Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Corruption Laws
Anti Corruption Laws
Uploaded by
Haja Mohideen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views12 pagesAnti Corruption Laws
Anti Corruption Laws
Uploaded by
Haja MohideenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
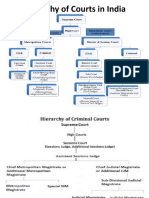
Hierarchy of Courts
Administration of Justice
• Most essential function of the State.
• Power exercised by the State through
judiciary to enforce rights and punish
wrongs.
• It involves two parties
- Plaintiff and Defendant – in civil cases
- Complainant and Accused or
- Prosecution and Accused – in criminal
cases
• Judicial Process involves
- A right claimed or a wrong complained by
one party against the other.
- Hearing of the parties by the Court.
- Judgment of the Court delivered at the
end of the trial.
- Execution of the operative part of the
judgment.
System of Courts in India
• At National level – Supreme Court of India
• At State level – High Court
• At District and Subordinate level –
Subordinate Courts (Civil and Criminal)
Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
• Court of Record. Has power to punish for
contempt. (A.129)
• Original Jurisdiction. (A.131)
• Highest Court of Appeal in the country.
(A.132,133,134 & 136)
• Writ jurisdiction.(A.32)
• Advisory Jurisdiction.(A.143)
• Law declared by the Supreme Court binding
on all Courts in India.(A.141)
Jurisdiction of the High Court
• Court of Record. Has power to punish for contempt.
(A.215)
• Original Jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters in
the case of some High Courts.
• Appellate jurisdiction in respect of criminal and civil
cases decided by Subordinate courts.
• Revisional Jurisdiction conferred under the Civil
Procedure Code and Criminal Procedure Code.
• Writ jurisdiction.(A.226)
• Administrative Jurisdiction over subordinate courts.
Civil Courts subordinate to the High
Court
• In Cities • In Districts
• First Grade • First Grade
Chief Judge and District Judge and
Additional Chief Judge Additional District
• Second Grade Judge
Assistant Chief Judge • Second Grade
or Senior Civil Judge Assistant District Judge
• Third Grade or Senior Civil Judge
Munsif or • Third Grade
Junior Civil Judge Munsif or
Junior Civil Judge
Criminal Courts Subordinate to the
High Court
• In Cities • In Districts
• Sessions Court (Sessions • Sessions Court (Sessions
Judge, Addl. Sessions Judge, Addl. Sessions
Judges and Asst. Judges and Asst.
Sessions Judges) Sessions Judges)
• Chief Metropolitan • Chief Judicial
Magistrate’s Court Magistrate’s Court
• Metropolitan Magistrates’ • Judicial Magistrates of
Courts First Class.
• Judicial Magistrates of
Second Class.
Sentencing Power of different Trial
Courts
• Sessions Judge and • Any sentence authorized by
Additional Sessions Judge law. But death sentence to
be confirmed by the High
Court
• Assistant Sessions Judge • Imprisonment upto 10 years
and fine authorized by law
• Chief Judicial Magistrate • Imprisonment upto 7 years
Chief Metropolitan and fine authorized by law
Magistrate
• Imprisonment upto 3 years
• Judicial Magistrate of I class and fine not exceeding Rs.
Metropolitan Magistrate 10000.
• Judicial Magistrate of II class • Imprisonment upto 1 year
and fine not exceeding Rs.
5000
Separation of powers
• In pursuance of the scheme of separation of
executive from the judiciary (u/A 50 of the
Constitution) – Two categories of Magistrates
created.
• Judicial Magistrates – Appointed and controlled by
the High Court and discharge judicial functions.
• Executive Magistrates – Appointed and controlled by
the State Government and discharge executive
functions, i.e., maintenance of law and order.
