL
and displays new
information.
You might also like
- Web Design and Technology Handouts - 1709657863Document53 pagesWeb Design and Technology Handouts - 1709657863vikikush22No ratings yet
- The History and Development of the World Wide WebDocument1 pageThe History and Development of the World Wide WebAlex verdeNo ratings yet
- World Wide Web - WikipediaDocument21 pagesWorld Wide Web - WikipediaGilbertNo ratings yet
- Web Programming FundamentalsDocument15 pagesWeb Programming Fundamentalsbaby100% (1)
- C Is A Global System of InterconnectedDocument3 pagesC Is A Global System of InterconnectedMaldito E-jayNo ratings yet
- 2 Chepter 2Document40 pages2 Chepter 2pankajusbNo ratings yet
- HTML CourseDocument192 pagesHTML CourseAshraf MazenNo ratings yet
- World Wide Web: Pages Are Hypertext Documents Formatted in Hypertext MarkupDocument20 pagesWorld Wide Web: Pages Are Hypertext Documents Formatted in Hypertext MarkupFred PianistNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & cyber security unit 4 (1)Document38 pagesIntroduction to Internet & cyber security unit 4 (1)Sameer RaiNo ratings yet
- Project Report BrowserDocument40 pagesProject Report Browserneha12242% (12)
- Seminar Report On WWWDocument7 pagesSeminar Report On WWWAmit BarikNo ratings yet
- Web Develpment - Lecture Notes - Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument32 pagesWeb Develpment - Lecture Notes - Chapter 1 - IntroductionDawit MNo ratings yet
- Web-2.0-and-3.0-1Document27 pagesWeb-2.0-and-3.0-1shivauneamarioNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4-The World Wide WebDocument5 pagesUNIT 4-The World Wide WebMary Jane PagayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - The InternetDocument16 pagesChapter 10 - The Internetnitish kumar twariNo ratings yet
- GEC7 ReportingDocument5 pagesGEC7 ReportingLouigen DagaydayNo ratings yet
- Web Design NotesDocument54 pagesWeb Design NotesVernon V IsmaelNo ratings yet
- IT8078 U01S01 Working of WebDocument25 pagesIT8078 U01S01 Working of WebLokith100% (1)
- Semantic Web and Social NetworksDocument63 pagesSemantic Web and Social NetworksANCY THOMASNo ratings yet
- Complete Notes On InternetDocument22 pagesComplete Notes On InternetdileepNo ratings yet
- Web_TECH_NOTESDocument87 pagesWeb_TECH_NOTESupdeshroy816No ratings yet
- Exploring the History and Development of the InternetDocument18 pagesExploring the History and Development of the InternetKim Howard LalapNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 WWW Q. What Is WWW?: Information and Communication TechnologyDocument8 pagesChapter-4 WWW Q. What Is WWW?: Information and Communication Technologyarbaz khanNo ratings yet
- CODE:-BCA - 204 SUBJECT: - Web Technologies Unit - IDocument51 pagesCODE:-BCA - 204 SUBJECT: - Web Technologies Unit - IPushkar bansalNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument12 pagesGroup 4 PresentationOthieno EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WWWDocument36 pagesIntroduction To WWWjohnhaile23No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 1Document28 pagesModule 1 - Part 1Ver Laurence CuevasNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: Aim: To Understand, Describe and Identify The Following Web TerminologyDocument8 pagesPractical 1: Aim: To Understand, Describe and Identify The Following Web TerminologyBijalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: An Introduction To The World Wide WebDocument23 pagesChapter-1: An Introduction To The World Wide WebSameer MittalNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument34 pagesCollege of Engineering and Technologydiro fufaNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument20 pagesUnit IPoonamNo ratings yet
- Understanding The World Wide WebDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The World Wide WebHarshita Chaturvedi100% (1)
- World Wide Web EditedDocument24 pagesWorld Wide Web EditedJanice Agbuya TamondongNo ratings yet
- Internet Chap 1Document50 pagesInternet Chap 1Hussen MossaNo ratings yet
- Internet and Internet ServicesDocument38 pagesInternet and Internet ServicesMehran AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet Programming FundamentalsDocument36 pagesIntroduction to Internet Programming FundamentalsAbenezer TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument183 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFAnas Omar MuffarrejNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HypertextDocument16 pagesChapter 4 HypertextRebecca ChenNo ratings yet
- WebSystemsAndTechnologies 01. IntroductionDocument36 pagesWebSystemsAndTechnologies 01. Introductionthanh thienNo ratings yet
- CS Module 1Document14 pagesCS Module 1vijayendrar219No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument34 pagesChapter 1 - Introductionدينا عوداتNo ratings yet
- World Wide Web & Database Management: Sourav J S MY - AR.P2COM20005Document7 pagesWorld Wide Web & Database Management: Sourav J S MY - AR.P2COM20005Dorime DabsNo ratings yet
