Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics of Neoplasia - 210424161410
Basics of Neoplasia - 210424161410
Uploaded by
Kareem DawoodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of Neoplasia - 210424161410
Basics of Neoplasia - 210424161410
Uploaded by
Kareem DawoodCopyright:
Available Formats
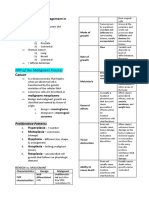
Good Behaviour
Slowly growing
Grows by expansion and compression of surrounding
tissue
Polypoid / Papillae
Well defined borders
Cystic
Usually capsulated
Complications of benign tumor:
1- Obstruction. e.g. larynx, CNS Less ulceration, hemorrhage & necrosis
2- Cosmetic Benign
3- May turn Malignant
Well differentiated cells
4- May be functioning: e.g. hormone secretion
Malignancy microscopic features absent
Less vascularity
No desmoplasia
No metastasis
No recurrence after complete surgical removal
Not fatal
Intermediate behaviour
Grows by infiltrating surrounding tissues
No distant metastasis
Locally malignant Behaviour
Slower rate of growth compared to malignant, but
faster than benign
Microscopic features of malignancy present
Normal mitosis
Bad behaviour
Useful
Rapid Growing
Limited proliferation
Grows by infiltration and invasion of surrounding tissue Hyperplasia
Cell Division Cells are normal in shape and pattern
Cauliflower (fungating)
Not capsulated
Infiltrating Irregular borders
Abnormal Aimless
Malignant ulcer
Causes of death in cancer:
Monoclonal
1- Vital organ destruction Not Capsulated
2- Vital organ obstruction
Unlimited proliferation
3- Malnutrition (GIT tumors)
Marked ulceration, hemorrhage & necrosis Malignant Neoplasia
4- Cachexia (loss of body fat, weakness,
anorexia & anemia) May or may not resemble tissue of origin
Cells differentiation range from well to undifferentiated
5- Anemia (malignant ulcer hemorrhage)
6- 2ry infection (toxemia, opportunistic infection) Not useful
Malignancy microscopic features present
may be capsulated
Marked vascularity forming malformed blood vessels
Desmoplasia may occur Basics of Neoplasia Oncology: Study of neoplasm
Metastasis present
Tumor: Neoplasmic swelling
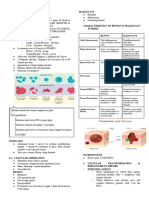
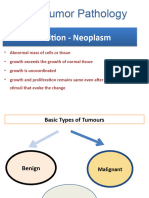
Classification of Tumors
Recurrence may occur
Invasion: spread of neoplasm into adjacent structures
Important Definitions
Fatal Metastasis: Spread of neoplasm to non-contiguous
sites
Benign - Papilloma
Definition: Extent of resemblance of tumor cell to its
Surface Epithelium tissue of origin
Malignant - Carcinoma
Epithelial Well differentiated - cells are highly similar to its
Benign - Adenoma parent cell
Generally less aggressive
Glandular
Malignant - Adenocarcinoma Definition: Cells which lose its resemblance to parent
Tumor cell Differentiation cells
Benign - Fibroma Cellular pleomorphism
Fibrous Tissue
Malignant - Fibrosarcoma Types Bizzare & giant cells
Benign - Lipoma Nuclear pleomorphism
Adipose tissue
Malignant - Liposarcoma Increased nuclear:cystoplasmic ratio
Cell morphology changes
Benign - Osteoma Hyperchromatism
Osseous (bone) Anaplasia
Malignant - Osteosarcoma Vesicular nuclei
Benign - Chondroma Microscopic criteria Multi-nucleation
Cartilaginous
Malignant - Chondrosarcoma Mesenchymal Mitotic figures
Tissue of Origin
Benign - Leiomyoma Cellular architecture changes - cells arranged
abnormally (Loss of polarity)
Smooth
Malignant - Leiomyosarcoma
Moderately differentiated
Muscular
Benign - Rhabdomyoma
Types Poorly differentiated
Skeletal
Malignant - Rhabdomyosarcoma Generally very aggressive, but often respond well
Undifferentiated
to chemotherapy
Benign - Hemangioma
Blood vessels
Malignant - Hemangiosarcoma
Vascular
Benign - Lymphangioma
Lymph vessels
Malignant - Lymphangiosarcoma
Blastoma: Tumor of primitive cells of an organ. e.g
Hepatoblastoma
Teratoma: Tumor of totipotent cells (cells that
differentiate along ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
You might also like