Executive Magistracy
• For Districts • For Subdivision
- District - Sub-Divisional
Magistrates Magistrate
- Additional District - Additional Sub-
Divisional
Magistrates
Magistrate
-Executive
- Executive
Magistrates
Magistrates
Thank You
You might also like
- Drafting Appearances and PleadingsDocument352 pagesDrafting Appearances and PleadingsLs NRMNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction and Powers of The Supreme CourtDocument143 pagesJurisdiction and Powers of The Supreme CourtAmartya ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Interim Orders.: (A) Commissions (Secs. 75-78, Order 26)Document5 pagesInterim Orders.: (A) Commissions (Secs. 75-78, Order 26)guneet0911No ratings yet
- Rights in The Indian ConstitutionDocument33 pagesRights in The Indian Constitutionmax lifeNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnonymous MUL9czYq2100% (1)
- Cooperative Federalism in IndiaDocument5 pagesCooperative Federalism in IndiaAkanksha baibhav100% (1)
- Handbook For Scheduled TribesDocument97 pagesHandbook For Scheduled Tribesexecutive engineerNo ratings yet
- State Centre State Relation VasanthDocument13 pagesState Centre State Relation VasanthApoorvaChandraNo ratings yet
- Jatin Project (Lok Adalat)Document20 pagesJatin Project (Lok Adalat)tarun choudhary100% (1)
- Hierarchy and Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument56 pagesHierarchy and Jurisdiction of Courtsaayush lathiNo ratings yet
- Law Notes - Evidence ActDocument35 pagesLaw Notes - Evidence ActVipul Shah50% (2)
- Tribunals in India: Tribunals (Articles 323-A and Article 323-B)Document6 pagesTribunals in India: Tribunals (Articles 323-A and Article 323-B)Anonymous d5TziAMNo ratings yet
- Hirarchy of Courts 33Document27 pagesHirarchy of Courts 33drishyasck123No ratings yet
- Defences in Criminal ContemptDocument4 pagesDefences in Criminal ContemptAmanth RaoNo ratings yet
- Stockholm DeclarationDocument6 pagesStockholm DeclarationMonika ButarbutarNo ratings yet
- 1819 PPT Burden of ProofDocument24 pages1819 PPT Burden of ProofPrateek BayalNo ratings yet
- The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 - Quick Over View - Law Notes .In - CPCDocument10 pagesThe Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 - Quick Over View - Law Notes .In - CPCAB236No ratings yet
- Advocates Act An Overview MainDocument19 pagesAdvocates Act An Overview MainPritee KishoreNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Criminal Courts in IndiaDocument11 pagesConstitution of Criminal Courts in IndiaMAnu PAnditNo ratings yet
- BA0160028 - BCI Disciplinary CommitteeDocument3 pagesBA0160028 - BCI Disciplinary CommitteearunNo ratings yet
- Bar Counsil of IndiaDocument8 pagesBar Counsil of IndiaAmitpal SINGHNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Considerations: Object of Criminal ProcedureDocument14 pagesPreliminary Considerations: Object of Criminal ProcedureSoumya ThakurNo ratings yet
- History and Development of Legal Profession in IndiaDocument22 pagesHistory and Development of Legal Profession in Indiahimanshi khivsaraNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Code: Res JudicataDocument12 pagesCivil Procedure Code: Res JudicataAnkita Shah JainNo ratings yet
- CRPC - Section 61 To 69 - One LinersDocument1 pageCRPC - Section 61 To 69 - One LinersEnkayNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Code, 1908 ExecutionDocument8 pagesCivil Procedure Code, 1908 ExecutionSatwant SinghNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument15 pagesEthicsRitick kumarNo ratings yet
- Appealsniharika Law CPCDocument5 pagesAppealsniharika Law CPCMadhu RondaNo ratings yet
- On Jurisdictions of Supreme CourtDocument8 pagesOn Jurisdictions of Supreme CourtD. Naarayan NandanNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of Civil CourtsDocument6 pagesJurisdiction of Civil CourtsChristopher Schultz100% (1)
- Daryao v. State.Document22 pagesDaryao v. State.AKSHADA DHAGAMWARNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Establishment of Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Authority (Sec 51-74)Document20 pagesProject Report: Establishment of Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Authority (Sec 51-74)Pravesh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Lokayukta Lokpal 49Document3 pagesLokayukta Lokpal 49Shyam kumarNo ratings yet
- Professional Ethics Notes BY SDFSDocument68 pagesProfessional Ethics Notes BY SDFSकुणाल पाटील100% (1)
- IOS Notes CombinedDocument27 pagesIOS Notes Combineddebjit bhowmickNo ratings yet
- Bar Council of IndiaDocument14 pagesBar Council of IndiaParag Dhurke0% (1)