- CE 8 Lesson 2Document12 pagesCE 8 Lesson 2Argie ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Web Programming: Basic ConceptDocument21 pagesWeb Programming: Basic ConceptArdi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Study Material GTU - 23042016 - 032646AM PDFDocument82 pagesWeb Technology Study Material GTU - 23042016 - 032646AM PDFVikalp Panseriya100% (1)
- The Internet and the World Wide WebDocument3 pagesThe Internet and the World Wide Webmumomainga7No ratings yet
- Data Communication CS-506Document19 pagesData Communication CS-506sania iramNo ratings yet
- اااااااDocument33 pagesاااااااmojaxe6262No ratings yet
- ICT REVIEWERDocument5 pagesICT REVIEWERpmjoygarciaandal09No ratings yet
- E-Notes PDF All-Units IWTDocument82 pagesE-Notes PDF All-Units IWTmysadidvd009No ratings yet
- Side Scripting, Web Server and Network Security Configuration, and Ecommerce DevelopmentDocument9 pagesSide Scripting, Web Server and Network Security Configuration, and Ecommerce DevelopmentAnusthan DhamalaNo ratings yet
- COMP 11 - Module 4Document4 pagesCOMP 11 - Module 4Nikolai VillegasNo ratings yet
- Introduction of WWWDocument9 pagesIntroduction of WWWsahidul islamNo ratings yet
- Web Design NoteDocument144 pagesWeb Design NotecroszNo ratings yet
- Assignment Roll NumDocument15 pagesAssignment Roll NumTuba MahamNo ratings yet
- Computing: Web BrowserDocument4 pagesComputing: Web BrowserAnonymous 0R582va5sPNo ratings yet
- HTML Hypertext Markup LanguageDocument11 pagesHTML Hypertext Markup LanguagePatriceTherriaultNo ratings yet
- Concept of WWWDocument57 pagesConcept of WWWSTUMBLE GUYSNo ratings yet
- WWW Overview: Internet and Web Is Not The Same Thing: Web Uses Internet To Pass Over The InformationDocument4 pagesWWW Overview: Internet and Web Is Not The Same Thing: Web Uses Internet To Pass Over The InformationwestoNo ratings yet
- JMeterDocument2 pagesJMeterRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Combo BoxDocument27 pagesCombo BoxJawwad RafiqNo ratings yet
- VModelDocument26 pagesVModelapi-3807044No ratings yet
- MasterNav CssDocument2 pagesMasterNav Cssreeder45960No ratings yet
- Soham Adhikari E-Commerce HTML FileDocument64 pagesSoham Adhikari E-Commerce HTML FileSoham AdhikariNo ratings yet
- OopsDocument23 pagesOopsJanani GowdaNo ratings yet
- Final Test of MariaDocument16 pagesFinal Test of MariaMaria ChryssanthouNo ratings yet
- Java Chapter 1Document11 pagesJava Chapter 1Manu KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Request Lifecycle - Laravel - The PHP Framework For Web ArtisansDocument6 pagesRequest Lifecycle - Laravel - The PHP Framework For Web ArtisansMatteo RicciNo ratings yet
- Essential Javascript & Jquery Design Patterns - Addy OsmaniDocument34 pagesEssential Javascript & Jquery Design Patterns - Addy OsmanibytenotesNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument3 pagesManualhalilNo ratings yet
- Agile MethodDocument19 pagesAgile MethodRama RajeshNo ratings yet
- PhpStorm Reference Card (Cheat Sheet)Document2 pagesPhpStorm Reference Card (Cheat Sheet)John SnowNo ratings yet
- WEDE5020POEDocument14 pagesWEDE5020POETatendaNo ratings yet
- What Is Byte-Code?: Class Book (Document10 pagesWhat Is Byte-Code?: Class Book (Kavi VeethaNo ratings yet
- Random starting loadouts for RP serversDocument6 pagesRandom starting loadouts for RP serversWachirarat Ton ChomchomeNo ratings yet
- Python Optimization Modeling Objects (Pyomo)Document17 pagesPython Optimization Modeling Objects (Pyomo)arteepu4No ratings yet
- VTU 8th Sem Cse QB With AnswersDocument137 pagesVTU 8th Sem Cse QB With Answersvmscse100% (1)
- Parts of MS Excel WindowDocument12 pagesParts of MS Excel WindowJewel Mae Mingo50% (4)
- KanchanSubhashYeware (6 0)Document6 pagesKanchanSubhashYeware (6 0)Amar Bhapkar100% (1)
- Event-Driven Service-Oriented Architecture (EDSOA)Document19 pagesEvent-Driven Service-Oriented Architecture (EDSOA)mustufarahiNo ratings yet
- Q1 CaDocument5 pagesQ1 CaAhana SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Classes & ObjectsDocument56 pagesChapter 4 Classes & ObjectsMoti King MotiNo ratings yet
- OReilly - SAX2Document241 pagesOReilly - SAX2Lucas CoutoNo ratings yet
- Install Odoo 11 on Ubuntu 16.04 in 14 StepsDocument13 pagesInstall Odoo 11 on Ubuntu 16.04 in 14 StepsRusdi AdamNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document22 pagesCH 3Bereket AlemuNo ratings yet
- IMS 15.2 System UtilitiesDocument660 pagesIMS 15.2 System UtilitiesAllanFellerNo ratings yet
- 2 V 2 Human Cooperative Doubles Tutorial Tennis ElbowDocument3 pages2 V 2 Human Cooperative Doubles Tutorial Tennis ElbowKory RosenNo ratings yet
- E-Street Project Report 05 - 157Document100 pagesE-Street Project Report 05 - 157Vaibhav GangwarNo ratings yet
- Installing Windows Server 2016 on a VMDocument8 pagesInstalling Windows Server 2016 on a VMNagavelli Aravind reddyNo ratings yet