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Paget's DiseaseDocument24 pagesPaget's DiseaseKim Gonzales100% (5)
- Lymph Node PathologyDocument4 pagesLymph Node PathologyGerardLum0% (1)
- NeoplasiaDocument78 pagesNeoplasiageetikaNo ratings yet
- Diseases Poultry Diagnosis SymptomsDocument15 pagesDiseases Poultry Diagnosis SymptomsTufail Banday100% (1)
- 1 Chapter Wounds Tissue Repair ScarsDocument10 pages1 Chapter Wounds Tissue Repair Scarsapi-275075644No ratings yet
- Prasanta Banerjee - Ask Your DoctorDocument29 pagesPrasanta Banerjee - Ask Your DoctorAsh D67% (3)
- Daftar PPK CP Per KSM 2019Document10 pagesDaftar PPK CP Per KSM 2019ayuNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Benign LesionsDocument4 pagesGyne - Benign LesionsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocument31 pagesMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesutisuryanjNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Benign and Malignant TumourDocument5 pagesDifferences Between Benign and Malignant TumourHanif GandohNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) JayloiseDocument6 pagesMedical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) Jayloisejeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Bhalani 4Document86 pagesBhalani 4Vanessa Cavill100% (2)
- 1.06 General Pathology - Neoplasia (Part 1) - Dr. Annette SallilasDocument17 pages1.06 General Pathology - Neoplasia (Part 1) - Dr. Annette SallilasCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 RleDocument10 pagesNCM 118 RleJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFChethranNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Management of Shock in Adults - UpToDateDocument36 pagesIntraoperative Management of Shock in Adults - UpToDateYessica RivasNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant TumorDocument4 pagesBenign and Malignant TumorShandy Suwanto PutraNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument6 pagesCellular AberrationNeslie Lagare SamonteNo ratings yet
- Finals Medsurg ReviewerDocument12 pagesFinals Medsurg ReviewerAlyssa SaludesNo ratings yet
- Submitted TO: Shivani Ma'am: Submitted By: Deeksha Thakur BSC 2 YearDocument20 pagesSubmitted TO: Shivani Ma'am: Submitted By: Deeksha Thakur BSC 2 YearPrajjwal PalNo ratings yet
- Prostate TumorsDocument17 pagesProstate TumorsElian Jesús JimenezNo ratings yet
- PPP of The Malignant Process: Oncology: Nursing Management in Nursing CancerDocument3 pagesPPP of The Malignant Process: Oncology: Nursing Management in Nursing Cancer알파No ratings yet
- Sheryl Ann Pedines Bsn-IvDocument1 pageSheryl Ann Pedines Bsn-IvSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Prostate TumorsDocument17 pagesProstate TumorsblablalbablablablaNo ratings yet
- Slo Neoplsia Ca3Document13 pagesSlo Neoplsia Ca3perymeearumugamNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia ReviewDocument22 pagesNeoplasia ReviewLegnaNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument3 pagesOncologyMichtropolisNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument13 pagesNeoplasiaTisha GrandeNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumors 2010Document6 pagesBenign Tumors 2010Bjørn Audun JørgensenNo ratings yet
- MABM 0312 Bioscience: 9.1 NeoplasmDocument15 pagesMABM 0312 Bioscience: 9.1 NeoplasmmayraNo ratings yet
- They Adhere To Any Part That They Seize In, Similar To A Crab's Behavior. Malignant, As AppliedDocument10 pagesThey Adhere To Any Part That They Seize In, Similar To A Crab's Behavior. Malignant, As AppliedbeylaNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument18 pagesCanceralexngNo ratings yet
- OncologynotesDocument22 pagesOncologynotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- What Is NeoplasmsDocument38 pagesWhat Is NeoplasmsRashid HussainNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing: Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANDocument142 pagesOncology Nursing: Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANJimmelyn PalosNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument31 pagesNeoplasiaAnin PrakashNo ratings yet