- Civil Procedure Code 1908Document584 pagesCivil Procedure Code 1908mohanjpr100% (1)
- Coastal Regulation Zone Notification (CRZ)Document15 pagesCoastal Regulation Zone Notification (CRZ)Sagar ApteNo ratings yet
- Sources and PrincipalDocument9 pagesSources and PrincipalSo NuNo ratings yet
- History and Admiralty Jurisdiction of The High CourtsDocument12 pagesHistory and Admiralty Jurisdiction of The High CourtsBhavini ModiNo ratings yet
- Decree and OrderDocument15 pagesDecree and OrderSajjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Legal Prof Notes-2Document20 pagesLegal Prof Notes-2Arhum KhanNo ratings yet
- History, Meaning and Concept: Civil Procedure Code-IDocument9 pagesHistory, Meaning and Concept: Civil Procedure Code-IAyush Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- CPC MainDocument13 pagesCPC MainShelly AroraNo ratings yet
- Civil CourtsDocument3 pagesCivil CourtsAnonymous MSJObDNo ratings yet
- Powers of Revenue Courts, Its Jurisdiction and Constitution. (U.P. Revenue CodeDocument6 pagesPowers of Revenue Courts, Its Jurisdiction and Constitution. (U.P. Revenue CodeKashif KhuhroNo ratings yet
- 2.judgment, Decree and OrderDocument16 pages2.judgment, Decree and OrderShohan SumonNo ratings yet
- Code of Criminal ProcedureDocument6 pagesCode of Criminal ProcedurebernardNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument10 pagesProject ReportSukhman BhinderNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: L. Chandra v. Union of IndiaDocument16 pagesCase Analysis: L. Chandra v. Union of IndiaTAQ - 247 - RNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy and Powers of Criminal CourtsDocument4 pagesHierarchy and Powers of Criminal CourtsRohit kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- MINERVA MILLS Vs UNION OF INDIA PDFDocument74 pagesMINERVA MILLS Vs UNION OF INDIA PDFpranavNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Code - A Quick Peak - IpleadersDocument1 pageCivil Procedure Code - A Quick Peak - Ipleadersannpurna pathakNo ratings yet
- Strike by AdvocatesDocument3 pagesStrike by AdvocatesArchit Virendra Sharma100% (1)
- Basic Features of Arbitration & Conciliation Act, 1996Document5 pagesBasic Features of Arbitration & Conciliation Act, 1996Pramod M Chaugule100% (2)
- Describe The Organization of Police, Prosecutor, Defense Counsel and Prison Authorities and Their Functions, Duties, and PowersDocument59 pagesDescribe The Organization of Police, Prosecutor, Defense Counsel and Prison Authorities and Their Functions, Duties, and PowersRajkumarKari67% (9)
- Zee Tele Films V Union of IndiaDocument16 pagesZee Tele Films V Union of IndiaNIKHIL CHANDRA R 1550241No ratings yet
- Administrative Law My PreparationDocument28 pagesAdministrative Law My PreparationmantraratnamNo ratings yet
- Arbitration Act 2001 PDFDocument11 pagesArbitration Act 2001 PDFCryptic LollNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowerDocument3 pagesSeparation of PowerAshfakul AlamNo ratings yet
- Good Article On Revision of Orders by Commissioner of Income-Tax - Section 264Document8 pagesGood Article On Revision of Orders by Commissioner of Income-Tax - Section 264Vipul ShahNo ratings yet
- AGD Pvt. LTd. - Madra HC - For Restoration of Co. - Power of HC - Useful in GandhiDocument23 pagesAGD Pvt. LTd. - Madra HC - For Restoration of Co. - Power of HC - Useful in GandhiVipul ShahNo ratings yet
- CH - 6 - An Application For Obtaining Sanction of The Charity Commissioner For Sale of The Immovable Property Belonging To A Public TrustDocument5 pagesCH - 6 - An Application For Obtaining Sanction of The Charity Commissioner For Sale of The Immovable Property Belonging To A Public TrustVipul ShahNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 - PUBLIC NOTICE BY THE TRUSTEES OF A PUBLIC TRUST INVITING OFFERS FOR SALE OF THE TRUST'S IMMOVABLE PROPERTYDocument2 pagesCH - 5 - PUBLIC NOTICE BY THE TRUSTEES OF A PUBLIC TRUST INVITING OFFERS FOR SALE OF THE TRUST'S IMMOVABLE PROPERTYVipul ShahNo ratings yet
- Agreement To Adopt The Preliminary Agreement1 PDFDocument9 pagesAgreement To Adopt The Preliminary Agreement1 PDFVipul ShahNo ratings yet
- Recent SC Decision On JurusdictionDocument25 pagesRecent SC Decision On JurusdictionVipul ShahNo ratings yet
- Bombay High Court Practice NoteDocument48 pagesBombay High Court Practice NoteVipul Shah100% (1)
- The Law On Taxability of Gifts Under The IncomeDocument26 pagesThe Law On Taxability of Gifts Under The IncomeVipul ShahNo ratings yet
- Google Search TipsDocument35 pagesGoogle Search TipsRohith NairNo ratings yet