Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp1 Series Impedance
Exp1 Series Impedance
Uploaded by
Kurl Vincent Gamboa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Exp1 Series Impedance(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesExp1 Series Impedance
Exp1 Series Impedance
Uploaded by
Kurl Vincent GamboaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
15.
Experiment 3
Impedance of a Series RLC Circuit
OBJECTIVE:
‘+ To investigate the impedance of a series RLC circuit and compare it
with the impedance of its constituent components.
BACKGROUND INFORMATION:
‘The behavior of a series circuit comprising all three kinds of circuit elements
(resistor, inductor and capacitor) will depend upon the relative magnitudes of the
Feactances X. and Xc. Remembering that inductive reactance and capacitive
reactance act opposite each other, it should be clear that the combination behaves
(1) like a R-L circuit or as an inductive circuit when X; is greater than Xc, (2) like a
R-C circuit or as a capacitive circuit when X¢ is greater than X; and (3) like a pure
resistance R circuit or as a resistive circuit when X;, equals Xc This latter condition
has a special significance and is said to produce resonance in the circuit.
PREFERRED EQUIPMENT:
& FeedBack Trainer Kit
Function generator
4 Multimeter (V.0.M.)
%& AC. Miliammeter 0 — 250mA
INITIAL SETTINGS:
Connect the power supply unit to the main supply line. DO NOT switch on
yet.
PROCEDURE:
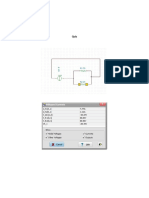
1. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 3.1.
2. Set the sine wave function generator to 100 Hz, with constant output amplitude of
4 Vrms a8 measured on the voltmeter.
3. On Table 3.1, following the results table, record the readings of total current,
voltage across the resistor, inductor and capacitor respectively.
What did you observe about the magnitude of the current flowing to the
resistor, inductor and capacitor? What is this parameter in the system?
Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual 2
16
4. On another sheet of paper, draw to scale a phasor diagram showing Vr, Va, Vi
and Vc set the current as reference.
What is the phase relationship between V, and Vc? How do you
combine the resultant value of V_ and Vc?
From your phasor diagram, what is the phase relationship between the
resultant of Vi and Vc to Va?
5. On Table 3.2, following the results table, calculate the required parameters.
6. Switch off the power supply unit.
Optionat Activity:
Determination of internal resistance and inductance of a practical inductor (coil):
4. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 3.2.
2. Set the sine wave function generator to 60 Hz, with constant output amplitude of
4 Vas a8 measured on the voltmeter.
3. On Table 3.3a and Table 3.3b, following the results table, record the readings of
total current, voltage across the resistor and then the voltage across the coil.
And then calculate the required parameters
4. On another sheet of paper, solve the internal resistance (r) and inductance (L) of
a coil using an analytical solution.