- MedSurg ReviewerDocument11 pagesMedSurg ReviewernicoleNo ratings yet
- TumorDocument5 pagesTumori gede ricky jaya purnawarmanNo ratings yet
- Composed of Cells That Look Less Like The Normal Cell of OriginDocument2 pagesComposed of Cells That Look Less Like The Normal Cell of OriginShekinah GageloniaNo ratings yet
- L2-Principles of Surgical OncologyDocument25 pagesL2-Principles of Surgical OncologyTofeeq101 WaNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Brain, Breast, Lung Cancer (Vid Lec 1-2 Mam Muji)Document22 pagesWeek 15 Brain, Breast, Lung Cancer (Vid Lec 1-2 Mam Muji)jmmacar19No ratings yet
- Bladder Tumors: Normal AnatomyDocument11 pagesBladder Tumors: Normal AnatomyPankaj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations (Basic Concepts of Oncology)Document12 pagesCellular Aberrations (Basic Concepts of Oncology)PATRIZJA YSABEL REYESNo ratings yet
- Cellular AbrasionDocument3 pagesCellular AbrasionFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing - OverviewDocument137 pagesOncology Nursing - OverviewMae DacerNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Tumor ManagementDocument5 pagesGeneral Principles of Tumor ManagementAlejandro DávilaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AbrasionDocument3 pagesCellular AbrasionFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Tumors - ExtDocument43 pagesSoft Tissue Tumors - Extvrp8zm25f9No ratings yet
- Onco CompiledDocument50 pagesOnco CompiledGeraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From Pathology BookDocument5 pagesExtracted Pages From Pathology Booked trsgf rgsfNo ratings yet
- Benign Gyne LesionDocument15 pagesBenign Gyne LesionPM Basiloy - AloNo ratings yet
- 02 Fungal ReproductionDocument2 pages02 Fungal Reproductionljcuison100% (1)
- 02.22.1 Neoplasia I Final PDFDocument79 pages02.22.1 Neoplasia I Final PDFSameeha AbbasNo ratings yet
- B ENB (Blue Keyword Pyq)Document6 pagesB ENB (Blue Keyword Pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqNo ratings yet
- 1 Classification Neoplasm Kel.4Document10 pages1 Classification Neoplasm Kel.4csulijayaNo ratings yet
- Netic Cancer Sem Jan 2022Document66 pagesNetic Cancer Sem Jan 2022AIMAN MUHAIMMIN HASNANNo ratings yet
- c4k 06 Jenkins Nrsoft Tissue SarcomasDocument11 pagesc4k 06 Jenkins Nrsoft Tissue SarcomasAde CahyanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument6 pagesCellular AberrationLance RaphaelNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument6 pagesCancerMark Anthony NamocaNo ratings yet
- Jamaoncology Patel 2020 PG 200003 1599155176.12055Document1 pageJamaoncology Patel 2020 PG 200003 1599155176.12055Tiara Sekar AyudhipashaNo ratings yet
- 04 Basic Tumor Pathology1Document9 pages04 Basic Tumor Pathology1tharindu manjulaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document8 pagesModule 4Pauline GamlangaNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant TumorsDocument22 pagesBenign and Malignant TumorsmoupriyanagNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Key PointsDocument16 pagesNeoplasia: Key PointsskNo ratings yet
- LaboratoryDocument3 pagesLaboratoryKrizzia OñateNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Basic PathologyDocument12 pagesNeoplasia: Basic Pathologyandroid tricksNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Fibro-sarcoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Fibro-sarcoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Gastritis and Peptic UlcerDocument30 pagesGastritis and Peptic UlcerKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentDocument56 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embr Yology Depar TmentDocument96 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embr Yology Depar TmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentDocument93 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- DR Rofanda BakeerDocument17 pagesDR Rofanda BakeerKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Practical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Document16 pagesPractical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Kareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Pancreaticobiliary Lesions: DR Rofanda BakeerDocument29 pagesPancreaticobiliary Lesions: DR Rofanda BakeerKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Mal AbsorptionDocument4 pagesMal AbsorptionKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Anti Diarrheal DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Diarrheal DrugsKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- GoodDocument7 pagesGoodana9filimonNo ratings yet
- Corynebacterium Diphtheriae Listeria Monocytogenes Erysipelothrix Rhusopathiae Lactobacillus Spp. Streptomycetes Spp. Nocardia SPPDocument1 pageCorynebacterium Diphtheriae Listeria Monocytogenes Erysipelothrix Rhusopathiae Lactobacillus Spp. Streptomycetes Spp. Nocardia SPPAbcd ReyesNo ratings yet
- The - good.Doctor.s01e05.Hdtv.x264 KillersDocument68 pagesThe - good.Doctor.s01e05.Hdtv.x264 KillersAlgorithove AlgorithoveNo ratings yet
- 8.health Communicable DiseasesDocument50 pages8.health Communicable DiseasesCatherine Joy De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Leiomyoma of The Esophagus: Open Versus Thoracoscopic EnucleationDocument5 pagesLeiomyoma of The Esophagus: Open Versus Thoracoscopic EnucleationYacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Hypocalcemia: Presented By: Ms. Manisha Thakur Nursing Tutor Child Health NursingDocument11 pagesNeonatal Hypocalcemia: Presented By: Ms. Manisha Thakur Nursing Tutor Child Health Nursingmanisha thakurNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Surgical Site Infections: Surgical Patient Care SeriesDocument11 pagesPrevention of Surgical Site Infections: Surgical Patient Care Seriestien duongNo ratings yet
- Radiologic Anatomy of The Brain - FinalsDocument11 pagesRadiologic Anatomy of The Brain - FinalsKate Sarah GabasaNo ratings yet
- Saving Lives Averting CostsDocument79 pagesSaving Lives Averting CostsAbhishek DebNo ratings yet
- Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature For Reporting Clinical D 2005Document8 pagesStandardization of Uveitis Nomenclature For Reporting Clinical D 2005Stephanie PfengNo ratings yet
- Mucinac 600 TabletsDocument6 pagesMucinac 600 TabletsNurmaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy-Immunology 19: Primary & Acquired Immunodeficiency Saber HusseinDocument18 pagesPharmacy-Immunology 19: Primary & Acquired Immunodeficiency Saber Husseinmmoney1No ratings yet
- Prader-Willi Syndrome: Related TopicsDocument4 pagesPrader-Willi Syndrome: Related TopicsDrBhaskar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Trends in Skin Mycoses Worldwide: Blanka Havlickova, Viktor A. Czaika and Markus FriedrichDocument14 pagesEpidemiological Trends in Skin Mycoses Worldwide: Blanka Havlickova, Viktor A. Czaika and Markus FriedrichRS Tk IV PekanbaruNo ratings yet
- GCSDocument13 pagesGCSFaroq AlshameriNo ratings yet
- Role of Viruses in The Development of Breast CancerDocument6 pagesRole of Viruses in The Development of Breast CancerАйгуль ШарипNo ratings yet
- Chromo Blas To MycosisDocument10 pagesChromo Blas To MycosisElina GNo ratings yet
- 5 dfgs34 24dDocument2 pages5 dfgs34 24dKenneth SyNo ratings yet
- Clobetasol Propionate BP: Scalp SolutionDocument1 pageClobetasol Propionate BP: Scalp SolutionRuhul AminNo ratings yet
- wp2 FinalDocument3 pageswp2 Finalapi-523698524No ratings yet
- If 96 Be 25 To 715 Up - Penelusuran GoogleDocument2 pagesIf 96 Be 25 To 715 Up - Penelusuran Googleyang baikNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJericha IsidroNo ratings yet