5. Switch off the power supply unit.
Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual 2
‘WIRING DIAGRAM:
Sine Wave
Function
Generator
Figure 3.4
Preferred Settings for Figure 3.1:
‘Sine Wave Function Generator = 4 Vans
Resistor (Ry) = 100 0
Inductor (L1) = 100 mH
Capacitor (C1) = 2.2 uF
{ L
CR) Rn. py
ae i jal i i
{ practical inductor |
Sine Wave i (coil) 1
Function @ 7 =
Generator
Figure 3.2
Preferred Settings for Figure 3.2:
‘Sine Wave Function Generator = 4 Vans
Resistor (Ri) = 100 0
Practical Inductor (coil) = 100 - 200 mH
Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual 2
PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET:
Experiment 3 - Impedance of a Series RLC Circuit
NAME: DATE:
COURSE/SECTION: GROUP #:
Table 3.1:
Total Total Resistor | Inductor | Capacitor
Frequency | Voltage | Current | Voltage | Voltage | Voltage
Hz (v7) (hr) (Va) (wi) (Vc)
Ven mArms Vems. Vans Vems |
400
200
300
400
500
Table 3.2:
Frequency
Formula Hz
100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500
‘Ohm's Law V,
(Measured R=
Values) Fe
V,
X,=—4
1, L
Vy
Xo=
Ie
V,
IZ a
r
Equation R=R
; Impedance X, = 2afL
1
xX,.=—
© 2afC
Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual 2
Frequency
Hz
Formula 100 _[ 200 [300 [400 | 500
Pythagorean =X,-
Theorem 4=%,-Xe
(Impedance =-JR?a x2
Triangle) IZ EVR? +X
0, = tant X
R
Complex =R+j(X,-
Number Z=R+ j(X_~ Xe)
(rectangular form)
Z=|Z|20,
(polar form)
Table 3.3a:
Measured Values
Total | Total | Resistor | Coils
Frequency | Voltage | Current | Voltage | Voltage
Hz (Vr) (h) (Weou)
Vem mArm: Vems. Vas
60
Table 3.3b:
Calculated Values
Total Total Coil’s | Coil’s Internal | Coil's
Current | Impedance | Impedance | Resistance | Inductance
(hr) ) (Zeon) w) ()
mAaus a o Q mH
Instructor's Signature
Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual 2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- OLA 3 Case Study (Fire Safety) GAMBOADocument3 pagesOLA 3 Case Study (Fire Safety) GAMBOAKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment-2 Leds GamboaDocument11 pagesExperiment-2 Leds GamboaKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp3 GamboaDocument7 pagesExp3 GamboaKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Organazing and Staffing Case Study 2Document5 pagesOrganazing and Staffing Case Study 2Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 LACAYANGADocument1 pageExperiment 1 LACAYANGAKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exercise-1 1Document1 pageExercise-1 1Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - GamboaDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 - GamboaKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document8 pagesExp 5Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 LACAYANGADocument2 pagesExperiment 2 LACAYANGAKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document3 pagesExp 8Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp5 GamboaDocument9 pagesExp5 GamboaKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp7 BarnuevoDocument10 pagesExp7 BarnuevoKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Laboratory Demo and ThermochemDocument1 pageElectrochemistry Laboratory Demo and ThermochemKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document2 pagesExp 7Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exp4 GamboaDocument3 pagesExp4 GamboaKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Ecea116 1Q2223Document12 pagesEcea116 1Q2223Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 6.1.2 CO3Document2 pagesExercise 3 6.1.2 CO3Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Applied Plotting, Charting & Data Representation in Python PDFDocument3 pagesApplied Plotting, Charting & Data Representation in Python PDFKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Electro Mag CourseraDocument8 pagesElectro Mag CourseraKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.3.4Document1 pageExercise 2.3.4Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Lab Report (Gamboa)Document12 pagesExperiment 5 Lab Report (Gamboa)Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Gamboa, Kurl Vincent P. EEA101 / B8 June 26, 2020 QuizDocument2 pagesGamboa, Kurl Vincent P. EEA101 / B8 June 26, 2020 QuizKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Quiz (June 26, 2020) PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz (June 26, 2020) PDFKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- MATH149 Linear Algebra Long Quiz 1 Set E 2 Quarter S.Y. 2018-2019Document1 pageMATH149 Linear Algebra Long Quiz 1 Set E 2 Quarter S.Y. 2018-2019Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Math-149 MatricesDocument26 pagesMath-149 MatricesKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Anderson - Why Counting Counts (Noli)Document22 pagesAnderson - Why Counting Counts (Noli)Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Advance Electronics Engineering Mathematics Laboratory: Mapúa University School of Ee-Ece-CoeDocument3 pagesAdvance Electronics Engineering Mathematics Laboratory: Mapúa University School of Ee-Ece-CoeKurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 (LAB REPORT and PDS)Document8 pagesExperiment 6 (LAB REPORT and PDS)Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 (LAB REPORT and PDS)Document11 pagesExperiment 7 (LAB REPORT and PDS)Kurl Vincent GamboaNo ratings yet